Skin structure
The existence of dermatology as a specialty already implies that the skin is not just a membrane covering the human body. It is replete with a variety of cells, each of which performs a specific function. Next, we will look at the structure of the skin layer by layer.
5 interesting facts about skin
- Skin weight averages 4-5 kg in a person of average build (5-6% of body weight).
- The air in the subway consists of 15% human skin.
- Approximately 1 gram of skin is shed per day from the entire surface of the body.
- There are on average about 150 pain points and 200 sweat glands per 1 cm² of skin.
- With vasodilation, the skin can deposit up to 1 liter of blood.
What layers does the skin consist of?
The skin has three layers: epidermis, dermis and subcutaneous fat. The first two are of the greatest interest, since they determine all the main functions of the skin.
Epidermis
The epidermis is the surface layer that is in direct contact with the environment. Epidermal cells are called keratinocytes. In the structure of this layer, in turn, there are also layers - there are five of them:
- The basal layer is the deepest. It is represented by only one row of stem cells, the main function of which is division. Some of these cells subsequently acquire specific properties, that is, they undergo differentiation and rise to the upper layers. The basal layer also contains melanocytes, which we will discuss later.
- The stratum spinosum consists of several rows of polygonal cells. Spicular cells are called spinous cells because they have many contacts with other cells in the form of peculiar “spines”.
- The granular layer is also represented by several layers of keratinocytes. The cells of this layer accumulate special protein granules, which is why they acquire a granular appearance. Gradually they lose the features of a living cell, and their membrane thickens several times.
- The stratum lucidum is present only in the epidermis of the palmar surfaces of the hands and the plantar surfaces of the feet. That is, in those places where the skin is thickest and densest. Keratinocytes of the stratum pellucida lack almost all organelles typical of living cells. Between them there are special lipids, as if gluing the cells together.
- The stratum corneum is the final stage of cell development. The cells of the stratum corneum are dead, they do not contain cellular organelles and are entirely filled with keratin. These cells are located very tightly to each other, and all the gaps are filled with adhesive lipid masses.
Figure 1. Structure of human skin.
Image: blueringmedia / Depositphotos The entire transformation path from stem cell to horn cell is called keratinization and takes about 40 days. Over time, the stratum corneum is shed into the external environment, allowing younger cells to take the place of older ones. These processes occur continuously throughout a person’s life.
Melanocytes determine the color of our skin
Melanocytes are large cells of the basal layer of the epidermis that contain the pigment melanin. The amount of the latter determines the color of our skin: the more melanin, the darker the skin. The skin's ability to tan is also based on the work of melanocytes. The fact is that the main function of these cells is protection from ultraviolet radiation, which is absorbed by melanin. The more sunlight, the more melanin is needed, so melanocytes increase its synthesis and the skin becomes darker.
Dermis
The dermis, or skin itself, is the framework of the skin, its foundation. It consists predominantly of connective tissue and contains a large number of structural elements and a wide variety of cells. The dermis also has layers, but there are only two of them: papillary and reticular.
The papillary layer received this name due to the fact that it adheres unevenly to the epidermis, forming outgrowths, or papillae. This structural feature increases the contact area of these two layers of skin, ensuring their strong fixation relative to each other. The papillary layer contains a large number of blood and lymph vessels, nerve endings and cells of the immune system.
Epidermal ridges, or where fingerprints come from
The papillae that form in the dermis slightly raise the epidermis above it.
Therefore, in those places where they are well defined and the epidermis is thick (that is, on the palms and soles of the feet), we can see the pattern formed by the papillae. This pattern is unique for each person, which is what the police use to find criminals. The reticular layer of the dermis is represented by loose fibrous connective tissue containing a large number of collagen and elastic fibers. There are also many vessels here. This layer determines the ability of the skin to stretch and then immediately return to its original shape.
Subcutaneous fat
The last layer is represented by dense fibrous tissue, between the fibers of which there are accumulations of fat cells. The latter provide the skin with some shock-absorbing properties and are also a reserve source of energy for the entire body.
Leather derivatives
The skin is inextricably linked with formations such as hair, nails, sweat glands and sebaceous glands. We will not dwell in detail on their structure, since this is a private topic that requires separate consideration. However, it is important to understand that some skin functions are realized through the sweat and sebaceous glands, and many skin pathologies in one way or another affect changes in nails and hair. Thus, there is a close anatomical and functional connection between the skin and its derivatives, which determines their joint damage in dermatological diseases.
Fingerprinting. Fingerprints are unique, each person has their own pattern. Photo: Alexandre17 / Depositphotos
Subcutaneous fat
Subcutaneous fat, or hypodermis, is the lowest layer of skin, located under the dermis. It consists of fat lobules separated from each other by connective tissue septa containing collagen and penetrated by large vessels. The main cells of fat lobules are adipocytes, the number of which varies in different areas of the body. Currently, PFA is considered not only as an energy depot, but also as an endocrine organ, the adipocytes of which are involved in the production of a number of hormones (leptin, adiponectin, resistin), cytokines and mediators that affect metabolism, insulin sensitivity, reproductive and immune functional activity. systems
What are the main functions of the skin?
There are 9 main functions of the skin, which include:
- Protective.
- Immune.
- Receptor.
- Thermoregulatory.
- Excretory.
- Secretory.
- Respiratory.
- Resorption.
Few organs can “boast” of such diversity. Below we will explain in more detail what each of these functions is.
Protective function
One of the main functions of the skin. The organ provides protection from many damaging factors:
- Mechanical damage (pressure, bruises, sprains) due to the thickness of the stratum corneum and strong connective tissue fibers. Fat fiber plays the role of a mechanical buffer.
- Impact of microorganisms due to the secretion of sweat and sebaceous glands, which form a water-lipid mantle on the surface of the skin, insurmountable for many microbes. The skin is also home to a large number of microorganisms that are symbiont for humans, which protect the skin from pathogenic bacteria.
- Exposure to ultraviolet and long-wave ionizing radiation (radiation) due to melanocytes and skin thickness, respectively.
- The body is protected from exposure to chemicals by a protein barrier located in the stratum corneum of the epidermis.
Immune function
The superficial layers of the skin (epidermis and upper dermis) contain a large number of immune cells that ensure the recognition and destruction of pathogens that have crossed the epidermis. In addition, keratinocytes themselves produce biologically active substances that attract immune cells from the blood into the skin and modulate the process of inflammation in it.
Receptor function of the skin
As we have already said, the papillary layer of the dermis contains many nerve endings, but what is striking is not so much their quantity as their “quality.” The nerve endings here are amazingly diverse: each type of sensitivity is responsible for certain nerve structures that have a bizarre shape and complex structure. Cold, heat, pain, vibration, gross tactile sensitivity, fine tactile sensitivity - for each stimulus there is its own receptor. The sensitivity of the receptors is so high that we can feel temperature fluctuations of 1 degree, the slightest touch and a light breath of wind.
Thermoregulatory function of the skin
This function is provided by a dense and branched vascular network of the dermis and sweat glands. When we are hot, the blood vessels dilate, which turns the skin into a kind of radiator that emits heat. At the same time, the sweat glands more actively secrete sweat, which, evaporating, cools the surface of the body. If we are cold, the opposite happens: the blood vessels constrict, and the sweat glands work at “minimum” power, which allows us to retain heat.
Metabolic function of the skin
The metabolic function combines the secretory, excretory, resorption and respiratory functions. Secretory involves the secretion of secretions by the sweat and sebaceous glands, forming a water-fat emulsion. The excretory system is closely related to the secretory system: among the secretion products of the sweat and sebaceous glands there are many organic and inorganic substances. Products of mineral metabolism, hormones, carbohydrates, enzymes are among them.
The resorption function of the skin is determined by its ability to absorb various substances. This is important in medicine: you can use drugs in the form of ointments, emulsions and solutions, which do not enter the systemic bloodstream and have virtually no side effects.
Also, vitamin D₃ is synthesized in the skin under the influence of sunlight, which is important in calcium metabolism and modulation of immunity.
Skin can breathe
Indeed, the skin is capable of absorbing oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide, just like the lungs! This ability is enhanced in hot conditions, during heavy physical labor and with the development of inflammatory processes in the skin. Of course, this function in humans is much less pronounced than in some newts, but it still exists.
Symptoms of skin disease
There are a huge number of skin diseases. Their symptoms are often very similar, which makes diagnosis very difficult even for dermatologists. Next, we will look at some common complaints of patients with skin diseases.
Figure 2. Common skin diseases. Image: IgdeevaAlena / Depositphotos
Rashes
Skin rashes are the most common symptom of dermatological diseases. They can be localized on any part of the skin and mucous membranes, be painful or painless, multiple or single. The following morphological varieties of loose elements are distinguished:
- A spot is a change in skin color in a limited area. The size and color of the spots vary widely. Coffee-colored spots are characteristic, for example, of pityriasis versicolor. Pink spots appear with atopic dermatitis, toxicoderma and many other diseases.
- Nodule, node and tubercle. These elements are distinguished by elevation above a healthy area of skin, firm to the touch and sometimes painful. The color can vary: bluish-red, purple, brown, pink. The size can also range from a few millimeters to several centimeters. Nodules appear with psoriasis, eczema, and lichen planus. Nodes and tubercles are characteristic of such dangerous diseases as syphilis, tuberculosis and leprosy.
- Blister. Everyone has seen blisters at least once in childhood after a nettle burn. These are pale pink or white elements, slightly rising above the skin, which quickly and disappear without a trace. Blisters occur with urticaria, pemphigoid, and dermatitis herpetiformis.
- Blister, bladder and pustule (abscess) are eruptive elements that contain liquid. It may appear as clear serous fluid (vesicle and blister) or yellow-green pus (pustule). Bubbles appear with eczema, herpes, and various dermatitis. Bubbles, larger formations, occur with pemphigus, streptococcal impetigo, and athlete's foot. Pustules form most often with staphylococcal skin infections.
The primary rash elements listed above can leave behind erosions, ulcers, depigmentation (changes in skin color), scars and atrophic areas of the skin. Often the rash is also accompanied by peeling, which is most characteristic of psoriasis and eczema.
Itching
One of the most unpleasant symptoms of skin diseases. Sometimes the severity of the itching is so great that it prevents a person from falling asleep. Itching makes you think only about it, which does not allow you to concentrate on work and everyday activities. This symptom is characteristic of many skin diseases, but it reaches its greatest severity with scabies, psoriasis and atopic dermatitis.
Important!
Watch out for scabies!
The occurrence of itching at night is a symptom of scabies. Scabies is a highly contagious disease that instantly spreads to close relatives of the patient. It is important to consult a dermatologist and follow his instructions for treatment and sanitization of the home to prevent infection of relatives.
Other symptoms
Like other infectious diseases, skin infections can be accompanied by general symptoms such as weakness and fever. Typically, these symptoms appear with extensive lesions of the skin or severe infection. For example, furunculosis, hidradenitis and carbuncle can manifest themselves this way.
Moles and freckles
39. Most moles are genetically predetermined even before we are born.
40. People with more moles on their body live longer and look younger
those who have fewer moles.
41. Almost every person has at least one mole.
42. Moles can appear anywhere
, including the genitals, scalp and tongue.
43. Freckles most often appear in people with light skin color.
44. Freckles fade in winter
, since melanin is not produced in large quantities during the winter months.
45. Freckles can be red, yellow, light brown and dark brown.
46. Unlike moles, freckles do not appear at birth.
, they appear after a person has been exposed to sunlight.
© Brainsil1
Prevention of skin diseases
Prevention methods are determined by the cause of the disease. Thus, measures aimed at preventing diseases of an infectious nature are mainly of a sanitary and hygienic nature. However, in dermatology there are many diseases of an allergic and autoimmune nature. In this case, prevention is determined by minimizing stress influences and contacts with a potential allergen.
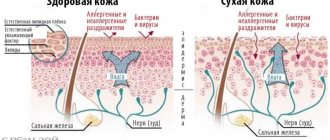
Figure 3. Features of oily and dry skin. Image: edesignua/Depositphotos
Skin hygiene
We are taught to observe the rules of hygiene from childhood. Nevertheless, there are points that are not obvious at first glance, and those that many people forget about:
- You cannot use other people's hygiene products. When we use another person’s comb, towel, washcloths and slippers, the microbiota from his skin easily transfers to ours. Fungal diseases are often transmitted this way. In this case, it is inappropriate to rely on confidence in the health of a loved one’s skin, since many diseases can simply go unnoticed.
- You should not touch your face with your hands, especially when outside the home. An incredible number of microorganisms pass through a person’s hands, but the skin of the palms is well adapted to such an “onslaught,” which cannot be said about the face. Various types of pyoderma, such as boils or folliculitis, often appear precisely because the infection spreads from the hands to the skin of the face. In addition, sweat from the palms negatively affects the protective function of the facial skin, making life easier for pathogenic microbes.
- It is not recommended to squeeze out any pustules yourself. It is more correct to wait for their independent reverse development, which usually occurs within 3-4 days, or contact a dermatologist in the case of multiple and/or persistent processes. It is difficult to follow this advice, but if you are going to get rid of pustules, then only by first treating your hands with an antiseptic, and then the skin around the defect.
Important!
If the abscess is large, swollen and has a purple-bluish color, then doing anything with it yourself is strictly prohibited. This is what boils usually look like, and treatment in this case can only be carried out by a doctor. This is especially true for boils localized on the face, which threaten serious complications if you try to remove them yourself.
Skin care
Some people tend to have dry facial skin, while others, on the contrary, tend to have excessive oiliness. The first condition leads to constant peeling, the second provokes acne. In any case, the protective function of the skin is somewhat impaired, which increases the risk of dermatological diseases.
For dry skin, it is recommended to regularly use moisturizing creams and vegetable oils, and for oily skin, alcohol solutions of salicylic acid or camphor, and calendula tincture. You can also avoid dry skin by washing your face with soft boiled water every day.
You need to take care of your facial skin daily. Photo: phakimata/Depositphotos
Stress and skin diseases
Stress factors play an important role in the pathogenesis of some dermatological diseases. In particular, we are talking about psoriasis and eczema. There are often situations when people holding responsible, leadership positions, businessmen, turn to a dermatologist with manifestations of psoriasis. In such cases, it is recommended to visit a psychotherapist from time to time, engage in sports and meditative practices. This has a positive effect on the psyche and reduces the frequency of exacerbations of stress-related diseases.
10 products for healthy and beautiful skin:
- Seafood.
- Avocado.
- Nuts.
- Tomatoes.
- Greenery.
- Cottage cheese.
- Flax seeds.
- Bitter chocolate.
- Liver.
- Cereals.
The products from the presented list are rich in omega-3 unsaturated fatty acids, vitamins E, B₃ and C, magnesium, phosphorus, calcium and numerous antioxidant substances. These substances help maintain healthy skin and slow down the aging process. It is also important not to forget to drink 1.5-2 liters of clean water per day to maintain skin turgor and normalize metabolic processes in it.