- Gallery
- Reviews
- Articles
- Licenses
- Vacancies
- Insurance partners
- Partners
- Controlling organizations
- Schedule for receiving citizens for personal requests
- Online consultation with a doctor
- Documentation
It is well known that a baby’s skin is soft and smooth, pleasant to the touch. Sometimes they say about it “velvet”, “silky”, it serves as a standard for the tenderness of the skin. Therefore, the appearance of any formations on the skin always causes concern among caring parents. The most common neoplasms in children are considered to be molluscum contagiosum and viral papilloma (HPV).
What is papillomavirus, how can a child become infected with it?
Papillomas, warts and condylomas are neoplasms of the skin and mucous membranes that occur when infected with the human papillomavirus (HPV). The virus can infect the outer layer of skin and the smooth, moist mucous membranes of the mouth, rectum, anus, and genitals in men and women. There are more than 100 different types of virus. Many of these types of virus cause warts and papillomas that appear on the arms and legs. HPV types 6 and 11 cause genital warts, and HPV types 16 and 18 can lead to cervical cancer and, less commonly, cancer of the vagina, penis, scrotum or rectum.
In newborns and young children, papillomatosis (or HPV) manifests as skin warts, genital warts, and juvenile recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. Adolescent girls may present with squamous intraepithelial lesions of the cervix.
In children aged 5 to 15 years, HPV types 1,2 and 3 predominate in skin warts, and in adolescents, HPV type 4 predominates. Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis is caused by HPV types 13, 39, 40 and 56.
Papilloma in children, causes, treatment and removal.
Papilloma in children. Basic principles of treatment.
Neoplasms on the skin or mucous membrane of the mouth, nose, pharynx, etc., which are viral in nature, are one of the most common skin diseases. They can appear in the form of moles, warts, papillomas. People of different ages suffer from this disease, among them, of course, children. With their appearance on the body, we can say that papillomavirus infection in children has been activated. The causative agents of the infection are human papillomaviruses, of which about 100 species are known today.
The main factors leading to the spread of the virus are decreased immunity and hormonal imbalances in the body. There are many ways of infection:
- Papilloma in children (especially the larynx) can occur after birth due to infection during childbirth if the mother had vaginal condylomas.
- Upon contact with a carrier of the virus, especially if there are microtraumas, cracks, or abrasions on the body.
- Autoinfection. If a child bites nails, hangnails, or tears off existing warts, more and more surfaces of the skin become infected.
In adults, infection also occurs through sexual contact.
So what does papilloma look like in children? How to treat them? Where are they most likely to be located? And, in general, how does papillomavirus infection occur in children?
Manifestation of papilloma in children.
Papilloma is a growth or tumor on the skin or mucous membrane, most often mushroom-shaped, on a thin stalk. Color varies from white to dark brown. The incubation period is on average 2-3 months, the virus is most active after 6 months of infection.
The forms of manifestation of papilloma are very diverse:
- warts (skin papillomas), most often observed on the hands;
- simple or vulgar papillomas. Most often they appear on the backs of the hands and knees in children. They look like hard bumps with a keratinized surface (from 1 to 10 mm);
- plantar papillomas. Quite painful formations that make walking difficult. Not to be confused with calluses, which have a smooth surface;
- flat papillomas. Smooth lumps of natural color can cause a lot of trouble for the child, in the form of redness, itching, inflammation and pain;
- A rare disease is epidermodysplasia verruciformis. Red-brown papillomas on the hands and feet, high risk of degeneration into malignant tumors (30%);
- juvenile laryngeal papillomatosis. Babies born from an infected mother are at risk. The growth of papillomas on the vocal cords can lead to speech impairment and even create breathing problems. It should be especially noted that the disease is quite rare.
Treatment of papillomas
Based on the fact that there is no single standard for the treatment of papillomas, parents must figure out for themselves what to do if papilloma is discovered in children. Of course, you need to watch her carefully. Is it growing, is there inflammation? How many tumors appeared? An appointment and consultation with a doctor will help dispel many doubts and fears.
Doctors, examining the tissue of papillomas, will be able to establish the correct diagnosis. Treatment of papillomas is complex. In the first place, of course, is the correction of immunity. As soon as the body’s natural defenses begin to work, it will become easier to fight the virus. There are many cases, especially in children, when papillomas disappeared spontaneously.
When fighting the human papillomavirus, a variety of antiviral drugs are used, and surgical removal of formations is also proposed.
Nowadays, there are a wide variety of surgical methods, where the removal of papillomas occurs quickly and painlessly. This can be cryodestruction (exposure to low temperatures), laser and/or diathermocoagulation (cauterization with electric
How is the virus transmitted to children?
HPV is spread through skin-to-skin or blood contact:
- A pregnant mother can pass the infection to her baby through the bloodstream before birth or through the vaginal canal during childbirth. This is called perinatal transmission.
- Children with warts on their hands can transmit the virus through skin-to-skin contact. The spread of the virus to the genital area occurs when touching it with your hands. This route of infection is called autoinoculation.
- A caregiver with warts can transmit the virus through skin contact with the child's hands or genitals. This is called heteroinoculation.
- HPV can be transmitted from a person's skin to the child's genital area through sexual contact - in the event of violence.
- Rarely, HPV can be transmitted through contact with inanimate objects or surfaces. If an adult who has warts uses a towel and then a child uses the same towel, the virus can be passed on to the child. This is called fomite transmission.
HPV is transmitted through skin-to-skin contact, even if there are no warts or papillomas on the skin. After infection, the virus remains in the body. A person may be a carrier
Molluscum contagiosum or infectious molluscum
Molluscum contagiosum or infectious molluscum is a skin tumor of a viral nature, benign in nature. She's contagious. The main routes of transmission from a sick baby to a healthy one are through direct close contact. The second option for infection may be the use of shared hygiene items.
Another great place to catch this virus is swimming pools - humid air, skin contact and a large number of people contribute to this.
Not everyone is equally susceptible to the virus - usually children from the group of frequently ill people, allergy sufferers, and digestive problems are more likely to suffer. Children with skin problems are more likely to get sick when there are areas of damage - abrasions, scratches, dermatitis - then it is easier for the virus to penetrate the thickness of the skin.
Rashes can appear on any part of the body - face, arms, neck, legs, shoulders, abdomen and even genitals - they cannot only appear on the palms and soles, which is why they differ significantly from papillomas. Usually they are not complicated - but if the child picks or combs them, microbes can appear.
Of course, in the case of a typical course and manifestation in several children, there is no doubt, but sometimes the mollusk is difficult to recognize. Therefore, let a pediatric dermatologist make an accurate diagnosis and treatment.
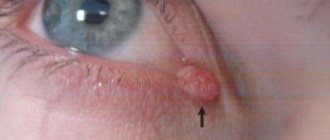
Treatment of this viral disease consists of removing the tumors by a pediatric dermatologist (or a pediatric ophthalmologist, if the molluscum is on the eyelid) using anesthetics. Further, it is possible to prescribe antiviral agents and certain treatment of skin areas where there were previously nodules, to exclude the possible reappearance of tumors. The main preventive measures are timely diagnosis of this disease and its treatment; therefore, it is necessary to conduct preventive examinations.
Preventing HPV infection
Like many other viruses, HPV becomes active and causes disease in people with weakened immune systems. That is why children are susceptible to the development of papillomatosis. In some people, HPV can clear up without treatment if the body mounts an immune response to the virus.
It is especially important to vaccinate girls, because... For them, HPV infection is fraught with the development of cancer. The best and most modern means of protecting against papillomavirus is vaccination. Girls should receive the vaccine (Gardasil, Cervarix) before they become sexually active
The most common vaccine is called Gardasil, which is currently used to immunize school-aged girls - nine years of age and older. The vaccine provides immunity against two strains of HPV that cause cervical cancer and two strains associated with genital warts. Vaccination is carried out with three injections of the vaccine over six months. It is recommended to get vaccinated before becoming sexually active. The vaccine is effective in protecting against HPV types 6, 11, 16 and 18. Vaccination is also possible after the onset of sexual activity before the age of 26 years. For boys, vaccination protects against colorectal cancer caused by HPV.
Rarely, the virus causes recurrent respiratory papillomatosis, in which viral warts grow in the larynx, causing a benign tumor of the larynx in children. These tumors are treatable, but, unfortunately, are completely incurable. In large numbers, neoplasms caused by HPV can cause airway obstruction.
Still have questions?
Get an online consultation from leading pediatricians in St. Petersburg!
A professional and experienced pediatrician will answer your questions.
Medical care for a child without leaving home at a convenient time.
sign up for a consultation
A Skype consultation lasts 45 minutes.
Soft fibroma
A benign skin tumor that usually appears in people over 35 years of age. It is a soft neoplasm of the skin, most often on a stalk of flesh-colored or light brown color, gradually taking the shape of a hanging pouch from 2 to 5 mm in diameter. Favorite localizations are the inguinal and cervical folds, armpits and occasionally the face. In the initial growth phase, it is indistinguishable from the so-called viral filamentous warts. The reason for contacting a doctor is a cosmetic defect or the patient’s oncological suspicion. Fibroids are not dangerous to health, however, injury caused by friction of fibroids on clothing or adjacent areas of the skin can cause inflammation, bleeding and lead to the development of an infectious process. You can avoid the danger by removing the fibroid. The most effective treatment methods are laser removal, electrocoagulation, and cryosurgery. When removing a small formation (up to 05 mm), anesthesia is not required.
Diagnosis of HPV
The pediatrician will definitely pay special attention to diagnosing HPV and genital warts in a child. If you see that your child has a wart, immediately visit a doctor and start treatment. There is no need to hope that “it will go away on its own” and “no big deal.” Just the opposite: scary, threatening cancer or big problems in the future. You especially need to monitor the presence of papillomas and warts if you have a daughter.
Any child with genital warts needs a full medical examination, which includes the following:
- Examination of the child's anus and genital area.
- Questioning parents about whether they have HPV infection, genital or common warts.
- Questioning the mother for an abnormal Pap smear result that may indicate HPV infection.
- Interview parents for any signs of possible child sexual activity and possible child abuse.
In mature girls, a colposcopy and Pap smear may be done to look for signs of problems that could lead to cervical cancer. Early detection of the problem allows for treatment.
Immunological testing for HPV types is possible to identify high-risk strains that can cause cancer.
Genital condylomas and simple condylomas in children
Condylomas are marked by rapid reproduction and association into large clusters, covered with a crust on top.
When we talk about condylomas, we mean genital warts.
Because flat and intraepithelial ones are much less common.
Warts, papillomas and condylomas appear from HPV.
The presence of warts and papillomas is considered practically harmless.
The presence of genital warts in a child requires parental supervision and constant medical supervision, because they tend to malignize.
Children are often infected with HPV vertically – in utero.
The incubation period is long, the first condylomas appear in two to five year old children.
Bathing together with parents or using hygiene items, household items and clothing can also cause infection.
Young children, in general, should be supervised by their parents and regularly examine their skin for the presence of condylomas.
Young children may not complain of skin itching or burning, and condylomas may appear asymptomatically.
This is especially true if one or both parents have HPV.
HPV in children
The formation of neoplasms - warts, papillomas and condylomas - is the most important symptom of papillomavirus.
Moreover, for both adults and children.
For preventive purposes, it is necessary to limit the child’s contact with sick adults and other children.
Because HPV is a very contagious disease.
Removing tumors is a half-hearted treatment.
It is necessary to prevent their recurrence.
It is necessary to use medications that destroy latent papillomaviruses when they are activated.
Children are treated with effective and safe alpha-2b interferon.
Its feasibility in general treatment has been proven.
But complex treatment, using local forms of interferon-containing drugs, is still better.
To increase the effectiveness of treatment and as a preventive measure for recurrent HPV.
The most oncogenic are considered to be genital warts that arise from HPV types six, eleven, sixteen and eighteen.
Incubation time ranges from one month to a year, but the average is about three months.
Children can become infected with HPV not only vertically, but also through household contact.
The contagiousness of HPV is quite high.
New growths need to be closely monitored:
- change in size and color, a reason to immediately contact a specialist;
- before prescribing treatment, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive study of the nature of the tumor;
- the result of such a study will be the prescription of complex therapy.
Initially, immunomodulatory therapy is used to raise the immune status.
Sometimes, neoplasms self-destruct without surgical or therapeutic intervention.
Advanced cases lead to the use of all kinds of ointments and other medications, as well as to surgical or chemical destruction of tumors.
What is the difference between condylomas and papillomas?
When HPV gets on the skin, warts most often appear.
And when genital warts appear on the mucous membranes of the penis, vagina, uterus, and perianal area.
If the presence of condylomas is prolonged, then this is a precancerous condition.
When soft new growths on the skin are pink or flesh-colored, then these are papillomas.
Condylomas are called genital warts because they have a characteristic shape.
The presence of condylomas and papillomas is always uncomfortable.
They are located in places of increased trauma.
Prone to the formation of cracks with subsequent bleeding.