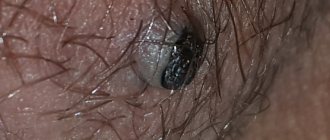
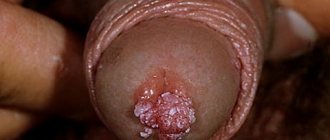
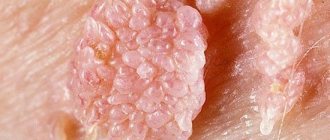
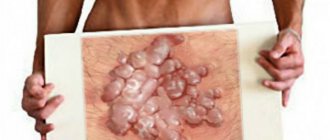
Genital warts are one of the most common types of sexually transmitted infections. They are caused by a certain type of human papillomavirus (HPV). It occurs more often in women than in men.
Cost of services in our clinic
| Appointment with a gynecologist with the highest category | 1000 rub. |
| Consultative appointment with a doctor based on test results and ultrasound results | 500 rub. |
| Extended colposcopy | 1500 rub. |
| Amino test for bacterial vaginosis | 300 rub. |
| Medical abortion (all inclusive) | 4500 |
| Make an appointment by phone: 8-800-707-15-60 (toll-free) |
| *The clinic is licensed to remove tumors |
The formations affect the mucous membranes of the genitals. These are small growths, often similar to cauliflower.
Some strains of genital HPV provoke the development of cancer cells. Vaccinations are used to prevent such health problems.
Symptoms
The content of the article
In women, genital warts can grow on the external genitalia, vaginal walls, the area between the external genitalia and the anus, the anal canal, and the cervix. In men, the glans penis, scrotum or anus is affected. These growths sometimes form in the mouth or throat after oral sex with an infected person. Symptoms of genital warts:
- The appearance of small, flesh-colored or gray swelling in the genital area.
- A cluster of several warts located close to each other.
- The occurrence of itching or discomfort in the genital area.
- Bleeding during sexual intercourse.
Genital warts can be so small and flat that they cannot be seen with the naked eye. Sometimes they form large clumps. You should see a doctor if a woman or her partner develops lumps or warts in the genital area.
Which people are susceptible to papillomas?
Based on the information we provided above, we can distinguish several “risk groups”, people in which are susceptible to the development of growths and neoplasms on the tongue and body.
The appearance of a process on the tongue is possible:
- In a situation where a person has reduced immunity as a result of stress, the presence of parasites in the body or ongoing inflammatory processes.
- If a patient with a growth in the mouth suffers from autoimmune diseases.
- In a person with HIV infection.
- In people who are promiscuous.
- In the event that a person has bad habits. Smoking and drinking alcohol especially contribute to the appearance of neoplasms in the form of growths on the tongue.
- If there was any trauma to the tongue or damage to the mucous membrane occurs systematically.
Risk factors
Factors that may increase the risk of infection include:
- unprotected sex with multiple partners;
- suppressed immunity (for example, people living with HIV are at increased risk of acquiring HPV);
- sexual activity at an early age.
Genital complications after illness:
- Cancer. The disease is closely related to infection of the genital organs. Certain types of HPV are also associated with cancers of the anus, penis, mouth and throat. Human papillomavirus does not always lead to cancer, but women should have regular Pap smears, especially if they are at high risk of contracting HPV.
- Problems during pregnancy. The formations may enlarge, making it difficult to urinate. Growths on the vaginal wall reduce the ability of vaginal tissue to stretch during childbirth. Large warts on the genitals or vagina bleed during labor. The mother often transmits the virus to the child, and the baby develops warts, which are especially dangerous in the throat. In this case, a thorough examination and removal of growths is required so that the child can breathe freely.
How and why we become infected with HPV:
- In most cases, HPV is transmitted through sexual contact.
- Infection is possible through household means, through touch, while staying in public places, such as baths, saunas, swimming pools, toilets or gyms.
- Self-infection, such as when you accidentally cut yourself while shaving.
- There are known cases of infection of a newborn during passage through the birth canal.
The danger of HPV lies in the fact that, once it enters the human body, it can remain in an inactive state for a long time, but then suddenly (during stress, a cold or other immune system failure) make itself felt in the form of the appearance of tumors on the body and growths on the tongue.
Prevention
To avoid the development of diseases associated with HPV, it is recommended:
- Use condoms during sexual intercourse.
This significantly reduces the risk of contracting genital warts. - Get vaccinated.
The drug Gardasil protects against four strains of HPV that cause cancer and is used to prevent genital warts. Another vaccine, Cervarix, protects against cervical cancer but not genital warts.
Routine HPV vaccination is recommended for girls and boys aged 11 and 12 years. If vaccinations were not given in childhood, it is recommended that girls and women under 26 years of age, and boys and men under 21 years of age, receive the vaccine.
The drugs are effective if given before they become sexually active. Research has shown that people under the age of 21 and from 21 to 30 years of age who have received the HPV vaccine are 50% protected from infection.
Side effects from vaccines are minor and include soreness at the injection site (shoulder), headaches, low fever, or flu-like symptoms. Sometimes dizziness or fainting occurs after the injection, especially in teenagers.
Human papillomavirus is the cause of warts, condylomas and papillomas
Human papillomavirus is a family of viruses that cause warts, papillomas, condylomas, dysplasia or cancer of the cervix and genital organs in humans. General family: Papillomaviridae . Latin name: Human Papillomavirus . Abbreviation: HPV or HPV (as written in tests). 1. Over 50 years, more than 100 types of human papillomavirus have been discovered. Pathogenic for humans - 80 types. 2. According to WHO, 70% of the world's population is infected with HPV. 3. HPV types 16 and 18 are more likely than other types to lead to cervical cancer. 4. HPV is the overwhelming cause of genital cancer in women and men. 5. The most effective prevention against cervical and genital cancer throughout the world is considered to be a vaccine against types 6, 11, 16 and 18 of papillomaviruses. Infection.
The source of the virus is the skin cell or mucous membrane of a sick person. If a patient has a papilloma, even a small one, it is the direct source of the virus! However, upon examination, the patient may not yet have a wart or condyloma. The changes may still be microscopic and not visible to the eye (subclinical stage of the disease). But such a person can already transmit the virus to another person. Infection usually occurs in childhood. Through microdamage to the child's skin (scratches, abrasions), the papillomavirus penetrates the skin and causes the appearance of warts. In adults, certain types of the virus (discussed below) cause the development of anogenital warts, or genital warts, on the genitals. The transmission mechanism of these types is predominantly sexual. But contact-household transmission is also theoretically possible - through general hygiene items, the toilet rim, taking a bath, visiting a bathhouse, swimming pool, etc. Through microtraumas of the genital organs, the virus is transmitted from one sexual partner to another. In this case, the patient may also not have any changes visible to the eye. But there may be microscopic changes in the mucous membrane of the genital organs. And these altered cells are the sources of the virus. Next, the virus penetrates the skin or mucous membrane and is met by various cells of the human immune system. In most cases, immune cells destroy the virus. But if the immune system is weakened, the virus manages to penetrate the cells of the basal layer of the epithelium of the skin or mucous membranes, integrates into the chromosomes of the cells and changes the functioning of these cells. The cells begin to divide excessively and grow in a limited area, externally turning into warts and papillomas. Remember: - HPV types that cause warts enter the body during childhood, - HPV types that cause genital warts enter the body primarily through sexual contact. In rare cases, the development of human papillomavirus infection in the human body can lead to malignancy (that is, degeneration into cancer). Therefore, all types of papillomaviruses are classified according to the degree of oncogenicity (that is, according to the degree of possible cancer development). Classification of HPV types by oncogenicity (according to studies by McConcl DJ, 1991; Lorincz A. T., 1992; Bosch E X. et al., 2002; Kozlova V. I., Puchner A. F., 2003; Syrjanen S., 2003; Shakhova N.M. et al., 2006;). 1) Types of papillomaviruses that never cause cancer: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 10, 28, 49 2) Types of low oncogenic risk (very rarely cause cancer): 6, 11, 13, 32, 34, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 51, 72. 3) Types of average oncogenic risk (average percentage of cancer degeneration): 26, 30, 35, 52, 53, 56, 58, 65. 4) Types of high oncogenic risk (of all types of the virus, these are the types that most often give rise to degeneration): 16, 18, 31, 33, 39, 45, 50, 59, 61, 62, 64, 68, 70, 73. This is especially important in women. By the way, sometimes the classification changes. For example, HPV type 58 in women is no longer highly oncogenic. It began to be classified as a type with average oncogenicity. Occurrence in diseases: • In 73-90% of cases with cervical cancer they find: 16, 18 and 45 types of HPV • In 77-93% of cases with cervical cancer they find: 16, 18, 45, 31 and 59 types of HPV • B In 80-94% of cases of cervical cancer, the following are found: HPV types 16, 18, 45, 31, 33 and 59 • Precancerous conditions in urology and gynecology are often combined with HPV types 61, 62, 68, 70, 73. The most common types found in tests are: • human papillomavirus 16 (written HPV 16) - 50% • human papillomavirus 18 (HPV 18) - 10% Symptoms and clinic Symptoms and manifestations of HPV infection are warts, papillomas and cervical dysplasia. A) Warts. They are caused by the following types of HPV - 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 10, 28, 49. • juvenile (or flat) warts - caused by types 3 and 5 of the virus. These are small flat elevations on the skin that occur mainly in children. • spinules (or plantar warts) - caused by types 1 and 2 of the virus (you can read more about them. • vulgar warts on the fingers - caused by type 2 viruses.
These are flat warts on the face
These are vulgar warts on the hand
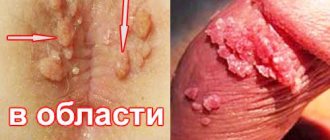
B) Genital warts. Localization : on the genitals, in the anus, in the oral cavity and on the lips (types - 6, 11, 13, 16, 18, 31, 35).
These are genital warts
The main mechanism of transmission of this disease in adults is sexual. Very rarely, a contact route of transmission can occur - through shared toilet items, through a dirty toilet rim, using a shared bathroom, in a bathhouse, etc. If a mother suffering from genital condylomatosis gives birth to a child, he will also become infected and subsequently may also develop genital warts or papillomatosis of the larynx and respiratory tract (discussed above). However, the frequency of such symptoms in infants is extremely low. Children have a fairly high level of immunity, which protects them from such manifestations of infection. B) Laryngeal papillomatosis. Multiple papillomas appear on the vocal cords. Caused by virus type 11. Sometimes it appears in children born to women with genital warts.
This is laryngeal papillomatosis
Remember: - cervical erosion and HPV are FAR from the same thing. A detailed article about what cervical erosion is and how it differs from dysplasia and HPV is here. Modern medicine declares with 100% certainty that cervical cancer is caused exclusively by papillomavirus types 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 40, 42, 43, 55, 57, 59, 61, 62, 66, 67. In the diagram - development of HPV infection over the years
E) Skin cancer of the penis (Bowen's disease). Caused by virus types 16 and 18. G) Today, some foreign scientists believe that the human papillomavirus is the cause of cancer of any location. Since cancer is a malignant tumor of the epithelium of the skin or mucous membrane, therefore, the HPV virus, which causes dysplastic phenomena in the epithelium, causes the appearance of cancer. And with cervical cancer this has been proven 100%. There is evidence for breast cancer and laryngeal cancer, although it has not yet been formalized into global recommendations. And, according to some cancer researchers, the day is not far off when cancer of other locations (for example, intestines) is also recognized as the result of the activity of the human papillomavirus in the human body. Remember: - any viral infection that is constantly present in the human body (and HPV is one of these) is activated only when immunity decreases. Diagnostics 1) PCR analysis. The main method for diagnosing papillomavirus is the PCR reaction. The most common types of HPV tests are virus types 16, 18, as well as a number of other highly oncogenic types. Material for analysis is taken from the mucous membrane of the woman’s vagina and cervix. In men - with the mucous membrane of the penis. The PCR reaction can also give a false result, both a false positive and a false negative result, especially if the conditions for its implementation are violated (even a push of the table on which the study is being carried out can lead to such a false result). Thus, according to modern researchers in the West, up to 20% of all PCR results for papillomavirus were false. And this fact did not depend on the complexity of the equipment and the quality of the reagents. 2) Digene test. New research gaining popularity in the medical community. This test is used to determine the presence of clinically significant concentrations of the virus. Thanks to this test, it is possible to identify whether the viruses in the patient’s body have a high or low degree of oncogenicity. The Digene test is used in conjunction with a cytological examination of the cervix, and they are also evaluated comprehensively. 3) Examination by a gynecologist and/or urologist. 4) Cytological examination. A smear taken during a gynecological examination is examined. This study is often called “liquid-based cytology”, or simply “cytology”. In this case, a laboratory doctor, under a microscope, determines the presence or absence of pathologically altered cells, which should not normally be present, but they appear only with the development of the disease. The presence of such altered cells may indicate the presence of CIN (or cervical dysplasia) in a woman. 5) Histological examination. A microscopic piece of tissue is examined, also taken during a gynecological or urological examination. Another name for this test is “biopsy.” Under a microscope, the doctor evaluates the degree of change in the tissue taken for examination.
How to interpret an HPV test?
The unit of measurement is the number of genome equivalents (in simple terms, the number of viruses) per 100,000 human epithelial cells (that is, by 10 to the 5th power). Abbreviated form: Lg Gradations: 1. < 3 Lg, that is, the number of viruses is less than 3 per 10 to the 5th power. This is a good indicator, the viral load is small, that is, the concentration of the virus is insignificant, the risk of developing the disease is low. 2. 3 – 5 Lg. This is a clinically significant indicator. The risk of developing the disease is average. It is necessary to undergo examination by a doctor. 3. > 5 Lg. High viral load. You should definitely undergo a full examination to exclude cervical dysplasia. What is a reference value? This means the average statistical indicators for a given study in a given age group. That is, in simple terms, reference values are the norm. For HPV, the reference values are negative. That is, normally there should not be HPV in the tests. What is KVM? KVM is the control of material taking. Normally, the doctor should take a scraping so that the sample of material contains at least 10,000 (or 10 to the power of 4, or 4Lg) epithelial cells. If the CME value is less than 4Lg, this means there are few cells for analysis. The analysis is not recommended, as it will be uninformative, and the doctor is recommended to repeat the collection of material. Treatment When treating human papillomavirus, you need to know: the virus may not be completely removed from the body. The main goal of treatment is to increase immunity, stabilize the virus, remove manifestations of the virus and reduce its concentration in the body so that the human immune system itself suppresses the virus. 3 areas of treatment are required (carried out by a specialized infectious disease specialist, immunologist, dermatologist or gynecologist): • taking antiviral drugs • strengthening the immune system • removing manifestations - warts, condylomas, dysplasia (erosion) or cervical cancer. All 3 areas are effectively carried out by modern medicine. Self-medication has low effectiveness and can lead to progression. Self-medication for diseases of the genital area is especially dangerous. 1) Antiviral drugs • Isoprinosine (or groprinosin), Allokin-alpha, • 5% Aldara cream. The active ingredient is imiquimod. 2) Drugs that enhance immunity Polyoxidonium, Reaferon, Roncoleukin, Immunal and others. The main drug for advanced forms at the moment is roncoleukin, which is used according to a certain scheme (prescribed by an immunologist or infectious disease specialist) 3) Removal of papillomas, warts, condylomas can be - Scalpel - classical surgery, electrocoagulation or an electric loop knife, radio wave removal, liquid nitrogen. These are outdated techniques that are traumatic, not always effective and can lead to relapses and post-burn scars at the sites of removal. -Laser - today this is the best method in terms of efficiency, safety, aesthetics. It is not recommended to use locally necrotizing drugs (acids, alkalis): Superchistotel, Solcoderm, Duofilm, Collomak, Verrukatsid, Ferezol, Condilin - and a number of others, since their application to the skin can contribute to the spread of the virus to healthy, previously uninvited areas of the skin, and also leads to skin burns and subsequent scarring
Required: a healthy lifestyle that improves immunity. Remember: First the doctor must make the correct diagnosis, and this is already half the treatment!!! Including treatment of human papillomavirus. Therefore, in the presence of multiple warts or relapses, it is recommended to first conduct a course of antiviral and immunomodulatory therapy under the supervision of an infectious disease specialist or immunologist!
Prevention of HPV Prevention is the best cure. Remember this phrase, especially when it comes to the sexual sphere. Nature has come up with a wonderful healing and prevention mechanism for humans, which then helps him not to get sick again. This is the immune system. If a person has already had warts or papillomas once, then he subsequently develops immunity to this type of virus. Therefore, juvenile warts, spinules and warts vulgaris very rarely appear in adults. This is why it is SO IMPORTANT to maintain your immunity at a high level. Let us list the main directions for the prevention of papillomavirus infection in humans: • Personal hygiene measures in public places • A healthy lifestyle that maintains immunity at a high level • Correct work and rest regime • Moderate physical training • Taking vitamins, fruits, juices • Only one sexual partner (in ideally) • Using a condom during sexual intercourse
We bring to your attention 3 videos on the removal of papillomas and warts at the Aurora clinic!!!
Find out more about the service and cost of tumor removal
PAP tests
It is important for women to undergo regular pelvic examinations and undergo a vaginal cytology smear (Pap smear). These studies contribute to the timely detection of changes in the vagina and cervix caused by genital warts or early signs of cervical cancer. A smear is taken during a gynecological examination of a special one from the outer and inner surface of the cervix. The procedure is painless and takes 5-10 seconds. The cells are examined under a microscope.
Warts on intimate places: diagnosis
It is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis only with an external examination.
To correctly determine the form of the disease, the doctor will need to conduct laboratory and instrumental studies.
Only a venereologist can reliably establish a diagnosis based on clinical manifestations.
If it is necessary to diagnose formations on the cervix/endourethral, instrumental methods (colposcopy, urethroscopy) are used.
In a number of situations, additional laboratory testing may be required (using PCR methods, histo-, cytological studies).
For laboratory tests, tests of blood and affected tissues are used.
A detailed diagnosis will help the doctor prescribe the optimal treatment.
Medicines for the treatment of genital warts
Preparations that are applied to the skin:
- Imiquimod.
This cream enhances the immune system's ability to fight genital warts. Sexual contact should be avoided while the cream is on the skin. This weakens the effect of condoms and the diaphragm and causes skin irritation on your partner. Side effects include skin redness, blisters, body pain, cough, rash and fatigue. - Podophyllin and Podofilox
. Podophyllin is a plant-based resin that destroys the tissue of warts on the genitals. When using Podofilox, you need to know the precautions to avoid causing irritation. This drug is not recommended for use during pregnancy. Side effects: mild skin irritation, itching. - Trichloroacetic acid.
This remedy burns genital warts and is used to remove internal warts. Side effects include mild skin irritation, ulcers or itching. - Synecatechin (Veregen).
The cream is used to treat external genital warts and warts in or around the anal canal. Side effects include skin redness, itching or burning.
You cannot self-medicate so as not to provoke serious complications.
What is the danger of developing growths on the tongue?
Often a person does not even suspect that HPV is present in his body, which manifests itself in the form of papillomas. If the growth is localized on the inside of the tongue, closer to the palate, then the patient may not notice the growth. And then the doctor accidentally finds the papilloma during an examination of the patient’s oral cavity.
Papillomas that are located on the tip of the tongue are less common, but they are always noticeable. Such growths interfere with talking and eating, so people with such growths most often seek help from a medical facility.
What else can you expect from a growth on the tongue, besides discomfort:
- Papilloma is a benign neoplasm that in itself does not pose a threat to human health. But in 1.2% of cases, malignancy of such processes occurs, i.e. The tumor goes from benign to malignant.
- The oral cavity is an extremely undesirable place for papillomas to be found. If in other parts of the body growths can “live” quietly, and the doctor will not recommend removing a tumor that does not pose a threat, then papillomas on the tongue are often injured. This can lead to inflammation.
How to get rid of papillomas?
If the growths on your tongue are present in small quantities and are small in size, then the process of removing such growths is quite simple. But this does not mean that you can remove the papilloma yourself, using such “effective folk remedies” as cauterization, cutting the “leg” of the tumor with scissors, etc. To remove the growth, you should contact a professional medical institution.
Methods for removing tumors:
- Excision of papillomas with a scalpel or electric knife. This affects not only the growth itself along with the stem, but also part of the healthy tissue around it.
- Laser removal of tumors.
- By using a tool such as a conchotome, shaped like a wire cutter. After removing the papilloma with such a device, galvanoacoustics is performed (cauterization of the localization of the growth using a platinum wire).
Ways to remove warts in the groin:
- Laser removal is the most popular and highly effective method, which has virtually no contraindications or complications. The wart is evaporated layer by layer with a laser beam. After the session, a barely noticeable mark remains at the site of removal of the skin formation.
- Medical removal. It involves the use of cauterizing liquids. It is better to carry out the procedure of cauterization of warts under the supervision of a doctor. If used independently, they can cause a chemical burn to the skin in the groin area.
- Cryodestruction. Freezing a wart with liquid nitrogen. After treatment, the wart turns into a blister filled with bloody fluid. Healing occurs as with a normal thermal burn. The method has a number of complications, such as burns of surrounding tissues followed by inflammation. The effectiveness of this method is very low.
- Electrotherapy. Removal of warts using high-frequency electric current. There is a risk of burns to surrounding healthy tissues; the effectiveness is low.
- Radio wave operation. The wart is cut off in layers using a radio wave knife. It is not always possible to remove the “roots” of the wart deeply enough, so the risk of recurrence is very high.
- Surgery. Classic removal with a scalpel. Use as a last resort. After the operation, a recovery period is required; a scar is possible at the incision site.
Rice. 6. Condilin is suitable for removing warts in the groin
It should be borne in mind that removing a wart in a man’s groin solves only a cosmetic problem and cannot get rid of the virus. Therefore, whatever method is chosen, it is simultaneously necessary to strengthen the immune system and fight the virus.
With constant monitoring and following recommendations, relapses of the disease can be avoided.
Visiting a doctor, diagnosis, treatment
The discovery of warts or condylomas is a reason to go to the doctor. It is difficult to predict what the doctor will do. Russian recommendations provide for a bunch of tests: for the presence of HPV and determination of its genotype, morphological examination of warts, testing for other sexually transmitted infections. Many Western sources do not recommend this, since it does not affect treatment tactics.
Anogenital warts are treated with surgical (excision, cryodestruction, electrocoagulation) and medicinal methods (medicines are applied directly to the affected area). Unfortunately, the likelihood of wart recurrence is high. Over time, they are rediscovered in at least 30% of patients. This may occur due to the circulation of an old human papillomavirus infection in the blood or due to re-infection.
How not to get sick
- The HPV vaccine protects against the types of virus that cause anogenital warts. Ideally, you should get vaccinated before you become sexually active.
- Using condoms during sexual intercourse. They protect against HPV at least partially. Also, this method of protection helps to recover from warts faster if both partners are infected with HPV.
- Smoking is a risk factor for HPV infection. But there is currently no evidence that quitting smoking helps cure warts.
- The fewer sexual partners you have, the lower your risk of developing warts.