Pruritus, the most common dermatological complaint, is characterized by an unpleasant sensation with a continuous need for a response of mechanical irritation of the skin, as a result of which it can cause effects such as skin damage, secondary infection, and scar formation. Itching can also significantly affect the general condition and quality of life of patients, causing emotional disturbances, insomnia, anxiety, and in severe cases, depression and suicidal thoughts [1].
Itching is one of the most common subjective symptoms in dermatology, second in prevalence only to complaints about cosmetic defects. With atopic dermatitis and urticaria, 100% of patients complain of itching, with psoriasis - up to 87% of patients [2]. According to clinical and epidemiological data from H. Alexander et al. [3], 35% of skin clinic outpatients suffer from itching caused by dermatological diseases such as prurigo nodosum, lichen planus, atopic dermatitis, eczema, xerosis, etc.
There is both histamine-induced and histamine-independent itching. Histamine-induced is caused by mechanical, thermal, electrical or chemical stimulation of unmyelinated histamine-sensitive peripheral C-type nerve fibers. Nonhistamine nerve fibers are also involved in the transmission of the itch signal, and therefore many forms of itch are insensitive to antihistamines. Itching is one of the forms of the skin analyzer, close to other types of skin sensation (touch, pain). Severe itching is relieved by severe self-harm, leading to the replacement of the sensation of itching with a feeling of pain [4, 5].
In this regard, it is worth mentioning the vicious cycle of itching—scratching—itching. Damage to the skin barrier and subsequent inflammation lead to the development of itching. In the skin, inflammatory cells activate sensory nerves, mast cells, fibroblasts, and macrophages. All of the above cells release itch mediators, which further increase inflammation. The itch signal is transmitted to the brain, causing the scratch reflex. Scratching further damages the skin barrier and increases inflammation. T lymphocytes and eosinophils migrate into the skin, releasing pruritogen mediators. Ultimately, sensitization of sensitive nerve fibers occurs and the activation threshold decreases. Growth factors released by eosinophils cause proliferation of nerve fibers. These changes increase the sensitivity of the skin, which becomes even more vulnerable to endo- and exogenous factors. This cycle is difficult to break. The itch-scratch-itch cycle leads to disturbances in sleep, concentration and perception, thereby limiting the social activity of patients [6].
Scratching the skin when itching
It is important to know about the vicious circle “itching – scratching – itching”.
This means that when the skin is damaged, followed by inflammation, itching is provoked. In the skin, inflammatory cells release itch mediators, which again increase inflammation. The itching signal is transmitted to the brain, causing a person to need to scratch. Scratching leads to disruption of the skin (excoriation), which again increases inflammation. The skin becomes more vulnerable to internal and external irritants. This is a vicious circle that is difficult to stop. The vicious circle of “itching – scratching – itching” disrupts sleep, reduces concentration and perception processes.
Prevention of itchy dermatitis
The most important method of preventing this condition is to control the underlying disease. When we know what can cause a problem, it is easier to prevent it.
- Food rich in iron will help prevent deficiency of this trace element, which will protect against prurigo. Iron is found in beef, liver, eggs, buckwheat, and apples.
- A hypoallergenic diet will help protect against eczema, another condition associated with itchy dermatitis. If you are prone to atopy, exclude nuts, soy, chicken eggs, whole milk and seafood from your diet.
- If prurigo is associated with celiac disease, gluten-containing products should be removed from the menu. This is wheat, products made from wheat flour, semolina porridge, bread kvass. Products containing rye and barley cereals are also dangerous.
- Managing stress helps a lot in preventing itching. Adequate sleep, calmness, and avoidance of emotional situations are important. It is useful to master breathing techniques and stress management.
- Protecting your skin from irritation and dryness is also an important preventative measure. Avoid prolonged contact with water, sweating, and staying in hot rooms. Use hypoallergenic skin care products. Use a humidifier and drink at least two liters of clean water a day.
Unfortunately, this disease has not been sufficiently studied, and it is not clear what exactly leads to its appearance, so there are no preventive measures that will guarantee that prurigo will not develop. But by following these tips, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of illness.
Types of skin itching
At the appointment, doctors usually clarify with the patient the following characteristics of itching due to dermatitis:
- Intensity: weak, moderate, intense;
- constant or increasing at certain times of the day, for example, in the evening and at night;
- permanent or periodic;
- common – itchy skin all over the body;
These criteria allow you to more accurately determine the causes of itchy skin and prescribe the necessary treatment.
It should be remembered that scratching itchy areas of the skin is dangerous due to possible microbial infection - the so-called secondary infection, which can significantly worsen the condition of the skin and complicate treatment.
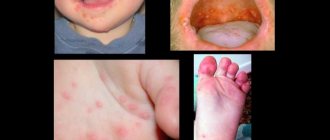
Why does dermatitis occur in children?
Children's skin is fragile and especially sensitive to friction and the effects of household chemicals familiar to adults, and also quickly demonstrates a gastrointestinal reaction to food products that are not suitable for the child's age or individual characteristics.
Aggressive environmental influences or hereditary factors can cause allergic reactions in the baby and manifest themselves on the skin in the form of various rashes. But don't be scared and panic. Let's figure out what types of rashes there are and what is their difference?
Types of dermatitis and diagnosis
Pruritic dermatoses and dermatitis are a group of diseases that are completely different in nature, which are united by a common symptom - itchy skin. It is not always easy to distinguish them even for an experienced specialist.
Table of itchy skin diseases, diagnosis
| Disease | Itching | Localization | Nature of the rash | Age of onset |
| Allergic contact dermatitis | Pronounced or strong, burning sensation | Any where the skin comes into contact with the allergen | Bubbles against the background of redness of the skin, clear boundaries of the lesion | Any |
| Atopic dermatitis | Pronounced or strong | Face, limbs; depends on the patient's age | Bubbles against a background of redness, weeping, crusts, cracks | Most often children's, can be any |
| Psoriasis | From weak to strong depending on the stage of the process | Scalp, natural skin folds or friction points | Psoriatic plaques with gray scales | Any |
| Seborrheic dermatitis | Weak to moderate, may be absent | Scalp, nasolabial folds, upper third of the body | Areas of redness with accumulation of yellow, greasy scales | Teenage, adult |
| Scabies | Strong, unbearable, worse at night | Between the fingers, stomach, groin, buttocks | Red spots or papules arranged in pairs | Anyone, usually children |
| Herpetic infection | Severe, burning skin | Most often the face (lips), along the nerves (shingles) | Small tense bubbles | Anyone, for shingles most often an adult |
| Microbial eczema | Moderate, burning, soreness | Most often limbs, asymmetrically, legs | Bright red spots 1-3 cm with clear boundaries, weeping, blisters and crusts | Anyone, usually an adult |
Causes of itchy dermatitis
It is not known exactly what causes prurigo, or why the skin reacts the way it does. Once itching occurs, rubbing and scratching makes the nerve endings in the dermis thicker and even more susceptible to irritation. This leads to more itching, thus making the condition worse.
In half of the patients, the exact cause cannot be detected, but there are some combinations of diseases that may be related.
- Up to 80% of patients with pruritic dermatitis are also prone to atopy, and may have conditions such as asthma, eczema and seasonal pollen allergies.
- Prurigo nodosa also develops in people with venous eczema (a condition where skin lesions occur due to venous blood pooling in the legs), and may be associated with nummular eczema (which is characterized by a well-defined, coin-shaped rash).
- In some people, nodular prurigo may begin after an insect bite,
- Several diseases may be associated with nodular prurigo, which must be excluded when pruritic dermatitis appears. This is bullous pemphigoid, in which blisters filled with fluid appear on the skin, like after a burn. Dermatitis herpetiformis is characterized by small, round blisters and is a symptom of gluten intolerance.
In 30% of patients, pruritic dermatitis develops as a consequence of a systemic disease, and metabolic and biochemical causes play a role.
- Nutrient deficiency. Here, iron deficiency comes to the fore, which may be associated with a lack of this microelement in food, increased losses (in women with menstruation), or poor absorption in the intestine (with gluten intolerance, after removal of a section of the intestine).
- liver disease,
- Uremia (a condition that develops with kidney failure),
- Severe diabetes mellitus.
Less common causes include thyroid disease, stroke, calcium metabolism disorders, and lymphoma (blood disease).
For the remaining 20%, psychological factors such as depression, anxiety and psychosis play a role. But even ordinary emotional stress can become a trigger. When under stress, people are more prone to scratching the epithelium. Thus, stress worsens the course of prurigo.
How to get rid of itchy skin
Before relieving the itching of dermatitis, it is necessary to establish its cause, since in most cases it will be difficult to get rid of the itching without eliminating the cause.
Regardless of the causes of itching, treatment usually uses remedies aimed at alleviating the patient’s condition, relieving the urge to scratch, and preventing the development of secondary infection in areas of scratching.
Among skin diseases, common causes of itching are atopic dermatitis, eczema, neurodermatitis, seborrheic dermatitis, and psoriasis.
Types of dermatological diseases
In medicine, there are more than a dozen varieties of this disease; let’s look at the most common forms of its manifestation. These include: contact, dry, atopic (or allergic, toxicoderma, eczema, urticaria), seborrheic dermatitis and the price of their treatment depends on the type of lesion.
Dry dermatitis
Symptoms of dry dermatitis appear only in the cold season, due to prolonged exposure to cold or, conversely, too dry air indoors. There is a decrease in immunity and a deterioration in the general condition of the body. A distinctive feature is the duration of the course and the seasonal manifestation of exacerbations.
Contact dermatitis
Foci of simple contact dermatitis form at the site of exposure to the primary irritant. It is distinguished by the absence of manifestations of an acute reaction and the further spread of the inflammation process after the exclusion of the irritating element. For example, when they often wear clothes made from synthetic fabrics, to the fibers of which the body is highly sensitive.
Atopic dermatitis
By atopic dermatitis, clinic doctors mean a chronic, often hereditary allergic disease with recurrent periods and significant complications. In the first stages (in children from 3 months to 2 years, and at 4-7 years), the development of the disease manifests itself in the form of redness with copious discharge and the formation of small blisters. And in the last stages, severe dryness and pallor of the skin predominates.
Toxidermy
Toxicoderma is accompanied by significant damage to the skin from toxic substances. It differs in that the allergen enters the body through the blood, respiratory system and oral cavity. This is a very serious and dangerous disease and at the first manifestations (shortness of breath, swelling of the mucous membranes, stomach pain), you must urgently contact specialists who will professionally provide first aid. It is impossible to remove toxic substances from the body on your own.
Treatment of itchy skin with medications
Considering that itching can be provoked not only by mechanical and chemical irritants, but also by emotional factors, treatment should be comprehensive and aimed at eliminating the cause.
Medical recommendations for the treatment of skin itching due to dermatitis highlight the following means to reduce the intensity of itching:
- Systemic medications for skin itching in dermatitis: antihistamines, mast cell membrane stabilizers, systemic hormonal agents, antidepressants, sedatives, immunosuppressants.
- External medications, which include external anesthetics, hormonal agents, tacrolimus, zinc, menthol and camphor.
Methods of infection
Sometimes we ourselves, without noticing it, put ourselves in danger, without thinking about what consequences allergic dermatitis can lead to when postponing a visit to the clinic. Ways of human contact with allergens that can cause disease:
- medicinal – manifests itself after the introduction of drugs into the body. For example, antibiotics, vitamins, analgesics, gamma globulins;
- food - allergens enter our body along with food;
- professional - observed in people who are constantly in contact with allergens, for example in production with a high concentration of cobalt, nickel, chromium;
- autointoxication – characterized by the accumulation of autoallergens, for example, in patients with pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract.
Eczema
Eczema is also a chronic disease and manifests itself in the form of acute inflammation of the skin and subcutaneous tissue under the influence of internal or external irritants. This allergy is manifested by areas of dry, flaky skin, cracks, redness, swelling and weeping lesions. In severe cases, even damage to the entire surface of the epithelium. Most often, workers in metallurgical plants, pharmaceutical and food industries suffer.
Seborrheic dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis is a disease caused by a certain fungus. Very often, the causes of its appearance are stress conditions, hormonal disorders and diseases of the nervous system.
Skin cap for itchy skin due to dermatitis
To combat skin itching in atopic, seborrheic dermatitis, eczema and psoriasis in adults and children from 1 year of age, external medications based on zinc pyriton activated SKIN-CAP have been successfully used, which:
- can help reduce the severity of skin itching within 5-7 days [1] after the start of use;
- reduce the need to use hormonal [2] and antihistamines [1];
- help prevent the development of secondary infections when scratching, thanks to the antibacterial and antifungal activity of activated zinc pyrithione;
- have a high level of safety, unlike, for example, hormonal ointments, since they have only one contraindication in the form of individual intolerance to the components of the drug [2].
Anti-itching cream for dermatitis and Skin-cap aerosol can be used in children from the age of 1 year.
Symptoms of itchy dermatitis
- Simple prurigo is characterized by the appearance of symmetrically located areas with intense itching. There, over time, small dome-shaped flesh-colored bumps (papules) form, which itch intensely. Sometimes they transform into blisters containing clear liquid. To a greater extent, the disease affects the outer surfaces of the arms and buttocks, but can also be located in other areas of the head, neck, torso and limbs. This type of prurigo can affect people of any age; it occurs in both children and adults. Over time, the papules that appeared at the beginning of the disease are scratched off and disappear, but new ones are formed. This condition leads to a significant deterioration in quality of life, the itching worsens at night and interferes with sleep.
- Pigmented prurigo is a simple variant when pigment accumulates in papules and they change color and become darker than the underlying skin.
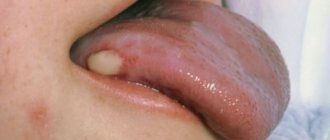
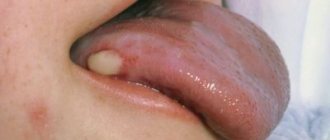
- With nodular prurigo, dense bumps and pimples appear on the skin, similar to warts, which bring a lot of discomfort. They may be darker than the skin surrounding these lesions. Their surface is rough, it is noticeably thickened, and many scratches and scratches are visible. The nodules are usually no more than a centimeter in diameter, they are very dense to the touch, can be sensitive, ulcerate, crust over and itch. The arms and legs are the areas most commonly affected, but the back, buttocks, shoulders and chest can also be affected by the disease. Scars and cicatrices are noticeable, differing in color from the underlying epithelium, which form at the site of scratching. Nodular prurigo is more common in young and middle age (30 - 60 years), equally common in men and women, and in representatives of all nationalities. The number of nodules gradually increases. This variant of prurigo is difficult to treat.
For diagnosis, a doctor usually only needs to examine the patient. The very appearance of skin rashes in combination with itching indicates itchy dermatitis. In some cases, a piece of the rash is taken and a biopsy is performed to clarify the diagnosis.