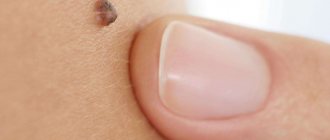
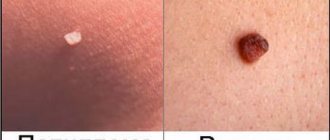
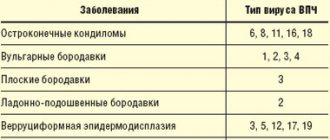
Papillomas in the groin (genital warts, genital warts) are observed quite often in adults. They are one of the varieties of viral warts and look like papillary soft formations on a small stalk, prone to merging with each other. As a result of the merger, colonies are formed, the surface of which resembles a cauliflower inflorescence (see photo).
The groin area is one of the favorite localizations of papillomas caused by certain strains of HPV
Neoplasms in the groin area cause discomfort in patients and create problems in intimate life, so if they appear, you should definitely consult a doctor.
Why do condylomas appear?
The cause of growths in the groin area is infection of a person with the human papillomavirus (HPV).
Susceptibility to infection is high. The course of the infection is chronic, with periodic relapses, which more often occur against the background of a weakening of general or local immunity.
Genital warts in women can be localized on the labia, mucous membrane of the vagina and cervix, and in men on the skin of the foreskin, glans penis, and around the anus.
HPV infection usually occurs through unprotected sexual contact (oral, vaginal, anal) with an infected partner.
Pregnant women with papillomas in the groin can transmit the infection to the fetus during its intrauterine development or infect it at the time of birth.
The human papillomavirus is quite widespread. Over 50% of sexually active adults are infected with it. About 100 strains of this virus have been described in the literature. Some of them have high oncogenic properties, that is, they can provoke the development of precancerous and malignant neoplasms in the body of an infected person.
In many infected people, the infection does not manifest itself clinically, and genital warts appear only when the immune system is significantly reduced.
Risk factors
Factors that increase the risk of contracting human papillovirus infection include:
- sexually transmitted diseases (genital herpes, candidiasis, trichomoniasis, gonorrhea, chlamydia);
- vaginal dysbiosis;
- having many sexual partners;
- decreased immunity associated with various factors (severe stress, infectious diseases, poor nutrition, alcohol abuse);
- pregnancy.
Options for the development of papillomas in the groin
Depending on the characteristics of the immune reactions of the human body, various ways of developing human papillomavirus infection can be observed:
- regression of genital warts until their complete disappearance (more often observed in women in the postpartum period);
- absence of disease dynamics over a sufficiently long period of time;
- growth and appearance of new tumors;
- malignant transformation of growths.
Depending on the risk of malignant tumors, HPV strains are divided into several groups:
- high oncogenicity;
- average oncogenicity;
- low oncogenicity;
- non-oncogenic.
Women who have been diagnosed with HPV infection with high oncogenicity should be monitored by a gynecologist and regularly undergo oncocytological examination for the purpose of early diagnosis of cervical dysplasia, which is a precancerous disease.
Pathogenesis and symptoms of the disease
HPV infection is transmitted from person to person. Simultaneous infection with several strains of the virus is often detected. Papillomavirus enters the body through damage to the skin or mucous membranes. It can remain in epithelial cells for a long time and not manifest itself clinically. Under the influence of various provoking factors leading to a decrease in the body's defenses, the virus begins to actively multiply. After a sufficiently large number of viral copies accumulate in the epithelial cells, the development of skin manifestations of the disease begins.
During latent infection, HPV is in episomal form, that is, located outside the chromosomal apparatus of cells. Having multiplied in large numbers, the virus enters the intrasomal form, characterized by the integration of viral DNA into the chromosomes of the affected cells. This leads to their uncontrolled and rapid division and growth. As a result, genital warts appear. Genital warts usually appear simultaneously; less often, their formation takes several days.
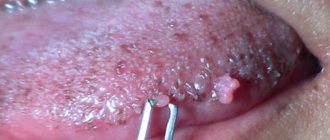
Papillomas in the groin in men are usually located in the area of the coronary sulcus, frenulum and the inner layer of the foreskin. Less commonly, they are located in the scrotum, body of the penis, urethral opening, or the area around the anus.
In men, papillomas are often located in the penis area
The formation of a genital wart in the area of the external opening of the urethra is accompanied by the appearance of dysuric symptoms and the spraying of a stream of urine.
The favorite localization of papillomas in the groin in women is the labia minora. Somewhat less frequently, growths appear on the labia majora, in the perianal area, in the vagina, on the cervix or in the area of the urethral opening. Genital warts of the vagina and cervix are usually detected only during a gynecological examination of the patient.
In most cases, the size of papillomas in the groin area does not exceed 2-3 cm. However, in patients with immunodeficiency or in pregnant women, neoplasms can reach a much larger size and become gigantic.
Treatment of papillomas
At the present time, complete destruction of the papilloma virus in the body is impossible, however, with proper treatment, the virus is blocked and rendered inactive. Treatment consists of several stages:
- Removing growths on the body
- Prescribing antiviral medications
- Increased immune system resistance
The first step is to remove all papillomas on the body. Our clinic provides several modern methods of getting rid of unwanted growths.
After removal of papillomas, it is necessary to take antiviral agents that prevent further replication of the virus. Thanks to them, the functioning of the infected cell will be disrupted and further formation of growths will be prevented.
The final stage is taking measures to increase immunity. This is done so that the body can fight the virus and keep it in an inactive, harmless state for a long time.
If you follow all the necessary instructions, then HPV in the body will not cause concern. The key point is the correct and safe removal of papillomas.
Diagnostics
If formations similar to the description of condylomas are detected in the groin area, the patient should consult a doctor (gynecologist, urologist or venereologist).
Genital warts require differential diagnosis with a number of physiological conditions and diseases:
- micropapillomatosis of the labia;
- papular necklace of the penis;
- condylomas lata with syphilis;
- molluscum contagiosum.
To clarify the diagnosis, the following research methods are used:
- colposcopy;
- urethroscopy;
- smear for cytology from the cervix;
- histological examination of neoplasm tissue;
- PCR diagnostics;
- immunological analysis for the presence of antibodies to the human papillomavirus in the blood.
If papillomas are detected in the groin, the patient must be examined for sexually transmitted diseases and HIV infection.
When should warts in the groin in men be removed?
Warts caused by the papilloma virus should be removed in all cases. The fact is that growths on the skin of a viral nature do not tend to disappear on their own. In addition, if nothing is done, such warts multiply uncontrollably and in a few days can spread throughout the perineum, groin areas and genitals. Skin formations in the groin of a different nature are treated differently. Manifestations of sexually transmitted diseases are eliminated with general medications, for example, tablets and injections. Benign soft fibroids can be left alone if they do not particularly interfere or cause pain. Cancers are treated according to all the principles of oncology.
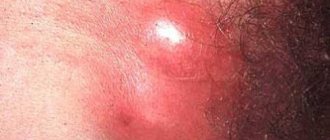
Rice. 2. Multiple warts in the groin
Treatment
The main method of treating genital warts is their removal, which can be done using various methods under local anesthesia and on an outpatient basis. Each of them has its own indications and contraindications. Let's consider the main methods of surgical treatment of papillomas in the groin:
| Method | Short description |
| Laser coagulation | It is carried out using a carbon dioxide or neodymium laser. The laser beam evaporates the condyloma tissue layer by layer. A dry black crust (scab) remains at the site of formation. After it falls off on days 7-12, an unchanged mucous membrane remains at the wound site |
| Radio wave method | The destruction of tumor tissue occurs under the influence of radio waves of a certain frequency. The procedure is practically painless, but does not allow tissue sampling for histological examination. |
| Cryodestruction | The neoplasm is deep frozen with liquid nitrogen. In nulliparous women, removing papillomas in the groin using this method is not recommended |
| Electrocoagulation | Papillomas are removed using an electrode to which a high frequency current is applied. The advantages of the method are the possibility of collecting material for histological analysis, low risk of postoperative complications |
| Chemical method | It is carried out using cytotoxic drugs (fluorouracil, feresol, imiquidom, podophyllin, podophyllinotoxin) |
Regardless of the method of removal, the risk of recurrence of genital warts is quite high – up to 30%. This is due to the fact that the virus persists in epithelial cells for many years. Therefore, after surgical treatment, patients are recommended to undergo antiviral and immunomodulatory therapy.
You should not try to get rid of papillomas in the groin on your own at home. Such attempts are associated with a high risk of complications, such as infection, increased growth, and malignancy.
How to remove papillomas in the groin
Before you get rid of papilloma in the groin, you need to undergo diagnostics. The results determine exactly how the removal will take place and what medications and procedures the doctor will prescribe. He must also determine the patient’s skin type. How and by what methods can you remove growths in the groin area?
First of all, treatment involves strengthening a weakened immune system. At this stage, medications that contain interferons are used. They help cope with the virus and stop further spread of the infection.
Such drugs are produced in the form of tablets, rectal suppositories, ointments, drops, etc. The most popular are:
- Interferon
- Viferon
- Genferon
- Grippferon
- Anaferon
- Amiksin
Important!
Taking medications without a doctor's prescription is strictly prohibited. Each of them has contraindications and side effects. Therefore, self-medication can be dangerous.
You can strengthen your immune system in other ways:
- Changing your diet
- Taking vitamin complexes
- Moderate physical activity
Along with the use of medications and lifestyle changes, it is necessary to think about removing papillomas using special procedures.
- Cryodestruction. Involves exposing the growth to liquid nitrogen. Used to eliminate growths that are located in the fold. This method is ineffective on the genitals.
- Laser therapy. Papillomas are destroyed using a beam of laser beams. With this treatment, the risk of complications is minimized. Find out more about laser treatment here.
- Radio wave therapy. The process uses a device called Surgitron. The tumor is removed without direct impact on the skin.
- Electrocoagulation. It is used least often to remove formations in the groin area. Involves burning out growths using high temperature.
If the listed procedures do not bring the desired result, the doctor decides on surgical intervention. The main indication for surgery is the transformation of a neoplasm into a malignant tumor.
What else can you do to get rid of growths? There are several options.
- Concentrated formic acid solution. It is applied directly to the papilloma, as it can lead to soft tissue necrosis.
- Lapis pencils. The active ingredient in most of them is silver ions. They have antiseptic and antiviral properties. Like formic acid, they are used locally, since they can cause burns if they come into contact with healthy skin. With regular use of the pencil, the growth gradually atrophies and is rejected by the skin.
- Immunomodulator Laferobion. Available in the form of injection solutions. Promotes the rejection of papillomas without any effect on them. An alternative to this drug is Promisan. But it is used only in cases where there is a high risk of the growth degenerating into a malignant tumor.
Find out about other three effective remedies for papillomas and warts here.
If there are no contraindications, you can use folk remedies for papillomas. However, before removing them in this way, you should consult a doctor.
Medicines prepared according to folk recipes are especially popular. They are distinguished by almost complete safety and natural composition, as well as high efficiency. The most commonly used is celandine.
Celandine-based products have been used several centuries ago. In order to remove papilloma, you need to lubricate it with juice that is squeezed out of the stem. After the procedure, seal it with a regular band-aid. If these are new growths, they will disappear in about 10 days. It will take several weeks to treat older tumors.
A remedy for eliminating papillomas can be prepared at home. To do this, the celandine must be thoroughly crushed and mixed with olive oil in a ratio of 1 to 1. Cover with a lid. Let it brew for a month. Strain. Lubricate the growths three times a day until they disappear completely.
Products containing celandine can also be purchased in pharmacies. These are Super celandine (alkaline aqueous solution) and Mountain celandine. Both substances are used to cauterize papillomas. At the same time, the surrounding tissues remain undamaged.
Walnut ointment is also quite effective. It is used for compresses. To prepare, you need to take 4 green nuts and a little refined kerosene. After mixing the ingredients, you should get a mass with a consistency reminiscent of thick sour cream. It should be applied to the papilloma. Place a piece of plastic film on top. Secure the compress with a bandage or plaster. Leave for 30 minutes. Repeat the procedure for about 10 days.
To prepare the following remedy you need to take:
- 2.5 g aspirin
- 2 g boric acid
- 2.5 ml 5% iodine
- 100 g alcohol
Mix all the substances and use to lubricate growths up to 4 times a day. Stir or shake the mixture before use.
An ordinary eggshell from 2 chicken eggs will also help eliminate papillomas. It's better if they are homemade. The shells must be placed in the oven, preheated to 250 °C, for 30 minutes. After this, grind to a powder state. Apply the powder to the neoplasm, cover with a piece of cotton wool and secure with a plaster or bandage. Leave for 2 days. Then replace with a new bandage. The course of treatment is 3 weeks.
Another option is to use table vinegar. Using it and wheat flour, you need to form a small ball. Apply it to the papilloma and securely fasten it.
Castor oil has also proven itself well. It owes its effectiveness in the fight against neoplasms to its constituent components, which have antiviral and regenerating properties.
There are two options for using castor oil.
- Rub the substance into the surface of the growth. Carry out the procedure as often as possible, since this determines whether it quickly dries out and falls off.
- Lubricate the papilloma with the product and seal it with a band-aid. Leave it on all day. Repeat in a day.
This treatment does not give quick results. However, it allows you to get rid of growths painlessly and permanently.
Forecast
Modern treatment methods do not completely rid a person of HPV infection. As a result, there is always a fairly high risk of relapse of the disease.
The human papillomavirus has weakly expressed antigenic properties. This is the cause of an insufficiently active response to infection by the immune system. In this regard, there is a possibility of re-infection if the sexual partner has not received the necessary treatment.
Women with papillomas in the groin are recommended to have an annual colposcopy and a cervical smear examination for oncocytology.
Women infected with HPV strains that cause the formation of papillomas in the groin are recommended to undergo regular gynecological examinations
be careful
The presence of papillomas and warts on the body is the first sign of malignant melanoma!
We hasten to warn you that most drugs that “treat” warts and papillomas are a complete deception of marketers who make hundreds of percentage points on drugs whose effectiveness is zero. They do not cure the disease, but only mask the symptoms.
The pharmacy mafia makes huge money by deceiving sick people.
But what to do? How to treat if there is deception everywhere? Doctor of Medical Sciences Anatoly Makhson conducted his own investigation and found a way out of this situation. In this article, the Doctor also told how to 100% protect yourself from melanoma, for only 149 rubles! Read the article in the official source via the link.