Human papillomavirus (HPV, HPV) belongs to the group of papillomaviruses and is one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases. This infection was already known in ancient Greece; Hippocrates himself studied one of the types of HPV - condylomas and gave them the name “genital warts”.
HPV is a virus that is transmitted only from person to person. Currently, about 600 types of HPV are known, some varieties can cause the growth of benign or malignant tumors.
How does the virus enter the body?
The content of the article
The main route of infection is sexual. Moreover, regardless of the form of sexual contact - anal, vaginal or oral. A condom reduces the risk of infection, but it is not a panacea.
With a much lower probability, HPV can enter the body through contact and household contact - through touching, hugging, personal hygiene products, manicure tools, etc. Most often, danger awaits in public places - bathhouse, swimming pool, sauna, bus, etc.
The presence of damage and microcracks on the skin favors infection. A vertical route of infection is also possible - from mother to child. The virus can be transmitted to an infant during fetal development or when passing through the birth canal.
HPV in women
HPV in women manifests itself not only as papillomas on the body, but also causes the development of cervical erosion , precancerous conditions, and cervical cancer . Condyloma in women is quite difficult to detect; it can exist in a woman’s body for a long time without any symptoms, and is discovered purely by chance at an appointment with a gynecologist. That’s why it’s so important to visit a specialist regularly, once every six months!
Symptoms of condyloma include:
- genital warts, which can appear on the genitals (condyloma on the labia, vaginal condyloma, cervical condyloma), in the oral cavity, on the skin of the anus (anal condyloma);
- disturbance in the maturation of epithelial cells (there are 3 stages of the process, the third stage is precancer);
- the development of a malignant formation from the epithelium lining the cervix.
Reasons for the appearance of formations
The presence of HPV in the body does not guarantee the development of its clinical manifestations - the appearance of growths. It may remain in standby mode for a long time until favorable conditions occur. Activation of the virus is associated primarily with weakened immunity. This condition is provoked by both environmental conditions and the presence of various diseases.
Human papillomavirus
Lifestyle reasons:
- stress and nervous tension;
- disrupted daily routine;
- unbalanced and unhealthy diet;
- presence of bad habits – smoking, drinking alcohol and drugs;
- avitaminosis;
- long-term use of cytostatics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics;
- unfavorable environmental conditions;
- excessive mental and physical stress;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- hypothermia, overheating.
Causes associated with the presence of diseases:
- acute respiratory infections, acute respiratory viral infections, influenza;
- HIV AIDS;
- herpes type 2;
- oncology;
- endocrine system disorders;
- anorexia;
- chronic anemia, etc.
Weak immune resistance can also be inherited.
HPV. Symptoms
The papilloma virus is constantly present in a person’s blood, but is activated only when immunity decreases. With weakened immunity, HPV begins to accumulate on the skin or mucous membrane and leads to the appearance of tumors.
At a young age, HPV manifests itself as warts that are located on the fingers, elbows, and knees. Then a papilloma grows on a person’s skin (a soft-to-the-touch round formation on a stalk, with the help of which the papilloma is attached to the skin). Most often, papillomas are located on the skin of the face, neck, armpits, and papillomas are also found on the labia.
One of the most common manifestations of HPV is condyloma (uneven to the touch, soft, attached to the body with a stalk or a wide base, grows quite quickly, sometimes in a few hours).
Thus, warts, papillomas and condylomas are different signs of the same papillomavirus infection. Papilloma is a benign formation that can “show off” on a person’s face and body, not too pleasing to him aesthetically, but without causing much harm. Unlike papilloma formations, human condyloma tends to inflame and damage the skin and mucous membranes.
Condylomas
Condylomas are formations on the skin of the genitals, on the pubis, inner thighs, in the urethra, around the anus (anal condylomas) and inside the anus, having a lobed structure, flesh-pink in color, pedunculated or with a wide base, from a few millimeters to ten centimeters (eg, giant Buschke-Levenshtein condylomas).
Condylomas usually come in 2 types:
- condyloma lata, wide neoplasms with a wide base with which they attach to the skin, these neoplasms are considered a sign of secondary syphilis;
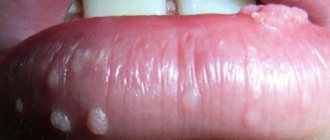
- genital warts, similar to soft pinkish bubbles with a thin stalk.
Condylomas acuminata
Genital warts are small flesh-colored formations that choose the genitals and anus as their location. In appearance, condylomas are sometimes confused with pearlescent papules, which are not a disease. Unlike pearlescent papules, genital warts are soft to the touch, attached to a thin stalk, and can be of different sizes.
Pointed papillomas are transmitted only sexually (through all types of sexual contact), therefore they belong to the group of sexually transmitted infections.
Causes of condyloma
There are various reasons for the appearance of condyloma, among which there are several main ones:
- having multiple sexual partners;
- long incubation period (time from infection to clinical manifestations);
- complex diagnostics;
- the presence of many types of PVI viruses;
- combination with other sexually transmitted infections;
- lack of protection effect using condoms from infection, etc.
1 Urethroscopy for diagnosing HPV
2 Urethroscopy for diagnosing HPV
3 Urethroscopy for diagnosing HPV
How to distinguish papilloma from condyloma
Knowing the difference between papilloma and condyloma is necessary to determine further actions. While some can remain on the body throughout life and cause only cosmetic discomfort, others carry the risk of malignant degeneration.
| Index | Papilloma | Condyloma |
| Structure | Homogeneous | Heterogeneous, small, papillary |
| Form | Round or oval, located on a soft stem | Arbitrary, located in clusters, in the form of ridges. Characterized by a narrowing from the stem to the end |
| Size | Up to 10 mm. As a result of traumatic exposure, it may increase by 2-15 mm. | Also capable of growing |
| Color | Weak or intense pigmentation | Virtually no different in color from surrounding tissues |
| Localization | Preferably on the skin | On the mucous membranes, mainly of the urogenital area; on skin folds subject to friction from clothing |
| Peculiarities | Causes aesthetic discomfort. Rarely inflamed, usually only due to injury | It often becomes inflamed and infected. Possible ulceration of the body of the growth, pain |
| Main route of infection | Contact and household | Sexual |
| Exciter type | Typically 2, 7 and 28 strains | 6, 11, 16, 18, 39, 54, 56, 73 strains |
| Risk of malignancy | No | Yes |
HPV types:
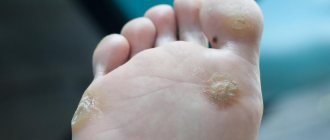
- HPV, which manifests itself as warts (HPV 1-5): warts (calluses) located on the soles of the feet - HPV types 1-4;
- flat warts - HPV types 3, 10, 28, 49;
- common warts - HPV type 27.
1
Diagnosis of papillomavirus infection
2 Diagnosis of human papillomavirus infection
3 Diagnosis of human papillomavirus infection
How to cure
To date, there is not a single proven treatment for HPV in the world.
The tactics for combating papillomas and condylomas are as follows:
- removal of formation;
- antiviral therapy – to suppress the activity of the virus;
- immunomodulatory therapy – to improve the functioning of the immune system.
To get rid of the growth, various methods are used:
- laser removal;
- cryodestruction;
- radio wave exposure;
- electrocoagulation;
- chemical removal;
- traditional surgery.
The choice of method is made by the doctor depending on the type of formation, its location, size, etc.
Diagnosis of genital warts (papillomas)
Genital warts are easy to identify by visual examination and it is rarely necessary to resort to laboratory diagnosis using biopsy and histological examination. It must be remembered that the cause of condylomas is the human papilloma virus, which can also affect the cervix. Despite the fact that the types of virus responsible for the formation of genital warts rarely have oncogenic potential, it is imperative to be vigilant and carry out oncological screening - cytological diagnosis of the cervix, determination of the type of virus by examining its DNA and colposcopy if indicated. You can read more about the cancer screening program at the Yauza Clinical Hospital here.
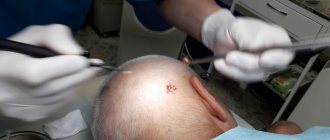
Laser removal
This is a modern method of excision of formation, which has become widespread.
Its popularity is due to its advantages:
- painlessness;
- low-injury;
- bloodlessness;
- speed of the procedure;
- minimal risk of infection;
- short rehabilitation period;
- no scars.
Thanks to the precision of the laser beam, it is possible to remove growths even in particularly sensitive areas, such as the intimate area, eyelid, etc.
Treatment
Condylomas and HPV require a systematic approach to treatment.
Medication
To combat condylomas in women and men, doctors act in three directions:
- against viruses;
- in order to increase immunity;
- for fortification of the patient.
Cycloferon and inosiplex act against HPV activation and its reproduction. Inferon and allokin-alpha stop viruses and help restore the immune system. To improve the general health of women and men, Immunal, Amixin, Poludan, etc. are prescribed. A complex of vitamins and minerals is also an essential component of treatment for condylomas.
Local
Condylomas are successfully treated using ointments and sprays of antiviral action (epigen-intim, condylen, etc.). Women and men will not have to think about condylomas if they are treated with inquimod, podophyllotoxin. For pregnant women, you can use trichloroacetic and nitric acids. Women need to fight condylomas in stages: first remove them, and then, or in parallel, act to reduce the number of viruses. Often (in every third woman) condylomas enter the stage of relapse (especially if preventive measures are not followed and the recommendations of the attending physician are ignored).
Removal
Methods for removing condylomas in modern medicine are varied:
- Electric coagulation. This method has disadvantages - many contraindications, painful procedure and long recovery.
- Cryotherapy. Condylomas are removed using liquid nitrogen. The positive aspects of this technique are the absence of scars, painless effects, and the absence of anesthesia.
- Surgical method. The growths are removed during surgery, and stitches are placed at the site of the wounds. Doctors use local anesthesia.
- Use of chemicals. This method is contraindicated during pregnancy and lactation.
- Laser therapy. Condylomas are removed with a laser beam; this is a treatment that does not affect healthy cells and leaves virtually no scars.
- Radiosurgical method. The use of a special device helps remove condylomas without contact with the body. Removal of growths is accompanied by simultaneous sealing of blood vessels. This technique is one of the most modern and in demand.
Cryodestruction
This removal method is only used for skin tags. It consists of a short-term effect on the formation of liquid nitrogen. Pathological tissues are destroyed by flash freezing.
Cryodestruction
The advantages of cryodestruction include easy tolerance by the patient, no need for anesthesia and no risk of scar formation. Disadvantages are difficulty in controlling the depth of impact and a longer rehabilitation period.
Papilloma virus. Diagnostics:
- Consultation with a dermatovenerologist . Only a dermatovenerologist can make a diagnosis during an initial examination, assessing the clinical picture, conducting a test with acetic acid, and, if necessary, using the dermatoscopy method.
- Laboratory diagnostics. It is necessary to conduct a HPV test using the PCR method, which will allow you to estimate the amount of the virus, as well as determine which type of HPV is present in this case (they are divided into types with high and low risk of oncogenicity). A PCR test must also be performed on all sexual partners of a patient with genital warts. A positive test result in the absence of clinical manifestations of the disease means that treatment is necessary to suppress the development of the virus in the body.
- Urethroscopy is a study of the condition of the urethral mucosa using special endourethral endoscopes. Considering the increase in recent years in the number of patients with endourethral condylomas, this study is necessary for all patients, both men and women.
- Extended colposcopy - examination of the cervix using a colposcope and performing a test with acetic acid and the Schiller test. It is necessary for all women to undergo laboratory confirmation of papillomavirus infection, since the presence of flat condylomas on the cervix is possible.
- Immunogram is a study of the state of the immune system. This will allow for the most effective HPV therapy.
Electrocoagulation
The method is aimed at cauterizing the growth using electric current. With its help, you can remove papillomas and condylomas on any part of the body, including delicate ones. However, for the urogenital area and eyelids, it is better to give preference to methods that are less painful.
Electrocoagulator
The formation is destroyed under the influence of high temperature, due to which the surrounding tissues are also damaged. In addition, patients note poor healing, and sometimes scarring and relapses. The advantages of this type of removal are sterility, bloodlessness, the ability to adjust the current strength and control the depth of exposure.
Asymptomatic carriage of human papillomavirus (HPV)
In reality, many more people are infected with HPV than statistics show. Most of them simply do not know about it, since there are no symptoms of condyloma.
The virus may not manifest itself in any way for a long time, since the human immune system does not allow it to develop to the required extent. However, at any time, with a decrease in both general and local immunity, this can happen, and then papillomas and/or condylomas appear.
1 Laboratory diagnostics
2 Dermatoscopy
3 Extended colposcopy
Folk remedies
On the Internet you can find many recipes and techniques for removing papillomas and condylomas. However, you should not self-medicate. Only a doctor can safely and effectively get rid of the problem. Any attempts to bandage the formation with thread, cauterize it with celandine juice and other popular folk methods can provoke complications.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
Healing after removal of condylomas
After removal of condylomas, the resulting wounds are usually recommended to be treated with Baneocin powder. Accordingly, for some time there may be profuse serous or minor bleeding after removal of condylomas, which is absolutely normal and should not frighten the patient.
After removal of condylomas, swelling and pain may occur, which can last from two to five days. Their duration is related to the size of the removed tumors and the individual sensitivity of the person.
In most cases, during the healing process, itching may occur after removal of condylomas, which is also absolutely normal, as for the healing of any other area of the skin.
After removal of condylomas, limit physical activity and exclude sexual activity for about 2-3 weeks until epithelization (healing) of the wound surface.
Why do papillomas appear?
The main reason for the formation of papillomas is infection of the body with HPV, which most often occurs through casual sexual contact.
Factors that can trigger the growth of warts include:
- decreased immune defense of the body
- alcohol abuse
- presence of chronic, regularly recurring infections
- pathology of the digestive system
- stress conditions and depression
- long-term antibiotic treatment
- visiting the swimming pool, public bath, sauna
The distinctive features of papillomas are:
- rapid appearance of growth
- spread of papillomas due to rapid growth
- increased risk of cancer
- high contagiousness of papillomas
- merging of warts into one large growth
When multiple neoplasms appear on the surface of the skin, this should be the reason for a full diagnosis for HPV infection and urgent treatment.
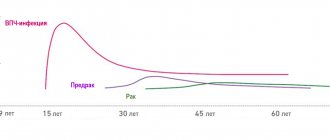
What is the relationship between HPV and human cancer?
The clearest causal role of HPV has been demonstrated in cervical cancer. Thus, high-risk HPV types (see Table 1) were found in 93 - 99% of women with cervical cancer. Previously, it was found that the most susceptible to cervical cancer are women who began sexual activity early, had an STI, and also had a large number of sexual partners, as well as those who were in contact with men whose partners had cervical cancer. It turned out that high-risk HPVs contain regions with high oncogenic activity (E6 and E7) in their genome. When HPV invades the genome of cells in the cervical mucosa, regions of the genome E6 and E7 stimulate the synthesis of corresponding proteins, which in turn interact with proteins that regulate cell division and cell death. The E6 protein suppresses the activity of the P53 gene (and the corresponding protein), and the E7 protein of the retinoblastoma gene, which stimulates the process of apoptosis (programmed cell death). This leads to the predominance of cell reproduction over cell death, which stimulates the uncontrolled malignant growth of cervical epithelial cells and the development of cervical cancer. Thus, the International Agency for Research on Cancer has concluded that high-risk HPV types are the leading cause of cervical cancer.
However, it is known that most women infected with HPV do not develop cervical cancer and the presence of HPV is “necessary” but not “sufficient” for the development of this disease. The development of cervical cancer in people infected with HPV is facilitated by smoking, long-term use of hormonal contraceptives, and the presence of other STIs, such as chlamydia, namely Chlamydia trachomatis, herpes simplex virus type 2. In addition, vitamin A deficiency, genetic predisposition and immunodeficiency contribute to the development of cervical cancer in the presence of HPV. In addition to cervical cancer, the causative role of HPV has been established in cancer of the anal area (especially in homosexuals), and in cancer of the vulva, vagina and penis. Some cases of cancer of the mouth, larynx and esophagus are also possibly related to HPV.
Every year, up to half a million new cases of cervical cancer occur worldwide. Most of these cases are registered in developing countries, where preventive programs of annual screening examinations for HPV, dysplasia and cervical cancer do not work or work poorly. The introduction of similar preventive programs in developed Western countries has reduced the incidence of cervical cancer by 75%. Although the incidence of other HPV-related cancers is much lower, the incidence of anal cancer among gay men is estimated to be 4 times higher than the incidence of cervical cancer in women (35 cases per 100,000 homosexuals per year, versus 8.3 cases per 100,000 women). population per year).
What is a mole
Moles or nevi (medical term) differ in shape, color and size.
They can be brown, black, purple and red.
They are located on the surface of the skin or slightly rise above the skin.
After six months of age, the first nevi may already form on the child’s body.
They can appear throughout life with varying intensity.
The formation of nevi is associated with the accumulation of melanocytes in certain areas of the skin surface.
A mole is a benign formation and does not pose a danger, but under the influence of negative factors it can degenerate into a malignant form - melanoma.
The neoplasm carries a mortal danger to humans, as it has the ability to very quickly metastasize throughout the body.