Laryngeal papilloma. Symptoms
Symptomatically, laryngeal papillomatosis can be represented by hoarseness, chronic cough, difficulty breathing, difficulty swallowing, recurring respiratory infections, and growth retardation in children. The presence of certain symptoms depends on the location of the papillomas. In children, the symptoms are more pronounced, since they have a significantly faster growth of papillomas, unlike adults. This can lead to situations in which emergency intervention is required for life-saving reasons, despite the histologically benign course of the disease. The prognosis is more favorable in terms of remission if the disease manifests itself in adulthood. The exception is the presence of HPV type 11 and the duration of the disease for more than 10 years.
Complications of tonsil cysts
A cyst on the tonsil is a chronic source of infection that can behave in an unknown way, causing various complications. The neoplasm in the pharynx is constantly rubbed with food, which leads to the formation of a chronic inflammatory process. The longer the patient does not seek medical help, the longer the infection progresses; along with the bloodstream, infectious pathogens are carried to all cells and organs, disrupting their normal functioning.
A long-term infectious process is accompanied by general intoxication of the body. Toxins produced during the activity of pathogenic microorganisms disrupt the functioning of the liver and kidneys, provoke the development of chronic fatigue syndrome, reduce immunity and make a person vulnerable to even the most harmless infections.
Only an otolaryngologist can choose the treatment for a cyst on the tonsils, based on the results of pharyngoscopy. If the doctor suspects the development of a malignant process, a consultation with an oncologist will be required. Other studies may also be prescribed: rhinoscopy, audiometry, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging of the brain, otoscopy. In advanced cases, the tumor can grow into nearby tissues, including brain structures.
Causes of laryngeal papilloma. Who is at risk?
The etiological factor is human papillomavirus (HPV), in most cases types 6 and 11. The latter leads to a more severe course of the disease. Less commonly, laryngeal papillomatosis can be caused by HPV types 16 and 18, which are viruses with a high risk of developing malignant neoplasms. However, the presence of HPV in the human respiratory tract does not always lead to papillomatosis. Determining factors can be immunodeficiency states and chronic infections. Concomitant infection with the herpes simplex virus and the Epstein-Barr virus contribute to a more aggressive course of the disease.
Causes of appearance and code according to ICD-10
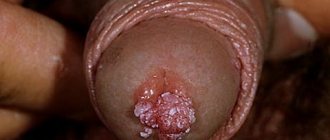
Papilloma of the palatine tonsil, according to the international classification, belongs to benign formations. The tumor occurs when infected with HPV. The specific localization of the growth is due to the huge concentration of the virus in the epithelial cells of the body.
Infection occurs through household contact and sexual contact.
Swimming pools, baths, and saunas are considered breeding grounds for infection. Warts appear in the oral cavity after kissing or oral sex.
The virus enters through damaged oral mucosa. The pathogen multiplies in the epithelium.
The papillomavirus remains dormant for a long time. Under the influence of provoking factors (against the background of weakened immunity, stress, hormonal imbalances, infectious pathology), HPV activation occurs. Doctors note a direct connection between the appearance of papillomavirus in people who often suffer from sore throats.
Inflammatory foci on deformed tonsils are a favorable habitat for the virus.
In the first stages, the disease is asymptomatic. The person is unaware of the presence of pathology. Over time, papilloma on the tonsil causes unpleasant discomfort. The disease is accompanied by a constant sensation of the presence of a foreign body in the throat, cough, and change in voice. The larger the size of the formation, the brighter the clinical picture of the disease.
If a growth is found in the mouth, the entire body should be carefully examined. Additional growths can be localized on any area of the skin.
Laser removal of papilloma in the throat. Progress in medicine helps.
The main thing is to keep up with it and take advantage of all the new opportunities. In the treatment of papillomatosis, these include the use of CO2 laser, narrow-spectrum endoscopy and certain antiviral drugs. But there is one prerequisite to achieve the best result - everything must be performed by a highly qualified surgeon with extensive experience in treating laryngeal papillomatosis. This is extremely important to understand.
Papillomatosis is characterized by the formation of exophytic growths that affect the mucous membrane of various parts of the larynx and underlying parts of the respiratory tract.
More than 10 years without recurrence of papillomatosis.
All patients treated by Professor Roberto Pujedo have not experienced a relapse of the disease for more than ten years .
“A comprehensive approach is a key success factor. Starting with detailed diagnostics using cutting-edge technologies, ending with careful monitoring in the postoperative period.”
Along with the expertly performed complete removal of papillomas, Professor Roberto Pujedo carries out targeted administration of antiviral drugs into the mucous membrane of the affected areas of the larynx.
Reliable source:
Enhanced contact endoscopy (ECE) in head and neck surgery
Many patients talk about dozens of surgeries in their history and endless relapses. It seems that it is impossible to cope with this disease. Each time the voice becomes worse, numerous scars form in the larynx.
Now this is history!
Treatment of tonsil cysts
Treatment of cysts can be either conservative or surgical. Often, specialists first prescribe effective drug therapy to relieve inflammation and prepare the patient for surgery. Conservative treatment of a cyst will not reduce its size, but can stop the active growth of the tumor and prevent complications. Treatment tactics should be selected by a competent specialist based on medical history, diagnosis and professional examination.
Conservative therapy for tonsil cysts includes the following measures and procedures:
- gargling with herbal decoctions, antiseptic solutions that disinfect tissues and have an anti-edematous and anti-inflammatory effect;
- physiotherapy: ultraviolet irradiation, massage, ultrasound - physiotherapeutic treatment methods are used to increase blood supply to tissues in the area where the tumor is located, to ensure lymph outflow;
- pumping out pus using hardware methods, which makes it possible to stop the development of the infectious process and the spread of infection to surrounding tissues;
- injection rinsing of the tonsils with anti-inflammatory drugs and antiseptics to cleanse plaque and purulent contents;
- strengthening the immune system with multivitamin complexes and immunostimulants;
- giving up bad habits that contribute to traumatization of the tonsils and the preservation of the chronic inflammatory process.
Some specialists practice opening the cyst and pumping out its contents. But, as a rule, the therapeutic effect does not last long and the tumor is filled with fluid again. Therefore, if the cyst has not disappeared after several weeks of active medical therapy, it is better to remove it surgically.
Possible methods of treating laryngeal papillomas.
Careful removal of papillomatous growths under a microscope and using a CO2 laser is fundamental. However, removal must be carried out exclusively within the mucous membrane, where the formations are located. Moreover, the normal mucosa must be preserved. The surgeon must be experienced and thoroughly understand the mechanism of papillomas formation. Otherwise, gross surgical intervention leads to loss of voice, severe scarring, and stenosis.
Studies have shown that intraepithelial administration of antiviral drugs can reduce the number of operations to remove papillomas, leading to partial regression of the growth of formations. Also, local administration of an antiviral drug avoids systemic toxicity.
The mechanism of action of interferons in laryngeal papillomatosis is unknown, however, they are often used as an additional treatment. Interferons are naturally produced by white blood cells in response to various stimuli, including viral infection. They bind to specific cell membrane receptors and change metabolism, providing antiviral, antiproliferative and immunomodulatory effects. The clinical effectiveness of interferons in the treatment of laryngeal papillomatosis is ambiguous and controversial. The main limitation for their use are side effects when administered intravenously: increased levels of transaminases in the blood, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia. Patients may experience weakness, nausea, fever, arthralgia, and headache.
Indol-3-carbinol can be extracted from cruciferous plants (broccoli, cabbage). In vitro studies have shown promising results on the growth of papillomas by influencing estrogen metabolism. When administered orally to a small number of pediatric patients, no adverse effects were observed. However, the clinical effectiveness of this drug remains in doubt.
Measles, mumps, rubella (MMR) vaccine . A prospective randomized controlled trial showed that intraepithelial administration of MMR vaccine could prolong the period of remission after surgical treatment.
HspE7. A new vaccine targeting oncogenic HPV types has also been used to successfully control relapses of laryngeal papillomatosis.
The presence of GERD was associated with an increased likelihood of complications. The irritating effect on the mucous membrane can act as a trigger for the proliferation and spread of papillomatous growths. Studies have shown that the use of drugs to treat GERD promotes better control of laryngeal papillomatosis and prolongs remission.
According to a Cochrane review, photodynamic therapy has not been shown to be effective in the treatment of laryngeal papillomatosis.
Watch the video BEFORE/AFTER surgery to remove laryngeal papillomatosis
Relapse-free postoperative follow-up for a year. Endoscopy in NBI mode. Credit: Professor Roberto Pujedo.
Look at the photos BEFORE/AFTER the operation by Prof. Roberto Pugedu
Photos “before” and “after” surgery to remove laryngeal papillomatosis. Credit: Professor Roberto Pujedo.
Move the slider to see the difference.
How to distinguish it from other formations and is it dangerous?
Need advice from an experienced doctor?
Get a doctor's consultation online. Ask your question right now.
Ask a free question
Papillomas on the tonsils should be distinguished from tonsillitis, tuberculosis, and oral cancer. In acute tonsillitis, the tonsils look inflamed and deformed. Pus plugs are yellow and white in color. When pressed with a spoon, they separate from the mucous membrane of the tonsils and may crumble. Papilloma is flesh-colored, soft in consistency with a rough surface. Tonsillitis is accompanied by a sore throat, high body temperature, weakness, and bad breath.
A malignant formation differs from warts in the presence of ulcerations and a hard consistency.
Atypical tissue grows tightly together with the surrounding dermis. Cancer is accompanied by general clinical symptoms of a malignant process: a sharp decrease in body weight, constant fatigue, pale skin, poor appetite, unmotivated weakness.