Author
: Grachev Ilya Illarionovich
Editor
: Efremov Mikhail Mikhailovich
Date of publication: 09/24/2018 Date of update: 06/08/2020
Regular psoriatic plaques can be seen not only on the elbows. No less often they are located on the skin of the anterior (extensor) surface of the knee joint. In some patients they remain unchanged for years, while in others they spread to neighboring and distant parts of the body. There are other manifestations of psoriasis on the legs. When should they be treated and is it worth doing if the disease does not progress? The answer to this question will be given by the specialists of the Paramita clinic.
Causes of psoriasis on the legs
Psoriasis is a non-infectious disease that affects the skin and produces bright pink rashes. Elements of the rash are most often represented by individual rashes - papules, which can sometimes merge and form plaques. Statistically, psoriasis accounts for 2% of all cases of skin diseases. Most often localized on the lower and upper extremities.
The exact cause of the development of the disease is difficult to trace; experts identify a number of etiological factors that become the trigger:
Often there is a combination of several causes, which complicates the diagnosis and prescription of etiotropic treatment to target the trigger.
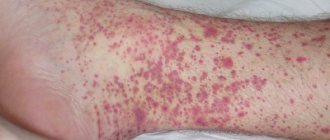
Photo of psoriasis on the legs, what psoriasis looks like on the legs
Photo 1. Psoriasis of the feet.
Photo 2. Psoriasis on the legs.
Photo 3. Symptoms of psoriasis: itching.
Photo 4. Symptoms of psoriasis: deterioration of nails.
Photo 5. Psoriasis on the heels.
Photo 6. Cracks on the heels from psoriasis.
To see what psoriasis looks like on the legs, you can look at photos of rashes on medical websites. Detailed photos of psoriasis on the feet will allow you to examine the shape, appearance and structural features of the psoriatic plaque.
How to distinguish psoriasis from mycosis?
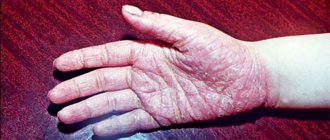
Nail psoriasis without cutaneous or joint involvement is possible, but occurs only in 5% of cases. So psoriasis usually affects the nail plate and the entire foot.
On the toenails we most often observe changes in the form of dimples, spots similar to vitiligo and normal pigmentation.
Common symptoms of nail psoriasis:
- thimble syndrome - microscopic crop-shaped depressions in the nail plate;
- yellowish-brown color of the nail, similar to a drop of oil;
- longitudinal and transverse grooves - splitting of the nail plate;
- leukonychia - white spots on the nails;
- raised hyponychium – masses of keratinized epidermis accumulate under the nail, which raise the hyponychium, deform the nail, and make it brittle;
- skin edema - painful and swollen skin on the nail folds.
The initial stage of psoriasis on the legs
From the photo you can see that the initial stage of psoriasis on the legs is similar to many dermatopathies, so it is sometimes mistaken for another disease and treated at home. The rash is represented by pale pink papules, on the surface of which there are white scales. Subjective sensations in the form of itching are not typical for psoriasis; pain may occur in the presence of cracks.
To differentiate psoriasis from other dermatoses, specific symptoms are checked:
In the progression phase, the rashes intensify, become intensely pink, unite into plaques, and are partially covered with white scales with a silvery sheen. As it progresses, the affected area grows and is completely covered with scales. There is itching and burning in places of close contact with clothing, cracks appear due to dryness of the epidermis.
In infants and when the rash is located in large folds of the skin (intertriginous form of psoriasis), the symptom complex is difficult to complete due to the rapid desquamation of scales.
Types of psoriasis
- Simple. Diagnosed in 85% of cases. There is redness in areas of the skin with white scales. This type of psoriasis is often found on the scalp. The skin under the scales is easily injured; wounds can bleed and cause pain.
- Back. Appears in folded areas: under the breasts in women, in skin folds, armpits, inner thighs, external genitalia.
- Pustular. This type of psoriasis causes clear blisters to form. There is red, inflamed skin around the pustule.
- Rupeeodny. In addition to the presence of plaques, this species is characterized by acute inflammation of the epidermis. The skin under the plaques is pink and wet.
- Teardrop-shaped. It is distinguished by a large number of small bubbles of red or purple color. They are shaped like dots or drops. This type of psoriasis appears on the arms, head, neck, shoulders, back, and thighs.
Is psoriasis transmitted?
This is a common question that concerns patients and their families. The disease is not contagious, since its cause is not associated with pathogenic microorganisms. It is assumed that psoriasis can only be transmitted genetically, that is, when there is a genetic predisposition. Psoriasis on the nails is often a concern for healthy people. After all, the patient touches any surface. However, there is no need to worry.
Symptoms of psoriasis on the legs
The specific clinical picture of psoriasis on the lower extremities depends on the location and form of the disease.
Vulgar or ordinary psoriasis is most often located in places of close contact with clothing and frequent friction: feet, extensor surface of the knees, legs. The rashes are round or irregular in shape and tend to rapidly coalesce and form plaques. Abundantly covered with white, silver and gray scales, which easily peel off when rubbed and scraped. Local hyperthermia, infiltration, itching and burning are noted.
Inverse psoriasis affects the flexural surfaces of the skin and areas of large folds: axillary, inguinal and intergluteal folds, elbow and popliteal folds. A complex form of the disease, similar to various types of dermatitis and allergies. The rashes are round in shape, bright pink in color, possibly a scarlet tint, not covered with scales due to high humidity and active work of the sweat glands. Moderate itching, burning, and pain are possible. pain, severe itching and burning.
The exudative form can be located over the entire surface of the legs. The presence of large, inflamed and weeping bright red plaques is noted on the skin. This form of psoriasis is characterized by the presence of dense scale-crusts of a yellowish-gray color on the surface of the rash.
The teardrop form of psoriasis is manifested by multiple small reddish papules covered with silvery-white scales. With this form of psoriasis, the fusion of individual elements into plaques is rarely observed.
Psoriatic erythroderma is the most severe form, manifested by redness and infiltration of the entire human skin. Pronounced large-plate peeling may be observed. This form of psoriasis is characterized by a disturbance in the general condition of the patient - there is an increase in temperature and a disturbance in general well-being.
Psoriasis on the feet
Psoriasis on the feet causes significant psychological discomfort and limits daily activities due to the presence of painful sensations. If psoriatic plaques are located on the dorsum and plantar part of the foot, stiffness of movement occurs and it is difficult to choose a pair of shoes.
Psoriasis on the feet is most often localized in areas of increased pressure on the skin. In these places, typical psoriatic rashes are formed, represented by infiltrated bright red plaques. On the surface of the plaques there may be pronounced peeling and deep cracks.
Seborrheic psoriasis
Seborrheic psoriasis, due to its external manifestations, can easily be confused with dandruff (hence the name). It also begins with red spots, localized mainly under the hair.
Manifestations
- papules with yellowish scales;
- peeling and itching, especially pronounced on the scalp;
- rashes can move from the head to the forehead (“psoriatic crown”).
Common sites of injury
- scalp;
- forehead;
- chest and interscapular area;
- nasolabial folds and places behind the ears.
Photo
Seborrheic psoriasis under hair
“Psoriatic crown” with seborrheic psoriasis
Seborrheic psoriasis on the scalp
Treatment of psoriasis on the legs
Before deciding how to treat psoriasis on the legs, it is important to rule out other skin diseases, such as a fungal infection. For this purpose, a skin scraping is most often taken for laboratory testing.
Treatment of psoriasis on the legs involves the use of medications for external and internal use, physiotherapy, adherence to the rules of personal hygiene, diet, sleep and rest.
For severe psoriasis on the legs, systemic anti-inflammatory (immunosuppressive and cytostatic) drugs or agents that affect the rate of cell division (synthetic retinoids) are used. Additionally or in milder cases, vitamin therapy and hepatoprotectors may be prescribed.
External treatment for psoriasis on the legs includes the use of medications (most often hormonal drugs are used in combination with salicylic acid or a vitamin D analogue) and care products based on salicylic acid, urea, tar, naphthalan oil.
Treatment
The use of hormonal ointments for the treatment of psoriasis of the legs is complicated due to sweating of these areas. Therefore, the most rational method is to use selective phototherapy. The Moscow clinic "ALODERM" successfully uses this technique, which is effective even in difficult places, such as nail plates.
UVB rays are used for phototherapy; they are the most effective for treatment. The difference is not only a better result, but also an almost complete absence of side effects. For treatment, it is not necessary to take additional photosensitizers, which can have a significant effect on the liver.
Losterine in the treatment of psoriasis on the legs
The line of non-hormonal products Losterin is specially created for the complex treatment of chronic skin diseases and the care of damaged skin. The drugs are suitable for daily long-term use. Active ingredients: deresined naphthalan, urea (urea), salicylic acid, D-panthenol, Japanese Sophora extract and almond oil do not cause addiction and “withdrawal syndrome”.
Carefully selected ingredients act directly on the affected areas, reducing inflammation and itching. For the purpose of complex treatment and preventive measures for exacerbation of psoriasis on the legs and feet, the following are used: foot cream, thick emulsion and Losterin shower gel. The drugs can be used during remission and as part of combination therapy.
Treatment can be supplemented with physiotherapy. The greatest therapeutic effect is observed from phototherapy (PUVA therapy. UVB-311 nm). This method significantly reduces inflammation within the lesion, reduces the need for medications and prevents relapse of the disease.
Sanatorium-resort treatment with hydrogen sulfide and sulfur sources during the period of regression and stationary form. The selection of an effective remedy for psoriasis on the legs is carried out by the treating specialist; the complex effect on the body is important.
Psoriatic nail care
Nails and feet affected by psoriasis require regular pedicures. Usually carried out every 2-3 weeks, and if you follow the podiatrist’s recommendations, gentle self-care and the right shoes, a visit to the office is required once every 5-6 weeks.
The podiatrist carefully trims the nails without damaging the adjacent tissues, as a result they do not peel off or crack.
A medical pedicure removes keratinization - a protective barrier that interferes with the external effects of ointments and creams on psoriasis lesions; in fact, keratinization of the feet nullifies the effect of external medications. A mandatory procedure in the complex treatment of the disease.
Prevention of psoriasis on the legs
Preventive measures include measures to prevent relapse of the disease:
- Wearing clothes made of natural light material. The underwear should be true to size, without squeezing elastic bands.
- Selection of shoes strictly according to size. Wearing orthopedic insoles.
- Keep affected areas clean and dry, carry out air baths.
- After bathing, pat your skin dry with a clean, soft towel.
- Trim nails regularly and inspect them daily.
- Treating feet with an antiseptic: Furacilina solution, Chlorhexidine.
- The use of moisturizing and wound healing agents.
- Avoid stressful situations.
- Normalization of weight.
- Maintain proper nutrition and daily routine. Rejection of bad habits.