Furunculosis is a disease of the epidermis caused by inflammation of the hair follicles and surrounding tissue. This disease causes severe discomfort, pain and itching.
In addition, after the disease, scars may remain on the skin, since it penetrates quite deeply.
In this article we will talk about the features of this disease, the causes and treatment of furunculosis.
What is a boil in humans?
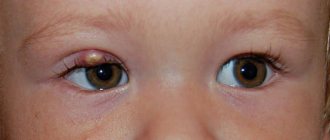
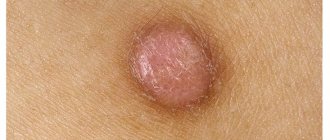
A furuncle (commonly called a boil) is an acute inflammation of the skin that has developed due to the activity of pyogenic bacteria (usually Staphylococcus aureus), localized around the hair follicle, affecting the sebaceous gland and nearby tissues. The lesion belongs to the group of pyoderma (purulent skin diseases). [2]
The general code for ICD 10 is L02 skin abscess, boil and carbuncle.
The pathology is characterized by purulent-necrotic inflammation (acute course) and a clear division of stages:
- Initial, manifested by the formation of an infiltrate, increasing in size, accompanied by redness and soreness of the skin. Initially, a small nodule appears at the site of the hair follicle; on the second or third day, purulent contents appear in its center.
- Necrotic, accompanied by the formation of a rod, increased redness and swelling. The top of the boil noticeably rises above healthy skin, pain increases, temperature rises (sometimes up to 39 degrees), and symptoms of intoxication are present. The stage takes on average 3–8 days.
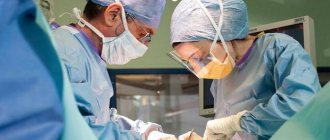
- An autopsy, during which the skin over the rod breaks through and the purulent contents come out. If the boil is located in an area with rough skin, self-opening may not occur and surgical intervention may be required.
After the cavity is freed from pus, healing begins, the timing of which depends on the size of the boil and the condition of the body. In some cases, complete cleansing requires installation of drainage. [3]
Antibiotic treatment
In cases where the boil is large or located in sensitive areas, and its development is accompanied by intoxication, chills and severe inflammation, the surgeon prescribes antibiotics.
For a large boil and a slight increase in temperature, a weekly course is prescribed: the doctor prescribes clindamycin or doxycycline.
At high temperatures and severe inflammation, a two-week course of treatment is most often prescribed, which includes stronger antibiotic drugs: rifadin, rimactan or other analogues.
Don’t forget, Staphylococcus aureus easily adapts to a variety of antibacterial agents, and as soon as the body’s defenses are slightly reduced, they multiply and form new abscesses. Therefore, people with reduced immunity should immediately consult a doctor and not self-prescribe medications. Keep in mind that if you relapse, they will no longer help you!
This article is for informational purposes only, please consult your doctor for details!
Views from photos
Despite the fact that all variations of boils are characterized by damage to the hair follicles, the course of the disease varies. The types of boils differ in the severity of the patient’s condition and the extent of the lesion. And although the main features of each of the variations can be seen in the photo, it should be borne in mind that only a specialist can make an accurate diagnosis. [4]
Furuncle
The “classic” version is characterized by damage to one hair follicle. The sizes may vary, but in the absence of complications the course is relatively mild.
It often opens up on its own; for treatment, local ripening-accelerating drugs and dry heat are often used. On average, it takes up to 10 days from the onset of inflammation to the release of the contents and the start of healing. [5]
Abscess boil
An abscess boil is a complication of a regular boil, when the core does not come to the surface or comes out incompletely, and the pus remains inside the dermis.
The danger of this condition lies in the risk of damage to neighboring tissues, their melting and the entry of pathogenic bacteria into large blood vessels. An abscess boil is treated surgically.
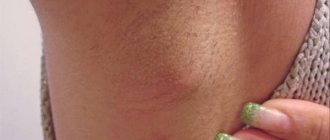
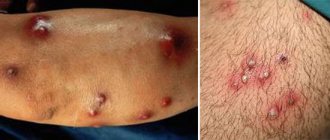
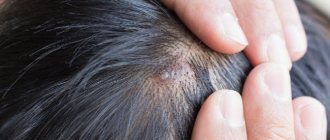
Furunculosis
The disease furunculosis is characterized by multiple formation of boils in a specific area or throughout the body. Acute and chronic course is possible, the latter is more common with serious problems with the immune system.
As a rule, furunculosis requires complex treatment - local use of dry heat and pus-pulling ointments together with the ingestion of antibiotics and immunomodulators. Before starting therapy, it is important to undergo tests to accurately identify the causative agent of the pathology. [3]
IMPORTANT: self-medication is contraindicated, consult your doctor in person! Furunculosis can be treated only under the strict supervision of a dermatologist. You shouldn't put your health at risk. Nothing good will come of this.
Carbuncle
A serious purulent-necrotic lesion of the dermis, affecting several follicles and sebaceous glands, quickly spreading throughout the skin and subcutaneous fat is called a carbuncle.
The course is more severe than with a normal boil, the symptoms of intoxication are more pronounced, and at the necrotic stage, deep tissue death, even muscle tissue, is possible. Surgical treatment is indicated. Lack of adequate treatment when a carbuncle occurs can lead to death.
Hidradenitis suppurativa
Despite the similar course and common pathogens, hidradenitis cannot be called a boil, since it does not damage the hair follicle, but the sweat gland.
However, after opening a boil in a place with increased sweating (primarily in the armpits), in the absence of proper disinfection, the development of hidradenitis suppurativa is possible. The nodes usually open on days 7–10, and the stem characteristic of boils is absent.
Disease detection
Diagnosis of the disease consists of conducting the following medical studies:
- Medical examination.
- Dermatoscopy.
- Examination of the boil contents for the presence of microorganisms.
Additional research methods include clinical tests of urine and blood, ultrasound, computed tomography, x-ray of the sinuses, and rhinoscopy.
How to distinguish a boil from a non-boil
Even knowing what a boil is, it is not always easy to differentiate it from other skin diseases. There are the following distinctive features characteristic of boils:
- increased temperature of the skin (with large ulcers - and the body), its redness;
- severe pain when palpated;
- the abscess is formed around the hair;
- inflammation goes quite deep into the dermis, swelling is present;
- a purulent core is observed.
Unlike acne, boils form at any age, often occur after a cold, and mature more slowly.
How to treat boils: 3 effective ways
In most cases, local therapy is indicated, aimed at accelerating the maturation of the abscess and drawing its contents out. [1] It is important to know that if a boil occurs, you cannot:
- squeeze it out;
- apply wet compresses (without special knowledge);
- self-medicate when the boil is localized on the face, head, groin area, armpits.
During treatment, treatment of the skin around the boil with antiseptic agents is indicated to prevent the spread of infection. If there is a prolonged increase in temperature, severe intoxication, or severe forms of the disease, it is imperative to consult a doctor to surgically remove the abscess and prescribe adequate (usually antibacterial) treatment.
IMPORTANT: It is important to consult a specialist before using the methods described below. Self-medication is contraindicated and can harm your health.
Ichthyol dressings
Ichthyol ointment with a characteristic odor has a number of properties that alleviate the condition of furunculosis:
- reduces inflammation;
- relieves pain;
- strengthens local immunity;
- disinfects, preventing the spread of infection, penetrates into the abscess;
- accelerates the ripening of boils;
- pulls out the purulent core;
- stimulates tissue regeneration.
The drug can be used both at the initial and necrotic stages. Ichthyol is applied to the boil and the area around it with a clean cotton swab, in a thick layer, without pressure. To avoid staining your clothes, it is recommended to cover the top of the ointment with a band-aid or gauze. Change the dressing every 4–8 hours. [7]
Aloe juice
The bitter plant effectively fights against ulcers, having the following effects:
- suppresses and destroys bacteria;
- relieves irritation and itching;
- stimulates tissue’s own protective reaction;
- draws pus to the surface;
- relieves inflammation;
- accelerates healing.
If used at the initial stage of development of a boil, it can prevent the formation of a purulent core, otherwise it speeds up and facilitates the opening.
On small abscesses, you can apply aloe leaves cut lengthwise, securing them with a band-aid. Large boils are easier to treat using gauze soaked in plant juice. It is recommended to change the sheet/bandage every 8-10 hours.
Dry heat
IMPORTANT: Russian dermatologists do not practice this method; it is more used in the USA. You should not self-medicate. Consult a specialist before using any method of getting rid of a boil.
Thermal effects accelerate metabolic processes in tissues, in mild cases it prevents the transition of the boil to the necrotic stage, in more severe cases it accelerates maturation. The boil should be heated without moistening it - for example, using a bag of salt or cereal, which can be brought to the desired temperature in a frying pan. The procedure is best performed at night, lasting up to 2 hours. The compress should be warm, but not scalding. [2]
It is important that you can only heat boils at the infiltration stage, when the only symptom is subcutaneous thickening, redness and swelling of the epidermis. After the formation of purulent contents, thermal exposure is contraindicated, as it can lead to the spread of bacteria into nearby tissues. In addition, you should not heat abscesses on the face and head.
There are other, no less effective folk remedies for treating boils at home; they are described in detail in a separate article.
Complications and consequences
In the absence of timely treatment, severely weakened immunity, or an unsuccessful attempt to squeeze out the boil, serious consequences associated with the spread of infection may develop.
The most common complications are:
- carbuncle;
- phlegmon - diffuse inflammation of subcutaneous fatty tissue;
- abscess;
- phlebitis - inflammation of the vein wall;
- thrombosis;
- meningitis;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes;
- blood poisoning with the spread of bacteria to internal organs.
Many of these consequences are extremely dangerous and can be fatal.
Reasons for appearance -
In most cases, the development of a boil is associated with infection of the hair follicle specifically by Staphylococcus aureus, less often by white staphylococcus or streptococcus. These bacteria are found on the skin of absolutely all healthy people and cause infection only when they penetrate into the deeper layers of the skin through a scratch, abrasion or cut (for example, when shaving).
Predisposing factors for the development of chiri -
- poor skin hygiene,
- with weakened immunity,
- if you have diabetes, oncology, rheumatoid arthritis,
- if you have acne (pimples and blackheads),
- if you have skin diseases such as psoriasis and eczema,
- for obesity,
- if you are taking prednisolone or its analogues,
- if you live in a hot, humid climate.
Prevention
Since treating boils is long and unpleasant, and complications pose a danger to health and life, it is recommended to take measures to prevent the occurrence of boils:
- keep your skin clean;
- avoid damage; in case of injury, immediately treat the wounds with bactericidal agents;
- If possible, wear loose clothing that does not chafe the skin;
- Eat a healthy diet with enough vitamins and minerals;
- strengthen the immune system - maintain normal activity, toughen up (but without fanaticism);
- in case of frequent interaction with contaminants, protect the epidermis with special clothing or film-forming sprays;
- be regularly checked for chronic and indolent diseases, and treat them in a timely manner;
- monitor normal hormone levels;
- minimize the use of pore-clogging cosmetics (especially for the fair sex).
It is also recommended to stop drinking alcohol and smoking, or at least not to abuse it.