Author
: Grachev Ilya Illarionovich
Editor
: Efremov Mikhail Mikhailovich
Date of publication: 09/25/2018 Date of update: 06/08/2020
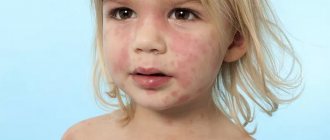
Very often, the manifestations of psoriasis on the skin of the hands are local in nature, without spreading to the surrounding tissues. With this course, many patients do not pay attention to the rash and do not rush to consult a doctor. But in vain, because in the presence of provoking factors, a “fire” can break out instantly in the form of severe complications, the treatment of which is far from as simple as single psoriatic plaques. Doctors at the Moscow Paramita clinic are well aware of how and how to treat psoriasis on the hands. From this article you can learn how this disease is treated at the initial stage and in severe cases.
Why does psoriasis start on the hands?
Psoriasis on the hands in the form of single regular plaques is only a seemingly local pathological process. In fact, even 1-2 elements of the rash indicate the presence of a chronic inflammatory skin disease. Medicine has not yet been able to unravel all the mysteries of this disease. The exact causes of psoriasis have not been identified. It is only known that the pathological process is based on burdened heredity and immune disorders.
Currently, the genes responsible for the hereditary transmission of predisposition to psoriasis, including on the hands, are being identified and studied. Under the influence of genes, a change in metabolism occurs and a decrease in the content of enzymes that destroy substances involved in inflammatory reactions.
Immunity is also impaired, which leads to a multiple acceleration of cell division in the surface layers of the skin. The cells do not have time to mature when new underlying cells push them to the surface. This is another cause of psoriasis on the hands.
Psoriasis of any localization can spread throughout the body, so do not delay treatment.
See how easily the disease can be cured in 10-12 sessions.
Such changes lead to the appearance of characteristic symptoms of the disease. What does psoriasis look like on the hands? Initially, a scaly spot appears on the hands, sometimes on other parts of the body, which quickly turns into a papule with a raised inflammatory base. The papules grow and merge, forming huge plaques.
But not all genetically predisposed people develop the disease. The reason is the lack of exposure (or minor exposure) to provoking factors. If you avoid these factors, you may never get sick, even if both parents have psoriasis.
Factors that provoke the onset of psoriasis on the hands
Factors that contribute to the development of hand psoriasis are divided into general and local. Common factors include:
- sedentary lifestyle, overweight, obesity;
- hormonal imbalances; the hormonal system is one and a failure in one link will certainly lead to numerous disorders in the body, including metabolic and immune disorders;
- improper irregular nutrition, consumption of large amounts of high-calorie food, meat, sweets;
- bad habits – smoking, alcohol abuse;
- prolonged stress, high mental and physical stress;
- What matters are long-term chronic diseases and foci of infection that contribute to the development of intoxication, under the influence of which metabolism is disrupted.
Red spots on the skin after stress
Diagnosis of skin diseases
Very often, psoriasis on the hands is provoked by the following local factors:
- constant mechanical injury to the skin of the hands - abrasions, scratches, wounds;
- frequent exposure of the skin to various chemicals: household chemicals, industrial hazards, etc.;
- constant exposure to the cold - this leads to spasm of small blood vessels and disruption of skin nutrition; therefore, disruption of metabolic processes is only a matter of time;
- any skin infections - bacterial, fungal, viral.
Pigmentation changes
Pigmentation disorders include depigmentation (loss of skin color) and hyperpigmentation (accumulation of skin color). Depigmentation can be caused by chemicals such as hydroquinine, phenol (and its derivatives), arsenic and mercury compounds. It can also be caused by ionizing and ultraviolet radiation, as well as thermal or physical trauma.
Hyperpigmentation can be caused by mineral oils, halogenated hydrocarbons, arsenic and various pharmaceuticals.
Symptoms of psoriasis on the hands
The disease can begin and progress differently depending on the form. Symptoms of psoriasis on the hands can also vary.
Vulgar form
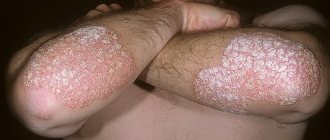
This is the most common form. On the hands, the skin of the extensor area of the joints, as well as the forearms, wrists, dorsum of the hands, and fingers are usually affected. In the area of the elbows, so-called standby plaques appear on both sides, which can remain in the same state for years without progressing. On the back of the hands, the disease progresses more often, since the skin in these areas is constantly exposed to various influences. Psoriasis often appears on the fingers. In case of damage to the little fingers and thumbs, the risk of injury to psoriatic elements increases.
The first signs of psoriasis on the hands are the appearance of one or more scaly spots, which quickly turn into papules with a raised inflammatory base. If you scratch the top of such a papule, a number of characteristic symptoms appear:
- type of stearin drop - multiple white flakes;
- if you scrape off all the scales, a transparent film will be visible;
- Slightly scraping the film leads to the appearance of droplets of blood on it.
These symptoms are the hallmark of a psoriatic rash. In the future, the primary symptoms of the disease may progress, with the papules increasing in size, merging with each other and forming large plaques, and new elements appear. Possible damage to nails. Over time, the progression stops, after which the recovery process begins: the rash slowly turns pale and disappears.
Exudative form
This form of the disease is less common. The skin on the back of the hands is usually affected. Often this type of psoriasis also affects the fingers. Characterized by the appearance of swelling, exudate on the surface of the rash elements, severe itching and a constant feeling of discomfort. As a result, the scales stick together to form grayish-yellowish crusts on the surface of the papules on the skin of the hands and fingers. In this case, peeling is not very noticeable, but the risk of bacterial infection increases. What exudative psoriasis looks like on the hands can be seen in the photo:
Palm shape
Psoriasis on the palms can occur in the form of plaque-fan-shaped, horny and pustular forms.
The plaque-fan-shaped form is characterized by the formation at the initial stage of rash elements in the form of scaly papules, merging into large plaques. The rashes are localized mainly on the palms and fingers. It often recurs and is difficult to treat. The reason for this is the constant exposure to various external factors. The skin between the fingers is affected. They turn red, swell, and become covered with cracks and scales. Often such rashes spread to the fingertips and nail plates.
The horny form is manifested by dry skin, thickening on the palms, the appearance of cracks and dry calluses.
Psoriasis on the palms of the hands may look like pustules. This is the so-called Barber pustular psoriasis. Purulent blisters appear on the surface of the palms, which can merge with each other, forming purulent lakes. The contents of the pustules are sterile. Photo:
Skin specialist
The skin acts as a natural barrier, protecting the body from harmful environmental influences. It also takes part in the thermoregulatory process and metabolism, and is responsible for sensitivity to pain and temperature changes. It happens that the skin reacts to stressful situations, poor nutrition, lack of vitamins, pathologies of internal organs, as a result of which noticeable signs and often painful symptoms appear. Skin diseases can also occur due to infections or parasitic insects.
To determine the cause of the deterioration of the skin condition and cure the disease, you need to consult a skin specialist - a dermatologist. This doctor examines the skin, diagnoses and treats skin diseases.
In what cases is it necessary to consult a specialist in skin diseases?
As a rule, dermatological diseases are not life-threatening, but they cause significant inconvenience to people. Patients experience unpleasant itching, acne, redness and other external imperfections that are very difficult to hide. As a result, people begin to experience psychological discomfort, become depressed, lose their appetite, experience insomnia, and disrupt the functioning of the immune system. If treatment for the disease is not started in a timely manner, it can develop quite rapidly, leading to serious complications and disruptions in the functioning of internal organs.
It is advisable to make an appointment with a skin specialist if you have the following symptoms:
- disruption of the sebaceous glands, too oily skin;
- dry skin with frequent peeling;
- change in skin tone;
- the appearance of warts or new moles;
- the appearance of ulcers, erosion, red spots, purulent formations;
- brittle nails, etc.
You should not self-medicate for skin diseases. Most of them are triggered by the penetration of a viral infection, bacteria or fungi. Sometimes dermatological diseases arise due to problems in the functioning of internal organs. Then the patient needs complex diagnostic and therapeutic procedures under the supervision of not only a skin specialist, but also other doctors.
What diseases does a dermatologist treat?
Skin disease specialists diagnose and prescribe treatment for the following pathologies:
- the appearance of warts, condylomas, herpes, molluscum contagiosum and other formations caused by viral infections;
- impetigo, pyoderma caused by bacterial infections;
- mycoses, various types of lichen, candidiasis and other diseases caused by fungal infections;
- scabies, pediculosis, resulting from exposure to parasites on the skin.
Skin specialists also help patients in getting rid of various non-communicable diseases that are associated with skin, nails and hair problems: psoriasis, eczema, acne, atopic dermatitis, lichen planus, rosacea. Dermatologists also remove benign skin formations, such as keratomas, papillomas, lipomas, moles, etc.
To restore and improve the condition of the skin, doctors prescribe cosmetic procedures. For preventive purposes, to prevent negative changes, a skin specialist can recommend special diets and effective cosmetics that will help maintain the elasticity and healthy appearance of the skin.
What does an appointment with a skin specialist include?
When coming for a consultation, the patient tells the doctor about the presence of unpleasant symptoms. The doctor listens carefully to him, then conducts a thorough examination of the affected areas of the body, writes out a referral for tests or diagnostic procedures. The dermatologist selects diagnostic methods depending on the nature of the disease. The specialist can ask the patient questions about the presence of hereditary diseases, lifestyle, bad habits, and medications taken. The doctor visually assesses the condition of the skin, the nature and extent of the pathology. If necessary, he performs non-surgical dermatoscopy and scraping from the affected area.
If the dermatologist decides that the cause of the pathology is caused by disturbances in the functioning of the internal organs, he will recommend the patient to visit another specialist, for example, an endocrinologist, immunologist, gastroenterologist, etc.
How is treatment done by a dermatologist?
Treatment of skin pathologies can be complex and include both medication and physiotherapeutic treatment, as well as modern surgical methods.
In many cases, the patient only needs to be prescribed medications. Depending on the type of pathogen, location of spread and phase of development of the disease, the doctor may prescribe anti-inflammatory, antiviral, antifungal drugs, and drugs that strengthen the immune system. Sometimes treatment includes a course of injections and IVs. Some pathologies are treated with external medications: ointments, creams, gels, etc.
Physiotherapeutic treatment is widely used for the treatment of skin diseases. It is especially effective for psoriasis, eczema, acne, herpes, etc. Among physiotherapy methods, UHF, ultraphonophoresis, inductothermy, medicinal baths and other procedures are often used.
Surgical intervention is needed to get rid of benign neoplasms: moles, papillomas, warts, etc. Modern surgical techniques allow you to achieve an excellent aesthetic effect, these include:
- cryodestruction;
- radio wave surgery;
- laser removal.
Treatment of skin diseases
In our clinic, experienced, highly qualified specialists provide diagnosis and treatment of skin pathologies. They provide physiotherapy and surgical procedures using state-of-the-art quality equipment.
To make an appointment with a dermatologist and find out the cost of services, call or fill out the feedback form on the website.
Author
Turchaninova Kristina Valerievna
cosmetologist, dermatologist, dermatovenerologist
10 years of experience
+7
Treatment methods for psoriasis on the hands
How to treat psoriasis on the hands? This problem arises immediately after diagnosis. Experts recommend comprehensive treatment, which includes:
- changing lifestyle, daily routine;
- getting rid of bad habits;
- proper nutrition;
Lifestyle recommendations
Patients with psoriasis localized on the hands need to:
- regulate wakefulness and sleep patterns;
- engage in feasible sports; Activities such as outdoor running, swimming, tennis are welcome; avoid contact sports (wrestling);
- important: after playing sports, be sure to take a shower - sweat irritates the skin and can provoke an exacerbation of the pathological process;
- wash only with soft washcloths using hypoallergenic detergents;
- After a shower, apply moisturizer to your body;
- use underwear made from cotton fabrics;
- in the cold season, wear gloves (mittens) with flannel lining;
- Avoid contact with household chemicals and any other chemicals.
Drug therapy
Good to know
- Treatment of psoriasis on the head
- Treatment of psoriasis on the elbows
- Treatment of psoriasis on the legs
- Treatment of psoriasis on nails
- Treatment of psoriasis on the face
- Treatment of palmoplantar psoriasis
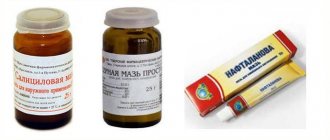
In mild cases, psoriasis on the hands is treated locally, using various external agents and procedures. Prescribed:
- keratolytics - medicinal ointments and creams that dissolve surface layers of dead epithelial cells (salicylic acid);
- emollients (tar-based psoriasis ointment);
- synthetic analogues of vitamin D (calcipotriol);
- synthetic analogues of vitamin A (retinoids);
- glucocorticosteroid (GCS) hormones - allow you to treat all forms of hand psoriasis;
- combination products that include GCS + salicylic acid (Diprosalik) or GCS and calcipotriol (Daivobet);
- creams and ointments with active zinc;
- medicinal baths with herbs (celandine, chamomile, calendula).
If the symptoms of psoriasis on the hands do not go away, the disease progresses, and general therapy must be prescribed. It should be carried out in a hospital setting:
- droppers with medicinal solutions that eliminate intoxication;
- injections of drugs that remove toxins (Unitiol, magnesium sulfate);
- desensitizing (eliminating allergies) and sedatives; 1st generation antihistamines (Suprastin, Tavegil) are most suitable;
- glucocorticoids - taken orally or by injection - have a pronounced anti-inflammatory and desensitizing effect, relieve itching;
- cytostatics - drugs that suppress too frequent division of epithelial cells;
- Immunosuppressants are medications that suppress the excessive sensitivity of the immune system.
Contact dermatitis
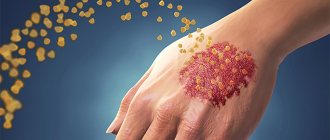
Most occupational skin diseases are limited to the hands and forearms, as they are most often in contact with hazardous substances. The most common skin condition is contact dermatitis (also known as contact eczema). Dermatitis is caused by inflammation of the skin. Symptoms include redness, dryness, itching, swelling, cracking, blistering, peeling and bleeding.
There are two types of contact dermatitis: irritant dermatitis and allergic dermatitis. They have the same appearance, but different reasons.
Irritant dermatitis
Irritant dermatitis can be caused by a physical or chemical agent that damages cells. Irritant dermatitis makes the skin more vulnerable to other hazards, such as bacteria and chemicals. When there is no longer contact with what causes irritation, the condition ceases.
Allergic dermatitis
Allergic dermatitis is caused by exposure to an allergen or sensitizer, usually a hazardous substance. When the affected immune system reacts to it, it becomes sensitized. Once sensitized, the problem usually persists throughout life, and any further exposure results in an allergic reaction.
Causes of dermatitis in the workplace
Both irritant and allergic dermatitis can be present together, and it is not uncommon for allergic dermatitis to develop after irritant dermatitis.
Causes of irritant dermatitis include cleaning products, organic solvents, metalworking fluids, cement and other chemicals, some plants and shrubs, and water.
Although hand washing requires water, prolonged exposure to water can cause irritant dermatitis. This is especially important when working wet. Wet workers include hairdressers, food workers and people who handle metalworking fluids
Allergic contact dermatitis can be caused by allergens such as cement, metals (such as nickel and chromium) and resins. Latex is a common cause of allergic dermatitis. It is widely used in the medical industry, where latex gloves are worn regularly.
Common risk factors for dermatitis include wet work and the use of gloves. While gloves can provide protection to workers, they can also pose risks. Gloves must be suitable for the job being performed and used properly. Using damaged gloves may give a false sense of security. Impermeable gloves form an impermeable barrier that can cause sweat to accumulate, meaning the wearer may have trouble performing the job.
Unique methods for treating psoriasis on the hands
The Moscow Paramita Clinic is a leader in the treatment of such a complex form of the disease as psoriasis on the hands. Experienced specialists who have undergone all the necessary training in the treatment of this disease try to take an individual approach to the treatment of each patient, using the most effective methods.
- PRP therapy is a method that has been used relatively recently, but has already gained well-deserved popularity, as it is very effective and safe; the method consists of enriching the patient’s blood taken from a vein with platelets and injecting it into the affected areas on the skin of the hands;
- autohemotherapy is a method that has been tested for decades: blood is taken from the patient’s vein and injected intramuscularly; excellent stimulating effect;
- herbal medicine – the use of medicinal plants using modern methods;
- reflexology – exposure to certain points on the body using various methods (acupuncture, massage, cauterization, etc.); exposure to one point or another has a reflex effect on the condition of the skin;
- vacuum therapy is one of the types of reflexology, when certain points and zones are affected using vacuum.
The clinic’s dermatologists prescribe complex therapy taking into account the patient’s age, general condition, the presence of certain concomitant diseases, as well as the nature of the course of psoriasis. As a result of this approach, the patient receives the necessary treatment for psoriasis in Moscow without side effects, which allows him to get rid of the symptoms of the disease for a long time.
To avoid relapses, it is necessary to eliminate the cause of the disease.
Read more about our unique method of treating psoriasis
Patients return to the clinic again and again for maintenance anti-relapse treatment and live for years without exacerbations. In the reviews, they note the high professionalism and attentive attitude of the doctors.
Sign up for a free initial appointment
Occupational skin infections
Occupational skin infections are often caused by contact with animals or plants. They include a range of diseases: from the relatively harmless but unpleasant scabies to the deadly anthrax.
Occupational skin infections are caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi or parasites. It is necessary to distinguish primary skin infections from skin infections secondary to pre-existing occupational dermatoses or pre-damaged skin, and colonization of the skin or mucous membranes with multidrug-resistant or potentially harmful infectious agents in the context of occupational activities. If an occupational skin infection is suspected, a detailed history should be obtained, including information about the workplace and its conditions.
Stages of hand psoriasis
The disease occurs in alternating phases of relapses and remissions. The course can be severe, moderate or mild. During an exacerbation, the disease goes through several stages. Psoriasis on the hands, stages:
- the initial stage of progression - a psoriatic rash appears, the symptoms of the disease quickly increase;
- stationary – no new elements appear, the rashes do not fade or become smaller;
- regressing - the rash turns pale, swelling subsides, all signs of exacerbation disappear, and gradually only white or brownish spots remain on the skin, which also disappear over time.
Any form of the disease, in the absence of adequate treatment, can be complicated by joint damage and erythroderma - inflammation of large areas of skin with severe swelling and redness.
Skin cancer
Skin cancer is the most common type of cancer and usually develops in exposed areas of the skin. The incidence is highest among workers, athletes and sunbathers and is inversely proportional to the amount of melanin pigmentation in the skin.
Skin cancer can be caused by ultraviolet rays (both solar and artificial), ionizing radiation, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, tar and resin products.
Skin cancer is often asymptomatic at first. The most common presentation is an irregular red or pigmented lesion that does not go away. Any lesion that appears to be enlarging should be biopsied—whether there is tenderness, mild inflammation, crusting, or intermittent bleeding. With early treatment, most skin cancers are curable.
How to eat healthy
Nutrition is of particular importance as it affects metabolism, the disturbances of which underlie the disease. It is useless to treat psoriasis without following a diet. Important: in the patient’s diet, 70% should be products of plant origin and only 30% should be animal products. Recommended to use:
- any fruits and vegetables (fresh, boiled, stewed) except those prohibited;
- fresh juices; Citrus juices are especially useful; lemon juice can be used as a salad dressing;
- more clean water.
Limit consumption (no more than a few times a week):
- lean meat and fish;
- low-fat cottage cheese and fermented milk products;
- cereals;
- some fruits and berries: plums, currants, cranberries, blueberries.
Exclude from the diet:
- fat meat;
- fatty dairy products;
- sweets, baked goods;
- vegetables from the nightshade family: tomatoes, eggplants, hot and bell peppers;
- all spicy, sour, smoked, fried, canned foods;
- drinks: sweet soda, cocoa, strong coffee, tea, alcohol.
Treatment of psoriasis on the hands with folk remedies
Folk remedies are widely used in the treatment of psoriasis on the hands. Celandine is especially often used for this purpose. For example, a serum infused with celandine helps a lot.
You need to take a glass of crushed fresh celandine herb, wrap it in a cotton napkin, tie it, put it in a 5-liter glass jar, fill it with three liters of whey, add 200 g of sugar, 20 g of sour cream and leave in a warm place for 15 days: during this time the whey will ferment ; this serum should be filtered and taken 70 ml in the morning 30 minutes before meals; store in a cool place; perfectly removes toxic substances, cleanses the body, activates metabolism; the symptoms of the disease go away.
Prevention of psoriasis on the hands
Prevention of the disease includes patient compliance with recommendations on daily routine, skin care and nutrition.
Psoriasis on the hands is best treated in the early stages of the pathological process. It is impossible to completely cure this process, since under the influence of any factors a relapse may begin. But if maintenance treatment is carried out periodically, remission for a long time is quite possible. At the same time, the person lives life to the fullest and does not remember relapses.