Oral papillomas are benign neoplasms in the oral cavity that grow from epithelial cells. Papillomas are discovered during a dental examination and look like separate growing seals on a small stalk, they are painless and have a white or pale pink color.
This type of neoplasm in the oral cavity is diagnosed most often. About 60% of patients are women aged forty years, about 20% are teenagers of any gender. Often, adults experience the appearance of individual papillomas, while children may experience so-called papillomatosis (multiple papillomas). In half of the cases, papillomas are localized on the mucous membrane of the tongue.
High oncogenic HPV type
The above-described viruses of types 16 and 18 are at high risk of cancerous degeneration of the epithelium.
Also included in this type are strains 70, 68, 64, 59, 50, 39, 33, 31.
The second group is of average oncogenic risk.
It is possessed by strains type 58, 56, 53, 52, 45, 35, 30.
Strains 73, 72, 61, 51, 44 to 40, 34, 32, 13, 11, 6, 3 are considered low risk.
Low-risk viruses often cause only the formation of benign papillomas or condylomas.
Such formations in men more often affect the skin of the penis (leaves of the foreskin, coronary groove, less often found inside the urethra on the mucous membrane).
In women, the location of these growths is the labia minora and majora, and the perianal region.
Risk areas include skin or mucous membranes injured during sexual intercourse and areas of epithelial maceration.
How to find out about HPV infection if there are no symptoms?
There is a study that finds the papilloma virus causing cervical cancer. This examination is recommended for all women over 30 years of age. Thanks to the analysis, the papilloma virus can be detected before it causes pathological changes in the cervix.
Do not confuse an HPV test with a Pap test. During a Pap test, a smear taken from the cervix is examined at the cellular level. If oncogenic HPV is suspected, both tests should be performed.
Why is papillomavirus dangerous?
The potential threat in viruses of this type is primarily the risk of growth of tumors of the urinary tract and genitals.
Slightly less commonly, viruses are responsible for tumor growth in the oropharynx area.
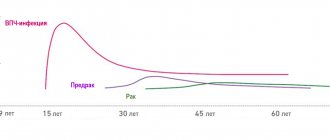
The long-term existence of the virus in epithelial cells sooner or later changes their structure and ability to divide uncontrolledly.
Any episode of infection should be diagnosed, monitored and, if possible, treated.
Errors in immune defense can occur at any stage of life.
In addition to external provoking factors, they can be caused by natural hormonal fluctuations.
Therefore, today there is an urgent question about creating artificial protection against papillomaviruses by vaccinating high-risk groups or children.
How to cure papillomavirus
Unfortunately, it is impossible to remove the papilloma virus itself from the body. But it is possible to cure diseases caused by this virus - genital warts, changes in the cervix, cervical cancer.
There are several ways to treat genital warts, all of which are painless and effective. If genital warts are left untreated, they can grow and multiply over time.
All women who are or have been sexually active should have regular Pap tests. Thanks to this precise diagnosis, changes in the cervix can be detected at the cellular level even at very early stages. Therefore, the problem will be solved before cervical cancer appears. Timely diagnosis is a prerequisite for effective treatment.
Oncogenic HPV: how is it transmitted?
From 60 to 70% of cases or carriers are infected through sexual contact.
All types of coitus play a role, since the virus can be on the mucous membrane of the mouth, vagina or rectum.
At the same time, anal contact reduces local resistance in a man, increasing the risk of infection.
The entry points for an infectious agent are often sites of injury or maceration of the mucous membrane or skin.
Peak infection occurs between 20 and 30 years of age.
Men and women are infected equally often.
Infection through household contact occurs much less frequently.
Here, wound surfaces of the skin or mucous membranes (extensive wounds, scratches, burns) also come first.
A vertical route of infection is also possible.
The fetus can receive the virus from the mother in utero.
Or when passing through the birth canal in cases where there is a clinically developed viral process in the mother.
Classification of oral papillomas
Based on the number and concentration of neoplasms, oral papilloma is differentiated from papillomatosis – a massive accumulation of neoplasms in one place.
According to their origin, papillomas are divided into the following types:
- Traumatic (reactive) papilloma. May appear after traumatic effects of a mechanical, chemical or temperature nature. A distinctive and characteristic feature of reactive type oral papilloma is that their growth stops immediately after the irritant that caused them is eliminated.
- True (neoplastic) papilloma. This type of papilloma begins to develop after the mechanism of cell division, growth, and differentiation is disrupted. In most cases, this type of papillomas appears in the distal part of the cheek, in the area located behind the molars and in the area of the pterygomandibular fold.
- Viral papilloma of the oral cavity. May appear after the patient has been infected with the human papillomavirus. This type of infection occurs through direct contact with a carrier of the virus. When the integrity of the oral mucosa is compromised (for example, due to microtrauma), a path for infection appears.
Genital herpes
Genital herpes is one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases. It is believed that every fifth adult is infected with the herpes simplex virus. However, the disease is often asymptomatic, so patients continue to infect their partners.
When the immune system is weakened, most patients develop painful blisters around the genital organs (penis, anus, buttocks, vulva). The herpes rash can also spread to the thighs and thighs.
How long will the window period last?
The window period usually lasts 6-8 weeks, but if the analysis was performed using 4th generation tests, this period can be reduced to 4-6 weeks. After the pre-test consultation, the patient is offered an HIV test, which involves detecting HIV antibodies and is called screening or initial testing.
If the initial screening is negative, it means the person is not infected. If the answer is positive, the study should be continued with confirmation methods (immunoblotting method, polymerization chain reaction method).
Diagnosis of children under one year of age born to HIV-positive mothers is carried out only by the polymerization chain reaction method.
What is human immunodeficiency virus? Why is it impossible to protect against it by vaccination?
HIV is a retrovirus and is characterized by strong mutagenicity—it changes its appearance very quickly. Therefore, it is very difficult to create a vaccine for it. In this case, the genotype of the virus changes from one person to another.
Members of the retrovirus family are characterized by a long incubation period, which means that a virus that enters the body lives there for years, multiplies, damages the body, but does not manifest itself clinically. A patient can be a carrier of the virus for 5-7 years, at the same time be a source of infection, and not know about it until a direct test for HIV infection is carried out.
Possible treatment for genital herpes
Modern medicine, unfortunately, cannot cure a patient with genital herpes, but it is possible to fight the virus. Antiviral treatment reduces the severity of the disease, reduces symptoms, and reduces the risk of transmission of the virus. Treatment is especially effective within the first 72 hours after symptoms appear. Suppressive therapy is usually used, in which the patient receives a small dose of an antiviral drug daily. As a result, relapses disappear. This treatment is recommended if a person has 6 or more relapses per year or has a weakened immune system (for example, infected with the human immunodeficiency virus). The risk of infecting a partner during suppressive therapy is reduced.
The correct use of latex condoms can reduce the risk of transmission of the virus, but such prevention does not eliminate it completely - the likelihood of infection remains.
Pregnancy and genital herpes
If the first outbreak of genital herpes occurs closer to the time of birth, the risk of infection in the newborn increases. Therefore, childbirth should be carried out taking into account safety measures.
Because herpes in newborns is a very serious condition, a pregnant woman should tell her doctor in advance. If the disease recurs several times during pregnancy, it is recommended to treat with acyclovir, and if childbirth coincides with a period of exacerbation, a caesarean section is prescribed.
How safe is HIV/AIDS?
AIDS is not transmitted through household items. It is dangerous to use only the patient's razor, scissors and other objects that come into contact with blood.
There is no risk of sharing a bathroom, bed linen, towels, dishes, kissing, hugging, studying or working in the same room with the patient. Doctors are often asked, is HIV/AIDS transmitted through mosquito and dog bites? No, HIV does not spread this way. There are only three routes of transmission: sexual contact, blood and vertical transmission.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
Symptoms
Symptoms characteristic of genital herpes appear suddenly. A rash appears in the area where the virus entered the body. Fluid-filled blisters become enlarged and painful. The affected area is very itchy. Then the bubbles burst, and the skin in this place becomes covered with a crust.
Often the disease is asymptomatic or with such a minor rash that the patient may not even notice it.
The rash appears a few weeks after infection and lasts about 2-3 weeks. Sometimes the inguinal lymph nodes become swollen and painful. Other symptoms may include joint pain, fever, headache, and sometimes even painful urination. Nausea, dizziness, and difficulty urinating are rare and indicate damage to the nervous system.
The rash may disappear, but this is not the end of the disease. After the initial outbreak, the virus enters a latent phase and continues to live in the spinal cord. The disease usually appears several times a year, although the symptoms are most acute during the first outbreak, then they become increasingly rare and less noticeable. The frequency of relapses varies from person to person. It depends on the type of virus and the person's immune system.
Where did AIDS come from?
AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome) was first described in the United States in 1981, when several cases of the rare diseases Pneumocystis pneumonia and Kaposi's sarcoma were diagnosed.
These diseases were previously found only in patients with immune system disorders, so doctors suspected immunodeficiency. They soon became convinced that they were dealing with a new disease, which in 1982 the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention officially registered as a new disease - acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS).
In 1983, the virus that causes the disease, called human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), was discovered.
During this time, many theories appeared about the origin and spread of the disease. Africa is the birthplace of AIDS. where the simian immunodeficiency virus, which causes the same disease as the human immunodeficiency virus, was discovered. As a result of mutation, the virus changed its appearance and became dangerous to humans.
The virus spread in Africa and spread to other countries where the blood of the African population was used for medical purposes. People infected with HIV-infected blood spread the virus through needles and syringes and sexual contact.
How does the infection manifest?
Symptoms of infection are determined by the type of virus and the type of illness it causes.
HPV can be located either outside the cell chromosomes, the so-called. benign form of the disease, and integrated into DNA, the malignant form.
The following development options are typical for human papillomavirus infection:
- latent course - without cell changes, without symptoms;
- the formation of warts, condylomas, papillomas, when the virus affects cells, provoking their growth;
- neoplastic changes (dysplasia) – changes in cellular structure under the influence of a virus;
- carcinoma formation - the appearance of numerous atypical cells characteristic of a cancerous tumor.
An important feature of HPV infection is its ability to self-heal.
In 90% of all episodes of infection, the virus is destroyed by the body within two years.
Clinical manifestations of infection are quite characteristic.
Thus, vulgar warts look like grayish-brown warty nodules, which are usually located on the fingers and the back of the hands.
Flat warts affect the face and hands and usually appear during adolescence.
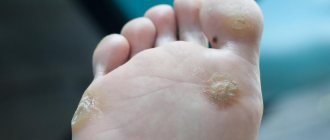
Plantar warts appear in areas where the skin rubs against shoes and are characteristic thickenings that are painful when pressed.
Genital warts are shaped like a rooster's comb or a cauliflower stalk, have a thin stalk and a wider head.
In women, such formations are usually located at the entrance to the vagina, in the area of the labia and anus. Multiple flat papules, as a manifestation of infection caused by HPV of low oncogenic risk, are called epidermodysplasia verruciformis.
With laryngeal papillomatosis, typical growths are detected in the larynx.
Dome-shaped and flat, smooth, velvety papules on the genitals are a characteristic manifestation of bowenoid papulosis.
The cause of which is predominantly HPV-16 (a representative of the high oncogenic risk group).
Malignancy of such formations is observed in approximately 3% of episodes.
Dysplasia (neoplasia) of the cervix is a process of atypical changes in epithelial cells in the zone of transition of squamous epithelium to columnar epithelium.
This condition is considered precancerous.
Depending on the severity of cell changes, different degrees of dysplasia and cancer itself (squamous cell carcinoma) are distinguished.
Promote the development of dysplasia:
- multiple pregnancies and births before the age of 20;
- early onset of sexual activity;
- promiscuity;
- chronic inflammation of the uterine cervix;
- damage by genital warts;
- smoking, etc.