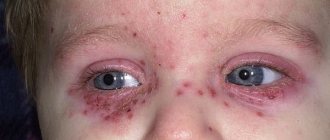
Skin hyperemia (redness in certain areas) is always caused by excessive plethora of small vessels - capillaries. They come close to the surface and are visible through the outer layer. Since the capillary bed has two bends (arterial and venous), redness can be caused by one of the types of vessels or be of a mixed nature.
Hyperemia cannot be considered a disease. We know many physiological conditions under which a healthy person develops a bright blush, a flush of embarrassment or shame on his face, or a pinkish body after a bath.
However, it is impossible to ignore such a symptom, which manifests itself paroxysmally or too often in unusual conditions. Therefore, when diagnosing various diseases, skin hyperemia is always taken into account as an essential sign.
Causes of hyperemia
Redness on the face is a clear and common sign of hyperemia.
Under the influence of external and internal factors, blood vessels dilate, which increases blood flow to the skin and leads to a change in their color. This is especially noticeable in people with fair and sensitive skin. Red spots on the face can appear for various reasons:
- Temporary stimuli . Among them are changes in external temperatures and wind, physical and emotional stress, sunburn or mechanical factors (friction, pressure). Redness of the skin can be caused by side effects of medications, incorrectly selected cosmetics and some types of caring procedures: peeling, resurfacing, microcurrent therapy.
- Physiological conditions.
Hormonal changes are often accompanied by systemic reactions, including skin reactions. Situations when red spots appear on the face cause psychological discomfort during puberty, pregnancy, menopause, etc. - Allergic and toxic agents.
They can enter the body through the gastrointestinal tract, respiratory tract, injection and contact (by direct contact with the skin). - Pathological conditions.
This is a large group of acute and chronic diseases, both of a purely dermatological and general nature, namely: disruption of the cardiovascular system and the hematopoietic mechanism; - acute infectious diseases and inflammatory processes in the body;
- damage to the gastrointestinal tract;
- pathology of ENT organs;
- endocrine and autoimmune diseases;
- disorders of the central and peripheral nervous system;
- dermatoses of various origins.
In such situations, it is possible to remove redness from the face only by simultaneously addressing the root cause and the symptom. Even true dermatological disorders are difficult to correct without improving the health of the whole organism.
Non-infectious manifestations
In accordance with the causes that caused them, erythema of non-infectious etiology is divided into:
- infrared - provoked by infrared radiation, the power of which was not enough for a full burn, and manifested in the form of a reddish vascular network;
- X-ray – caused by exposure to X-rays or high-frequency electromagnetic waves;
- symptomatic - appearing after contact with an allergenic agent in the form of hyperemic convex spots of irregular shape;
- idiopathic - formed under the influence of heredity as an increase in the diameter of capillaries at the junction with the vascular network, with redness of the palmar surfaces;
- cold - formed when the skin is exposed to low temperatures, manifesting itself in the form of a bluish-reddish rash with local swelling and itching;
- ultraviolet - appearing as a result of exposure to ultraviolet radiation on the skin.
In most cases, when the action of the provoking factor ceases, the redness disappears after some time. In some cases, symptomatic help is required.
Diagnosis of hyperemia
Red facial skin can be both a protective reaction to irritants and a signal of disturbances in the human body. Timely diagnosis and treatment help delay the development of serious pathologies. Studying the problem begins with collecting complaints and medical history. Thus, episodes of skin color changes should be carefully analyzed.
If the redness on the face is of a short-term local nature, has a clear connection with any cause, goes away on its own after it is eliminated and is not accompanied by other symptoms, then a person can cope with the change in skin color without outside help.
In cases of systematic red spots on the face, the causes of which are unclear, the help of a specialist is necessary. The reason to urgently contact him is the simultaneous combination of redness on the face and peeling, itching, burning, microcracks, as well as general weakness, fatigue and disruption of the internal organs.
In such cases, laboratory tests of blood and urine, available instrumental studies of the cardiovascular system (measurement of blood pressure and pulse, ECG and assessment of the condition of blood vessels) are performed. Taking into account preliminary data, the doctor may prescribe dermatological and allergological tests, determination of the hormonal profile, and in-depth instrumental procedures (radiography, ultrasound, MRI, CT).
Modern laboratory and instrumental equipment will provide the opportunity for comprehensive general clinical observation, and the joint work of several specialists will make it possible to more accurately determine the nature of facial redness and its causes.
Infectious pathologies
Various pathogens can provoke the development of infectious inflammation of the skin - bacteria, fungi, viruses or parasites. This form is characterized by an acute course, which can turn into a chronic form. The patient needs immediate medical attention.
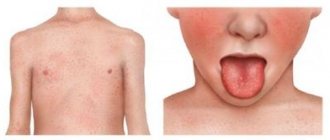
In its acute form, the most common erythema infectiosum in children is caused by parvovirus B19. It is characterized by the sudden onset of the disease, the characteristic signs of which are:
- rapidly rising body temperature;
- muscle pain, headache;
- the appearance of a red rash covering the face and body on the third or fourth day after the onset of the disease;
- gradual increase and closure of spots.
After some time, clinical manifestations gradually fade away until they disappear completely. If left untreated, the process can become chronic. The patient remains able to transmit the infection to healthy people for several days after recovery.
Solving the problem yourself
Temporary, or transient, redness of the facial skin is not considered a pathology. It disappears on its own and does not cause much discomfort other than psychological. To remove occasional cases of hyperemia on your own, you should follow simple steps:
- Remove the irritating factor
. Change the environment, wash off the allergen or toxic substance from the surface of the skin, try to calm down. - Restore natural skin color
. Folk remedies and herbal remedies help with this. You must first make sure that you are not allergic to the components. - Take care to strengthen the protective barrier
. To do this, it is advisable to carry out a set of measures aimed at improving the health of the body as a whole and maintaining the functional properties of the skin.
The following recommendations can also help get rid of a red face, but will require a long time and lifestyle adjustments.
Gentle cleansing and care.
You should wash your face with warm water, without contrasting temperatures, and dry with a soft towel with light blotting movements.
Prevention of infections.
An important rule is to never touch your face with your hands unnecessarily. The habit of removing pimples yourself can lead to infection not only local, but also general. Even with minor damage and scratches, it is worth immediately treating the area of microtrauma with an aseptic substance.
Lifestyle.
The diet must contain foods rich in fiber and vitamins.
It is worth avoiding the consumption of salty foods, smoked meats, spicy seasonings and alcohol. Good sleep and a calm microclimate also help remove redness on the face. Caring cosmetics.
The beauty industry provides a wide range of cleansing, lipid-restoring and healing products. It can be difficult to understand them on your own, however, dermatologists recommend not to get carried away with cosmetics based on alcohol solutions and to carefully choose them. Individual consultation
What does an allergy look like on the face?
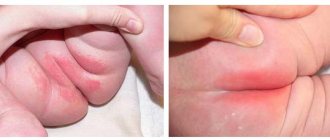
There are many manifestations of allergies, and they depend on the form, location and intensity. The main indicator of the disorder is sudden swelling of the eyes and lips, one or both. Changes also affect the structure of the skin. It becomes lumpy, swollen, with a small scattering of small dots. Red, uneven spots of varying sizes often appear. Cracks and a scaly structure may be observed. If you give in to temptation and start scratching the itchy areas, the condition will quickly worsen.
Depending on the type of disorder and the affected area, allergic rashes on the face are likely, the treatment of which requires an integrated approach. Along with pharmaceutical drugs, cosmetics have a fairly good effect. Plasma therapy with the Japanese drug CURACEN perfectly restores appearance, but only after the acute period ends and the condition stabilizes.
Why are allergies on the face dangerous?
A scattering of small specks or red spots not only look unsightly, but also pose a hidden threat. Acute inflammation, accompanied by swelling, can spread to the neck and make breathing difficult.
Violation of the structure of the skin, accompanied by a feeling of tightness, reduces the natural resistance to external influences. Weeping areas, as well as cracks in the upper layer of the epidermis, create a favorable environment for the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria, which leads to the appearance of pimples and ulcers. When such a condition occurs and is not treated, there is a high probability of it becoming chronic. In addition, an unpresentable appearance can cause a sensitive blow to pride and cause problems in communication.
If an allergic rash appears on the face, a specialist from a clinic or health center will tell you how to treat it. It is better to contact him at the first signs in order to make a timely diagnosis and receive an effective treatment regimen to avoid complications.
Artificial
Artificial spots on the skin are spots that appear when dyes are artificially introduced into the skin. Such spots include tattoos and contour makeup.
Any spots on the skin require close attention. They can change over time, become malignant and become life-threatening. This is especially true for so-called moles. Therefore, specialists at the Dermatology Clinic advise you to be on guard with spots and if they transform - enlargement, changes in shape and color, or itching - immediately consult a dermatologist.
Pigment
Pigment spots on the skin are spots that appear as a result of an increase or decrease in the amount of melanin pigment. In case of increased pigmentation, the spots are called hyperpigmented, in case of lack of pigment or its absence, depigmented or hypopigmented.
Hyperpigmented spots on the skin are divided into:
- congenital (these include birthmarks, lentigo);
- acquired (freckles, chloasma).
Depigmented spots are divided into:
- congenital (for example, albinism);
- acquired (vitiligo, leucoderma).
Secondary depigmentation can occur in patients with psoriasis, eczema, rosea or pityriasis versicolor at the site of the primary painful rash. These rashes turn pale against the background of tanned areas of the skin because in the area of inflammation, the ability of melanocytes to produce pigment is weakened. Such areas of depigmentation are called secondary leukoderma, or pseudoleukoderma.
Preventive measures
In order not to look with disappointment at your reflection in the mirror and not to wonder how to get rid of allergies on your face once again, you should listen to the simple but effective advice of specialists.
- Adjust the daily menu by removing from the diet foods that provoke the appearance of characteristic symptoms of an immune disorder.
- Do not use cosmetics based on alcohol and other aggressive substances, giving preference to soft and neutral ones.
- Do not stay in the sun for a long time, and in winter, protect your skin from the cold as much as possible.
- During seasonal exacerbations of hay fever, use inhaled isotonic saline solutions to reduce the concentration of pollen in the nasopharynx.
- Always keep in your medicine cabinet an antihistamine recommended by an allergist-immunologist.
It is worth remembering that angioedema alone cannot be prevented. Other types of allergies are completely preventable, and this is much more effective than constantly treating exacerbations. Immunity support should take the leading place in the list of mandatory activities.