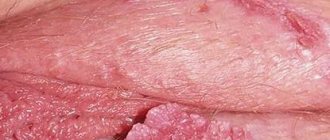
Papilloma is a benign tumor caused by a viral disease. This small piece, known for its ugly appearance, appears completely harmless.
However, you should not ignore your doctor's advice, since in some cases papilloma can cause cancerous tumors. Doctors warn that papilloma is especially dangerous for the fair sex for various reasons.
What does papilloma look like???
Signs of mild tingling, itching and slight redness in the infected area are common symptoms of papilloma. In most cases, papillomas form in the form of skin warts, similar to warts, but with a more complex structure.
Papilloma resembles cabbage, cones or mushroom caps. The size is usually limited to two centimeters. Typical areas of the body where papillomas occur are usually the shoulders, neck, face, arms (especially the arms).
However, papilloma can also occur in other parts of the body. Only the most popular papillary transmission sites are listed here.
Why does papilloma occur???
Unfortunately, the carrier of the papilloma virus is not always aware of his disease, since papilloma may not form immediately.
Typically, when entering the human body, the virus infects the basal epithelial layer. Infection in this area is caused by the transformation of squamous epithelium to columnar epithelium.
Cells infected by a virus can be benign or malignant. The benign form is characterized by the fact that it is located outside the chromosomes of cells. Moreover, a malignant tumor is inserted into the genome of the cell itself.
Doctors and cosmetologists know several causes of papilloma:
- One of the reasons for the appearance of papillomas is associated with two factors: microdamage to skin tissue and accidental contact with infected objects.
- The second cause of papilloma is sexual contact with an infected person, which has unintended consequences: anogenital warts, also called genital warts, occur in various parts of the body and in the genital area.
- Surprisingly, this virus can occur not only in adults, but also in small newborns. Some children may have signs of laryngeal papillomatosis at birth.
Main types of papillomas
Papilloma can take different forms. In some cases, the papilloma virus does not cause any characteristic symptoms. However, sometimes the papilloma virus can cause the development of acute condyloma. Fortunately, papilloma in women rarely causes cervical cancer.
- Simple papilloma (or papilloma) Looks like small bumps with an uneven crust. Usually they do not exceed 1 mm. Simple growth occurs in all parts of the body, from the feet to the chin. However, the most common sites for this papilloma to spread are the hands, fingers and knees. A simple papilloma is an isolated structure that can exist for months or even years. They usually don't change over time. However, this does not exclude the situation of transformation and scaling.
- Plantar papilloma has a cone-shaped shape and rough growth.
A distinctive feature of this papilloma is that the sole has a protruding edge (hence the name “sole”). This growth is formed in singular or plural. Typically, the appearance of plantar papilloma can lead to infections in nearby areas of the body, which can lead to other growths. Pain when walking is another sign of plantar papilloma. Usually this growth interferes with walking. Sometimes the papilloma disappears when walking. However, its disappearance does not mean complete removal of the virus. In any case, consultation with a doctor is necessary. - Flat papilloma This is a small flat sprout, similar to ordinary yeast. However, flat papilloma has an unusual geometry and several angles. The color of flat papilloma matches the color of healthy skin. Therefore, flat papillomas cannot always be detected immediately. Distribution parts: hands, face. Flat papillomas cause not only unpleasant itching, but also severe pain.
- Filar papilloma Mostly suitable for people aged 40 to 50 years.
The place of distribution is the most unexpected: armpits, groin, eyes. However, filiform papillomas most often occur on the neck and shoulders. Filamentous papilloma looks like small yellow bumpy formations. They tend to change gradually. Over time, they will change shape and become thinner, like short wires (5-6 mm). An inflammatory process sometimes occurs at the site of filamentous papilloma. - Papilloma acuminata - Condyloma acuminata - These are papillary formations that usually appear on the mucous membranes of the genital organs. In some cases, genital papilloma does not cause serious health problems. However, sometimes these papillomas can lead to malignant neoplasms.
How to treat papilloma?
Firstly, do not take the medicine yourself as it will have negative effects. Under no circumstances should you remove the papilloma yourself, burn it, or use ointment or any medicinal gel. Your doctor will help you find your
a way to cure or eliminate growth.
The dermatologist conducts a special examination of papilloma, and then offers one of the treatment options:
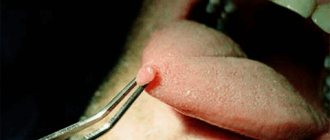
- Use a laser device to remove papilloma and stop natural bleeding after removal. After this procedure, the growth disappeared without a trace, leaving no scars or scars. This method is commonly used to remove simple plantar acuminate papillomas.
- Cryotherapy is one of the most effective ways to remove papillomas. Use liquid nitrogen to remove sediment. This method is used in dermatology and cosmetology to remove all types of papillomas.
- Radiosurgery Resection-surgery of papilloma with a radioknife. Using this instrument, the specialist will remove the affected area of skin and conduct a thorough histological examination. This is a painless way to remove papilloma; the process takes very little time and does not require re-treatment.
- Electrocoagulation was additionally removed. This process is also called "diathermic curing". Apply high frequency current to it.
- Surgical intervention is the classic method of papilloma resection. Use a traditional surgical scalpel to remove the growth. This method is often used for simple papillomas.
Measures after resection of papilloma
Removing a papilloma does not mean completely removing the virus. Therefore, be sure to attend courses to strengthen your immune system after surgery. The goal of this course is to reduce the activity of the virus.
After some methods of removing papillomas, the skin will be noticeable: scars, scars, ulcers, etc.d. A month later the tissue was completely healed.
Symptoms
This pathology is not obvious until the growths themselves appear. Until this time, the patient may not even realize that he is infected. As statistics show, today 9/10 people are infected with HPV, so many are wondering how to get rid of papillomas .
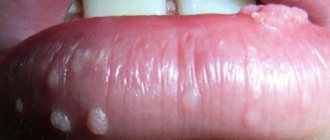
Papillomas have the shape of thin nipples. The new growth can be silky or denser, and the color can range from light to black.
The symptoms papillomavirus can vary significantly and are closely related to the type of virus and location.
Development of vulgar papillomas in the form of bumps with a hardened crust. Their diameter is more than one mm, they can connect with each other, forming a wide area of infection. As a rule, they appear in the knee area and on the palms.
Formation of flat papillomas and warts with a soft crust. They have a similar tint to healthy skin, but cause itching and pain.
The formation of small bumps with a glossy coating on the feet is plantar papillomas. During walking, such papillomas cause pain.
papilloma virus treatment
Thread-like papillomas in the eye area, papillomas on the neck and under the armpits in the form of small yellow bumps. Over time, they transform from small cones into long formations.
Formation of papillomas on the mucous membranes of the mouth and lips.
The formation of various red-brown growths on the hands and feet is called Lewandowsky-Lutz papillomas.
These types of bumps develop on the vocal cords, and their development is very dangerous as they can cause speech defects. Increasing in size and quantity, they prevent the free circulation of the air mass, so in this case the question arises of how to remove papilloma .
Papillomas in the vaginal and cervical area in the fairer sex and in the urinary area in the stronger sex.
How are papillomas removed?
Currently, there are a number of effective methods for removing skin tumors:
- using a laser - effectively, quickly and accurately, no scars remain.
- using liquid nitrogen - rapid freezing of tissues causes their necrosis and death, no defects remain, and recovery occurs quite quickly.
- using current - quickly and effectively, but in some cases, when removing large papillomas, small scars may remain.
- using a radio knife - the advantages of the method are rapid healing of the skin, absence of scars and pain during the procedure.
Details about methods for removing tumors
After removing the papillomas, the doctor gives recommendations on caring for the wound. When they are performed, healing occurs quickly and without complications.
Reasons for formation
The reasons for the formation of such growths include HPV, as mentioned earlier. A huge number of people are carriers of this virus. Having penetrated inside the body, the virus begins to spread, but for a long period of time they may not be reflected. Under the influence of many factors, the virus can form on the skin in the form of papillomas. Such factors include internal infections, consumption of junk food, systematic stressful situations - in general, those factors that cause a weakening of the immune system.
The main criteria that cause the development of the virus and the severity of its symptoms include:
- sexual relationships without contraception, built with different partners,
- bad habits,
- weakened immune system,
- metabolic disorder,
- gastrointestinal disorders,
- failure to follow basic hygiene rules,
- heredity - the virus can be transmitted during pregnancy.
Depending on the location, the patient may need the help of a specialist who can prescribe an effective ointment for papillomas . In a situation where pronounced symptoms are not observed, but a person wants to know for sure whether he can transmit the above-mentioned virus, then he needs to contact our medical specialists: immunologists, dermatovenerologists.
Is human papillomavirus (HPV) a sexually transmitted disease?
HPV - in more detail stands for “a virus that causes a benign tumor of epithelial origin in the form of a papilla” - papilloma (papilloma: Latin papilla - nipple and Greek -oma - tumor). It is classified as a sexually transmitted disease (STD). The concept today has, unfortunately, become much broader, and if earlier we heard about several “terrible”, as it seemed to us, classical diseases of Venus, which are actually treated simply and are detected quickly (syphilis, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, chancroid), then The list of “new” STDs - insidious, difficult to diagnose, and sometimes difficult to treat and completely incurable (HIV) - is constantly growing.
So, we include the following “new” STDs: chlamydia, mycoplasmosis, ureaplasmosis, gardnerellosis, genital herpes, candidiasis, and human papillomavirus. If growths from papillomavirus have formed in the areas of the genital or perianal organs, then they are called “pointed candylomas,” but in fact they are the same virus, only its different strains (types).
Complications
Although papillomas for the most part imply benign formations, their formation cannot be ignored. Many types of viruses can cause cancer, so many people wonder how to prevent the spread of papilloma after infection. The following types of HPV are distinguished depending on the degree of threat of cancer:
- not implying the appearance of oncology,
- having a low degree and a high degree of oncology.
When is it recommended to contact a specialist? If there are formations, you should immediately contact a doctor specializing in the relevant profile.
What will happen to the skin after papillomas are removed?
The next day after the procedure, a brown crust forms at the site of the removed tumor. Healing takes from 2 to 7 days, it all depends on the size of the removed papilloma. After healing, the crust will come off on its own. The main thing at this time is not to wet or injure this area.
After the procedure, the doctor gives some simple recommendations for further skin care.
In our clinic, it is carried out using modern equipment by highly qualified doctors, which allows us to solve problems of papillomas removal quickly, efficiently and safely. We use disposable consumables, which guarantees maximum patient safety.
Diagnosis of papillomas
HPV tests are performed in the clinic. As for indicators in the form of standard genital papillomas on the body , the final and correct diagnosis can be made only after a professional examination by a doctor. But due to the fact that today there are a large number of types of the virus, a specialist may prescribe secondary examinations to confirm the diagnosis, which include:
- general and biochemical blood test,
- taking a sample for biopsy,
- polymerase chain reaction method.
PCR helps:
- detect the presence of HPV,
- determine the type of virus,
- correctly determine the number of viruses,
- understand whether the pathology develops in acute or chronic form.
papillomavirus test
Human papillomavirus infection (HPV) - symptoms and treatment
In 90% of cases, a healthy human immune system copes with human papillomavirus infection on its own within a period of six months to two years from the moment of infection, after which a complete recovery occurs with the disappearance of the virus from the body. In this case, intense lifelong immunity is not formed, that is, a person can become infected again.
In other cases, in the presence of predisposing factors, the disease takes on a chronic form, prone to a long latent course with periodic relapses and the possible development of severe complications.
From the moment the virus enters the body to the development of precancerous conditions and, especially, the appearance of cancer, quite a long time can pass, sometimes tens of years. Therefore, regular preventive examinations, timely detection and treatment of precancerous conditions are a very real and effective way to avoid the worst case scenario.[13] To this end, the World Health Organization recommends that all women over 30 years of age undergo not only a “routine” cytological examination during initial screening, but also a test for the presence of HPV.[10]
Regular visits to the gynecologist (if there are no complaints - once a year) with a Pap test allows you to timely detect the initial signs of dysplasia and take all necessary measures to prevent the progression of the process and its transition to cancer.
The use of barrier contraception methods, although not completely protects against infection, somewhat reduces its likelihood.
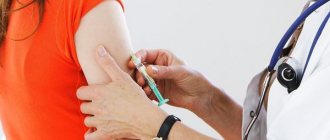
The main method of primary prevention of human papillomavirus infection is vaccination . [11] Modern vaccines are developed to protect against the most dangerous, highly oncogenic strains of HPV, responsible for 70-80% of cases of cervical cancer. A standard course of three vaccinations provides quite reliable protection.
It is advisable to vaccinate children (girls, and boys to curb the spread of infection) from 9-10 to 17 years old, as well as young women (18-25 years old) before engaging in sexual activity, since the vaccine prevents infection, but is not a means of treatment. developed infection. If the patient is already sexually active, then before vaccination she needs to undergo testing for the presence of human papillomavirus infection. However, even if one of the strains included in the vaccine is identified, vaccination can still be carried out, since this is not a contraindication.
Treatment
The treatment plan is drawn up on an individual basis, focusing on the type of human papillomavirus, the degree of development of the pathology and the distinctive characteristics of the patient.
If, during the examination, a virus was detected in a person, the symptoms of which are absent, then the doctor may prescribe preventive treatment using cytostatics. This treatment helps stop the virus for a certain period of time.
If the patient has papillomas, then they can be eliminated. A removed papilloma eliminates unnecessary discomfort and helps a person live a full life. The choice of elimination method depends on the location. The final cost will depend on the method.
Available methods for removing papillomas - skin growths:
- cryodestruction – exposure to low temperatures and liquid nitrogen,
- electrocoagulation - the use of electric current of various frequencies,
- getting rid of papillomas with laser,
- radioknife - the use of high frequency radioactive waves,
- surgical intervention.
Let's take a closer look at ways to treat papillomas in the comfort of your own home.
These include:
- removal using celandine,
- constant use of tea tree oil,
- use of aloe vera,
- systematically rubbing the formations with banana peel.
The use of the above-mentioned medications for papillomas will be effective only for standard types of papillomas. If blood discharge comes out of the formation, there is pain, etc., then there is an urgent need to see a doctor.
how to treat papilloma virus
Pregnancy with papilloma virus
Infection from mother to fetus during childbirth occurs in almost 98% of cases. For a baby who passes through the birth canal, literally strewn with condylomas, the virus enters the mouth and eyes, so all women planning a pregnancy should be tested in advance and, if necessary, treated for HPV and all types of STDs. Only after completion of treatment can you plan to conceive.
If the disease was in a latent form and was first discovered during pregnancy, and this happens often (immunity weakens during pregnancy), then it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor: treatment of papilloma during pregnancy is possible.
What tests does the doctor refer for for papillomas?
If papillomas are detected, it is necessary to undergo tests to clarify the diagnosis.
It is important not only to establish the fact of the presence of HPV, but also what type of virus it is - highly oncogenic or not.
Diagnostic tests are also carried out when planning pregnancy, as well as to clarify the causes of infertility, miscarriage and other pathological conditions during pregnancy. It is especially important to get tested for HPV for all sexual partners.
HPV is easily transmitted through unprotected sex.
If papillomas are detected, the doctor will refer you for cytological studies.
For this purpose, smears are taken from the cervical canal in the female population, and from the urethra in the male population.
The method is simple and cheap, but it has low reliability.
Often, laboratory assistants doing analysis see something that is not what actually exists.
This leads to false results.
In addition to cytological studies, histological studies are carried out.
Women's cervix is examined using colposcopy.
But the best and most reliable result is obtained by using the PCR diagnostic method.
Moreover, for this it is important to follow the rules of the analysis, because without this you can get a false positive or false negative result.
Which doctor treats papillomas in men's intimate places?
For papillomas in men, you should contact a dermatovenerologist, urologist or andrologist.
Papillomas of the perianal area and on the anus are treated by a proctologist.
He performs not only a visual examination, but also anoscopy in order to have maximum information about HPV and the directions of its spread throughout the body of an infected man.
Most often, malignancies are observed on the penis and larynx.
In people infected with HPV, papillomas do not necessarily grow.
This requires a decrease in immune defense.
It occurs if:
- history of severe inflammatory diseases
- there was psycho-emotional stress
- were treated with hormonal drugs
- there was insolation
- consumed alcoholic beverages and tobacco products
For rashes to occur, you also need increased sweating or high humidity.
Such conditions are observed inside the elbow, in the groin and under the arms.
Which doctor should I contact for papillomas on the body, neck, groin and armpit?
If neoplasms are detected, you should immediately contact your family doctor.
The general practitioner will carefully examine you and refer you to a dermatovenerologist.
If you need advice from other specialized specialists, then you should definitely do it.
HPV may have caused pathology in other organs and systems in the body, and the sick person should know about this.
It is necessary to consult a specialist if:
- papillomas on the body;
- warts all over the body;
- Condylomas appeared (external genitalia and perianal area).
Most types of HPV are low-oncogenic, but formations cannot be injured so as not to provoke the degeneration of a benign neoplasm into a malignant one.
When a benign papilloma is traumatized, it becomes infected with a secondary infection and suppurates, which can lead to sepsis.
A sick person cannot determine for himself which strain of HPV he is infected with – high-oncogenic or low-oncogenic.
You need to contact a specialist and get diagnosed.
To exclude or confirm the presence of highly oncogenic, primarily HPV types sixteen and eighteen.
Development and localization
To begin with, it is important to note that there are more than 600 strains of this virus. That is, there is not one diagnosis, one version of the consequences and one version of the manifestations. There are many different situations involving infection.
If the immune system is strong, it can easily cope with the virus on its own and within a few years “displace” it from the body. But at the same time, re-infection or illness with a different strain is also possible.
Papillomas and other symptoms of HPV in the form of formations that develop as a result of infection can appear in different places:
- on the skin anywhere;
- in the anogenital area;
- in the oral cavity, bronchi and upper respiratory tract;
- in the rectum, etc.
Formations can grow and form entire groups, or they can gradually dry out and disappear - it all depends on the specific situation.