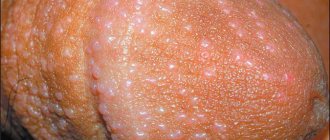
Due to their anatomical structure, the male genital organs are exposed to constant contact with the environment, which increases the risk of infection and spread of infection. Redness on the head and foreskin is a fairly common phenomenon and occurs in every tenth man. An unpleasant disease is called balanoposthitis and can appear at any age and has various causes.
Despite its apparent harmlessness, it can lead to very serious and dangerous consequences. An infection or fungus can cause a serious illness that requires long-term and expensive treatment if you do not seek medical help in time.
What are the causes of the disease, how is it treated and are there any preventive measures, explains urologist-andrologist Alexander Anatolyevich Tsybulin.
Contact dermatitis of the penis
Contact dermatitis is a dermatitis that occurs as a result of contact with a specific substance.
It may itself be irritating or cause hypersensitivity reactions.
Based on the mechanism of development of inflammation, contact dermatitis is distinguished:
- simple - occurs when an irritating substance comes into contact with the skin (in fact, this is a consequence of a chemical burn)
- allergic - develops when a chemical compound comes into contact with the skin of the penis, causing hypersensitivity reactions
Redness of the head and foreskin: causes
One of the most common pathologies is infectious lesions of the genitourinary system.
Today, most males suffer from them.
In addition to sexually transmitted diseases, the causes of redness of the genital organ are:
- 1. Injuries;
- 2. Inflammatory processes;
- 3. Rubbing;
- 4. Allergies.
If redness of the head or foreskin appears, the causes and treatment can be varied.
If redness appears on the head, this may be a signal of an infection.
Such diseases include:
- Gonorrhea;
- Trichomoniasis;
- Chlamydia.
Redness and pain of the head in such diseases is one of the leading symptoms.
In this case, burning and itching occurs.
You can often notice the presence of hyperemia on the head of the genital organ.
Let's take a closer look at what causes the appearance of redness and itching on the head of the penis.
Redness on the head due to rubbing
Rubbing the genitals is quite easy.
At the same time, various unpleasant symptoms begin to be felt.
A man may feel a burning sensation and swelling in the foreskin area.
Redness of the mucous membrane and skin of the penis appears.
After some time, small bubbles appear followed by the formation of erosions.
There are several reasons for the appearance of unpleasant symptoms.
Mechanical damage can occur as a result of prolonged sexual intercourse or masturbation.
Chafing of the penis can be noticed after sexual intercourse.
If there are no pathological processes, then the skin of the penis will be slightly hyperemic with slight swelling.
In this case, transparent discharge will appear.
The problem may occur due to insufficient lubrication.
Another reason for the appearance of chafing may be poor-quality synthetic underwear.
Wearing such underwear leads to skin irritation.
Failure to comply with hygiene rules contributes to the growth of bacteria.
As a result, redness and itching appears.
Chafing of the penis brings a lot of discomfort.
This condition should normally go away after a few hours.
There are cases when the symptoms are pathological and require immediate treatment.
Pathological signs include:
- 1. The presence of an unpleasant odor;
- 2. Painful excretion of urine;
- 3. Presence of redness and ulcers.
If such signs appear, it is recommended to shave and see a doctor.
Redness on the head due to allergies
Often the cause of redness at the tip of the head is an allergic reaction.
Appears when the genital organ is exposed to allergens.
One of the reasons is the use of various lubricants, creams and lotions.
Medicines can also have an effect on the penis.
The appearance of redness on the head of the penis may be a consequence of the administration of vitamins and vaccines.
How to distinguish allergies?
When exposed to skin, erythema appears, which is the formation of red spots on the skin of the penis.
Symptoms develop very quickly.
After using antihistamines, itching and other symptoms disappear.
After some time, the rashes disappear, leaving no traces behind.
If the reaction is severe, medical attention may be needed.
It is recommended to consult a doctor if the symptoms persist.
If personal hygiene is not carried out regularly, allergies will not be long in coming.
This occurs due to the fact that secretions begin to accumulate in the foreskin, provoking the proliferation of bacteria.
If the head itches and redness appears, it is necessary to identify the allergen and limit its effect on the genital organ.
Redness on the head may occur when using hormonal ointments.
You should not use these drugs for a long time and without a doctor's prescription.
If a reaction occurs, you should see a doctor.
Redness on the head due to an STD
The appearance of redness, itching of the glans and foreskin is a sign of sexually transmitted infections.
Often the cause of transmission of an infectious agent through sexual contact will be a defect in the mucous membrane.
The onset of symptoms causes severe discomfort.
There are a number of reasons for the appearance of blisters, redness and itching of the head of the penis.
These include:
- Injury to mucous membranes and skin;
- Inflammatory processes;
- Disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- Narrowing of the foreskin.
The appearance of a white coating and redness on the head may be the result of unprotected sexual intercourse.
Infection occurs from a sexual partner.
The presence of such signs is a consequence of infection with one of the diseases:
- 1. Trichomoniasis;
- 2. Gonorrhea;
- 3. Chlamydia;
- 4. Genital herpes;
- 5. Gardnerellosis;
- 6. Mycoplasmosis;
- 7. Candidiasis.
When infectious agents are introduced, an infectious process begins to develop.
There is a problem with urination.
The appearance of discharge of various types is noted.
Attention! For each disease, the discharge will have a characteristic color and consistency.
Sometimes severe rashes appear in the groove.
This is typical when affected by herpes.
Causes and symptoms of contact dermatitis of the penis
Simple contact dermatitis is rare.
This is due to the fact that it occurs as a result of contact with industrial liquids, household chemicals and other substances with which the male penis comes into contact extremely rarely.
Most of the work is done by hand.
Therefore, it is on the hands that this type of dermatitis most often develops.
However, there are sometimes cases where similar phenomena are observed on the penis.
This is possible if a man:
- spilled a liquid that has irritating properties on yourself
- used a liquid hazardous to the skin for self-medication (when trying to remove warts, to fight pubic lice, to disinfect a scratch, etc.)
More often, contact dermatitis of the penis develops in people who practice self-medication.
Including the use of folk remedies that are mistakenly considered safe only because of their natural origin.
Also, a considerable amount of industrial substances can cause a chemical burn.
Among them:
- phenol
- paint solvents
- sodium hydroxide
- acids
- detergents
- kerosene
With a single contact of the skin of the penis with an irritating substance, dermatitis does not last long.
Symptoms usually go away on their own after a few days.
With extensive skin burns, they persist for several weeks.
Repeated contacts lead to a long course of the disease.
It can last for months and even years.
However, when contact dermatitis is localized specifically on the penis, such cases are very rare.
This is due to the fact that even the most avid lover of traditional medicine understands after some time that applying acids, kerosene or herbal tincture to the penis leads to inflammation of the skin.
Therefore, he stops trying to self-medicate.
Simple contact dermatitis can occur in acute, subacute and chronic forms.
In the acute form of the disease, red plaques appear on the skin of the penis.
They have clear boundaries.
Upon examination, local tissue swelling is detected.
There are many small vesicles on the surface of the plaques.
They are small bubbles with transparent contents.
There is no umbilical depression in the center.
Point erosions appear.
A clear liquid is released from them.
After a few days, crusts form at the site of erosion.
If acute dermatitis of the penis develops as a result of one contact with an irritating substance, then repeated contacts with a less aggressive chemical compound leads to subacute dermatitis.
It is characterized by peeling on the surface of the plaques.
There are no vesicles.
But often many small papules appear.
These are cavityless elements of red color, slightly rising above the surface of the skin.
Chronic contact dermatitis on the penis is very rare.
It develops only in people who persist in self-medication.
And also among those who perceive the symptoms that arise not as a consequence of inadequate therapy, but as an exacerbation of a disease requiring further treatment.
It is often not so easy to determine that skin lesions that occur are related to a certain substance.
Because after the first application there is no reaction.
Subsequently, after systematic use, it gradually develops, the intensity of changes increases.
However, after each application there is no sudden deterioration.
Therefore, patients do not always understand that the substance they are using is toxic to the skin.
With constant application of an irritating chemical compound to the head of the penis, foci of lichenification occur.
The epidermis in the affected area thickens.
The skin pattern intensifies.
Transverse stripes or diamonds are formed.
May be present:
- skin redness
- small papules, usually flat
- scratching, as patients often suffer from itchy skin
Over time, the skin becomes pigmented.
It becomes darker than in adjacent areas.
What complications can there be?
To effectively treat redness of the glans and foreskin, you must consult a doctor at the first sign.
Otherwise, cicatricial phimosis will cause discomfort. This is a pathology that is characterized by deformation of the tissues of the penis. As a result of constant inflammation and deformation, scars form on the tissues. The foreskin gradually narrows, causing the development of phimosis.
In the absence of therapy at this phase, paraphimosis develops - a pathological condition in which the head is pinched. The condition is usually accompanied by painful swelling.
If the form is advanced and without timely treatment, surgical intervention may be required. Also a serious danger is posed by atrophy of the head receptors with a decrease in sensitivity, which, in turn, leads to erectile dysfunction and decreased libido. This negatively affects the quality of sexual life.
With prolonged redness of the head of the penis and foreskin, without timely medical intervention, urethritis develops. Gradually, the infection leads to the development of complications: prostatitis, cystitis, pyelonephritis, orchiepididymitis.
Causes of the disease
The main factors for the spread of infection are:
- poor hygiene;
- the use of antiseptic solutions after sexual intercourse;
- frequent washing of the genitals with soap, leading to skin irritation;
- mechanical damage to tissue integrity;
- uncontrolled treatment with antibacterial drugs;
- anatomical features of the structure;
- hormonal imbalances;
- the presence of certain autoimmune diseases;
- infections.
The disease can be caused not only by sexual (genital) contact, but also by oral and anal contact. Sometimes six months pass before the first symptoms appear.
Symptoms
- Burning in the genital area.
- Pain during sexual intercourse, when urinating.
- Swelling, sharp and burning sensation.
- Exposing the head becomes difficult and pain occurs.
If you have unpleasant symptoms, there is no need to self-medicate and try to find an ointment or gel on your own that will relieve burning and swelling. This always leads to the development of even greater complications, and the infection goes deep into the genitourinary tract.
Diagnosis of contact dermatitis of the penis
Contact dermatitis can be defined clinically based on symptoms.
Sometimes there is a need for pathomorphological examination of the skin.
Then a biopsy is taken.
Of no small importance in diagnosis is the differentiation of simple contact dermatitis from allergic one.
The differences are as follows:
- with simple acute contact dermatitis, papules do not appear on the penis, but with allergic dermatitis, they form quite often
- against the background of chronic simple contact dermatitis, cracks form on the penis, but this does not happen with allergic reactions
- with simple dermatitis, the affected area is limited strictly to the area affected by the toxic substance, while with allergic inflammation it spreads to adjacent areas of the skin
- with allergic dermatitis of the penis, general symptoms are possible, but with simple dermatitis there are none
- the severity of the symptoms of simple dermatitis depends on the concentration of the irritating substance applied to the skin of the penis, while with the allergic nature of the inflammation, the amount of the allergen does not matter
If a patient is allergic to a certain substance, then after sensitization has occurred, each subsequent contact with the allergen will be accompanied by symptoms of dermatitis.
Whereas with chronic simple dermatitis of the penis, the reaction does not develop immediately, but after a certain time after regular application of a toxic substance to the penis.
Scleroderma is a fairly common chronic skin disease in the practice of a dermatologist. Recently, there has been an increase in the number of patients with this dermatosis, while the number of patients with both plaque and linear forms of the disease, as well as lichen sclerosus, is increasing. However, it is necessary to focus the attention of specialists on the group of patients with rashes on the skin of the penis for a number of reasons. Firstly, the number of such patients has recently increased. Secondly, this contingent has become “younger”. So, previously men aged 40-50 years old came to us, but now this problem also occurs in men 20-30 years old. Thirdly, it is patients with limited scleroderma who complain of unpleasant sensations. Such complaints include difficulty exposing the head of the penis, pain during intercourse, and the appearance of cracks after intercourse. Moreover, all patients who contacted us were sexually active. Fourthly, all patients came to us at the stage of atrophy development, while patients with the plaque form of scleroderma come mainly at the stage of hyperemia and induration. Also noteworthy is the fact that all patients in this group did not immediately turn to a dermatologist, but were treated for some time by other specialists (urologists). In addition, this group of patients is also ignored in the specialized literature. The main attention is paid only to the presence of erectile dysfunction in patients suffering from systemic scleroderma [1-3]. However, other problems of patients with limited scleroderma with rashes on the skin of the penis are not considered in the specialized literature.
Currently, there are two forms of scleroderma: limited, in which the skin is affected, and systemic, in which the pathological process affects the skin and internal organs. In turn, limited scleroderma is divided into plaque form, linear form, and lichen sclerosus. The linear form of scleroderma includes strip-shaped, saber-shaped and ring-shaped forms.
The clinical picture of limited scleroderma is represented on the skin of the penis by a ring-shaped focus of hyperemia, which subsequently becomes denser, and then atrophy develops over time. However, most patients at this stage do not pay attention to the change in skin color in the penis area. Over time, the skin in the area of the lesion acquires a whitish tint, becomes thinner and causes a narrowing in the area of the shaft of the penis or foreskin. When the lesion is localized in the area of the foreskin, the narrowing can cause difficulties in exposing the head of the penis, tears in the skin and cracks in the area of the foreskin, and pain during sexual intercourse. The development of a limited form of scleroderma in the penile area may lead to the need for circumcision.
This disease must be differentiated from keloid-like nevus, penile leukoplakia, linear keloid, stripe-like skin atrophy and penile candidiasis.
Keloid-like nevus is characterized by the appearance in the first weeks of life, the absence of dynamics of the process and atrophy.
Leukoplakia of the penis is characterized by a delicate clouding of the mucous membrane or skin, reminiscent of a grayish film that does not come off when scraped. Subsequently, the lesion begins to rise above the unchanged skin, its surface is uneven, there may be outgrowths and foci of keratinization, as well as cracks and ulcerations. However, leukoplakia does not lead to atrophy.
Stripe-like skin atrophy is characterized by symmetrical foci of atrophy in areas of increased skin stretching and has the appearance of narrow stripes of varying lengths located below the level of unchanged skin. At the initial stage, the lesions have a pinkish-bluish color, which changes to whitish over time. The surface of the lesions is smooth and shiny or wrinkled and folded.
Linear keloid is a lesion protruding above the surface of unchanged skin, dense on palpation without atrophy.
Candidiasis is characterized by the formation of a whitish coating and superficial erosions on the glans penis or the inner layer of the foreskin. Patients complain of itching, burning and soreness.
During the period from January to October 2016, 88 patients (65 women and 23 men) suffering from limited scleroderma applied to the Warsaw branch of the Moscow Scientific and Practical Center of Dermatovenereology and Cosmetology of the Moscow Department of Health. Of the 23 men, 13 patients were diagnosed with limited scleroderma, a plaque form on the skin of the trunk and limbs, 10 patients had a ring-shaped form of limited scleroderma in the penile area, and in 1 patient the focus of limited scleroderma was located on the skin of the scrotum with transition to the shaft of the penis. Thus, patients with rashes on the skin of the penis accounted for 43% of all male patients suffering from limited scleroderma who contacted our branch during the described period. Patients paid attention to the presence of subjective sensations: difficulty exposing the head of the penis, tears in the skin and cracks in the foreskin, pain during sexual intercourse. Patients were aged from 22 to 58 years (Fig. 1) with disease duration from 3 months to 3 years (Fig. 2).
Rice. 1. Age of patients.
Rice. 2. Duration of the disease.
It is noteworthy that all patients with rashes on the skin of the penis came to us no earlier than 3 months after the appearance of the first symptoms. Moreover, four patients had been treated by urologists for 1-2 months before contacting us.
Objectively, on the skin of the penis there were ring-shaped foci of a pinkish-lilac color with induration (Fig. 3, a) or whitish foci of atrophy (see Fig. 3, b).
Rice. 3. Limited scleroderma on the skin of the penis. a - ring-shaped lesions of a pinkish-lilac color with induration; b — foci of atrophy are whitish in color.
During examination, difficulty was noted in exposing the glans penis; four patients had skin tears in the area of the foreskin. Upon admission, patients were prescribed penicillin drugs, and then prednisilone at a dosage of 30 mg/day with gradual withdrawal of the drug over 1.5-2 months. It should be noted that during the therapy, 9 patients showed improvement, and there was no need for circumcision (Fig. 4, a, b).
Rice. 4. Limited scleroderma on the skin of the penis. a - before treatment; b - after treatment.
Thus, I would like to draw the attention of colleagues to the fact that treatment of this group of patients requires the prescription of glucocorticosteroids due to the fact that the narrowing will intensify, which may lead to the need for circumcision. However, this operation does not always give a positive result, since sclerosis may, in turn, develop at the site of the scar, which will cause further narrowing and dysfunction of the organ. It also seems to us that interdisciplinary cooperation with urologists is necessary in view of the fact that the primary treatment of patients with this disease is often faced by doctors of this related specialty.
Korsunskaya I.M. — https://orcid.org/0000−0002−6583−0318
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Treatment of contact dermatitis of the penis
The most important thing is to find out the irritant and eliminate it.
Acute simple contact dermatitis of the penis does not require treatment if the reaction occurs after a single contact with the substance.
It is enough not to repeat its application to the penis, and the symptoms will go away over time.
If the clinical manifestations are severe, the help of a doctor may be required.
When large bubbles form, they are punctured.
But the lid of the bubble is not removed.
Subsequently, bandages moistened with antiseptics are used to avoid infection.
To reduce symptoms, weak topical corticosteroids may be used.
In severe cases, systemic glucocorticoid therapy is used.
Allergic dermatitis on the penis
The disease develops as a delayed allergic reaction.
In childhood, this type of dermatitis practically does not occur.
But in adult men this is a very common phenomenon.
Allergic dermatitis is a classic delayed-type reaction mediated by T lymphocytes.
After the first contact, no changes are observed on the skin of the penis.
Because it takes time for sensitization to occur (the body produces antibodies to the allergen).
How long it takes depends on how strong the allergen gets on the skin of the penis.
If it is weak, sensitization may occur only after several months or even years.
Strong allergens cause rapid sensitization, so with repeated contact with them, signs of dermatitis on the penis may appear within a few days or weeks.
The main subjective symptom is itching.
Less commonly observed general symptoms:
- hyperthermia
- weakness
- headache
- chills
It is important for the doctor to find out what substance the reaction occurred to in order to prevent further contact with it.
Common causes of contact dermatitis include:
- antibiotic neomycin
- paraphenylenediamine, which may be contained in fabric dyes (if it is present in underwear, then dermatitis will occur not only on the penis)
- creams with sulfonamides
- procaine, benzocaine (local anesthetics)
- formaldehyde, mercury - can be part of antiseptics
Allergens are often included in lubricants, spermicides, cosmetic creams and preparations.
If the drugs are not used by a man, it is worth checking whether the woman is using them intravaginally.
If the patient's partner uses them, it is possible that it is to the components of these drugs that a reaction occurs after sexual intercourse.
Some men are allergic to latex.
This is a natural substance from which condoms are made.
Causes
The cause of inflammation of the head of the penis can be infectious or non-infectious. One of the main non-infectious causes is poor hygiene of the genital organs, as a result of which secretions begin to accumulate under the foreskin, which causes an inflammatory process. Other causes of inflammation of the head of the penis include:
- infectious and inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system (urethritis, cystitis);
- skin diseases (psoriasis, dermatitis);
- narrowing of the foreskin (phimosis);
- trauma to the skin of the penis (burns, scratches);
- allergic reactions to hygiene products, underwear or contraceptives.
A common cause of inflammation of the glans penis in a child is uncomfortable underwear. It causes discomfort, rubs and injures the skin, causing balanitis in boys.
Symptoms of allergic dermatitis of the penis
Clinical manifestations are generally the same as for simple contact dermatitis.
However, there are some differences.
In acute allergic dermatitis, the skin rash goes through the following stages:
- redness
- formation of papules (a characteristic difference from simple contact dermatitis of the penis)
- appearance of bubbles
- after opening them, erosions (superficial skin defects) form in their place.
- crusts form after drying
- Peeling is observed during healing
Chronic allergic dermatitis occurs in the same way as simple dermatitis.
The differences are as follows:
- no cracks appear
- symptoms worsen or appear almost immediately after contact with the allergen (if by this time the immune system has already become “acquainted” with this substance)
Against the background of existing allergic dermatitis, contact urticaria may occur.
It is characterized by the appearance of blisters.
Frequently asked questions about inflammation of the head of the penis
How can balanitis be dangerous?
Balanitis is dangerous, first of all, because of its complications. Complications such as gangrene and the spread of the inflammatory process to the genitourinary system pose a particular threat.
How long does it take to treat inflammation of the head?
How long to treat inflammation of the head of the penis depends on the stage of the disease, clinical manifestations and how to treat balanitis. Pathology in a simple form with proper treatment goes away in about 7 days. Treatment of balanitis is carried out on an outpatient basis, in rare cases - inpatient.
What effective remedies are there?
Ointment for inflammation of the glans penis in men is one of the most effective dosage forms, as it acts directly on the affected area. Depending on the etiology of balanitis, the ointment can be antifungal (Clotrimazole), antiseptic (Levomekol), or glucocorticoid. Antiseptic baths also have a beneficial effect. For severe forms of the disease, antibiotics are used.
Diagnosis of allergic dermatitis of the penis
Typically, a doctor diagnoses allergic dermatitis of the penis based on symptoms and medical history (contact with certain substances).
They also help him distinguish this type of skin inflammation from other types of the disease:
- blood test for allergies
- pathological examination of the skin
- tests with a potential allergen
The doctor asks the patient what exactly he has been putting on his penis lately.
Applying this substance to any area of the skin will cause the same reaction.
This test is called a patch test.
It can only be carried out on those substances that are used by the patient.
In addition, there are kits of allergens that can be tested for in the clinic.
Application or other skin tests are prescribed no earlier than 2 weeks after the elimination of the main symptoms of dermatitis.
Treatment of allergic dermatitis of the penis
The most important thing is to eliminate the allergen.
As long as contact with him continues, dermatitis on the penis will recur again and again.
And no drugs will help get rid of rashes once and for all.
To eliminate symptoms, ointments with corticosteroids are mainly used.
In severe cases, they are taken orally.
Taking antihistamines and other antiallergic drugs for contact allergic dermatitis of the penis usually has low effectiveness.
Seborrheic dermatitis on the penis
There are quite a few sebaceous glands on the penis.
Therefore, this organ can be affected by seborrheic dermatitis.
It is characterized by redness and peeling of the skin.
This type of dermatitis occurs mainly during puberty or in young men with high testosterone levels.
Seborrheic dermatitis develops against the background of increased sebum secretion.
Risk factors:
- heredity
- young age
- oily skin type
- immunodeficiencies, including HIV infection (with weak immunity, there is excessive growth of microflora that feeds on sebum)
Treatment
After receiving and analyzing the diagnostic results, the urologist determines how to cure balanitis and relieve inflammation of the head. Treatment of balanitis begins with strict adherence to personal hygiene. It is necessary to wash the penis with soap several times a day. By adhering to this rule in the early stages of the disease, you can stop the pathological process of inflammation of the head of the penis and avoid other types of treatment.
For more serious forms of inflammation of the head in men, drug treatment is prescribed. Medicines for balanitis have an antiseptic effect. Most often, inflammation of the glans penis is treated with ointments or creams.
In addition to ointments, the doctor can also prescribe drug therapy: tablets for the treatment of balanitis in men, for example, Suprax, Azithromycin.
In rare and complicated cases, surgical treatment is used - excision of the foreskin.
Symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis on the penis
Often seborrheic dermatitis develops simultaneously in several areas of the body.
The scalp, folds, and face also become inflamed.
On the penis, lesions of seborrheic dermatitis look like yellowish crusts.
Plaques often form that mimic psoriasis.
There are also cases when psoriasis is combined with seborrheic dermatitis.
There is even a separate medical term for this condition: sebopsoriasis.
Diagnosis of seborrheic dermatitis on the penis
In most cases, a clinical picture is sufficient to establish a diagnosis.
Not only the appearance of the skin is taken into account, but also the excess secretion of sebum.
Patients often experience excessive sweating.
In controversial diagnostic cases, the diagnosis can be confirmed using a skin biopsy.
A rash similar to seborrheic dermatitis occurs when:
- zinc deficiency
- vitamin deficiency RR (practically not found in civilized countries, achieved only experimentally)
- Parkinson's disease
Treatment of seborrheic dermatitis on the penis
Most men experience seborrheic dermatitis in one form or another.
And there is nothing wrong with inflammation of the skin of the penis.
In summer there is usually an improvement, in winter the disease can worsen.
The disease is chronic.
Therefore, it requires constant maintenance therapy and certain lifestyle changes.
Many patients benefit from ultraviolet radiation.
For ethical reasons, natural sunbathing is not possible for most patients.
But the problem is solved by a solarium or special ultraviolet lamps.
To reduce sweating, it is advisable to shave the hair in the intimate area.
In severe cases (with severe symptoms), topical corticosteroids can be used.
They help well, but the possibilities of such therapy are limited.
The problem is that the disease is chronic.
But corticosteroids are not suitable for long-term use because they cause skin atrophy.
To suppress lipophilic fungal flora, creams with ketoconazole are used.
For maintenance therapy, exfoliants are used (usually salicylic acid 2%).