The appearance of condylomas in the vagina and labia of women occurs due to infectious infection. The causative agent is the human papillomavirus, transmitted through sexual intercourse. It is important to treat this disease in a timely manner, since most often these growths indicate a precancerous condition.
General information
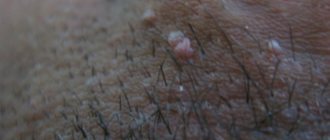
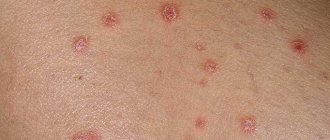
In appearance, condylomas are similar to small warts. The increase in growths begins to occur from small pimples, which are very difficult to identify. To detect the presence of condylomas, you need to conduct a special test for HPV. It can be taken at any hospital. Condyloma is a benign tumor. Based on their appearance, growths are divided into papillary and warty. With timely measures taken and proper treatment, condylomas are not life-threatening for a woman. But most often, HPV is accompanied by additional diseases that are associated with microflora disturbances:
- ureaplasma;
- mycoplasma;
- gardnerella;
- candidiasis.
All these pathologies can cause the appearance of HPV, which is characterized by the growth of warts in the vagina and labia.
Reasons for education
Once HPV enters a woman’s body, it quickly activates and spreads. This is where the main danger lies. It is necessary to take appropriate measures to treat the pathology as quickly as possible and prevent the subsequent proliferation of growths. The virus divides in the cells of the vagina. This process is responsible for the rapid development of tumors, which cause a lot of inconvenience to women. One of the main reasons for the appearance of condylomas in the vagina is the presence of these growths in one of the partners. During unprotected sexual contact, the virus is naturally transmitted to another partner. HPV is activated only under certain factors:
- lack of sleep, irregular routine, stress;
- weakened immunity;
- excessive physical activity;
- excessive doses of antibiotics;
- the presence of wounds on the vaginal mucosa;
- poor nutrition, hormonal imbalance;
- hypothermia.
Prevention
It is almost impossible to avoid the initial entry of papillomavirus into the human body. Experts have come to the conclusion that HPV first enters the bloodstream during puberty and the active beginning of intimate life. For a long time, the virus may not manifest itself in any way, but with a decrease in immunity, hormonal imbalance, damage to the mucous membranes of the genitals and the action of other predisposing factors, papillomavirus infection develops. Unprotected intimate contacts and frequent changes of sexual partners predispose to the onset of the disease. As a result of contact with a man who has viral warts on the genitals, a woman can become infected even if she has a strong immune system.
Prevention of the appearance of genital warts of the vagina and external genitalia includes, first of all, the prevention of accidental intimate contacts without the use of barrier contraceptives. It is recommended to adhere to the principles of a healthy lifestyle, carefully monitor the quality of intimate hygiene, and if any signs of gynecological pathologies and external inflammatory processes appear, contact qualified specialists.
Methods of infection
When diagnosing HPV, it is also worth taking your partner to the doctor for full treatment. You need to be treated at the same time and, naturally, abstain from sex during this time. There are many ways to get infected with a virus:
- Wearing clothes of an infected person. During contact with things affected by the virus, you can become infected with HPV.
- Using other people's hygiene products.
- Going to the sauna. Even if you practice proper hygiene, you can become infected with HPV. It’s no secret that public places of this kind collect all the “sores”.
Childbirth with condylomatosis
I would like to remind you that condylomas themselves are a manifestation of the human papillomavirus (HPV). This virus may pose a risk of fetal infection and laryngeal papillomatosis in the unborn child. Research does not confirm that 100% of women who carry the virus become infected in the fetus. Unfortunately, it is impossible to predict whether a child will become infected with the virus during pregnancy and childbirth. Undoubtedly, the presence of condylomas increases the risk of infection, so it is better to remove the tumors.
The need for delivery by cesarean section in women with condylomatosis is decided individually. It is preferable to give birth on your own, even despite the presence of formations in the area of the external or internal genital organs that are present before childbirth. There are cases that children born by cesarean section from pregnant women with HPV carriage suffer from laryngeal papillomatosis. Caesarean section is performed on pregnant women in the presence of extensive condylomatosis of the external genitalia, when this prevents vaginal delivery, or in combination with other complications and diseases during pregnancy.
It should be noted that termination of pregnancy for condylomatosis of the anogenital area is usually not performed.
Condylomas in the rectum (anus) area
Anal condylomas, like other types of similar neoplasms, are the result of infection of the body with the human papillomavirus. Condylomas in the anus are a rather complex disease, which is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- the appearance of a formation in the anus;
- an increase in the number of warts in this area;
- traumatization of warts due to mechanical impact.
Condylomas of the rectum must be treated without fail. A specialized doctor who is able to correctly diagnose this disease is a proctologist. As soon as you experience one of the above unpleasant sensations, you should immediately consult a doctor. Condylomas in the anal area are also called perianal by experts.
Papillomavirus is transmitted through sexual intercourse. In this case, anal sex plays a role.
First signs
The first symptom of condylomatosis is the formation of growths on the vaginal mucosa and labia. These small warts are usually found on the vulva.
Other severe symptoms:
- significant discharge with purulent contents;
- feeling of itching, inflammation in the vagina;
- irritation in areas of the mucous membrane;
- bleeding during washing and sexual contact (injury to neoplasms).
The symptoms described above also accompany some other diseases to which women are susceptible, for example, when thrush or gardnerella appears. Therefore, if any suspicions arise, you need to contact a gynecologist.
Clinics specializing in diagnostics and treatment in Moscow:
- Solntsevo Belomorskaya Orekhovo
Diagnostic methods
A qualified gynecologist can make an accurate diagnosis for condylomas and viral warts in the vagina. Based on the examination, the specialist draws conclusions about the development of papillomavirus infection. Additionally, the woman is prescribed an extended colposcopy and PCR test.
A cytological examination of a smear from the cervical canal area allows one to identify atypical cells and confirm or exclude the presence of dysplastic processes in the cervix. Immunological studies help determine antibodies to papillomavirus in the blood. Additionally, it is necessary to conduct screening for common sexually transmitted diseases and HIV infection.
Types of condylomas
There are two main types of condylomas:
1. Pointed.
When examining the vagina, you can see growths that resemble papillae.
This type of condylomas is called genital warts. They look like a neoplasm on a leg, most often they are flesh-colored. They can appear either singly or in groups. Usually located on the walls of the vagina. 2. Flat.
These growths are difficult to notice. The shape of condylomas can be round or oval. The growths are not distinguished by their shade and merge with the mucous membrane. Neoplasms have a slow growth rate and do not cause discomfort to the woman. Diagnosis of condylomas When suspicious growths are detected, consultation with a gynecologist is a mandatory procedure. The examination involves the following activities:
- examination in a gynecological chair;
- examination of a smear from the cervical canal;
- colposcopy;
- blood analysis;
- histology;
- PCR diagnosis.
There is a guaranteed way to diagnose condylomas in the vagina - using a vinegar solution. The mucous membrane of the labia should be treated with vinegar. As a result, a spasm of the vessel occurs, which feeds the skin tumor. Over time, the growths will lighten and stand out, due to this, their exact number and diameter can be determined. It is even possible to see subcutaneous tumors that are located in the deep layers.
Treatment options
Methods for getting rid of condylomas in the vagina involve radical removal of growths and conservative treatment, supplemented with traditional medicine. Only the doctor decides how to treat condylomas. Conservative therapy There are many conservative ways to treat condylomas of the anal area, vulva, and vagina. This is the use of antiviral drugs, cytostatic agents, drugs with a general strengthening effect, and immunostimulants. If the growths are located in the area of the vulva, and their coverage area is no more than 10 cm2, you can use cauterizing agents (Condilin, Podophyllin, Verrucatsid, Collomac, Solcoderm). These are drugs that cause necrosis of the treated surface. Therefore, medications are not recommended for the treatment of the anal area and urethra. Prohibited when carrying a child. Removal of condylomas in the vagina is usually done surgically, sometimes supplemented by the use of antiviral drugs. This group includes Panavir, Interferon, Isoprinosine. Therapy is often supplemented by the use of drugs that increase immunity, for example, Polyoxidonium, Aldara, Immunal. Radical treatment Today, to get rid of condylomas, electrocoagulation, cryodestruction, surgery, laser vaporization, and a radio wave knife are used. But not all methods are suitable for treating condylomas. The use of nitrogen in this case is more traumatic and not as effective as other methods. As for the surgical removal option, this process is invasive and is prescribed only in very severe cases. When treating, the choice is generally made in favor of an electrocoagulator, a radio wave knife and a laser. All these methods are used under anesthesia, so they do not cause discomfort to the woman during surgery. They are practically non-traumatic, unlike surgical intervention, they have a fast healing time. The difference lies in the operating principle of the device. A radio wave knife and laser evaporate infected tissue layer by layer. The electrocoagulator cauterizes the growths by applying current at high frequencies. Any of the methods has certain contraindications, but, in general, these treatment methods can be used to remove tumors in women on the clitoris, labia minora, cervix, and vagina. Folk methods Turning to folk methods, you can find many recipes that are recommended for getting rid of growths. The most popular remedies include celandine juice. It is used to get rid of various skin growths. But during the processing process, you need to act carefully so that the composition does not get on healthy tissue. Iodine can help cure condylomas, as it has a drying effect. The product can only be used on the surface of the skin; if applied to the mucous membrane, a burn will occur. Traditional recipes also have certain contraindications. In addition, none of them are suitable for getting rid of condylomas in the vagina. Therefore, folk treatment can only complement the main one. Before use, you should definitely consult your doctor. Condylomas during pregnancy Growths during pregnancy are also common. In this case, of course, there are certain features that need to be taken into account both during conservative treatment and when removing the tumor using various methods. The formation of growths provokes, first of all, the appearance of hormonal imbalance, as well as a weakening of the immune system during gestation. Large condylomas will affect the birth process and complicate it. When diagnosing condylomas, doctors recommend giving birth to a child by caesarean section.
How and what is the best way to remove condylomas
The gynecologist at our clinic will conduct a comprehensive gynecological examination to identify these formations and begin treatment only after the necessary examination and confirmation of the diagnosis! This will allow you to cauterize condylomas in intimate places quickly and without complications. At the following link you can read about what tests you need to take for condylomas.
PRELIMINARY DIAGNOSTICS
- Examination on the chair,
- Extended colposcopy,
- Flora smears, PCR,
- HPV tests,
- Cytological analysis (according to indications),
- Biopsy of the cervix (if indicated),
- Anoscopy or rectoscopy (according to indications),
- Blood tests - hepatitis B and C, syphilis, HIV.
Radio wave removal of condylomas
Depending on the results of HPV tests and indications, the treating doctor selects the most suitable method for removing intimate papillomas (radio wave surgitron or solcoderm). If you choose a clinic in Moscow where to remove condylomas from intimate places, prices can be found at the bottom of the page. Please note that our gynecologists perform this procedure under modern local anesthesia, absolutely without pain, so even young patients avoid unnecessary anxiety and unnecessary stress!
Removal of condylomas using the radio wave method (Surgitron or Fotek) has such advantages as speed, absence of long-term cosmetic defects and postoperative complications. Gynecologists resort to chemical methods (Solcoderm) mainly in cases of single, few formations of the mucous membrane of the external genitalia.
Preventive actions
After getting rid of HPV, lifelong immunity does not appear. The growths in the vagina may reappear after treatment. This happens due to the activation of a virus already in the body or due to infected sexual partners.
Preventive measures consist of:
- strengthening the immune system;
- healthy lifestyle;
- prohibition on uncontrolled sexual relations;
- using condoms during sexual acts;
- timely treatment of diseases;
- periodic examinations by a doctor.
These simple tips will reduce the risk of condylomas in the vagina and curb the activity of HPV, which is already present in a woman’s body. And if symptoms begin to appear again, you need to urgently consult a doctor.
Genital warts, genital warts (AC), exophytic warts, venereal warts, Genital warts in the English literature - benign formations caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV) 6, 11, 30, 42, 43, 44, 45, 51, 52 types, but in 90% of cases types 6 and 11 are found. Genital condylomas have the appearance of warts, papillomavidous or broad-based formations. Histological examination reveals a picture typical of the cytopathogenic effect of HPV - thickening of the epidermis, acanthosis, thickening and elongation of interpapillary wedges, koilocytosis of superficial keratinocytes [4]. Most people who become infected with HPV, including the low-oncogenic type, do not develop symptoms of the infection. The source of infection, of course, is a sick person. In 65% of people, clinical manifestations occur within 90 days after contact with a sexual partner, although the exact timing is unknown, since it is impossible to reproduce the disease in experimental animals. Sexual transmission is not the only route for genital warts; the household route is equally dangerous - through contaminated underwear, hands; infection of a child during childbirth is well known. The established fact of positive HPV tests in pubic hair follicles is very important. It is known that in healthy men, HPV is detected in 17-21% of cases; in patients with genital warts, pubic hair follicles are infected in 32-55%. Thus, regardless of the type of sexual contact, skin-to-skin contact is dangerous [6]. This “unpretentiousness” of the virus in choosing its habitat determines the extreme prevalence of both the pathogens themselves and the diseases they cause. The lowest frequency of OC lesions was recorded in Russia - 34.7 per 100 thousand population (2009), while in Germany (2006) the frequency of exophytic condylomas in young women was 462 per 100 thousand, in England and Wales (2000) - 715 per 100 thousand population (cited from 2). There is probably an underestimation of this pathology in Russia. The most important feature of low-oncogenic HPV types is their ability to associate with highly oncogenic ones. Every fourth patient with AC is diagnosed with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia of varying severity [7], and removal of genital warts does not eliminate viruses of high oncogenic risk. This is what determines the development of cervical or vaginal cancer in women who have OK. It should be noted that genital warts can also be accompanied by a rare type of cancer - verrucous (giant cell condyloma of Buschke-Levenshtein). It is associated with viruses of types 6, 11 and has a tendency to local invasion.
Factors that contribute to the persistence of HPV infection are well known: age under 21 years at first sexual intercourse, 4 or more sexual partners in a lifetime, immunodeficiency conditions, and the presence of other STIs. From a practical point of view, atopy is a very important suppressive factor, no matter what clinical forms it has, which affects the therapeutic effect and the high probability of relapse in patients with genital warts. There are many myths about genital warts: for example, warts only occur during unprotected intercourse. But, unfortunately, even “protected sexual intercourse” does not guarantee safety, since condoms are not able to protect the skin of the pubis and perineum, where the infection also persists.
Diagnosis of OK is simple; genital warts are well identified visually and when examined with a colposcope. Condylomas are localized on the cervix, vaginal walls, perineum, perianal area, and the external opening of the urethra and clitoris are often affected. Colposcopically, condylomas may appear as pointed growths, have a rounded papule-like shape, or resemble papillary formations. The size of the growths varies - from small single ones to massive ones, blocking the entrance and vaginal cavity. A biopsy of condylomas is carried out if the diagnosis is unclear, there are signs of atypia, warts are stained, their increased density and fixation on the underlying tissues, bleeding or ulceration.
Clinical symptoms do not always depend on the degree of damage. There are often situations when, in the presence of single OCs, itching, burning in the vagina, constant discomfort or discomfort during sexual intercourse, and even pain are bothered, while extensive lesions do not cause any complaints. If OK is obvious, HPV testing is not recommended because it will not lead to a change in treatment.
Genital condylomas should be differentiated from molluscum contagiosum, squamous cell papilloma, condyloma lata, fibroepithelial polyp, and much less often from dermatitis and psoriasis.
Molluscum contagiosum is caused by a DNA pox virus. Typical for this disease are single or grouped small, smooth papules 3-6 mm in diameter with a pinpoint depression in the center. The rashes, even if they are multiple, never stick together, although they can form plaque-like foci.
Squamous cell papilloma is a multiple papillary formation located in the vestibule of the vagina below the hymen ring. Sometimes papillomas are localized on the medial surface of the labia minora. Papillomas are covered with stratified squamous epithelium and are often an accidental finding in the absence of complaints. Their connection with HPV has not been proven, the origin is unclear.
Fibroepithelial polyp is a benign papillomatous formation without vascular atypia, histologically it has characteristics characteristic of a polyp.
Condylomas lata with syphilis are flat, dense, pink-red formations on a wide base.
If you suspect dermatitis, psoriasis, or in unclear cases, consult a dermatologist. It is worth remembering about vulvar and vaginal cancer, where only a comprehensive assessment will allow you to avoid mistakes.
There are two approaches to the treatment of genital warts: traditional - complete elimination of all lesions or removal of condylomas as a cosmetic nuisance. There is no consensus regarding male HPV carriers without clinical manifestations. Currently, preventive treatment for men is not accepted, since there is no reliable data on its effectiveness. Spontaneous recovery is known - the reverse development of genital warts in 29-39% of patients. Often, children in whom the appearance of condylomas at the age of 2-3 years is associated with intrapartum infection are spontaneously cured. The effectiveness of various methods of treatment of OK, even taking into account repeated courses, is 60-80%. Relapses in 25-50% of cases occur within the first 3 months after treatment and are most often caused by reactivation of the virus [5]. Destructive physical treatments are the most popular, and the first choice of method may be electroexcision, laser vaporization, cryosurgery, radio wave excision or photodynamic therapy. Electroexcision frees viruses within a radius of 20 mm from the center of the lesion. Conservative treatment of small lesions is carried out with podophyllin, trichloroacetic acid or solcoderm. In English-speaking countries, 5% imiquimod cream (Aldara) or 15% synecatechin ointment is used, treatment is carried out for 16 weeks. There is currently no evidence that local interferon injections lead to regression or reduction in the recurrence rate of genital warts.
Material and methods
We tested various types of therapy (medicinal and destructive) in 397 women with genital warts of the vagina and vulva; in some we used the domestic drug Panavir, which is available in various forms: injection solution, suppository and gel. The mechanism of action of the drug is multifaceted and, as experience shows, its use is effective for various viral diseases. The drug prevents adhesion and inhibits the penetration of the virus, stops the opening of the viral capsid, disrupts the transcription and replication of viral DNA, the synthesis of capsid proteins, stops the assembly of viral particles and their exit from the cell, and has a complex immunomodulatory effect [1, 3]. The basis of the drug is a biologically active heteroglycoside - panavir.
The age of the patients ranged from 16 to 40 years, all women complained: 119 (30.1) experienced itching and discomfort in the vagina, 90 (22.8) had chronic leucorrhoea, 88 (21.8) had discomfort during sexual intercourse. 5%), recurrent candidiasis - 5 (11.3%), cosmetic defect bothered 55 (13.9%). Viruses 6, 11 types were isolated from 327 (82.2%) women, of which 48 were in combination with HPV types 16, 18, 25 were isolated from types 42, 44, 51, 45 were not infected with HPV was found. Two women had massive lesions, the rest had condylomas of the vagina or vulva with an area of 5-8 cm2. Among concomitant infections, chlamydia was found - in 35 (19%), herpes virus - in 19 (4.8%), ureaplasma - in 97 (24.4%), Candida
- in 49 (12.3%), trichomonas - in 9 (2.2%). The remaining patients had nonspecific bacterial microflora in various titers. Chronic cervicitis was noted in every third woman with OK, bacterial vaginosis - in every fourth, colpitis - in every fifth. Stage I cervical epithelial dysplasia was diagnosed in 48 (12.1%) patients.
At the first stage of treatment, the concomitant infection was treated in accordance with the identified pathogen, followed by antiviral therapy with Panavir in 140 women (group 1). The comparison groups included 165 women (group 2) who received only electrical excision of condylomas and 92 patients (group 3) in whom electrical excision was supplemented with the use of α-interferon in suppositories vaginally for 2 weeks after surgery.
The treatment regimen with panavir of the 1st group consisted of using a combination of two forms of the drug: rectal suppositories (1 suppository every other day, N10) and vaginal gel 2 times a day for 14 days. After antiviral therapy, condylomas were removed by electroexcision.
Results and discussion
The results were assessed by the frequency of relapses, elimination of viruses and regression of complaints (see table).
As follows from the table, the most effective method was the use of Panavir and subsequent electroexcision of condylomas compared with the results in groups of women who received only electroexcision or its combination with the use of α-interferon. It should be noted that immunocorrection in the treatment of HPV is necessary and this fact is generally recognized. Local therapy is more effective if accompanied by the use of systemic immunomodulatory drugs, as this leads to a more lasting anti-relapse effect. This was confirmed in our study by the fact of elimination of viruses, including highly oncogenic types. Of the 28 women of the 1st group with combined HPV types 6, 11, 16, 18, negative results of the polymerase chain reaction test were found in all of them; moreover, herpes viruses were not found during repeated analysis. Subjective sensations of discomfort in the vagina also disappeared in all patients. Among patients in group 2, 18 women had combined HPV infection caused by viruses of low- and high-oncogenic types. The performed electroexcision had no effect on their presence, and the persistence of these types of virus remained. Viruses 6 and 11 types were isolated from 59 (35.7%) of 165 women in this group, which probably determined the high rate of relapses 3 and 6 months after treatment, as well as the persistence of complaints in every third patient.
The use of electroexcision and α-interferon in the postoperative period led to the elimination of viruses in 76.2% of women. Highly oncogenic types of the virus identified in 2 women in this group persisted after treatment. Symptoms such as leucorrhoea continued to bother me (in 16 women) and itching in the vagina persisted (in 12). It should be emphasized that our proposed treatment regimen with Panavir differs somewhat from that recommended by the manufacturer, but purely empirically this option was accepted as optimal. Only local use of Panavir gel in combination with destructive methods is equal in effectiveness to the use of a combination of α-interferon and the destruction method, while the combination of a fairly long-term systemic treatment with Panavir (rectal suppositories) and local therapy (vaginal gel) in combination with the destruction of condylomas gives a good lasting effect .
The cost of treating genital warts is high worldwide. Relapses of the disease, repeated courses of therapy and, at the same time, insufficient effectiveness lead to an increase in the cost of treatment so much that it can be compared with the treatment of AIDS. The use of Panavir in the proposed version is a one-time cost, but it is highly effective, amounting, according to our data, to 99.3% at 6-month follow-up and 92.5% at 2-year follow-up. The ability of the drug to provide an immunomodulatory effect, proven in numerous studies, and an antiviral effect in various diseases is encouraging in the treatment of infections caused not only by low-oncogenic HPV types, but also by highly oncogenic ones, which can help prevent cervical cancer.
conclusions
1. The proposed treatment regimen for patients with genital condylomas with a combination of fairly long-term systemic and local use of Panavir in combination with subsequent electrical excision of condylomas gives a good and lasting effect.
2. The ability of Panavir to have an immunomodulatory and antiviral effect is encouraging in the treatment of infections caused not only by low-oncogenic but also highly oncogenic types of HPV.
Behavior after removal of condylomas
Inform the patient that it may take 1 to 6 months for condylomas to disappear. During this time, relapses of the disease are possible, but a complete cure will still occur.
Reassure the patient that due to the long persistence of the virus after infection (the presence of the virus in the body in an inactive state), the appearance of condylomas in only one sexual partner in a permanent relationship does not mean sexual contact on the side of the other partner.
Smokers who do not respond well to treatment should quit smoking, as there is a link between smoking and genital warts.
Advise the use of a condom to reduce the risk of recurrent or additional infection.
It is recommended to avoid excessive solar radiation (tanning) and use sunscreen while vacationing in the south, since excessive sun exposure stimulates the development of the virus, if present in the body tissues.
Warn about the inappropriateness of various warm-ups (sauna, steam bath, hot bath), this can also provoke the activity of the human papillomavirus when carrying the virus.