How long does it take for symptoms of a tick bite to appear in humans: consequences of the bite and prevention of infection
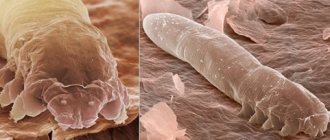
Not many people know what a tick bite looks like; the symptoms in humans are quite specific. Ticks are not insects. They belong to the arachnids.
The danger to humans is that ticks can carry pathogens of various diseases, for example, the tick-borne encephalitis virus. A person can encounter ticks everywhere (at the dacha, in the garden, in a park in the city, in the forest). Diseases transmitted by these organisms are called transmissible. Most often, arachnids bite humans in the spring and summer seasons. At this time their activity is highest.
What does a tick bite look like and what symptoms may appear when a person is infected with vector-borne diseases?
Where and when are you most likely to get bitten?
People living in disease-endemic areas, as well as those who visit these areas during periods of particular tick activity - from May to mid-June and from late August to late September - are most at risk of contracting a serious illness from a tick bite.
But the danger of being attacked by ticks remains throughout the warm period of the year when visiting almost any forested areas, parks and other areas where there is grass and shady shelters. You can even get a tick bite in your dacha or in the local area of your private home, if the grass there is not mowed.
The maximum number of bites from infected ticks is recorded annually in Siberia, the Urals and the Volga region. However, a considerable number of those bitten annually seek medical help in almost all regions of Russia, including Crimea and the Caucasus.
Habitats
Almost everywhere, these arachnid creatures live on everything
continents (except perhaps Antarctica) and in all climatic zones. As habitats, many species of ticks prefer wet places near water bodies: thickets near river banks, flooded meadows, forest ravines. Some ticks are able to live both in salt water of seas and oceans, and in fresh rivers and lakes. There are mites that live in houses and apartments, in animal fur (house mites, flour mites, dust mites).
What does a tick bite look like on a person?
A tick bite on a person (see photo) can often manifest itself in different ways. What does a tick bite look like in its usual manifestation? The most harmless manifestation is a slight redness around the place where the arthropod was found or a complete absence of marks on the skin, except for a small hole in the place where the proboscis was located.
The bite site may become slightly inflamed. An allergic reaction may also occur, provoked by saliva and existing microtrauma of the skin. A tick bite in a person can also lead to more dangerous skin reactions.
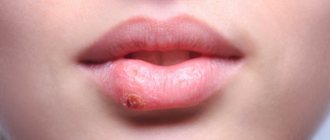
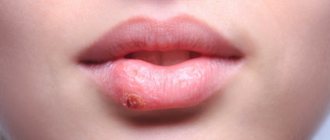
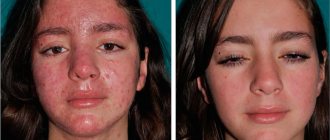
It is quite easy to recognize the location of a tick bite in a person infected with borreliosis. The area around the bite resembles erythema. The spot can increase in diameter to an average of 15-20 cm. Sometimes the red spot can reach 60 cm, covering not only the bite site, but also a significant part of the body. The spot in this case can have any shape. A characteristic sign of a tick bite that has suffered from borreliosis is the appearance of a distinct bloody border around the spot on the skin. In this case, the entire central part of the spot acquires a whitish or unhealthy, bluish color.
In addition to an allergic reaction, parasites can infect humans with dangerous illnesses. In most cases, the consequences of a tick bite are unpredictable. Not all parasites are carriers of dangerous pathologies. The sooner the bloodsucker is removed, the lower the risk of infection with various pathologies.
Nutrition
According to their diet, ticks are divided into:
Saprophage mites do not pose a threat; moreover, they also bring benefits, as they participate in the formation of humus.
Blood-sucking ticks are a completely different matter; these parasitic ticks wait for the victim, hiding in ambush on blades of grass and tree branches. Then they quietly jump onto her body, using paws equipped with special suction cups, attach themselves to the victim’s body and slowly drink blood from it. It is interesting that not only various large animals and humans, but also other herbivorous mites or thrips can become victims of ticks.
A tick bite is very dangerous, as they can be carriers of various diseases, especially encephalitis. Despite their unpretentiousness in food (as we wrote above, some ticks can go without it for up to three years), they can be incredibly voracious and can sometimes even increase in weight up to 120 times!
Also, in addition to blood-sucking ticks, there are ticks that feed on plant sap; these ticks sometimes cause great harm to agriculture. There are granary mites that eat flour and grain, ear mites that feed on juice from the ear canals, and subcutaneous mites that feed on the fat found in human hair follicles.
Signs of an allergic reaction to a tick bite
An allergy occurs in response to tick saliva entering the wound. The individual reaction of the body depends on the state of health as a whole. The consequences of tick bites are more severe in allergy sufferers, children, the elderly and people with weakened immune systems. A mild allergic reaction can be relieved with antihistamines.
Common signs of allergies:
- nausea;
- dizziness,
- weakness;
- drowsiness;
- aching joints;
- headache;
- temperature increase;
- itching and rash in the bite area and other parts of the body.
With a strong individual allergic reaction, anaphylactic shock may occur, which is preceded by:
- difficulty breathing;
- hallucinations;
- Quincke's edema (rapid and massive swelling of the face, throat or limbs);
- loss of consciousness.
Anaphylactic shock can be relieved by administering prednisolone and adrenaline. If symptoms after a tick bite indicate a severe allergic reaction, an urgent call to the ambulance is necessary, otherwise death is possible.
Consequences of a tick bite for humans
In the worst situation, a tick can infect a person with the following infections:
- Hemorrhagic fever. It is an infectious disease caused by a virus. Signs of infection include: intoxication of the body, the onset of fever, subcutaneous hemorrhages, changes in the composition of the patient’s blood. Experts distinguish between Crimean and Omsk fever. If you consult a doctor in a timely manner, the prognosis is favorable. Treatment consists of taking antiviral medications, vitamins that strengthen blood vessels;
- Tick-borne encephalitis . It is a viral disease, the main symptoms include: hyperthermia, intoxication, damage to the human central nervous system (meningitis, encephalitis). The consequences of the course of the disease include: neurological pathologies that lead to personality changes, in some cases to disability, even death. The first signs of the disease are observed in the first seven days; prevention should be carried out for several days after the bite;
- Borreliosis or Lyme disease . It is an infectious disease of a bacterial nature. General intoxication of the body is accompanied by a sharp increase in temperature, headache, constantly migrating rash, and fatigue. Bacteria are capable of infecting human organs and systems (especially the nervous and musculoskeletal, cardiovascular). Delayed assistance leads to disability.
Considering the danger of a tick bite for a person, be sure to pay attention to such a nuisance and, if necessary, visit a doctor.
Eggs
In the spring or late summer, having had enough of the blood of its victims, the fertile female tick makes a clutch consisting of 2.5-3 yew. eggs What do tick eggs look like? They are a very large cell, which consists of a nucleus and
cytoplasm, also covered with a two-layer membrane of different colors. Tick eggs come in a variety of shapes, from oval to square, flattened and elongated.
Signs of the development of tick-borne encephalitis
The incubation period of tick-borne encephalitis can last from 4 to 14 days. During this period, the infected person does not experience any external health problems. Then the temperature rises sharply to 38-39 °C, the patient has a fever, loss of appetite, pain in the muscles and eyes, nausea or vomiting, and severe headache.
Then remission occurs, during which the patient feels some relief. This is the second phase of the disease, during which the nervous system is affected. Subsequently, meningitis, encephalitis, and paralysis may develop. If left untreated, death is likely.
The problem is that the signs of the disease in the initial stage are often confused with the flu and acute respiratory infections, so they do not consult a doctor, but self-medicate. If a high temperature appears after a detected or suspected tick bite, you should not waste time - a blood test and treatment in a hospital are necessary.
Antiparasitic tablets
Treatment of demodicosis is not limited to the use of local drugs. Patients with this diagnosis must be prescribed medications for oral use. Antiparasitic drugs are usually used for a long period of time, since the likelihood of relapse is quite high.
- Trichopolum
. This is a broad-spectrum antimicrobial drug. Prescribed during the pastular-pupular stage of the disease. The duration of the course of therapy may be delayed, but does not exceed 10 days. - Metronidazole
. The antimicrobial drug is active against subcutaneous mites. Taking it daily significantly reduces the number of parasites. For medicinal purposes, the medication is taken one tablet every 8 hours. - Efloran
. The active ingredient is metronidazole. The medicine is used for pustular rashes or in case of bacterial infection.
It is recommended to supplement the course of treatment with antiparasitic drugs with Detox. It has an anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effect, helps cleanse the body of decay products of subcutaneous mites. The medication effectively soothes the skin and helps restore the secretory activity of the glands.
Symptoms of borreliosis
If a tick carrier of borreliosis is bitten, the bite site takes on the appearance of specific erythema, which gradually increases to 10-20 cm, and sometimes up to 60 cm in diameter. The erythema patch may be round, oval, or irregular in shape. The victim may experience burning, itching and pain at the site of the bite, but more often the first signs are limited to erythema alone.
After some time, a border of rich red color forms along the contour of the spot, while the border itself looks slightly swollen. In the center, the erythema becomes pale white or bluish. After a few days, a crust and scar forms in the area of the bite, which disappear without a trace after about 2 weeks.
The incubation period before the first symptoms appear ranges from several days to 2 weeks. Then comes the first stage of the disease, which lasts from 3 to 30 days. During this period, the patient experiences muscle aches, headache, weakness, fatigue, sore throat, runny nose, stiff neck muscles, and nausea. Then, for some time, the disease can go into a latent form for up to several months, during which the heart and joints are affected.
Unfortunately, erythema is often mistaken for a local allergic reaction, without giving it much significance. And malaise during the first stage of the disease is attributed to a cold or overwork at work. The disease passes into a latent form, and openly declares itself after a few months, when serious damage to the body has already been done.
Interesting Facts
- The smallest tick in the world, measuring only 0.08 mm in length, is even listed in the Guinness Book of Records.
- Three adult ticks, if placed together, will look like the dot at the end of a sentence in size.
- At birth, not a single tick is a carrier of dangerous infections; they only acquire them after parasitism.
- A female ixodid tick can eat 100 times more food than a male. After such a hearty meal, the female can increase in size by 150 times.
What should I do if bitten by a tick?
Since the likelihood of contracting dangerous infections increases significantly with prolonged contact of the human body with a tick, the main thing that needs to be done is to remove the arthropod. But the removal procedure should be carried out correctly so as not to crush or damage the tick, since this can further contribute to infection. In addition, the tick can and even should be examined in the laboratory for the fact of infectiousness, and for this it must remain intact.
Therefore, if you do not have the skills to remove ticks, but there is a possibility, it is better to contact the nearest medical institution, where they will expertly remove the arthropod and give recommendations on further actions. In addition, you can ask all your questions regarding tactics of behavior in the presence of a tick on the body by calling 103 (by calling an ambulance).
Description, structure, characteristics
Many people mistakenly believe that ticks are insects; in fact, they are not. They are part of the order Arachnids.
The body length of a tick rarely reaches 3 mm, on average it ranges from 0.1 to 0.5 mm. Do ticks have wings? Like all arachnids, ticks literally do not have wings at all. But adult ticks have four pairs of legs, and what’s interesting is that juvenile ticks that have not yet reached puberty have only three pairs of legs.
Ticks also lack not only wings, but also eyes, but this is not a problem for them at all; without eyes, ticks are perfectly oriented in space with the help of a developed sensory apparatus. And by the way, thanks to this device, they are also able to smell the scent of their possible victim at a distance of up to 10 meters.
Based on their structure, mites are conventionally divided into leathery mites, which have a fused chest and head, and armored mites, whose head is movably attached to the body. Also, leathery mites breathe through the skin and trachea, while oribati mites have special spiracles.
How can you remove a tick yourself?
It is best to remove ticks with a special device that is sold in pharmacies. This could be a “lasso pen”, UNICLIN TICK TWISTER, etc. If there is no pharmacy nearby, you can use ordinary cosmetic tweezers or sewing thread.
The person who will remove the tick must take care of his own safety - wear rubber gloves or wrap his fingers in a bandage. It is also advisable to prepare in advance a plastic container with a lid or a plastic bag for the tick (so that it can be delivered safely to the laboratory).
The removal procedure itself must be carried out as follows:
- Grab the arthropod with tweezers or a special device as close to the proboscis as possible (this is the part of the animal’s body that is in the skin). If a thread is used, a loop should be made from it, which must be carefully tightened over the head of the tick embedded in the skin.
- Smoothly pull up. In this case, you should not apply great force, as this may simply cause the tick to burst, and all its contents will end up on the skin and into the wound. In addition, with a sharp jerk, the arthropod’s proboscis remains in the wound, which can cause inflammation and even suppuration.
- After removing the tick, wash the skin with soapy water and treat it with any product containing alcohol. There is no need to apply a bandage. If the head of an arthropod remains in the skin, you should try to remove it from the body with a sterile needle like a splinter.
After removing the tick, it is advisable to do the following:
- Mark on the calendar the date when everything happened.
- Call your general practitioner or family doctor, explain the situation and ask about the need and timing of blood tests and taking some preventive measures (in some cases, to prevent the development of tick-borne encephalitis, victims of tick bites are given immunoglobulins, antiviral drugs are prescribed, etc.) .
- Take the tick to the laboratory. Information about laboratories can be found on the website of Rospotrebnadzor in your region.
It is necessary to visit a doctor in the following cases:
- If there are signs of inflammation in the bite area (swelling, redness, etc.).
- If, between 3 and 30 days after the bite, red spots appear on the skin.
- If your body temperature rises, muscle pain, unmotivated weakness and other unpleasant symptoms appear (these signs are especially important to monitor during the first 2 months after the bite).
Traditional methods of treatment
Traditional methods of treatment are also used for demodicosis. However, they should be used as a supplement to the main course and after consultation with a doctor. Below are several recipes on how to deal with subcutaneous mites:
- To prepare an infusion of celandine, you will need to mix 250 g of crushed plant roots and 200 ml of vegetable oil. It is better to place the container with the product in a warm place for 2 weeks. Then the mixture should be strained and refrigerated. Before treating affected surfaces, it is recommended to add a small amount of sour cream. The product can be instilled into the nose and eyes.
- To remove subcutaneous mites, some use a 6% solution of apple cider vinegar. You can soak cotton swabs in it and treat your legs, arms or chin.
- If the entire head is affected by demodicosis, a decoction of calendula and chamomile should be used to cleanse the affected areas and rinse the hair.
It is difficult to completely cure demodicosis using only folk recipes. However, their regular use helps eliminate unpleasant symptoms. Also, some traditional methods can be used for preventive purposes.
Chatterbox recipe
Twice a day you can lubricate the mite-affected areas with mash. This is a decades-tested remedy. It is prepared at home according to the following recipes:
- 4 tablets of Levomycetin and Trichopolum must be crushed to a powder state. Then add 100 ml of salicylic alcohol to the mixture and pour into a glass bottle. This product can be used as a tonic by rubbing the affected areas morning and evening.
- Mix a tablespoon of castor oil with two crushed Trichopolum tablets. It is recommended to use the product before bedtime. After applying to mite-affected areas, do not rinse off and leave until morning.
To avoid drying out the skin after treating it with mash, it is necessary to apply any nourishing cream. Preference should be given to products that are simple in composition. You can even use regular baby cream.
Boltushka is a potent remedy and is not suitable for all patients.
For example, it is not recommended for use if there are open wounds on the skin. It is also important to avoid getting the composition on the mucous membranes. It is not suitable for oral use and is rarely prescribed to children. To know all the restrictions on use, you should consult a dermatologist.
Where to go if you have symptoms of a tick bite in a person?
When bitten by a tick, you need to follow a special algorithm. The first step is to remove the tick. After which it is submitted to a special accredited laboratory. This will reveal the presence of infectious agents. The study is carried out using the PCR method, directly in the body of the tick. A person needs to donate blood to detect antibodies. After all, bites can cause serious consequences. The victim is recommended to undergo a course of treatment based on the results of laboratory tests. If symptoms of a tick bite appear in a person, you need to know where to go.
Where can you submit a tick and how to check it. It is necessary to find a hospital that does such research. Laboratory addresses and telephone numbers can be found on the Internet. Just visit the Ukrpotrebnadzor website. In fact, every hospital that has a laboratory should accept ticks. Most importantly, the research is completely free! It is recommended to clarify this information. Results are provided on the day the tick is submitted or the next day.
Listed below are laboratories where you can submit ticks for analysis in Moscow and the Moscow region; they conduct tests for encephalitis, borreliosis and other infections.
- FBUZ "Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology in the City of Moscow": metro station Alekseevskaya, Grafsky lane, building 4 (entrance from the yard, 2nd floor). Telephone
- Branch of the Federal State Institution "Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology in Moscow": metro station 1905 Goda Street, Krasnogvardeisky Boulevard, building 17 building 1. Telephone: 8 (499) 256-24-40
- Institute of Poliomyelitis and Viral Encephalitis: Moscow Region, Vnukovo, Moskovsky village. Telephone
- Children's Clinical Hospital No. 13 named after Filatov: metro station Barrikadnaya, Sadovaya-Kudrinskaya street, building 15. Telephone
- Infectious Clinical Hospital No. 2: Sokolinaya Gora metro station, 8th Sokolinaya Gora Street, building 15. Telephone
If you are afraid to remove the tick yourself, go to the emergency room, where they will professionally remove it and treat the wound. There you will also find out which laboratory the tick can be taken to.
Nymph. Is a nymph dangerous?
Having eaten someone else's blood, the tick larva eventually turns into a nymph. The latter has larger dimensions (1-2 mm) and already has four limbs. As a result, the tick nymph can choose larger animals as objects for parasitism, and even attack humans.
Just like adult ticks, nymphs are carriers of various infections, and therefore dangerous.
Prevention of bites and other recommendations
The likelihood of a tick attack on a person depends on:
- epidemiological well-being of the territory of residence;
- a profession associated with frequent presence in the forest or field;
- the likelihood of visiting places unfavorable from the point of view of tick-borne infections.
Prevention of consequences associated with a tick bite is based on:
- vaccination, but this is a preventive measure; it cannot be used if a person is infected;
- specific immunotherapy is a therapeutic measure (administration of immunoglobulin only in case of infection or suspected infection after a bite);
- health insurance to pay for possible treatment;
- using special clothing and devices to prevent ticks from getting on the body;
- the use of agents to repel and kill ticks;
- limiting the number of ticks in biotopes and places where people are likely to be found.
Recommendations for choosing a vaccine
Vaccination significantly reduces the risk of disease; it is indicated for all people living in disadvantaged regions and people professionally associated with forests (drillers, geologists, surveyors, foresters). Anyone who is interested in it can be vaccinated if they wish, provided there are no contraindications.
Primary vaccination is possible from the first year of a child’s life, and then at any age. Adults can be vaccinated with domestic and imported drugs, children are better off with imported ones. In Russia, six vaccine options are available from four manufacturers from Russia, Germany and Switzerland.
Vaccines against tick-borne encephalitis produced in Russia:
- The concentrated inactivated vaccine is indicated for use from three years of age and older;
- Encevir (EnceVir), Russia, is indicated for those aged eighteen and older.
Vaccines against tick-borne encephalitis produced in Switzerland:
- FSME-Immun Junior, indicated from one year to sixteen years;
- FSM-Immun Inject (FSME-Immun Inject), similar indications.
Vaccines against tick-borne encephalitis produced in Germany:
- Encepur Children, indicated from twelve months to eleven years;
- Encepur adult, indicated for ages twelve years and older.
Two vaccination schemes: preventive and emergency:
- Preventive vaccination provides protection against ticks during the first year, and after revaccination – for three years. Repeated vaccinations are carried out every three years.
- Emergency vaccination provides a short-term protective effect. Indication: urgent trips to regions unfavorable for encephalitis.
Vaccination is carried out after a preliminary survey of the patient for allergic reactions, clinical examination, and thermometry. Persons with health problems are not allowed to get vaccinated. There are contraindications and restrictions.
In Russia, “Human immunoglobulin against tick-borne encephalitis” is produced, produced by the Federal State Unitary Enterprise NPO “Microgen”. The drug contains ready-made antibodies to viral encephalitis. It is administered intramuscularly for the purpose of treatment, usually after infection or when there is a threat of infection. Doses and frequency of administration can be obtained from your doctor.
Recommendations for insurance of expenses associated with the treatment of tick-borne encephalitis
It is advisable to recommend insurance as an addition to vaccination or as the only measure if vaccination is not possible. Insurance against tick-borne encephalitis is carried out within the framework of VHI - voluntary health insurance. Payments are provided to compensate for the costs of expensive treatment of tick-borne encephalitis and other similar infections. When choosing an insurance program and insurance company, you need to pay attention to:
- the policyholder has permits for the execution of voluntary health insurance;
- the cost of VHI services and the reputation of the policyholder;
- availability of documents for the right to provide medical and preventive care or an agreement with a person authorized to provide such assistance on behalf of the policyholder;
- Availability of a 24-hour toll-free emergency telephone line.
Recommendations for using products to repel and kill ticks
For these purposes, repellents and acaricides can be used.
Repellents repel ticks and insects - these products are suitable for application to exposed parts of the body and for treating clothing. The active ingredient is DEET (diethyltoluamide).
Preparative forms of repellents:
- Gall-RET – aerosol;
- Raptor - aerosol;
- DETA-prof - aerosol;
- Ultraton (Ultraton) USA – lotion, aerosol;
- Biban (Czech Republic) – aerosol;
- DEFI-Taiga – solution, pencil, lotion, emulsion, aerosol, balm, cream, gel;
- Off extreme – aerosol;
- Breeze anti-mite aerosol.
Acaricides (destroy ticks) - have only a contact effect. They should be used exclusively for treating outerwear fabric and anti-tick treatment of areas and premises! Modern acaricides are made based on permethrin and alphacypermethrin:
- Raftamid-taiga is an aerosol that can be used to treat an anti-encephalitis suit, dry it and wear it over underwear with long sleeves and pants. The acaricidal effect lasts up to 10-15 days;
- Picnic Anti-mite – aerosol, apply in the same way;
- Tetrix (concentrate) - a liquid suitable for treating cabins, produced in 0.25 l bottles and 1 l and 5 l canisters;
On sale you can find acaricides recommended for application to the skin. But they should be used carefully - allergies and poisoning are possible.
Recommendations for the destruction of ticks in biotopes and places where people are likely to be found
To prevent the spread of ticks, you should regularly:
- clean the bushes, remove fallen leaves (mites lose their own moisture in the sun, and restore balance in damp shelters);
- destroy small rodents that feed ticks (circulation of the pathogen in wild fauna is a natural source of infection);
- mow the grass in the area (ticks guard the victim in the grass, usually at a height of 0.6 m, maximum height is 1.5 meters; in a hungry state, ticks live from two to four years, according to some data up to seven years; development from egg to adult individuals - imago takes two to three years or more);
- carry out treatment of places where ticks are likely to be concentrated (middle zone ticks move within 5-10 meters, southern ticks - up to 100 meters, orienting with the help of receptors, concentrate along paths, forest edges - in places of likely contact with the victim).
Anti-tick treatments based on knowledge of tick biology are effective when carried out annually. In many regions there are organizations that carry out decontamination, deratization, disinfestation, sell equipment for mowing grass, and chemical agents for anti-tick treatments.
Popular analogues
Not all patients are suitable for the medications prescribed by the doctor. For some, they cause allergies; for others, treatment is too expensive. Therefore, the specialist tries to select analogues.
| Drug name | Active substance | Manufacturer | Price |
| Permethrin ointment | permethrin | Pharmaceutical technology | 1300 rub. |
| Zinc ointment | zinc oxide | Biosynthesis | 30 rub. |
| Benzyl benzoate | benzyl benzoate | Nizhpharm | 20 rub. |
| Demoten | sulfur oxide | Geltek-Media | 380 rub. |
| Manting | allantoin, ginseng | JIUXIN | 1700 rub. |
The listed products differ in composition and price. However, they are all used to get rid of demodicosis. A competent choice of analogue is the key to successful treatment.