What is papillomavirus
The Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is a group of small viruses that contain DNA. These viruses cause pathologies of epithelial tissue. The main method of transmission of infection is unprotected sexual contact. Scientists have discovered more than 200 strains of HPV, of which 29 strains are oncogenic. Dangerous strains cause malignant degeneration of epithelial cells.
The relationship between HPV infection and the development of malignant tumors has been scientifically proven. The papillomavirus is integrated into the human genome, which leads to a failure of the program embedded in the DNA. When epithelial cells divide, the affected gene is transferred to new cells. This is how the virus penetrates into the deep layers of tissue.
The infection is asymptomatic until cells with an altered genome begin to reproduce cancer cells. HPV causes cancer:
- cervix;
- vulva and vagina;
- penis;
- anal canal;
- throat and larynx;
- neck and scalp;
- stomach and esophagus.
The growth of benign tumors is also possible: papillomas, condylomas, anogenital warts. Complications include recurrent respiratory papillomatosis (in adults and children). This disease leads to difficulty breathing and obstruction of the airways.
Types of warts
Today there are over 100 types of HPV, each of which gives rise to a certain type of warts and papillomas. The incubation period is about 2-6 months, but it largely depends on the human immune system: a strong and healthy body easily fights the occurrence and proliferation of growths. The following types of warts are distinguished:
- ordinary (simple, vulgar);
- plantar (pinuses);
- flat (juvenile);
- senile (age-related keratomas).
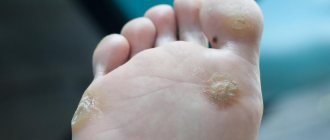
Ordinary (simple, vulgar) - warts in the form of small dense dry nodules with an uneven and rough surface, variable sizes and a rounded shape. They do not cause itching, pain or discomfort. Simple warts reach from 3 to 10 mm in diameter. They are usually flesh-colored, sometimes pink, yellowish, or light brown. Due to the accumulation of contaminants in the porous surface, they can turn dirty gray. The favorite localization of simple warts is the back of the hands and fingers. Sometimes they are observed on the knees and elbows, rarely on the face and feet. After some time (it’s different for everyone), the tumor increases in size, and the skin in its place begins to peel off. The progression of the pathology is manifested by the formation of a large “mother” wart with a scattering of small ones around. When removed, small ones usually self-destruct over time. Plantar warts (spikes) are warts in the form of several fused nodules with a roll of keratinized skin around them. Inside the growths, many small black dots are visible - thrombosed capillaries. Plantar warts are round in shape, rise above the skin by 1-2 mm and can reach up to 2 cm in diameter. However, 75% of the tumor is located in the deep layers of the epithelium, so their main feature is inward growth. Outwardly, these warts resemble calluses, which is why they are often confused with each other. It's important to remember that, unlike a callus, a ring of dead skin forms around a wart. Spines are localized on the feet, rarely on the palms. Usually colored yellow or dark brown. This type of wart causes significant discomfort, itching and pain, aggravated by walking, and may even bleed. In 50% of cases it self-destructs without treatment, but this may take from 8 to 18 months. As the pathology progresses, the number and size of warts will increase, which may lead to the inability to walk due to unbearable pain. Flat (juvenile) - warts in the form of small flat papules with a smooth (sometimes scaly) surface, slightly raised above the surface of the skin. Traditionally it affects people aged 10 to 25 years. They are formed in multiple clusters or singly, which is quite rare. Usually the growths are flesh-colored, sometimes white, brown, yellowish or pink. They appear on the face, neck, knees, elbows, back, legs and arms (especially on the fingers and back of the hands), sometimes on the head of the penis. As a rule, they are painless and do not cause discomfort unless they are subjected to mechanical pressure or damage. Flat warts can suddenly disappear on their own just as they appeared, especially in childhood. But sometimes they are quite difficult to treat. Senile (seborrheic keratoses) are warts in the form of dark, flat, round or oval plaques that appear in old age. They reach a diameter of 0.2-3 cm, sometimes 4-6 cm. The pathogenesis is not clear, but their appearance is definitely not associated with HPV. Senile warts can affect any part of the body except the palms, soles of the feet, and mucous membranes. As a rule, they appear in multiple clusters (about 20 foci). Initially, they appear as small light brown spots or papules with clear contours. Over time, keratoses may retain their appearance and resemble freckles, or they may harden, forming a warty surface covered with easily removable thin crusts. In most cases, senile warts take on a mushroom shape and are dark brown or black in color. They develop very slowly, over decades, never degenerating into a malignant form. Typically, seborrheic keratoses are removed for aesthetic reasons or because they become itchy and irritating. If the growths, especially large and warty ones, are injured (rubbed against clothing, touched by something), they may bleed or become inflamed.
Classification of viral strains
All HPV strains are divided into cutaneous and mucosotropic. Skin viruses lead to the formation of benign tumors on the skin. Mucosotropic provoke the appearance of neoplasms on the mucous membranes.
Skin strains provoke the development of different types of papillomas:
- Flat. Round nodules with a diameter of up to 10 mm. They do not turn into cancer.
- Pointed. Shaped like a cockscomb. These are pink formations covered with horny cells.
- Thread-like. Round papillomas on a thin stalk. Diameter up to 7 mm.
Mucosotropic strains cause the following diseases:
- Bowenoid papulosis. The appearance of spots and plaques on the genitals.
- Dysplasia. Pathological degeneration of cervical tissue.
- Inguinal condylomas. Ball-shaped tumors on a stalk.
If benign tumors appear, you should consult a doctor. A dermatovenerologist will determine the type of papillomavirus and the degree of its danger, and prescribe a treatment regimen for the infection.
What are papillomas
Papillomas are also benign formations. They come in a variety of shapes - leaf-shaped, spherical, filamentous or lobed, often resembling cauliflower in appearance. The growths have a soft, loose structure and are located on a thin stalk. Initially, their size is about 2 mm, but gradually they are able to grow up to 1-2 cm. The color of papillomas also varies from white to dark brown. The favorite location is areas of the body with thin and delicate skin, folds and mucous membranes, i.e. these are the neck, eyelids, nasolabial fold, armpits, area under the mammary glands, genitals, groin area, perianal fold, around the anus, in the rectum, urethra, bladder, etc. Quite rarely, papillomas can form in the oral cavity and on the vocal cords. The growth can be either single or multiple. Basically, there are 5-20 papillomas in one area. Their prevalence largely depends on the immune system and its ability to resist the virus. The main feature of this type of neoplasm is the increased threat of transition to a malignant form. This is especially true for papillomas that form on the mucous membranes of the female genital organs. If left untreated, they cause cancer.
Stages of HPV development
After infection, the latent stage of the disease begins. The virus is already present in the body and is localized in epithelial cells. But so far there are no symptoms that would suggest a human papillomavirus infection. When the virus is dormant, laboratory tests may show a negative result. The latent stage lasts from a couple of weeks to tens of years.
Papillomavirus multiplies in epithelial cells. The number of affected cells increases, and the disease enters the subclinical stage. The first small tissue pathologies appear, not yet visible to the naked eye. The presence of papillomavirus can be determined in a laboratory. The affected epithelium becomes more sensitive to bacterial and chemical influences.
At the clinical stage, formations appear on the skin. To stop the spread of infection and prevent complications, you should consult a doctor in time.
Degrees of oncogenicity of strains
- Non-oncogenic. Provoke the development of benign tumors. The DNA of these viruses is not prone to mutations that cause cancer.
- Low degree of oncogenicity. They can lead to the formation of a cancerous tumor in combination with other risk factors (heredity, weak immunity, bad habits).
- High degree of oncogenicity. Directly provoke the growth of malignant tumors.
Laryngeal papillomatosis
You can also distinguish papillomatosis of the respiratory tract. With this disease, the tissue that lines the nasopharynx grows from the nose to the lungs. The larynx is also often affected. Respiratory tract papillomatosis is also a type of disease caused by the papilloma virus. In this case, formations are classified as benign. Local and ENT doctors cannot always identify this disease. More often they simply shrug their shoulders and prescribe rinses. In this regard, we recommend that you contact a private clinic.
Symptoms of virus infection
At the clinical stage, visible signs of infection appear. The symptom complex depends on the strain of the virus and the location of the affected area. Possible symptoms include:
- the appearance of warts and papillomas on various parts of the body;
- in women: a feeling of discomfort in the vagina, painful sexual intercourse, bleeding from the cervix outside the menstrual cycle;
- copious discharge with an uncharacteristic odor;
- the formation of benign tumors on the genitals, in the anus, in the urethra;
- associated diseases: inflammation of the cervix (cervicitis), bacterial vaginosis, dysplasia of the cervical epithelium.
Indirect symptoms of the disease are chronic fatigue, problems with concentration, physical weakness, and enlarged lymph nodes.
What are warts
The content of the article
Warts are rounded elevations of the skin in the form of a papilla or nodule with clear contours and a dense structure, arising due to the active growth of the upper layers of the epithelium. They can appear in absolutely every person, at any age and on any part of the skin, from the head to the soles of the feet. The most common “targets” are exposed areas of the body that are often subject to injury: arms, elbows, knees, head. Warts can reach sizes from 1 mm to 15 mm: this directly depends on its type and location of formation. They are located on the body singly or in small groups, and their distribution depends on the functioning of the immune system. There is also a rapid increase in the number of growths when the integrity of the wart is damaged. Sometimes several warts merge, forming a large tumor with a wide base in the form of a cone or hemisphere. When they appear, the growths are flesh-colored, and over time they can acquire a brown or even black tint, sometimes gray or yellowish. Their surface can be smooth, slightly rough or pimply. Outwardly, they resemble acne or calluses, so they are quite easy to confuse. A feature of warts is the high probability of spontaneous remission, especially if they arose in childhood.
Causes of HPV infection and development of the disease
Infection with papillomavirus can occur at the stage of birth of a child, while he is passing through the birth canal. The virus can be transmitted through contact and household contact in the first years of life. In adults, most cases of infection occur through sexual contact.
Risk factors include:
- Illness of one of the parents or family members.
- Frequent change of sexual partners, unprotected contacts.
- Gynecological manipulations: installation of a spiral, abortion.
- Long-term use of hormonal contraceptive pills.
- Hormonal imbalance caused by other reasons.
- Pregnancy and the postpartum period in women.
- Various diseases of the reproductive system.
- Hypothermia of the pelvic organs.
- Smoking, drinking alcohol and drugs.
- Chronic stress, diseases of the nervous system.
Infection with a virus does not always lead to the development of disease. Human papillomavirus infection can be suppressed by a strong human immune system. Therefore, the HPV treatment regimen sometimes includes taking immunomodulator pills.
Types and symptoms
Neoplasms caused by HPV infection can form on the skin and mucous membranes of various parts of the body, including the face, neck and décolleté. They can also form on the arms, legs, back, genitals, including the perineum, labia minora and majora, vulva, vagina, cervix, penis, especially along the coronary sulcus and frenulum. Damage to the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, tongue, nasopharynx, esophagus, bladder, conjunctiva of the eye, trachea and other internal organs is possible.
The human papillomavirus can lead to the appearance of neoplasms of various types. In general, they can be divided into 3 groups, although in all cases the cause of their appearance is the same - infection with the human papillomavirus.
- Papillomas are benign neoplasms of pink, white, pearl or light brown color, most often forming on the eyelids, lips, chest, armpits, and neck. They are located singly and usually do not tend to merge even with multiple lesions. Papillomas are usually round or lumpy, resemble the head of a cauliflower, and often have a stalk.
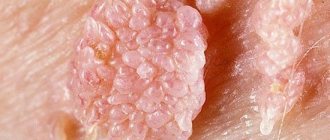
- Condylomas are benign formations of a dirty brown or paler color in the form of a cock's comb or many villi united by a common base. They are most often found in the genital area, anus and near the mouth. They tend to merge with each other and, as a result, cover large areas of the body. Their appearance is caused by infection with HPV types 6 and 11. There are pointed, flat and intraepithelial condylomas.
- Warts are uneven, light, benign tumor-like formations in the form of a plaque or small nodule on the surface of the skin of the hands, near the nails, feet, face, and front of the body. Warts can be similar to papillomas, but differ from them in that they have a wide base. They usually occur when infected with HPV types 1-5, 7-10, 12, 14, 15, 17, 19-24.
Such tumor-like formations can vary in size from a few millimeters to large growths covering large areas of the skin or mucous membranes.
Also, neoplasms may differ in appearance, which directly depends on the type of HPV that entered the body. The most common ones are:
- Vulgar or ordinary - protrusions of dense consistency with a diameter of more than 1 mm. They tend to merge and be located in groups.
- Plantar warts are protruding above the surface of the skin, often painful bumps with a shiny surface and rim. A characteristic feature is the absence of a skin pattern. They provoke the formation of HPV types 1, 2, 4.
- Flat papillomas are soft, smooth, flat, usually round growths that have a normal skin color or slightly yellowish, pinkish. They can provoke itching, so they are often injured, painful and inflamed. The reason for their formation is HPV strains 3 and 10.
- Filiform (acrochordas) are one of the most common papillomas, especially among elderly patients. Most often they are found on the face, around the eyes, in the groin, armpits, and neck. They are yellowish in color and tend to gradually enlarge, turning into bumps with a dense but elastic consistency.
- Genital warts in the perineal area, genitals.
Papillomas can be visible to the naked eye or located deep in the skin or mucous membranes. In the latter case, they are called endophytic and one of their manifestations is cervical dysplasia. Damage to the female internal genital organs by papillomatosis may be indicated by:
- itching, burning, weeping in the perineal area;
- profuse leucorrhoea;
- spotting, particularly after sexual intercourse;
- discomfort during intimacy.
Sometimes papillomatosis can provoke pain in the back and pelvis, weakness, swelling of the legs and causeless weight loss. Such signs are among the most alarming, as they may indicate the development of complications of HPV infection.
Diagnosis of infection at the Private Practice clinic
Several tests are required to make a diagnosis of HPV. Analyzes in our modern laboratory are done quickly using highly accurate methods. You will find out the result on the day of the smear test.
Polymerase chain reaction
PCR determines the presence or absence of viral DNA in a biomaterial. For analysis, a smear is taken from the mucous membranes and directly from the neoplasms themselves, papillomas, condylomas and erosions. The location of the smear depends on the location of the skin tumors. PCR identifies the types of viral strains in the body. The cost of analysis starts from 300 rubles.
Cytological analysis. PAP diagnostics
Papanicolaou test - examination of a smear under a microscope. A smear is taken from the affected area and applied in a thin layer to laboratory glass. The preparation is stained to improve the visibility of cells.
Examining the drug under a microscope, the diagnostician pays attention to the size and shape of the cells. Cytological examination reveals the presence of atypical cells, dysplasia, and malignant mutations. The detected virus is assigned a Pap class.
Colposcopy in women
Examination and examination of the cervix. The procedure is performed in a gynecological chair. For diagnosis, the cervix is stained with safe Lugol's solution. If it is affected by a virus, the area with infected cells is different in color. After a positive colposcopy, a biopsy is performed. It is necessary to clarify the degree of oncogenicity of the virus. A survey colposcopy in our clinic is included in the cost of an appointment with a gynecologist.
Biopsy
A biopsy is used to accurately determine the cellular composition of tissue. This is a reliable method for diagnosing cancer. A biopsy is prescribed when the doctor suspects that malignant degeneration of epithelial tissue has already begun. The cost of diagnostics starts from 1500 rubles.
Despite many similarities, neoplasms have an impressive list of differences
| Index | Warts | Papillomas |
| Form | Mostly round with clear contours | Mostly leaf-shaped or lobed with fuzzy, ragged contours, looks like cauliflower |
| Color | From flesh to light brown, sometimes pink, can even acquire a black tint due to the accumulation of dirt | White to dark brown |
| Localization | On open areas of the body: arms, legs, scalp, etc. | In folds and mucous membranes: armpits, genitals, neck, face, etc. |
| Structure | Dense | Soft |
| Fastening | Wide base | "Leg" |
| Size | Capable of shrinking and growing | Only increasing |
| Peculiarity | Capable of self-destruction without treatment | Do not disappear on their own, must be removed |
| Treatment | Removal, possibly drug treatment | Delete only |
| Tendency to malignancy | Almost never reborn | High probability of transition |
HPV: can it be treated or not?
It happens that papillomavirus is cleared from the body within two years after infection. But this is typical mainly for children and young people. However, since the prevalence of the virus is high, there is a risk of re-infection (relapse). Immunity after an illness is not formed for life, but for 1–3 years. It is this fact that underlies the statement that HPV cannot be cured.
In most cases, in adults, the papillomavirus does not leave the body on its own, but is integrated into the genome, provoking the development of tumors, including cancer. We advise you not to rely on luck, but to start treatment at the first symptoms of the disease. Human papillomavirus infection is successfully treated with modern medicine. New growths on the skin are removed using destructive methods.
Effective treatment is possible only according to the regimen proposed by the attending physician. When prescribing therapy, the dermatovenerologist takes into account the HPV strain, the degree of oncogenicity, and the patient’s immune system. Self-selection of medications will most likely not give the desired result. After therapy, you need to get tested for HPV every 2 years to avoid relapse of the disease.
Local immunomodulators for HPV and HSV
Among the “universal” drugs that can be prescribed for various viral infections - from common respiratory infections to herpes and human papillomavirus - are interferons. In particular, preparations of human recombinant interferon alpha-2b.
Interferon alpha-2b has antiviral, immunomodulatory and antiproliferative properties. It suppresses the replication of RNA and DNA viruses, enhances the activity of macrophages, and increases the cytotoxicity of lymphocytes to target cells. The use of drugs containing interferon alpha-2b is accompanied by an increase in the level of immunoglobulins type A and normalization of IgE [5]. However, these therapeutic effects are fully manifested when the drug is administered systemically.
when its high concentration in the blood is reached. It should be noted that quite powerful side effects can develop, including fever, loss of appetite, headaches, muscle pain, joint pain and many other adverse reactions.
Due to the specific safety profile, injectable interferon preparations are prescribed only in very serious cases, when the risk of side effects is justified - for example, in the treatment of hepatitis, a number of oncological diseases, etc. HSV and HPV infections do not apply to such situations and are not indications for systemic interferon administration. At the same time, the Russian Federation has registered a very impressive list of local forms of interferon alpha-2b, including ointments/creams for treating mucous membranes with genital herpes.
Theoretically, local interferon preparations should have all the advantages of injectable ones and not have their side effects, since local forms are either very slightly absorbed into the systemic circulation or do not penetrate into the blood at all. However, today there is no sufficiently reliable evidence of the effectiveness of interferons when applied topically. However, in domestic practice they are quite often prescribed as part of the complex treatment of recurrent genital herpetic infections.
Along with local forms containing only interferon alpha-2b, several combination drugs are also registered in the Russian Federation:
- Interferon alpha-2b + acyclovir + lidocaine, ointment. Indications: HSV.
- Interferon alpha-2b + taurine + benzocaine, vaginal and rectal suppositories, prescription. Indications: HSV, HPV. Taurine, according to the instructions, acts in combination as a reparative, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory component.
+
High safety profile.
!
The feasibility of using local forms of acyclovir for genital herpes is subject to serious doubts due to insufficient activity, which is confirmed in Western recommendations [3]. Interferon alpha-2b preparations, both mono- and combined, are available with or without a prescription, depending on the indications of the dispensing rules in the instructions for a particular drug. It is important to draw the visitor’s attention to the fact that the first-line treatment for HPV - oral forms of acyclovir and valacyclovir - must be prescribed by a doctor, so you should be advised to immediately consult a doctor.
Drug treatment of HPV at the Private Practice clinic
To treat human papillomavirus infection, doctors at our Private Practice clinic prescribe complex therapy. Medications reduce the concentration of the virus in tissues and strengthen the body’s immunity. Medicines eliminate the symptoms of the disease and improve a person’s well-being.
Attention! Self-medication can be dangerous to your health. Drugs for the treatment of HPV in women and men should be selected by a dermatovenerologist.
Antiviral tablets
Lavomax has a combined effect. This medicine suppresses the virus, stops its reproduction and stimulates the immune system. Take one tablet containing 125 grams of active ingredient, once a day, every other day. Do not reduce the interval between taking the medicine so as not to harm your health. The treatment course includes twenty tablets.
Isoprinosine is a universal drug. Prescribed to combat tumors on the skin, larynx, and genitals. This medicine suppresses the activity of the virus and stimulates the development of immunity. The dosage regimen is prescribed individually. The treatment regimen may include taking six to eight tablets per day. The course lasts from five days to several months.
Lykopid strengthens the body's defense against infections. Activates hereditary immunity, helps form an acquired immune response. Take one tablet (10 mg) once a day (half an hour before meals). The treatment course lasts from ten days.
Gepon is an immunomodulator. The drug activates the body's immune responses. Has anti-inflammatory and antiviral effect. Take one tablet (10 mg) per day. The duration of treatment depends on the individual response to the drug.
Unfortunately, all of the listed tablet drugs have very low effectiveness for the treatment of HPV. We have observed in many cases where patients undergoing treatment for human papillomavirus infection only with tablets experienced an increase in papillomas and condylomas while taking these medications.
Vaginal suppositories
Suppositories (candles) are prescribed by gynecologists at our clinic for the treatment of the vagina and cervix. Medicines for the treatment of human papillomavirus infection in women:
- Genferon. Double action drug. It contains interferon, which suppresses the development of the virus. Candles eliminate the unpleasant symptoms of the disease: pain and burning. For treatment, administer two suppositories per day: morning and evening. The treatment course lasts ten days;
- Viferon. Combined candles. Inhibits the reproduction of the virus, eliminates the symptoms of the disease, stimulates the immune system. Use suppositories twice a day, morning and evening, for five days.
Intramuscular injections
To treat papillomavirus, a dermatovenerologist may prescribe intramuscular injections. A popular injection drug is Ferrovir. 5 milliliters of medication should be administered twice a day. Duration of treatment course: two weeks.
Cycloferon is used for both intramuscular and intravenous administration using a special technique. Enhances the production of interferon in virus-affected and immune cells, which prevents its active reproduction.
Intravenous injections
The most effective drugs are administered intravenously in drip courses. Typically, polyoxidonium, panavir, and cycloferon are used, which suppress viral replication by activating the appropriate antiviral defense mechanisms.
The courses of treatment are long and combine well with general intravenous ozone therapy.
Cytostatic drugs
To combat skin defects, cytostatics and coagulants are used. These are topical medications. They do not suppress the development of the virus, but eliminate the external symptoms of infection. They are prescribed as an element of complex therapy. Medicinal substances are contained in a solution that is applied to the skin.
Podophyllin. It removes genital warts well. Burns through the cells of skin formations, causing necrosis. The solution is applied to the condyloma twice a day, with an interval of 12 hours. The duration of the treatment course is three days. The drug should not come into contact with healthy skin.
Solcoderm. Used to remove benign tumors. This is a powerful drug. We do not recommend using it without medical supervision. To remove papilloma, warts or condyloma, it is enough to apply it once. The skin lesion will become necrotic and darken, and then fall off.
Antibiotics
HPV is not treated with antibiotics. They act on bacteria, not viruses. Antibiotics are prescribed if diagnostic results reveal concomitant diseases (for example, bacterial vaginosis).
Topical antiviral drugs for the treatment of HPV (papillomavirus)
Some topical antiviral drugs active against papillomaviruses, in contrast to a number of drugs that help against the herpes virus, have a strong evidence base and are used throughout the world to treat manifestations of HPV - in particular, condylomas.
Imiquimod
An immune response modifier that does not have an antiviral effect. It exhibits activity due to the ability to induce the production of interferon-alpha and other cytokines. Indicated for the treatment of genital warts in the urogenital area [5].
Release: by prescription.
+
Solid evidence base. The drug definitely reduces the viral load. The use of imiquimod cream 5% 3 times a week at night for 16 weeks has been proven to be effective and safe for the treatment of condylomas. The relapse rate is estimated to be low [8]. Imiquimod is recommended for the treatment of genital warts by the authoritative American regulator FDA [8].
!
When applying imiquimod, itching and pain are observed in more than 10% of cases [5], which the buyer should be warned about.
Destructive and surgical treatment methods
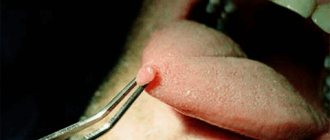
To quickly eliminate warts, condylomas, and papillomas, destructive techniques are used. Unlike conservative treatment, they do not allow you to wait until the tumor necrotizes and falls off on its own. In the office of a dermatovenerologist, skin defects can be eliminated in one visit. Removal of pathologies in hard-to-reach places is carried out only by surgical methods.
Electrocoagulation
During electrocoagulation, defects are removed with an electric knife. It generates electrical waves that cut off skin growths and destroy pathological tissues. Electric waves cauterize small vessels, there is no bleeding after surgery. Removing one defect takes from a few seconds to five minutes. Removal of small papillomas on the skin with an amount of more than 20 pcs. costs 200 rubles. for 1 unit. Large tumors are removed under local anesthesia at a cost of 1000–1500 rubles.
Cryodestruction
Liquid nitrogen is used for cryodestruction. The temperature of the substance is -190 degrees. When liquid nitrogen gets into the defects, necrosis occurs. Extremely low temperatures cause cell destruction, blockage of oxygen, and blockage of blood vessels. A thermal burn is formed and the tissues die. The operation is carried out under the supervision of an experienced doctor, who ensures that the substance does not come into contact with healthy skin. The effect of the procedure does not occur immediately, but after 5–10 days, when the necrotic papilloma tissue is completely rejected. The cost of cryodestruction usually ranges from 500 to 1500 rubles. per element.
Radio wave surgery
The operation uses a device that emits radio waves at high frequencies. Radio waves destroy skin defects using thermal energy. The device is operated by an experienced doctor. It directs radio waves, focusing the flow on the growth, avoiding touching healthy skin. This is the most effective and cost effective method for removing papillomavirus tumors on the skin and mucous membranes. The cost of the procedure is from 300 rubles. for the destruction of multiple small papillomas, up to 1500 -2000 rubles, for the removal of large tumors.
Laser defect removal
A directed beam of laser beams removes skin defects. Under the influence of the laser, the cells evaporate. A protective crust is formed at the site of the removed growth. Destruction of the defect takes from 5 seconds to two minutes. Healthy skin forms under the horny crust. About a week after the intervention, the crust disappears. The cost of laser removal of large papillomas is from 1000 rubles.
Removal of affected tissue
Invasive intervention techniques are used for deep tissue damage, when the process of malignant degeneration has already begun. Knife conization is used to remove pathological areas of the epithelium. When HPV is advanced and oncology begins to develop, they resort to removing the cervix with a scalpel.
Our doctors use an integrated approach to the treatment of HPV, which provides close to 100% effect from the therapy. It includes a combination of injectable, tableted immune, antiviral and topical medications. Removal of tumors is carried out using the chosen method against the background of drug treatment, which allows you to completely get rid of papillomas and condylomas and other manifestations of HPV, and prevent recurrence of the infection.
Papillomas on the body
Papillomas on the body
Human papillomavirus is an infectious disease that manifests itself externally in the formation of skin growths of various shapes, colors, sizes, and localizations on the body. The number of strains included in the group of HPV viruses includes about 100 units. The infection is highly contagious. Today, according to scientists, at least 70% of the planet’s population are carriers of one strain or another.
Causes of papillomas
Why do papillomas appear? The cause is the penetration of the virus into the body through damaged areas of the skin. However, in some infected people, HPV does not manifest itself in any way, remaining in a latent state for many years. In others, a strong immune system is capable of destroying pathological microorganisms within two years of infection.
However, spontaneous healing is the exception rather than the rule. A pathological formation on the skin is a sign of activation of the virus. This occurs when factors favorable to the active phase appear, many of which are practically inevitable in the life of a modern civilized person. This is why papillomas appear on the body:
- Decreased immunity.
- Chronic depression and stress.
- Alcoholism and smoking.
- Diseases of the digestive system.
- Long-term use of antibiotics, corticosteroids, oral contraceptives.
- Frequent colds and flu.
- Chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
- Taking cytostatics or immunosuppressants.
Interestingly, overweight and obese people have an increased risk of developing papillomas on the body due to sweating of the skin folds. In women, growths form under the breasts, in the abdomen and back, in men - in the groin area. Age does not matter: papilloma on the body can appear in a young, elderly person and even a child.
Routes of entry of the virus
The cause of papillomas is always associated with damage to the epithelial layer of the skin through which the infectious agent penetrates. Close contact with an HPV carrier or a person who already has tumors on their body is the main route of infection. During sexual intercourse, the use of a condom does not provide any guarantee, since papilloma, as a source of infection, can be located on any part of the body and mucous membrane.
The virus in the external environment, especially warm and humid, remains viable for a long time outside the human body. That is why infection often occurs in public places: baths, saunas, swimming pools, health centers. Household infection can occur in a cosmetology office, a beauty salon, even a hairdresser, if the master uses unsterile tools and objects.
Cases of transmission of the virus from mother to newborn are also not uncommon. If the mother is a carrier, the baby becomes infected with HPV during birth or subsequently when skin-to-skin contact becomes constant.
Treatment methods
Most HPV strains are not dangerous to human life and health, and the papillomas they provoke extremely rarely degenerate into cancerous tumors. However, such a risk, albeit minimal, still exists, especially if the neoplasm is constantly exposed to mechanical stress. Inflammatory reactions, the rapid spread of growths, and injury can give impetus to the transformation of “wart” cells into atypical ones.
Whatever the reasons for the appearance of papillomas on the body, treatment of pathological growths is mandatory: you should not ignore them in the hope of self-cleansing the skin. There is no universal and 100% effective medicine to combat HPV. Complex therapy is required, which is prescribed by a dermatologist after verification of the strain.
Complex treatment methods include:
- destruction of neoplasm;
- drug treatment aimed at activating the immune system;
- external antiviral treatment to reduce the external activity of HPV.
Diagnostics, which determines the type of virus, helps the doctor adjust treatment and make it more effective. The reason for failures in trying to cope with the problem on your own is precisely because a non-specialist will not be able to select the optimal drug and adequate treatment regimen.
Medications to combat a viral attack are divided into three types according to their effects:
- antiviral (Panavir, Izorpinazine, Viferon, Inosiplex);
- immunostimulating (Likopid, Immunomax);
- growth-destroying destructor agents (Supercleaner, Verrukacid, Dermavid).
The viral infection that causes the skin lesions does not respond to any one treatment method. Only an integrated approach guarantees a positive result.
Do I need to remove growths?
Papillomas on the body are considered by many to be an aesthetic problem. But the danger is that the virus is able to influence the genome of cells and provoke their uncontrolled division. This means that the skin growth is potentially dangerous, since it can become a source of formation of atypical cells.
Removal of growths is mandatory in the following cases:
- The papilloma is constantly injured (located on the neck, face, axillary and intimate areas), and experiences mechanical friction.
- The growths are growing rapidly.
- Located on the genitals.
- Changed color, increased in size, became painful, bleeding, with separated contents.
An important nuance: removal of formations does not mean a complete cure for HPV. The virus can be in an inactive state in the body, which can be achieved with timely antiviral treatment and maintained throughout life due to strong immunity.
Methods for removing skin lesions
The destruction of papillomas is carried out in clinics using special instruments and devices. Excision performed by a specialist is effective and safe, but each method has its own characteristics.
Surgical method. Traditional removal of papillomas with a scalpel is gradually being replaced by modern, less traumatic methods. Surgical removal is accompanied by a long healing period, the risk of complications and scarring.
Chemical destruction. Possible in relation to a single growth and several small neoplasms. The destruction of papilloma is carried out with a chemical preparation based on organic and inorganic acids. The method has a high rate of relapse: in half of the cases, papilloma reappears.
Cryodestruction, or freezing with liquid nitrogen. The neoplasm is exposed to ultra-low temperatures, which destroy living cells. The effectiveness of the method is the same as with chemical destruction: 50%.
Electrocoagulation. The method is painful and traumatic. Papilloma is removed using electric current. After the procedure, there is a long recovery period, and the risk of post-coagulation syndrome is high.
Laser removal. A modern, highly effective and most preferred method used for pathological neoplasms of any location. It has many advantages, ensures complete removal of the growth without damaging adjacent healthy tissue.
Advantages of the laser method
The use of a laser beam is indeed preferable if it is possible to choose a method for removing papillomas. The method is 100% effective, completely safe and virtually painless. However, that's not all. Other advantages of the method are also undoubted.
- Bloodless and atraumatic. The laser beam acts only on the affected tissue, while simultaneously sealing small blood vessels. After removal of the growth, no scars remain and healthy tissue is not injured.
- Elimination of the risk of skin infection due to the non-contact method and high beam temperature. The laser has disinfecting properties.
- No pain. The patient will only feel a slight burning sensation that lasts less than a second.
- The ability to use a laser on any part of the body and mucous membranes.
- Complete removal of papilloma from the skin with guaranteed absence of relapse.
- Fast and comfortable recovery period.
Laser removal of tumors is carried out quickly, within a few minutes. The technique has practically no restrictions and is used at any age, including children.
How is the procedure performed?
Removal is carried out in a sterile cosmetology office and does not require preparation or hospitalization. All additional conditions that will have to be met relate to increasing the effectiveness of the procedure.
The growths are removed during one session, which takes from 5 to 15 minutes. In exceptional cases, when the affected area is large, the doctor will prescribe 2-3 procedures to reduce discomfort.
Anesthesia is not performed: it is not necessary. If the growth is large, local anesthesia may be used at the patient's request.
The doctor covers the treated skin with a sterile adhesive plaster and gives recommendations for further body care.
Rehabilitation period
Laser removal involves a violation of the skin, and therefore requires a certain amount of time for the area of the body cleared of papilloma to heal. As a rule, complete tissue restoration occurs within a week, in exceptional cases it lasts up to ten days.
During the entire rehabilitation period, you need to follow certain rules that will ensure rapid regeneration of the skin and prevent secondary infection. Recommendations for the entire recovery period are as follows.
- Do not take long water treatments (swimming pool, bathhouse, sauna) and do not swim in open water. Instead of a bath, for hygienic purposes, limit yourself to a shower.
- Make sure that the treatment area does not overheat or overcool.
- Avoid exposure to direct sunlight; in extreme cases, use sunscreen with a high UV filter (at least 35). Do not sunbathe in a solarium.
- Avoid mechanical impact on the skin, as well as contact with strong chemicals.
- Do not try to speed up the natural healing process by tearing off dense epithelial crusts. As a result, scars or long-lasting red spots may form.
A correctly performed procedure does not cause any complications and does not require a follow-up visit to the doctor. You should come for a consultation only if unfavorable signs appear: thickening of the tissue at the site of the papilloma, redness, swelling, pain.
Remember that only professional removal of papilloma in a specialized clinic guarantees complete cleansing of the skin and reduces the risk of complications to zero.
Prevention
Unfortunately, there is no reliable protection against HPV. The high viability of the virus during direct contact makes infection, if not inevitable, then very likely.
You can prevent the appearance of papillomas on the human body if you reduce the likelihood of infection to a minimum. You need to follow the simplest preventive rules:
- Avoid public places with a dubious reputation. Do not visit baths, swimming pools and saunas where sanitary standards are not observed.
- Do not use personal hygiene items of a stranger.
- Do not use reusable samples of cosmetic products from distributors and cosmetic stores.
- Use the services of a reliable cosmetologist, massage therapist, or hairdresser, paying attention to the reputation of the specialist and the level of sanitation in the room where the procedure is performed.
- Do not try on shoes and clothes if there is damage to the skin on your body.
- Enter into intimate relationships deliberately, have one sexual partner.
- Strengthen the immune system: eat right, get enough exercise, stop smoking, don’t abuse alcohol.
It is important to undergo regular preventive medical examinations to identify hidden diseases. Consultation with an andrologist-urologist for men and a gynecologist for women once a year is mandatory. If you notice a growth on your body, be sure to consult a dermatologist. The earlier treatment for papilloma is started, the higher the likelihood and the easier the path to a successful outcome.
You can undergo a full course of treatment for HPV infection with removal of papillomas using a laser at the Galaktika aesthetic medicine clinic (Moscow).
Treatment of HPV with folk remedies
Is it possible to cure HPV only with folk remedies? From the point of view of official medicine, it is impossible. Traditional recipes help strengthen the immune system and eliminate external symptoms of the disease. But they do not suppress the development of the virus, like medications.
Recipes for clear skin
Do not apply active ingredients with bare hands. Use gloves and cotton swabs to treat the affected area.
- Lubricate the wart, papilloma, condyloma with 70% vinegar essence. Repeat the treatment two to three times a day. The tumor will become covered with a white crust and then fall off. Often there are complications in the form of deep non-healing ulcers.
- Treat skin defects with iodine solution. Apply iodine twice daily for two weeks. During this time, the defect should dry out and fall off.
- Grind the celandine and mix it with medical alcohol in a 2:1 ratio or buy a ready-made tincture at the pharmacy. Treat the defect three times a day. Celandine does not act immediately. The course of treatment can last up to three weeks.
- Essential oils of sea buckthorn, thuja, and tea tree help cleanse the skin. They soften tumor cells, which promotes its death. Mix one of the listed oils with castor oil 1:1. Treat defects twice a day. The duration of the course is not limited.
Using folk remedies only on the recommendation and under the supervision of a doctor, wait until the defect is completely necrotic. Do not tear off the tumor until it falls off on its own, otherwise you may provoke bleeding or introduce an infection into the wound. The active substance should burn the wart, papilloma, condyloma to the roots. Otherwise, the tumor may grow again in the same place.
Recipes to boost your immune system
Prepare or buy herbs: horsetail, nettle, plantain and lemon balm. If you harvest your own herbs, dry them and grind them into powder. For the recipe you will need a tablespoon of each herb. Mix the herbs in a saucepan and pour 200 ml of boiling water (about three glasses) over them. The decoction should be infused for three hours. Take the decoction for a week, 50 ml per day.
For the second recipe you will need two tablespoons of spruce or pine needles. Add 100 ml of water (about a glass and a quarter). Bring the mixture to a boil. When the water boils, reduce the heat. Keep the broth on low heat for half an hour. It needs to be insisted for the same amount of time. Drink two tablespoons of decoction three times a day. You should drink it for one to two weeks.
Attention! We do not recommend treatment with traditional methods without first consulting a doctor in order to avoid possible undesirable consequences.
How to treat HPV
How to treat the papilloma virus in women is a question often faced by patients who have received positive test results. As a rule, in the absence of cancer risk and clinical signs, HPV treatment is not required. For many people, the body clears the virus on its own.
When is HPV treatment needed:
- Detection of high-risk types (16, 18, etc.);
- Abnormal colposcopic picture;
- Unsatisfactory result of oncocytology.
☑ For information:
The doctor who treats HPV in women is a gynecologist. If questions or problems arose at a young age, under 16 years of age, then pediatric or adolescent gynecologists work with the patient.
Which doctor treats HPV in men? Typically, young people with this disease turn to a urologist or dermatovenerologist. This specialist will prescribe treatment for the infection and, if necessary, will be able to remove formations in the anogenital area.
HPV vaccine
At what age are girls vaccinated, can it be given to boys, as well as women after 30 years of age and older? Reviews from doctors about the effectiveness after infection, where to get vaccinated against papillomavirus in Moscow and is it given in clinics or antenatal clinics for free? We will try to answer these and other questions in more detail below.
As far as we know, cervical cancer is closely related to the human papillomavirus, which is present in almost 90% of the world's population. At the same time, articles have been periodically published on the Internet for several years now stating that the HPV vaccine, the Gardasil vaccine, leads to infertility. How correct is this information? Is it possible to get infertility due to the HPV vaccine?
The WHO Global Advisory Committee on Vaccine Safety regularly reviews the evidence on the safety of HPV vaccines. Clinical testing and monitoring of the drug has consistently demonstrated that it is safe and effective in preventing infections caused by human papillomavirus and also protects against the development of dysplastic phenomena and cervical cancer. There is no evidence that this vaccine causes infertility.
Many people are diagnosed with HPV at some point in their lives. Most infestations do not develop into cancer. But in a small number of women, HPV can become a chronic condition and lead to the development of invasive cervical cancer. There are certain negative factors in which HPV infection will lead to such consequences. These are, in particular, a certain type of HPV with a high cancer risk, the immune status of the woman herself, the presence of any concomitant sexually transmitted infection, the number of children born, as well as tobacco smoking.
The HPV vaccine is recommended for boys and girls aged 11-12 years. Women and men can be vaccinated with Gardasil up to age 26. People ages 27 to 45 who have not previously been vaccinated against HPV are now also eligible for Gardasil (Gardasil 9 in the US for women over 30).
According to the instructions, the vaccine protects against types of PVI that are associated with malignant diseases of the anogenital zone, and also prevents certain types of HPV that cause condylomas and papillomas in intimate places in both women and men.
Those wishing to get vaccinated against the human papillomavirus for free should know that this is not possible. Clinics and antenatal clinics in Moscow do not provide vaccinations against HPV and cancer free of charge - it is not included in the list of services under compulsory medical insurance and is not covered by government guarantees and subsidies.
PRICES FOR HPV VACCINATION
Vaccination against human papillomavirus, the price of which in commercial clinics starts from 11,000 and reaches 19,000 rubles per course injection. Having started the vaccination course, experts recommend completing it completely and completing it with the third injection 6 months after the first injection.
Girls and teenagers in Moscow can be vaccinated against papillomavirus in our clinic at the patient’s (or his legal representative’s) own request. However, doctors recommend undergoing a preliminary examination by a pediatric/adolescent gynecologist and passing HPV tests.
HPV treatment in Moscow
Doctors who treat HPV, including women and teenage girls, effectively and with good results, according to patient reviews, work at the Gynecology Clinic on Kutuzovsky! Effective regimens, courses and drugs that help get rid of papillomavirus types 6, 11, 16, 18, 31, 33, 45, 51, 52, 56 and other types of high and low oncogenic risk.
Reasonable prices, good results and 20 years of experience in gynecological treatment! HPV is not scary if precious time is not lost - make an appointment with a gynecologist right now! Phone number of the clinic in Moscow ☎
HPV prevention methods
For the development of the disease, it is enough for several small viruses to enter the body. Prevention methods will help prevent infection or recurrence of the disease:
- Use barrier contraception during sexual intercourse.
- Avoid public swimming pools, baths, saunas.
- Strengthen the body's immune system.
- Avoid stress and nervous overload.
- Dress warmly and avoid hypothermia.
We advise women to undergo a gynecological examination and tests for infections at least once a year. This will help maintain the health of the reproductive system.
What is HPV
The human papillomavirus affects only humans, and its main mode of transmission is sexual. Therefore, HPV is most common among sexually active people. This explains the fact that most often infection occurs at a young age at the beginning of sexual activity and at its peak, i.e. 15-25 years. Moreover, several strains (types) of HPV can be present in the human body at the same time, provoking the appearance of different types of tumor-like formations on the skin and mucous membranes.
The disease caused by HPV is called papillomatosis.
Infection with the virus occurs when it comes into contact with the skin or mucous membranes with particles of exfoliated skin or mucous membrane of an infected person. They attach to the membranes of immature epithelial cells, from where they penetrate into the cytoplasm of the cell, and subsequently into the nucleus. It is the cell nucleus that contains DNA, which is damaged by HPV. As a result, when the affected cell divides, the consequence will be the formation of not healthy new cells, but those that already have altered genetic information, which leads to failures in the mechanism of their reproduction and differentiation. This causes the appearance of tumors on the skin and mucous membranes.
HPV infection can lead not only to the formation of papillomas, but also warts, as well as flat and genital warts. However, it can also be asymptomatic. In this case, the patient will not show external signs of human papillomavirus infection, but he will act as a carrier and can infect others through unprotected sexual intercourse or at home.
Thus, HPV infection does not always lead to the formation of papillomas. This depends on the strength of the person’s immunity, but more often the first small papillomas appear 1-6 months after infection.
The human papillomavirus is intracellular. Therefore, with sufficient strength of the immune system, the body successfully suppresses its activity and does not allow it to provoke cell proliferation. But when the immune system is weakened as a result of certain factors, the body’s defenses fall, the virus becomes more active, which leads to the formation of papillomas.
All strains or types of HPV can be divided into 4 groups:
- non-oncogenic – strains 1-5, 63;
- low oncogenic risk – strains 6, 11, 40, 42-44, 54, 61, 70, 72, 81;
- medium oncogenic risk – strains 26, 31, 33, 35, 51-53, 58, 66;
- high oncogenic risk - strains 16, 18, 39, 45, 56, 59, 68, 73, 82 (types 16 and 18 are considered the most dangerous).
HPV strains of high oncogenic risk have special genes in their DNA that are responsible for the synthesis of specific oncoproteins (E6 and E7). Therefore, when it is integrated into the DNA of a human cell, its anticancer protection decreases. Oncoproteins destabilize the genome of skin cells, provoke their active reproduction and suppress the ability to differentiate. Therefore, this is fraught with a high risk of developing cancer when infected with strains of the human papillomavirus of high oncogenic risk.
The magnitude of the danger that papillomas pose directly depends on the type of HPV. Infection with strains with a high oncogenic risk is dangerous due to the development of:
- cervical cancer;
- malignant tumors of the anus, vulva, penis;
- oropharyngeal cancer, etc.
70% of cases of cervical cancer are caused by infection with types 16 and 18 of HPV.
But even when infected with strains of low oncogenic risk and the formation of papillomas, they should be treated carefully. Convex neoplasms are often injured by items of clothing, bleed and tend to become inflamed. At the same time, perhaps the greatest discomfort is caused by formations on the genital organs, which cause severe discomfort and complicate the conduct of an intimate life. In such cases, a secondary infection may occur, which can cause the development of purulent-septic complications. In addition, papillomas can form on the mucous membranes of almost any internal organ, which leads to disruption of their functioning. Thus, papillomatosis of the upper respiratory tract often occurs, which causes difficulty breathing.
Possible complications
Human papillomavirus infection can cause severe or mild complications. The most severe possible complication is the development of malignant tumors. Oncogenic strains of the virus cause cellular mutations that contribute to the transformation of benign tumors into malignant ones.
Cervical dysplasia precedes the development of cancer. Papillomas on the larynx grow and cause attacks of suffocation. HPV increases the likelihood of cancer of the stomach, intestines, and respiratory system.
Benign formations on the skin seem less dangerous than cancer. But we do not recommend delaying their treatment. Condylomas, papillomas and warts can accidentally come off. In their place, a bleeding wound forms, into which pathogenic microorganisms easily penetrate. Large defects can leave unsightly scars if the removal is not carried out in the office of a dermatovenerologist.
Intraurethral condylomas may be accompanied by inflammation and bleeding from the urethra.
Why are neoplasms dangerous?
The main danger that warts and papillomas pose is the threat of degeneration into a malignant form. The degree of their danger depends on the type of papillomavirus:
- high (oncogenic) – 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 52, 58, 59, 68;
- low (non-oncogenic) – 6, 11, 26, 41, 42, 50, 61, 73, 82, etc.;
- absent – 1, 2, 3, 4, 5.
There is a high probability of malignancy if warts and papillomas are constantly injured (rubbed against clothing, touched by something, etc.). In this case, infection with harmful bacteria may occur. To prevent the degeneration of a benign tumor into a malignant one, it is necessary to regularly visit a dermatologist and not hesitate to detect suspicious symptoms. Particularly dangerous are genital warts that affect the internal genital organs of a woman, since they can cause serious diseases: pseudo-erosion of the cervix, ectopia of the columnar epithelium, and cervical cancer. In addition, their presence is manifested by a number of unpleasant symptoms: burning and itching in the vagina, unpleasant odor, pain in the lower abdomen, pain and discharge of ichor during sexual intercourse. In men, the lack of treatment for papillomas leads to decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, and infertility. It can also provoke dangerous diseases: adenocarcinoma, anal cancer, diseases of the penis, oral cavity or larynx.
Many varieties are not dangerous, but ignoring the treatment of warts and papillomas will provoke an increase in their number. And the constant attack of the body by viruses will ultimately lead to a deterioration in the overall health of a person.
When to see a doctor
There is no universal way to get rid of the papilloma virus in the body. The treatment regimen is prescribed by a dermatovenerologist after reviewing the test results and the patient’s medical history. When should you visit a dermatovenerologist:
- Since childhood, your skin has had many warts, papillomas, and condylomas;
- skin defects have begun to appear en masse recently;
- you notice strange discharge from the genitals;
- you began to feel itching and burning in the perineum;
- unpleasant sensations appeared during sexual intercourse;
- you started self-treatment for HPV, but did not get results;
- you are planning to have a child (then both partners should be checked);
- you have not been tested for sexually transmitted infections for more than a year.
We recommend getting tested regularly for HPV, even if you have no symptoms and are not planning a pregnancy. Sometimes the latent stage of the disease can last for years. The virus may be present in the body, but not manifest itself in any way. Early diagnosis will help avoid the development of complications.
Establishing diagnosis
Before treating human papillomavirus in men, the pathology must be confirmed by laboratory tests. After the examination, the doctor may prescribe the following tests:
- urethroscopy;
- urethral smear;
- PCR;
- biopsy of growths.
Since condylomas have an oncological risk, you should not delay your visit to the doctor. Timely treatment allows you to stop the disease and minimize its consequences.
Advantages of the Private Practice Clinic
- Certification in all areas of work.
- The consultation is conducted by experienced dermatovenerologists and gynecologists.
- The latest methods of treating diseases.
- Possibility of removing papillomas and condylomas using all currently known modern methods without pain and serious scars.
- Results of express tests on the day of treatment.
- Individual approach to each patient.
- Polite and friendly staff.
- You can undergo diagnosis and treatment anonymously.
- Convenient location of the clinic in the center of Moscow and Southern Administrative District.
- Parking for visitors to the medical center.