Herpesvirus infections are a group of infectious diseases that are caused by viruses from the Herpesviridae family, can occur in the form of localized, generalized, recurrent forms of the disease, and have the ability to persist (the virus is constantly present) in the human body.
Herpesvirus infections (HVI) are among the most common human viral diseases. Their infection and morbidity rates are increasing every year. In all countries of the world, 60-90% of the population is infected with one or another herpes virus.
Etiology
Herpes viruses contain double-stranded DNA and have a glyco-lipoprotein envelope. The sizes of viral particles are from 120 to 220 nm.
Today, 8 types of herpes viruses that have been identified in humans have been described:
- two types of herpes simplex virus (HSV-1, HSV-2),
- varicella zoster virus (VZV or HHV-3),
- Epstein-Barr virus (EBV or HHV-4),
- cytomegalovirus (CMV or HHV-5), HHV-6, HHV-7, HHV-8.
Based on the biological properties of viruses, 3 subfamilies of herpes viruses have been formed: (alpha herpes viruses, beta herpes viruses and gamma herpes viruses). A-herpesviruses include HSV-1, HSV-2, VZV.
Betaherpesviruses include CMV, HHV-6, HHV-7. They, as a rule, multiply slowly in cells, cause an increase in the affected cells (cytomegaly), are capable of persistence, mainly in the salivary glands and kidneys, and can cause congenital infections. Gammaherpesviruses include EBV and HHV-8.
Folk remedies
All of the following recipes for plant herbs (optional) are prepared as follows: leave one tablespoon of herbs in a glass of boiling water for 20-30 minutes, cool and consume 1/2-1/3 cup 2-3 times a day to relieve mild pain and nervous excitability , as well as for insomnia.
- Valerian root, mint leaves - 3 parts each, watch leaves - 4 parts.
- Mint leaf, watch leaf - 2 parts each, valerian root and hop cones - 1 part each.
- Fennel fruits and chamomile flowers - 1 part each, marshmallow root, licorice root, wheatgrass rhizome - 2 parts each (recommended for children).
- Valerian root – 2 parts, chamomile root – 3 parts, caraway fruit – 5 parts.
- Valerian root, hawthorn flowers, mint leaves, mistletoe herb, motherwort herb - 1 part each.
- Valerian root, motherwort herb, green oat straws - 1 part each.
- Tatar leaves, green oat straw, caraway fruits - 2 parts each, hawthorn flowers, chamomile flowers - 1 part each.
- Mint leaves - 1 part, heather grass, lemon balm leaves - 2 parts each, valerian root - 4 parts.
- Heather leaves, cudweed herb, thyme herb, valerian root - 2 parts each, chicory root - 1 part.
- Motherwort grass, cudweed grass, heather grass - 2 parts each, hop cones, caraway fruits - 1 part each.
The use of medicinal pharmacopoeial herbs is justified in mild forms of the pathogenesis of herpes zoster.
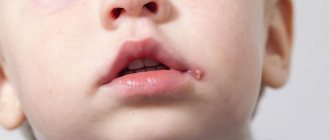
Herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2
The term “herpes infection” (HI) is usually used to refer to diseases that are caused by HSV-1 and HSV-2. The source of HSV infection are sick people with various forms of the disease, including latent ones, as well as virus carriers.
HSV-1 is transmitted by airborne droplets and contact. When the virus gets on the skin during a cough or sneeze, it is contained in droplets of saliva and survives for an hour. On wet surfaces (washbasin, bathtub, etc.) it remains viable for 3-4 hours, which is often the cause of disease outbreaks in preschool institutions. Infection can occur through kissing, as well as through household items that are infected with the saliva of a patient or virus carrier. HSV-2 is transmitted sexually or vertically. With the latter, infection occurs during childbirth (contact with the mother's birth canal), transplacentally or through the cervical canal in the uterine cavity. Due to the fact that viremia occurs during generalization of infection, transfusion or parenteral transmission of HSV-2 infection is also possible. HSV-2 usually causes genital and neonatal herpes.
Children are most susceptible to GI between 5 months and 3 years of age. Depending on the mechanism of infection, acquired and congenital forms of HI are distinguished. Acquired HI can be primary and secondary (recurrent), localized and generalized. A latent form of GI is also isolated.
No infection has such a variety of clinical manifestations as the herpes virus. It can cause damage to the eyes, nervous system, internal organs, mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract, oral cavity, genitals, can cause cancer, and has a certain significance in neonatal pathology and the occurrence of hypertension. The spread of the virus in the body occurs through hematogenous, lymphogenous, and neurogenic routes.
The frequency of primary herpesvirus infection increases in children after 6 months of life, when antibodies received from the mother disappear. The peak incidence occurs at the age of 2-3 years. HI often occurs in newborns; according to a number of authors, it is diagnosed in 8% of newborns with general somatic pathology and in 11% of premature infants.
According to WHO, diseases caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV) are the second leading cause of death from viral infections after influenza. Solving the problem of diagnosing and treating herpesvirus infection with manifestations on the oral mucosa is one of the most important tasks of practical medicine.
In the last decade, the importance of herpesvirus diseases as a public health problem has been constantly growing throughout the world. Members of the human herpesvirus family infect up to 95% of the world's population.
Primary forms of GI include: infection of newborns (generalized herpes, encephalitis, herpes of the skin and mucous membranes), encephalitis, gingivostomatitis, Kaposi's eczema herpetiformis, primary herpes of the skin, eye, herpetic panaritium, keratitis. Primary HI occurs due to initial human contact with HSV. As a rule, this occurs in early childhood (up to 5 years). In adults aged 16-25 years who do not have antiviral immunity, primary HI may more often be caused by HSV-2. 80-90% of initially infected children carry the disease latently, and only in 10-20% of cases are clinical manifestations of the disease observed.
Secondary, recurrent forms of GI are herpes of the skin and mucous membranes, ophthalmic herpes, and genital herpes.
Epstein-Barr virus infection
An infectious disease caused by the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and characterized by a systemic lymphoproliferative process with a benign or malignant course.
EBV is isolated from the body of a patient or virus carrier with oropharyngeal secretions. Transmission of the infection occurs through airborne droplets through saliva, often when a mother kisses her child, which is why EBV infection is sometimes called the “kissing disease.” Children often become infected with EBV through toys contaminated with the saliva of a sick child or a virus carrier, when using shared utensils and linen. Blood transfusion and sexual transmission of the infection are possible. Cases of vertical transmission of EBV from mother to fetus have been described, suggesting that the virus may be the cause of intrauterine developmental anomalies. Contagiousness during EBV infection is moderate, which is probably due to the low concentration of the virus in saliva. The activation of infection is influenced by factors that reduce general and local immunity. The causative agent of EBV infection has a tropism for the lymphoid-reticular system. The virus penetrates the B-lymphoid tissues of the oropharynx and then spreads throughout the body's lymphatic system. Infection of circulating B lymphocytes occurs. The DNA virus penetrates into the nuclei of cells, while the proteins of the virus give infected B-lymphocytes the ability to continuously multiply, causing the so-called “immortality” of B-lymphocytes. This process is a characteristic feature of all forms of EBV infection.
EBV can cause: infectious mononucleosis, Burkitt's lymphoma, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, chronic active EBV infection, leiomyosarcoma, lymphoid interstitial pneumonia, hairy leukoplakia, non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, congenital EBV infection.
Varicella zoster infection
Varicella-zoster virus causes chickenpox and herpes zoster. The source of infection for chickenpox can only be a person with chickenpox or herpes zoster, including the last 24-48 hours of the incubation period. Convalescent chickenpox remains infectious for 3-5 days after the skin rash stops. The disease cannot be transmitted through a third party. Intrauterine infection with chickenpox is possible in the case of a pregnant woman. Chickenpox can occur at any age, but in modern conditions the maximum number of patients occurs in children aged 2 to 7 years. Herpes zoster develops after primary infection with the Varicella-zoster virus, after the infection passes into a latent form, in which the virus is localized in the spinal, trigeminal, sacral and other nerve ganglia. Endogenous reactivation of the infection is possible.
Period of rash
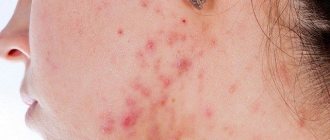
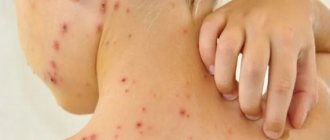
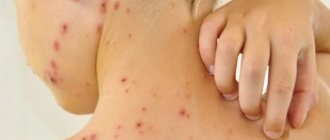
The time when rashes characteristic of shingles appear. The symptoms and nature of the rash depend on the severity of the inflammatory process. At first, the rashes look like pockets of pink spots 2-5 mm in size, between which there are areas of healthy skin.
- In the typical form of the disease, the next day, small, closely grouped vesicles and vesicles with transparent serous contents form in their place, which becomes cloudy after 3-4 days.
- In severe gangrenous form of herpes, the contents of the vesicles may be mixed with blood and black in color. Herpetic rashes have a wave-like course, as with chickenpox, that is, fresh rashes with vesicular elements appear at intervals of several days. The bubbles seem to crawl from one place to another, encircling the body, hence the name of this disease.
In mild forms of the inflammatory process, the transformation of skin nodules into pustules does not form and their ulceration does not occur, and the manifestation of herpes is also possible only of a neurological nature - pain without a rash, otherwise it is also called herpetic neuralgia and is often mistaken for manifestations of intercostal neuralgia, osteochondrosis or heart pain. And therefore, inadequate treatment may be prescribed.
Cytomegalovirus infection
An infectious disease that is caused by cytomegalovirus (CMV) and is characterized by a variety of clinical forms (from asymptomatic to severe generalized with damage to many organs) and course (acute or chronic). CMV transmission factors can be almost all biological substrates and human secretions that contain the virus: blood, saliva, urine, cerebrospinal fluid, vaginal secretions, sperm, amniotic fluid, breast milk. Potential sources of infection are organs and tissues in transplantology, as well as blood and its products in transfusiology. Routes of transmission of CMV infection: airborne, sexual, vertical and parenteral.
There are congenital and acquired forms of CMV infection. Congenital CMV infection. During antenatal infection of the fetus, infection occurs predominantly transplacentally. During intrapartum infection, CMV enters the body through aspiration of infected amniotic fluid or secretions from the mother's birth canal.
In older children, acquired CMV infection occurs in a subclinical form in 99% of cases. The most common manifestation of this form of CMV infection in children over one year of age is mononucleosis-like syndrome. As a rule, a clinical picture of acute respiratory disease is observed in the form of pharyngitis, laryngitis, and bronchitis.
Infections caused by the sixth, seventh and eighth types of herpes viruses Type six herpes viruses (HHV-6) can cause erythematous and roseolous rashes (sudden exanthema), lesions of the central nervous system and bone marrow in immunocompromised children. Herpesvirus type seven (HHV-7) causes neonatal exanthema
For the diagnosis of herpes infection, cytological, immunofluorescent, serological and PCR methods are valuable. Virological testing for herpes infection reveals complement-fixing antibodies to HSV-1 or -2 in the mother's blood, fetal cord blood and amniotic fluid. PCR method. The material for testing for herpes is blood, throat swabs, the contents of blisters, ulcers, and urine.
The study of specific antibodies of various subclasses: IgM, IgG1-2, IgG3 and IgG4 to herpes viruses is important. The detection in the blood serum of children of specific immunoglobulins M, IgG3, IgG1-2 in a titer > 1:20, viral antigen and specific immune complexes with antigen indicates the severity of the infectious process (active phase), and the determination of only specific IgG4 is regarded as the latent phase of infection or carriage of maternal antibodies.
Consequences
A quick and painless recovery from herpetic lichen is due to the general good health of the patient. A young and strong body with normal immunity copes better with the virus. In general, this disease rarely goes away without any complications - in only 30% of cases. Neuralgic pain after a virus infection can last from six months to several years.
The consequences of herpes zoster can be very serious:
- transverse myelitis with transition to motor paralysis;
- heart failure;
- progression of oncological processes;
- Ramsay-Hunt symptom: paralysis of facial muscles, complete or partial hearing loss;
- damage to the oculomotor nerves;
- brain lesions: encephalitis, serous meningitis, meningoencephalitis;
- blindness caused by retinal necrosis.
Improperly treated herpes zoster can develop a relapsing course with subsequent coverage of other nerve trunks. In addition to a neurologist and a skin clinic, you should definitely visit an immunologist for proper correction of immunity.
Treatment
Herpetic infection occurs in 3 stages:
- Stage 1 – in the active stage or during exacerbation of the chronic course of the disease;
- Stage 2 – prolonged treatment with maintenance doses during the period of remission;
- Stage 3 – identification and sanitation of chronic foci of infection, examination of family members to identify the source of infection.
In all cases, drugs, their combination and duration are selected individually, taking into account the manifestations of the disease, the characteristics of the child’s immune system, age, and course of the disease.
Author of the material: pediatrician at the clinic on Rodionovskaya Telitsyna E.V.
Initial period
Prodromal, characterized by general malaise, neuralgic pain of varying intensity, this lasts on average 2-4 days:
- Headache
- Low-grade body temperature, less often fever up to 39C
- Chills, weakness
- Dyspeptic disorders, gastrointestinal dysfunction
- Pain, itching, burning, tingling in the area of the peripheral nerves in the area where the rash will later appear.
- Most often, during an acute process, regional lymph nodes become painful and enlarged.
- In severe cases of the disease, urinary retention and other disorders of certain systems and organs may occur.
After the temperature decreases, other general intoxication disorders also weaken.