Furunculosis is a disease manifested in the appearance on the skin of two or more foci of purulent inflammation of the hair follicle. These lesions are called “boils”. Furunculosis in children requires special attention from adults, and before using any treatment (especially antibiotics), the exact causes of the disease should be determined. In addition, not all treatment methods can be applied in pediatrics.
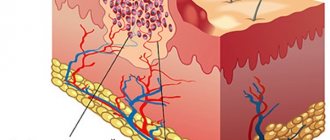
Boils are formed as a result of penetration of golden (sometimes white) staphylococcus into the hair follicle and sebaceous gland. Furunculosis is an unpleasant and quite dangerous disease, especially when this problem occurs in a child, and pustules appear on the face or in the neck area.
What is a boil?
Since furunculosis involves inflammation of the hair follicles , this abscess can form on any part of the child’s leg where hair growth is expected. Popularly it has another name - boil. How to distinguish a boil from a regular pimple? Unlike the latter, the boil goes through several stages in its development, presented:
- the appearance of itching on a small area of the leg;
- redness and thickening of tissue structures;
- the formation of a compacted abscess rod with a white dot at the base;
- opening of the abscess, rejection of pus and healing of damaged tissue.
It has been noted that very often the course of furunculosis in children is characterized by a rapid development and milder symptoms than in adults, but still the problem should not be left without due attention.
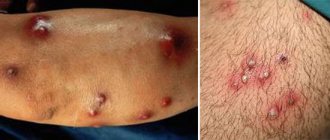
A distinctive feature of furunculosis on the leg is the purulent nature of the abscess and its large size, which a regular pimple cannot achieve. In addition, the pathology in many cases is accompanied by specific symptoms that are not characteristic of other skin problems.
How to treat boils
Only the doctor will prescribe the correct treatment and explain to the parents what to do with the abscess, taking into account the stage of development the boil is in. As a rule, at the initial stage of the disease (before the formation of pus), it is enough to treat the abscess with local ultraviolet irradiation, and antibiotics are not required.
If the boil has entered the ripening stage, then the doctor may prescribe antibiotics, or rather, inject them into the affected area. Furunculosis can also be treated with ichthyol ointment, applying it to the abscess twice a day and covering with a thin layer of cotton wool. This treatment is repeated until the boil opens. For furunculosis on the face, you can take other treatment; there is a decent arsenal of drugs for this.
When treatment has led to the opening of the abscess, the resulting ulcer should be treated with furatsilin or hydrogen peroxide. After this, a bandage with sodium chloride solution should be applied to the wound.
Causes of appearance on a child’s leg
Contacts with staphylococci are not always accompanied by the appearance of boils , because for this, certain provoking factors must play a role, represented by:
- regular damage to the skin, as well as the lack of timely treatment and treatment;
- failure to comply with the rules of personal hygiene (a striking example is the rare bathing of a child);
- improper nutrition, in which the child’s body does not receive the required amount of useful minerals, trace elements and vitamins;
- diseases of the endocrine and nervous systems;
- immunodeficiency;
- regular stress;
- metabolic disorders;
- hypothermia of the child's body.
Stye on a child’s eye – causes and how to treat
The natural protection of the eye, the eyelid, consists of five main elements: the anterior (external) skin, muscle fibers, cartilage tissue, the posterior (internal) mucous membrane-conjunctiva and the ciliary row along the edge.
In addition, evolution has provided a system of small glands, which are located partly in the conjunctiva (additional lacrimal glands), partly in the inner space of the eyelid (sweat and sebaceous glands). Moll's sweat glands and Zeiss' sebaceous glands emerge between the eyelashes or communicate with each other; Meibom's sebaceous glands are located deeper and open from the conjunctiva. In general, the secretion of the glands serves to hydroregulate the skin and ciliary roots, as well as to reduce friction during blinking.
Despite the fairly simple structure of the eyelid, each of its structural elements is susceptible to many pathological processes and conditions. Most of them are infectious and inflammatory in nature and are caused by viral, bacterial or fungal pathogens, as well as a skin parasite - the smallest Demodex mite, which settles at the base of the eyelashes, in the hair follicles and glands.
Thus, patients constantly turn to ophthalmologists with all kinds of blepharitis, conjunctivitis, dermatitis, as well as various combinations thereof. Such inflammations occur with varying frequencies, which depend on many factors - regional, age, etc. However, among these diseases there are undisputed leaders: conjunctivitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane) and hordeolum, or barley.
Both diseases are so widespread that, probably, any earthling will encounter them at least once during his life - if not in himself, then in his closest relatives. And when a child with barley appears at the reception, one can often only be surprised at how little parents know about the causes and patterns of this “national” pathology, and what strange and sometimes dangerous methods they try to cope with it.
Symptoms
The main sign of the pathology is a rapidly developing abscess , which can be localized on almost any part of the child’s body, including the legs.
In its development, the boil goes through several stages, starting from a small compaction that causes pain on palpation, and ending with the formation of an abscess with a yellowish core at the base and purulent contents.
Furunculosis may be accompanied by characteristic symptoms:
- an increase in temperature, which can be either minor or more serious;
- deterioration of health, weakness and drowsiness;
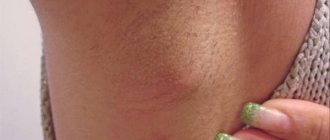
- enlargement of lymph nodes located in close proximity to the inflammatory focus;
- headaches and loss of appetite;
- soreness and itching of the inflamed areas.
The child may also complain of pain when walking , which is due to the localization of the boil on the leg.
Danger of boils
Failure to see a doctor in a timely manner can lead to dire consequences, since this pathology belongs to the category of dangerous diseases:
- a boil on a child’s head can cause meningitis;
- a boil on a child’s lip can cause inflammation of the nerves of the nasolabial triangle;
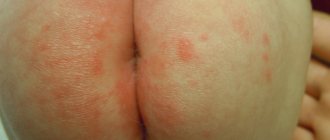
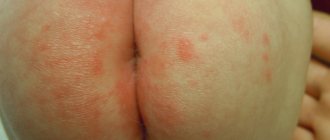
- a boil on the child’s bottom makes it difficult to sit;
- a boil on a child’s face can lead to meningitis;
- a boil in a child’s nose can cause inflammation of the respiratory system;
- a boil in a child’s ear can cause inflammation of the hearing organ;
- A boil on a child’s neck can lead to inflammation of the lymph nodes and severe intoxication.
In the absence of timely medical care, a carbuncle, which is a collection of boils, may develop. Possible consequences are also:
- infection of the deep layers of skin tissue;
- scar formation after healing;
- sepsis.
The appearance of multiple boils causes discomfort in the child, increased temperature, and deterioration of well-being.
The consequences of the formation of a boil can be prevented if you promptly contact the pediatric department of JSC "Medicine" (clinic of Academician Roitberg), which offers the services of qualified experienced specialists in various fields of medicine.
Our clinic is located in the center of Moscow at the address: 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskaya lane, 10, a five-minute walk from the Mayakovskaya metro station.
Why is boil dangerous for children?
In most cases, single boils are not dangerous , but when identifying them, it is extremely important to follow one simple rule: unlike a regular pimple, squeezing a boil is strictly prohibited. Reckless actions to independently open the pathology are fraught with sepsis, infection, phlegmon, thrombophlebitis and chronic furunculosis.
READ ALSO: Alveolitis after tooth extraction: what you need to know?
If furunculosis develops against a background of weakened immunity, several lumps may form simultaneously. In this case, the young patient risks experiencing severe swelling, redness of the skin, high fever and headaches.
Consultations with other specialists
Contacting specialists in various fields of medicine is necessary, since boils of bacterial origin (staphylococcus) can provoke:
- formation of a focus of chronic infection (sinusitis, sinusitis, tonsillitis);
- diseases and pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract (cholecystitis, dysbacteriosis, etc.).
The formation of boils may indicate a urinary tract infection, iron deficiency anemia, immune diseases, or the presence of a latent infection (herpes, cytomegalovirus infection).
Basic treatment methods
Parents bear full responsibility for the condition of their child , therefore they must take a responsible approach to the treatment of any disease, including furunculosis. It is better to entrust the prescription of treatment to a qualified specialist who, first of all, will carry out all diagnostic measures.
We are talking about a general blood test, x-ray examination of the respiratory organs, blood culture for sterility, its biochemical analysis, as well as the study of immunological status.
The results obtained will help determine not only the optimal treatment in each individual case, but also establish the causes of the development of the boil, without eliminating which therapy may be ineffective.
Today, treatment of boils on the leg in children is carried out using conservative therapy , surgery and folk remedies.
The use of local products is advisable in the early stages of the development of the disease and is aimed at accelerating the maturation and self-opening of the abscess.
It is recommended to treat the inflamed area with Bactroban, Levomekol, Azelik, Fucidin, gentamicin, heliomycin and other antibacterial ointments. Vishnevsky ointment, ichthyol ointment, and also Vinilin can also speed up the opening of an abscess.
Treatment of complicated forms of furunculosis should be general, therefore local treatment of inflamed areas should be supplemented with antibiotics, immunostimulants, and vitamin complexes.
Among the antibiotics most often in the treatment of furunculosis in a child, experts recommend giving preference to Azithromycin, Clarithromycin, Augmentin, Kefzol. The duration of treatment with the listed drugs should be at least 5 days.
READ ALSO: Atopic dermatitis, or neurodermatitis | #04/98 | “The Attending Physician” is a professional medical publication for doctors. Science articles.
It is also recommended to eat well and fill the diet with healthy foods rich in vitamins and microelements.
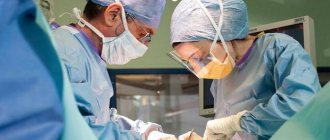
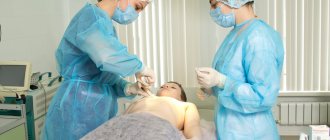
If there is a clear danger of serious complications, which were discussed above, as well as if drug treatment is low, the young patient may be prescribed surgery.
The operation involves the formation of a cross-shaped incision in the upper part of the abscess and the subsequent removal of purulent contents along with the necrotic core. Local anesthesia is recommended for the operation.
Treatment of a boil on a child’s leg can also be done using folk remedies , but before using them it is better to consult a doctor who treats children. In order to speed up the maturation of the boil, it is recommended to treat it regularly:
- a mixture of onions, garlic, honey and salt , which should be mixed in equal quantities and heated in the oven;
- a tandem of Vishnevsky ointment with fir oil, mixed in equal proportions;
- a mixture of baked onions with a little honey.
Diagnostics
Due to the fact that the foci of inflammation are superficial (except for ulcers in the ear), it is not difficult to diagnose furunculosis. However, with long-term, treatment-resistant furunculosis, there may be a need for extensive diagnostics to establish the exact causes of the disease. In this case, immunodiagnostics, a detailed blood test are performed, and the boil is examined for bacterial seeding of the purulent contents. If the study does not produce results, it is necessary to do a full examination of the body, since furunculosis may be the result of some general disease (blood disease, diabetes, etc.).
Disease prevention
Since the development of a boil on a child’s leg is most often associated with weakened immunity and non-compliance with personal hygiene rules, parents are obliged to pay due attention to the prevention of this pathology. The main preventive methods are presented:
- strengthening the immune system;
- bathing the child regularly and avoiding contamination;
- timely treatment of skin damage;
- minimizing hypothermia, stressful situations and other factors that may not have the best effect on the state of the child’s defenses.
With a responsible approach to the treatment and prevention of furunculosis, you will be able to save your child from such unpleasant problems forever. Stay healthy!
News MirTesen
What's really going on?
Barley is an acute, purulent clinical, infectious inflammatory process in origin. From this exhaustive definition, the reasons for its appearance, patterns of development, and the choice of adequate treatment and preventive measures clearly follow.
In the vast majority of cases, hordeolum is caused by the introduction of a bacterial (more precisely, Staphylococcal aureus) infection with subsequent rapid proliferation of the pathogen in the hair follicles, glands of Moll and/or Zeiss, less often in the meibomian glands (in this case, the “internal” barley is turned by the fistula canal towards the conjunctiva ).
Constant, often recurrent styes in a child always indicate the presence of some hidden or obvious systemic pathology. Usually this is a decrease in immunity due to an incorrect, unnatural lifestyle for children (physical inactivity, lack of sunlight, fresh air, etc.), hypovitaminosis, endocrine or gastroenterological disorders, recent diseases or operations, and the presence of worms.
Hypothermia and overheating, untreated or undertreated infectious foci, for example, in the oral cavity or nasopharynx (caries, tonsillitis, etc.) contribute to the development of stye.
But the main factor that makes styes a global problem and an almost inevitable companion to childhood is children's curiosity, combined with unwashed hands and a lack of strong sanitation and hygiene skills.
The crowding of children's preschool and school groups, the use of common towels or pillows, the habit of examining everything, so to speak, by palpation, the reflexive impulse to intensively rub the eyes in case of any discomfort - all this creates extremely favorable conditions for the spread of staphylococcal infection.
In addition, adults make a significant contribution to increasing the adaptability and survival of staphylococcus: uncontrolled and inadequate use of antibiotics leads to mutations and the formation of drug-resistant bacterial strains.