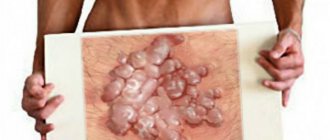
The external genitalia of a woman have a thin folded structure. This is due to the protective mechanisms necessary to prevent infection. However, there are situations in which one or more lumps are found on the labia or surrounding tissues. There can be many reasons for this, and not all of them are harmless. Almost all pathologies are accompanied by burning, itching, pain, swelling and heat (due to the inflammatory process). Here it is better not to wait for complications to develop and seek help from a surgeon.
Inflamed hair follicle
The appearance of a ball on a woman’s labia may be associated with the occurrence of a boil (inflammation of the hair follicle). The intimate area has a large number of hairs. Wearing uncomfortable underwear, damaging the protective layer of the skin during depilation and hair removal, and discharge from the genital tract create a favorable environment for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms inside the follicle.
As a result, a ball with whitish contents and a purulent core is formed. The disease is characterized by painful compaction, a red edging around the affected area, and absence of itching. Treatment should begin immediately by treating the affected area with an antiseptic and applying an antibacterial ointment (for example, Levomekol). If symptoms increase and swelling of the surrounding tissues develops, you should consult a surgeon to open the abscess surgically.
Diagnostics
You can determine why a lump appears on your lip using diagnostic procedures:
- Inspection and palpation of the growth on the lip, detailed questioning of the patient, study of the anamnesis.
- Taking general and biochemical blood and urine tests.
- Hardware studies: ultrasound, x-ray, probing of gland ducts, sialography.
Instrumental diagnostics are used for neoplasms on the lip: cysts, tumors.
Inflammation of the Bartholin gland
The Bartholin gland is a paired exocrine gland, which is located in the thickness of the labia majora and is designed to secrete secretions that maintain normal moisture of the mucous membranes. It can become inflamed for a number of reasons:
- improper hygiene;
- decreased immunity;
- traumatic injury due to tight underwear;
- inflammatory process in neighboring tissues.
As a result, a painful ball forms on the labia, which can reach several centimeters in diameter. The compaction causes discomfort when walking due to its large volume and pronounced inflammation. At the initial stage, a pea-sized ball can be felt (most often on the labia minora). A burning sensation and increased temperature are felt in the same place. A complication is the formation of a cyst or abscess at the site of the lesion, which can only be treated surgically.
Temporary seals
When wearing underwear that is too tight, a pimple may appear, which in appearance resembles a wen or a lump caused by bartholinitis, but after eliminating the traumatic factor, the pimple goes away.
Sometimes acne occurs due to contact with dirty hands or the use of products to which an individual allergic reaction is detected.
Temporary formation of a lump occurs after hypothermia or a cold, but after recovery it disappears.
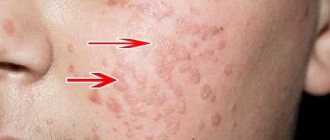
Thrush
A disease caused by pathological reproduction of the fungus of the genus Candida. Infection occurs through sexual contact, although transmission of the pathogen from mother to child can also occur. The acute course is manifested by copious curdled discharge, a white coating and pronounced itching. In the absence of adequate treatment, over time it can become chronic, which is characterized by the appearance of small swollen whitish tubercles on the mucous membrane of the perineum and a rash on the labia. Treatment of the disease should be carried out comprehensively, including the following points:
- antifungal therapy to combat the causative agent of the disease;
- measures aimed at increasing the body's immune defense;
- normalization of vaginal microflora (lacto- and bifidobacteria, lactic acid).
A timely visit to a doctor will help get rid of thrush in 5-10 days.
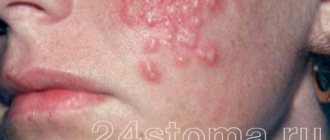
Herpes genital
The disease is caused by herpes virus type 2 (the second name is genital). The resulting balls are of soft consistency and small in size. Often grouped together and filled with watery contents. They cause significant discomfort and can manifest as severe, unbearable vaginal itching. When scratching the affected area, small ulcers form, and the infection spreads to adjacent tissues.
The rashes disappear about a month after the first blisters appear. Even with adequate treatment, the pathology can recur, causing serious discomfort to the woman. It is transmitted sexually, so treatment of both partners is considered mandatory.
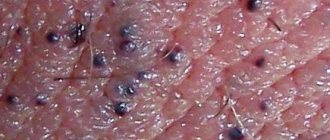
Photo of balls on the labia
Syphilitic chancre
Syphilitic chancre is the primary sign of the development of syphilis. Infection occurs through sexual contact, although contact also occurs. Initially, chancre looks like an area of redness on the skin or mucous membrane. As it develops, it is separated from healthy tissues by compaction along the periphery with the formation of a hard bottom. It may appear as a pea-sized ball on the labia. Its size most often does not exceed 1 cm, but in rare cases two-centimeter chancres are also found.
It does not cause discomfort to the woman and proceeds without itching, burning or pain. This is often the reason for the detection of the disease in late stages, when a number of other symptoms are added. The disease is treated at the first or second stage with antibacterial therapy for three weeks; it rarely becomes chronic.
Stages
Currently, the generally accepted classification of lip cancer is TNM (T-size of the tumor, N-damage to the lymph nodes, M-metastases). Based on the size of the tumor, there are 4 stages of lip cancer.
Table 1. Stages of lip cancer
| Stage | Tumor size |
| T1 | Less than or equal to 2cm |
| T2 | More than 2-4cm |
| T3 | More than 4cm |
| T4a | The tumor grows into the cortical layer of the bone, tongue muscles, maxillary sinus and skin |
| Т4в | The tumor grows in the bed of the masseter muscle, the pterygoid process, the internal carotid artery and the base of the skull |
If on the affected side there are single enlarged lymph nodes, the size of which is less than 3 cm, this is stage N1 lip cancer. At stage N2, enlarged lymph nodes are detected on the affected side, the diameter of which is more than 3 cm. If the patient has single enlarged lymph nodes on the affected side measuring 3-6 cm in size, this is stage N2a of lip cancer. At stage N2, oncologists determine multiple metastases to the lymph nodes. Their size is equal to or greater than 6cm. In the presence of bilateral metastases in the lymph nodes measuring 6 centimeters, they speak of the N2c stage of lip cancer. If the diameter of the lymph nodes exceeds 6 cm, this is stage N3 of the disease.
In the absence of distant metastases, oncologists determine stage M0 of lip cancer, if there are distant metastases - M1, in the case of distant metastases that cannot be assessed - MX. The diagnosis of “early stage lip cancer” is made in the presence of a tumor less than or equal to 2 cm, the presence of single enlarged lymph nodes less than 3 cm on the affected side and the absence of distant metastases. This is T1 N1 M0.
Benign neoplasms
Benign diseases are not seriously life-threatening, but can cause serious discomfort. Possible causes of a ball on the clitoris, labia and perineum include:
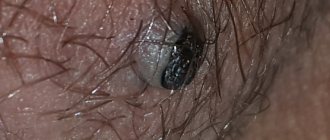
- Lipoma. Neoplasm from adipose tissue. It has a capsule that separates it from surrounding tissues. It can be felt as a soft, moving ball on the labia majora (less often the labia minora). The main reason for the development is the increased tendency of the skin to secrete fat in combination with hormonal imbalance.
- Atheroma. It is a cyst of epidermal tissue, the cavity of which is filled with fatty secretion. Develops when the main duct of the sebaceous gland is blocked. A characteristic feature is a black dot in the middle of the compaction.
- Fibroma. A tumor from the submucosal layer of the vagina, consisting of collagen fibers. The consistency ranges from soft to very dense formation.
- Myoma. A tumor of muscle tissue located in the labia majora. Characterized by slow growth.
- Hemangioma. A neoplasm developing from vascular tissue. It is characterized by the most aggressive growth among all benign tumors. It is more common in childhood and manifests itself as a hard ball on the labia minora.
- Hidradenoma. Tumor of sweat glands. It has small sizes (up to 1 cm) and a low growth rate. Color can vary from light yellow to bright pink.
All benign tumors are surgically removed and sent for histological examination. Its purpose is to determine the tissue identity of the tumor and exclude a malignant process.
2.Atheromas
Atheroma
is a cyst filled with a yellowish fluid formed by fat cells, epidermis and sebum. Since all this in the cyst is in a state of stagnation, when opened, the substance that is usually removed has an unpleasant odor. Causes of atheroma: increased oily skin, acne, poor cleanliness, hormonal changes, heredity. Atheromas form where there are many sebaceous and sweat glands. When they grow to a size of 5 cm, tension occurs on the surface of the skin and even internal inflammation is possible. It is always recommended to remove atheromas without waiting for complications, although they also degenerate extremely rarely.
The atheroma is completely removed by isolating it from the tissue. At the same time, they try not to disrupt its integrity and make sure that no particles of the cyst shell remain, otherwise this may cause a relapse in the same place.
Visit our Gynecology page
Malignant neoplasms
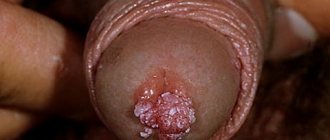
The main oncological disease affecting the external genitalia in women is vulvar cancer. Occurs more often in the postmenopausal period. It is detected late, as in the first stages it does not cause any discomfort.
Additional symptoms with the development of pathology are itching at the site of the lesion and pathological discharge mixed with blood. The disease is a life-threatening condition. Treatment includes surgery, radiation and chemotherapy.
Conclusion: Diseases, the symptom of which is a lump on the genitals, most often do not pose a serious threat to the life and health of the patient. However, in any case, it is necessary to consult a gynecologist to diagnose the formation and decide on its treatment.
Treatment
Pre-hospital assistance
Avoiding uncomfortable underwear and intimate hygiene products that irritate the skin and mucous membranes can help reduce swelling of the vulva. Regular hygiene procedures are necessary. For inflammatory processes, baths with herbal decoctions and antiseptic solutions are indicated. In case of intense pain, a single dose of an analgesic is acceptable. Increasing swelling, foul-smelling or bloody discharge, severe pain, and general health problems are reasons to immediately contact a gynecologist.
Conservative therapy
The treatment plan is drawn up individually after determining the cause of swelling and a comprehensive assessment of the condition of the reproductive organs. Etiopathogenetic and symptomatic agents are used. Drug therapy is supplemented with physiotherapeutic procedures and local techniques. For STIs, medications are prescribed to both sexual partners at the same time. The following groups of drugs are used:
- Antimicrobial
. Depending on the pathogen identified, antibiotics, antimycotic, anthelmintic or antiprotozoal medications are prescribed. - Antihistamines
. Indicated for allergic reactions, severe itching. Helps reduce inflammation and alleviate the patient's condition. - Hormonal
. Local treatment with hormonal ointments is carried out for kraurosis of the vulva, atrophic vulvitis in premenopausal women. - Local action
. Taking into account the etiology of the disease, intravaginal suppositories, tablets, suspensions with antimycotics and antibiotics can be used. To restore the vaginal microflora, suppositories with acidophilus bacteria are recommended.
Patients with acute vulvitis are prescribed SMT, UHF, and ultraviolet radiation. For chronic inflammation, mud applications, ozokerite, paraffin, and infrared laser treatment are effective. Women with vulvar cancer undergo chemotherapy and photodynamic therapy.