Causes of stye on the eye
One of the main reasons for the appearance of stye on the eye of an adult is a bacterial infection - Staphylococcus aureus or Staphylococcus aureus. Normally, this bacterium lives on the skin and does not cause any harm to the body, but under the influence of a number of unfavorable factors, a suitable environment is created for its reproduction.
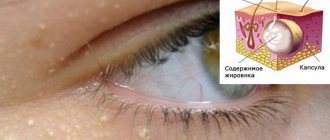
At the same time, inside the eyelid there are clusters of sebaceous and meibomian glands. The latter produce the oily part of tears, the purpose of which is to ensure the stability of the tear film and the smooth sliding of the eyelids over the surface of the eye. Disruption of these glands can lead to their inflammation and the formation of a small purulent pimple.
You can also identify a number of the most common factors that provoke stye on the eyelid:
- weakening of the immune system;
- diabetes;
- worms;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- cold;
- hypothermia;
- neglect of hygiene rules;
- use of other people's cosmetics;
- stress.
Another possible causative agent of the inflammatory process is the parasite Demodex. This mite lives on the skin of 80% of the world's population. It is not dangerous for a healthy person, however, if there is a weakened immune system, endocrine disorders, gastrointestinal diseases, skin diseases, demodex can cause various inflammations, including the formation of barley.
Is it contagious to others?
This disease is not transmitted by airborne droplets. However, upon contact with a person who has an abscess, especially an external one, an infection can be acquired. Infection occurs due to the fact that fluid is formed at the site of inflammation, which is then released through the pores onto the surface of the skin, and along with it the infection comes out. It, in turn, can spread to a healthy person through clothing, household items, cosmetics, a handshake, etc.
Transmission of a dangerous pathogen can easily occur if a patient’s abscess ruptures. Its contents usually come out throughout the whole day, so it is very important all this time to carefully monitor the hygiene of not only your own hands, but also treat the site of inflammation with antiseptics in order to protect others and prevent the spread of infection.
What is local therapy?
Local therapy is symptomatic treatment. It includes hygiene procedures, eyelid massage, etc. For scaly blepharitis of the upper eyelid, it is imperative to wash the eyelids once a day and treat them with ointments at least 5-6 times. To do this, you can use tetracycline or albucid ointment, which your doctor will recommend. The medicine should be carefully applied with your finger to the front edge of the eye.
If a patient is diagnosed with ulcerative blepharitis of the upper eyelid, then the crusts that form on the eyelids must be removed. The easiest way to do this is after they have dried. The exposed skin surface, which has a pink tint, should be lubricated with a solution of brilliant green. Upon completion of the manipulation, it is necessary to instill any disinfectant drops.
If blepharitis of the upper eyelid occurs due to demodicosis, then massage sessions should be performed. They are performed with special sticks and only on an outpatient basis. This method of treatment is considered traumatic. Therefore, this procedure must be carried out only in a hospital. The massage is performed by a specialist. Self-sessions can be dangerous to the eyes.
Symptoms and first signs
Sometimes the disease occurs in a mild form, without causing any discomfort, and manifests itself only by the formation of a small tubercle on the lower or upper eyelid. But most often, the symptoms of stye on the eye bring a lot of inconvenience in the form of pain, itching, swelling, headache and redness of the eyes.
It is best to start treatment before a pimple appears on the skin. At the beginning, a person notices slight swelling of the eyelid and redness. After a few hours, itching appears, which only intensifies over time. After about a day, you can feel a lump forming under the skin, resembling a boil or pimple.
Pathologies
Inflammatory diseases of skin folds are acute and chronic. It can affect the upper, lower eyelid, or both eyes at the same time.
Acute
Among the most common acute ones:
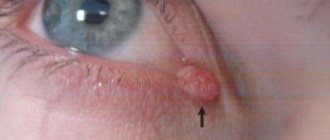
- Barley. External (purulent inflammation of the hair follicle) or internal (meibomian gland). Caused by Staphylococcus aureus disease.
- Furuncle. Purulent necrotic inflammation of the hair follicle, sebaceous glands and surrounding connective tissue. Localized on the upper eyelid, in the eyebrow area. Rarely on the edge of the eyelid in the area of the outer canthus. The causative agent is staphylococcus.
- Dacryoadenitis is inflammation of the upper eyelid. Complications after common infections (flu, sore throat, etc.)
- Dermatitis. Occurs as a result of allergies, gastrointestinal disorders, autoimmune diseases. To the symptoms listed above are added itching, peeling, and rashes in the form of blisters.
Less common are eyelid abscess and phlegmon.
Chronic
Chronic diseases include:
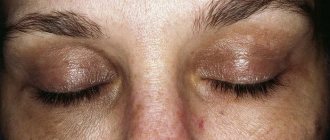
- Blepharitis is inflammation of the edges of the eyelids. Caused by skin bacteria. Demodectic blepharitis - caused by mites of the genus demodex. There is redness and swelling of the edges of the eyelids. Itching. Eyelash loss. With ulcerative blepharitis, there are ulcers and purulent crusts.
- Chalazion is a proliferative inflammation of the meibomian gland and the cartilage around it. It can occur both after barley and independently.
Blepharitis and chalazion are often combined with conjunctivitis.
Classification
Depending on the number, ulcers can be multiple or single. Unlike single ones, multiple formations cause more intense symptoms and are accompanied by general malaise. This situation requires immediate consultation with an ophthalmologist.
If the disease appears for the first time, they speak of an acute course of the disease, but in the case when inflammation in the eyes appears with some frequency, barley is called recurrent.
According to localization, the abscess can be internal or external.
Interior
A small pimple appears on the side of the conjunctiva, caused by inflammation of the meibomian glands. In the first 2-3 days, a tubercle forms on the inner surface of the eyelid, accompanied by pain and itching. After 3-4 days it opens, and a small scar forms in this place.
Outer
Swelling occurs at the eyelash edge, and after a few days it fills with pus. Usually the barley opens after 3-4 days, the contents come out, the wound ceases to be painful and soon heals.
Stages of the disease
There are several stages in the development of the disease:
- Infiltration. A small bump appears on the inner or outer surface of the eyelid, which can easily be confused with a speck that has gotten into the eye. In this area, itching, redness, and slight swelling occur, which intensify over time.
- Suppuration. After some time, the swelling increases, fills with pus and causes serious discomfort when touched or blinked.
- Breakthrough of the abscess. In the normal course of the disease, after 3-4 days the abscess ripens and ruptures itself, the contents coming out to the surface of the skin. if this does not happen, the purulent capsule will have to be opened surgically in the doctor’s office.
- Healing. The affected area ceases to be painful, the wound heals, a crust forms, which falls off over the next few days, revealing healthy tissue.
Hygiene procedures for blepharitis of the upper eyelid
Blepharitis is difficult to cure if hygiene procedures are not followed. Their implementation plays an important role in the treatment and prevention of this ophthalmological disease. The main hygienic procedure is daily eye washing. It is best to use sterile dressings and exclusively boiled water for this. Medicinal infusions of chamomile, marshmallow, rose hips, thyme or calendula, which have an anti-inflammatory effect, will have a good effect.
The prepared solution should be at room temperature. This will avoid damaging the damaged skin of the eyelids. It is necessary to rinse both eyes at once, even if only the eyelid is inflamed. Individual cotton swabs or bandages should be used for each. Reuse of hygiene products is prohibited. This can lead to infection of the visual organs and cause serious complications.
Diagnosis and treatment
To quickly and effectively treat the disease, you should seek medical help as soon as possible. Before choosing the appropriate therapy, the ophthalmologist at the First Clinic Orekhovo will prescribe tests to determine the nature of the inflammation and the sensitivity of pathogenic bacteria to antibiotics. Based on the results of laboratory tests, a treatment plan is drawn up, which includes not only the use of antibacterial drugs, but also the external use of appropriate drops and gels.
Will it go away on its own?
In many cases, the abscess goes away on its own and does not require special treatment, but you should not neglect visiting a specialist. The doctor will give the necessary recommendations and ensure that the recovery process proceeds safely and quickly. However, it happens that over time the barley remains intact and the abscess does not open. Such inflammation on the eyelid can persist for more than one month and can often be eliminated only through surgery.
Treatment with folk remedies
It often happens that treatment for blepharitis is delayed for many months. It is highly undesirable to use medications during this period. In such situations, traditional medicine becomes a good alternative. Infusions and decoctions of medicinal herbs are usually used, for example:
- sage;
- chamomile;
- calendula;
- Kalanchoe;
- eucalyptus.
A well-proven remedy is onion decoction with the addition of boric acid. It is recommended to wash your eyes with it no more than twice a day. Propolis is considered an effective remedy. A teaspoon of crushed substance is mixed with 100 grams of Vaseline. After this, place it in an opaque container. The damaged area of the eyelid should be carefully lubricated with a thin layer of the resulting solution.
Traditional medicine is “rich” in a variety of recipes for the treatment of ophthalmological diseases. You can use various plants. It can be aloe, and drupe, and parsley. The main thing is to follow the recipe and consult with your doctor before starting to use such products.
What not to do with barley
Under no circumstances try to squeeze out the abscess. Purulent contents can spread through the blood throughout the entire eye, which leads to blood poisoning, eyelid abscess and other extremely dangerous consequences.
If an abscess appears, it is also not recommended:
- rub and comb your eyes;
- perform any manipulations with dirty hands;
- apply cosmetics;
- use contact lenses;
- warm or cool the site of inflammation.
What is an eyelid abscess?
Purulent inflammation can sometimes occur in the eyelid , in which the affected area begins to redden, swell and swell , and the patient feels pain and general weakness in the body.
This symptom is characteristic of most infectious diseases.
Technically, such inflammations are concentrated in certain foci, which in ophthalmology are called abscesses.
Reference! The danger of such a disease is that it can quickly spread to other organs of the head, and it is difficult to predict how long after the diagnosis of the disease this can happen.
The worst case scenario is the spread of purulent processes to the brain, which is located in close proximity to the organs of vision.
to begin treatment of an eyelid abscess immediately after diagnosis , while the use of folk remedies and methods in this case is unacceptable, and all procedures should be carried out only in a hospital setting .
Complications
If you ignore the disease and do not start treatment on time, there is a high risk of developing the following complications:
- Conjunctivitis is the spread of pus throughout the eyeball and inflammation of the mucous membrane.
- Orbital phlegmon is a purulent inflammation of the orbital tissue of the eyeball. When purulent contents are released, the infection can spread to the deeper layers of the skin and eye tissue.
- Chalazion - stye degenerates into a round formation on the outer side of the eyelid. It is painless, but causes discomfort, as it puts pressure on the eyeball and reduces the quality of vision.
- Vascular plexus thrombosis is a circulatory disorder in the central vein or its branches due to blockage of blood vessels.
- Meningitis is inflammation of the brain due to the spread of infection.
- Sepsis is blood poisoning when purulent contents enter it.
Sources
- Samuylo E.K., Kozlov R.S., Krechikova O.I., Sukhorukova M.V. Bacterial infections in ophthalmology: standardization of pharmacotherapy based on objective data // Problems of standardization in healthcare. - 2013. - No. 3-4. — pp. 21-28
- Trubilin V.N., Polunina E.G., Angelova D.V., Evstigneeva Yu.V., Chinenova K.V., Kumar V., Pozharitsky M.D. Algorithm for the treatment of meibomyitis, barley and chalazion // Ophthalmology. — 2022 — No. 16(4). — pp. 515–521.
- Deibel, J.P.; Cowling, K. Ocular inflammation and infection // Emergency Medicine Clinics of North America. — 2013. — May (vol. 31, no. 2). - pp. 387-397.
- Lindsley K, Nichols JJ, Dickersin K. Non-surgical interventions for acute internal hordeolum. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jan 09; 1:CD007742.
- McAlinden C, González-Andrades M, Skiadaresi E. Hordeolum: Acute abscess within an eyelid sebaceous gland. Cleve Clin J Med. May 2016; 83(5): 332-4.
Stye in a child
In children, due to the characteristics of the immune system and their lifestyle, this purulent disease occurs quite often. Inadequate treatment or untimely medical care can provoke eyelid abscess and other equally dangerous complications.
It is important to understand that in children under one year of age, the orbital tissue of the eyeball is especially fragile, so an ordinary stye can turn into an abscess even faster - within a few hours. Therefore, it is important to closely monitor the child’s health and, at the first suspicion of a disease, immediately contact a specialist.
Signs of the upper eyelid
The inflammatory process that forms along the edges of the eyelids is blepharitis. The disease is quite common in adults and children. However, adults are predisposed to lesions of the upper eyelid. Signs of the disease become noticeable almost immediately. You shouldn't ignore them. The list of the most common symptoms includes:
- itching and burning;
- redness in the eye area;
- the occurrence of edema or swelling;
- increased visual fatigue;
- serous or purulent discharge;
- feeling of heaviness of the eyelids;
- photophobia.
In some cases, there is an increase in temperature. But it may not always be observed and depends on the state of the body’s immune system. Sometimes ophthalmologists note a thickening of the thickness of the eyelid, which indicates the “addition” of such ailments as, for example, barley, etc.
Disease prevention
To prevent the development of barley, the following recommendations should be followed:
- regularly clean the surface of the eyelids;
- strengthen the immune system;
- eat foods rich in vitamins and microelements;
- eliminate alcohol consumption and smoking;
- reduce the number of stressful situations;
- establish a sleep schedule;
- Visit your ophthalmologist regularly for preventative eye examinations.
The ophthalmologist at our medical clinic has extensive experience in treating inflammatory eye diseases and will do everything necessary to effectively and quickly cope with the pathology once and for all. You can make an appointment by phone or by leaving a request on the website.
Diagnosis of inflammatory diseases of the eyelids at the Yauza Clinical Hospital
Specialists at the Yauza Clinical Hospital make a diagnosis based on examination, clinical picture, and medical history.
Blepharitis. To identify the disease we use:
- bacteriological culture of a smear from the conjunctiva
- bacteriological examination of eyelid discharge
- biomicroscopy of the eye
- biopsy with histological examination of tissue
- microscopic examination of eyelashes for demodex mites
Barley. The ophthalmologist conducts a visual examination of the patient, a bacteriological examination of a smear from the conjunctiva, a microscopic examination of eyelashes for demodex mites, etc.