How to distinguish diseases
To begin the fight against the disease, it is necessary to identify the disease. You need to pay attention to the nature of the rash: its color, peeling, discomfort and the condition of the skin next to the plaque. Each pathology has distinctive symptoms that cannot be ignored.
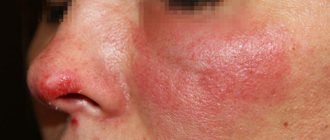
Ringworm spots often appear one at a time on the forearms, legs, face or torso. The rashes are dry, flaky and itchy. Allergic lichen has a clear outline, but this symptom also applies to other types. The appearance of multi-colored skin is often confused with pigmentation: small dark spots are noticeable on the body, which slowly grow and merge into large burgundy lesions. There is no itching, but the patient may notice peeling of the skin with the appearance of light scales. Lichen ruber, on the contrary, itches a lot, but does not peel off. As can be seen in the photo, the affected surface is shiny and smooth.
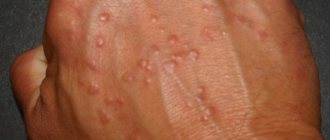
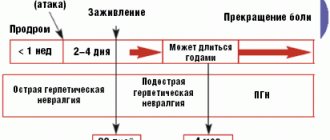
Shingles appears due to the herpes virus (almost all children get it in childhood, the name of the disease is “chickenpox”) and affects the back, chest and abdomen. Small red blisters with liquid inside form on the body, itching and causing pain. Painful sensations are explained by damage to the nervous system. If the disease is not treated, it may develop into neuralgia in the future.
Ringworm (in other words, trichophytosis or microsporia) affects smooth skin, nails and scalp. The spots quickly spread throughout the body, covering new areas; the disease can infect surrounding people. The rashes have a light pink color, a clear shape and contours. Affected hair breaks off or falls out, and profuse yellow dandruff appears.
Eczema is very similar to lichen, but it is possible to distinguish it. In appearance, the two pathologies are similar: the skin is dry, flaky, inflamed and has a reddish tint. When you scratch the lichen, dead cells of the dermis come off, but if you scratch the eczema, a weeping wound appears. You cannot delay going to the doctor, otherwise the disease will affect large areas.
All types of dermatitis have a common symptom - a chaotic rash anywhere on the body. Unlike lichen, with all dermatitis the skin is inflamed and swollen. The contours of the rash are unclear, rough spots of different sizes, several lesions can merge into one large plaque. Most often, dermatitis appears after contact with chemicals or cosmetics after a short period of time. In a child under one year of age, dermatitis is the body's reaction to unsuitable washing powder, shampoo, soap or diapers.
A non-contagious pathology is psoriasis, which at first glance also looks like lichen spots. If you examine the plaques on the skin in more detail, you will be able to make an accurate diagnosis. The rash also peels off and becomes covered with a white coating, but when scratched, it first becomes wet and then begins to bleed. The disease tends to progress quickly, for this reason it is worth consulting a doctor as soon as possible.
Sakania Luiza Ruslanovna
Dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist, trichologist
Ask a Question
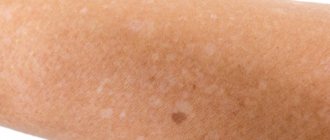
The last similar defect is pigmentation of the dermis, which appears when the production of melanin is impaired. The rash can be pink to brown. There is no peeling, itching or pain, no fluid or blood is released when scratching. Pigmentation often occurs on the arms, legs, face or chest, but never affects large areas.
Reasons for the development of pink lichen of Zhiber
Although the disease has been known for a long time, its pathogenesis still remains unclear. Various factors and pathogens have been proposed as causes:
- infectious;
- viral;
- bacterial;
- fungal;
- Mycoplasma pneumoniae;
- “toxic rash due to unknown gastrointestinal infection”;
- insect bites;
- isomorphic response;
- autoimmune disease;
- psychogenic cause.
Insect bite
Early research suggested a connection to new, unused clothing. Lassar and Rosenthal attributed this role to flannel and knitwear.
The development of a peculiar skin plaque was observed at the site of insect bites, especially fleas, as well as on old scars, with healing gunshot wounds, and at the site of intramuscular injections, which suggests that pink dandruff is simply an isomorphic reaction.
Some scientists have tried to show that pityriasis rosea is a psychogenic disease and is more common in "highly stressed" or mentally ill people. According to them, stress can aggravate the lesion and cause itching. Others consider the psychosomatic theory unlikely.
Attempts have also been made to hypothesize that RP is a “toxic rash of gastrointestinal infection,” the result of dietary error and gastric dilatation.
In 1970, Birch and Rowell postulated an autoimmune cause of the disease, in which the predisposition was genetically determined and sensitized by microorganisms.
However, the infectious background of the disease is most widely considered. Clinical features of the pathology, such as the irregular occurrence of prodromal symptoms and the severity of morbidity in the autumn-spring period, indicate a viral etiology. There appears to be an association with a recent upper respiratory tract infection in some patients.
The spread of the disease in the family, among children at school, among soldiers in the barracks, among people using Turkish baths has not been confirmed, so many experts believe that it is a non-infectious disease.
However, pityriasis rosea has been found to be more common among dermatologists than among otolaryngologists, suggesting that it is spread through contact with low infectivity, leading to increased incidence with increasing number of contacts.
In addition, the pathology is more common in people with weakened immune systems, for example, pregnant women and patients with bone marrow transplantation. Spontaneous resolution and relapses, occurring in less than 3% of patients, are also consistent with the theory of a viral origin of the disease.
There is some objective evidence to support the viral theory of the disease. In 1968, scientists demonstrated the presence of picornavirus-like intranuclear bodies in the tissues of African green monkeys inoculated with a liquid that affected the color of the lesions, and in electronic sections of these lesions. However, none of the studies have identified the genome of picornaviruses. Pityriasis rosea has also been described in a patient with proven Echo virus infection.
The HHS-7 virus, a Roseola virus from betaherpesviruses, is also suspected. Viruses of this family cause acute and chronic infections. They can also remain latent for many years, and a weakened immune system leads to their activation. HHS viruses have been detected in children with RP and adults with pink dandruff in serum, white blood cells, and biopsies of skin lesions.
However, the relationship between pityriasis rosea and HHS-7 remains controversial according to some scientists, due to the low DNA sequence index of HHS-7. The virus has also been detected in the plasma of healthy people.
It has been suggested that the disease is associated with bacterial infection, including syphilis and tuberculosis. In 1942, student. Benedek explained the occurrence of the disease by the reactivation of latent foci of Baccillus endoparasiticus.
The role of Staphylococcus albus and hemolytic streptococci was also increased. In recent years, infections with Legionella micadadei, L. longbeachae, L. pneumophila, Chlamydia pneumonie, Ch. trachomatis, but the opinions of dermatologists about their role in the pathogenesis of RP are divided. Thus, the issue of the involvement of these microorganisms requires further research.
The clinical appearance of the mother's plate, with morphological features often resembling a lesion of mycosis, especially ringworm, suggests that the cause of pink dandruff may be a fungal infection.
Some medications also sometimes cause skin lesions similar to pityriasis rosea. Among them:
- captopril;
- metronidazole;
- isotretinoin;
- D-penicillamine;
- levamisole;
- diphtheria toxoid;
- bismuth;
- gold;
- barbiturates;
- ketotifen;
- clonidine;
- terbinafine;
- omeprazole
Pityriasis rosea has been reported following administration of BCG, IFN-alpha and hepatitis B vaccines.
Now scientists are inclined to conclude that such a reaction of the body can be caused by various factors, and this is very important to take into account when diagnosing pathology. By identifying the suspected cause, you can quickly and permanently get rid of unpleasant symptoms.
The most likely reasons are a weakened immune system and the activation of one of the types of herpes viruses against this background. Therefore, it is necessary to consider all causes that weaken the immune system.
Methods for dealing with spots on the body
In order to get rid of body rashes forever, you need to undergo an examination. Only a specialist can make a correct diagnosis and prescribe effective therapy. Each disease is treated differently; the patient's age, health status and other factors should be taken into account. Depending on the type of spots, a person may be prescribed one of the following treatment methods:
- Pityriasis rosea goes away on its own; for other types, the patient is prescribed the use of antifungal agents in the form of tablets or ointments. Antihistamines - Loratadine, Clemastine, Tavegil - will help relieve itching. It is allowed to treat the affected skin with Zinc ointment or creams with glucocorticosteroids. Such products will have an anti-inflammatory and disinfecting effect, which will significantly speed up the restoration of the dermis. During therapy, it is recommended not to wet the affected skin so as not to cause the spread of lichen.
- Dermatitis can be cured, but the course of treatment sometimes takes several months. It is necessary to find out the cause of the rash, remove inflammation and restore the diseased epidermis. If the rashes are very itchy, the patient is prescribed anti-allergy medications in the form of tablets or creams for topical use. In case of a large affected area, treatment should be carried out with hormonal medications - Betamethasone or Prednisolone. Sometimes you need to resort to sedatives or sedatives to restore sleep, disturbed by itching and poor health. It is allowed to apply bandages with silver or boric acid to the spots. It is better to treat the skin with brilliant green, furatsilin or other antiseptics.
- To treat an allergic rash, it is imperative to avoid contact with possible irritants. During therapy, it is better to adhere to a diet without exotic foods. It is recommended to replace your usual cosmetics or care products with fragrance-free baby soap and cream. Antihistamine tablets will help with itching. If you were unable to identify the irritant yourself, you will have to visit an allergist and take samples. Sometimes allergies appear in adulthood even to familiar foods.
- It is impossible to completely cure psoriasis. It is necessary to adhere to the therapy prescribed by the doctor to prevent the condition from worsening. It usually involves the use of keratoplasty preparations, emollient creams and hydrocortisone-based products. Sometimes the patient needs to undergo a course of photochemotherapy (UV radiation along with special medications) to stop the spread of lesions throughout the body.
You should start drug treatment only as prescribed by your doctor. Independent use of any pharmaceutical products, especially for young children, can lead to worsening. However, you can try to get rid of rashes using traditional medicine recipes. They are able to relieve discomfort and restore health to the skin; these products need to be applied for a long time to notice the result.
If there is no itching, pain or swelling, you can use available products. Mumiyo, birch tar or tar soap will quickly restore the dermis, lighten it and heal small wounds. The products are applied to the skin several times a day and left until dry. Tar soap can replace shower gel; it dries the skin perfectly and removes inflammation. You can try to burn out the stains with garlic and lemon juice, but it is better to consult a doctor before using. Squeeze the juice out of 2 cloves of garlic and mix with a tablespoon of lemon juice, mix thoroughly, and then apply to the rashes. The resulting solution will have a disinfecting effect, but a burning sensation may occur during use.
If spots on the skin similar to lichen appear, it is recommended to visit a dermatologist or therapist. Sometimes the rashes do not bother you for a long time, but at the same time healthy cells are affected. In addition to the spread of lesions throughout the body, infection of family members or surrounding people is possible. There are many reasons for the appearance of a rash; only a specialist can accurately determine the type of disease after laboratory tests. The duration of therapy depends on how quickly the disease was detected.
You can ask your question to our author:
Diagnosis of pityriasis rosea
The diagnosis can most likely be made based on the history and clinical picture. Differentiation should take into account, among other things:
- mycosis;
- psoriasis;
- seborrheic dermatitis;
- drug allergies;
- eczema;
- parapsoriasis.
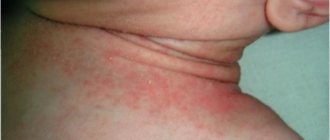
Seborrheic dermatitis
These diseases produce similar symptoms, but require special treatment.
To make a diagnosis, you need to carry out a number of special tests, for example, scrapings of the affected areas, serological studies. Blood and urine tests are also prescribed to understand whether there is inflammation in the body and its consequences.
Some patients, after reading articles from the Internet and looking at pictures, make a diagnosis for themselves, refusing tests. The result of such behavior is often sad. As a result, they get advanced contagious lichen or another equally unpleasant disease.
Infections
Sometimes red spots on the skin indicate the presence of a certain infectious disease.
Such diseases include:
- chickenpox;
- scarlet fever;
- rubella;
- measles;
- venereal diseases (syphilis).
In any case, to find the right treatment, you need to see a doctor.
Photos of manifestations of infectious diseases
Syphilis
When suffering from syphilis, the appearance of red spots on the patient’s skin is considered to be the primary and secondary signs of this disease.
Stages of syphilis:
- The primary stage lasts about seven weeks. The red spot first appears flat and small in size. After a few days, the spot grows in height, becoming a noticeable bump. After this, the process of tissue death begins in the center of the tubercle. As a result, an ulcer remains on a person’s skin, ringed with hardened edges - a chancre. It does not cause painful sensations.
- Second stage Syphilis is much more diverse, which makes it similar to other diseases. It is characterized by a rash on the skin, the so-called syphilitic rash. The rash usually has the following features:
- the color of the rash is red, dark in color;
- characteristic unpleasant sensations (itching, pain) are absent;
- the rash is round, clear, does not increase in size and does not merge;
- the rashes are densely located;
- peeling is weak or completely absent;
- Self-healing is possible without atrophy and scarring.
Manifestation of syphilis in the photo
Which doctor should I go to if my child has shingles?
As we have already mentioned, a doctor who diagnoses and treats dermatological diseases is a dermatologist. Since the structure and functioning of the skin of a small child is significantly different from the skin of an adult, it is the pediatric dermatologist who should make the diagnosis.
Features of children's skin that determine high sensitivity to external irritants and pathogens are:
- skin thickness (in an adult it is three times thicker);
- loose epidermis;
- lack of elastic fibers;
- weak ability to form skin pigments (low protective function);
- low degree of thermoregulation, etc.
Diseases of the skin and its appendages (hair and nails) can be a consequence of various pathological processes in the child’s body (systemic or autoimmune diseases, etc.), so additional consultation with a pediatric neurologist, immunologist, infectious disease specialist or other specialists may often be necessary.
Allergy
Red spots on the skin may be signs of an allergic reaction to something. More precisely, one of the types of allergic reactions, since it can manifest itself in different ways. Spots on the body appear due to the body’s contact with an irritant - it can be different, from food to various medications.
Photos of allergies
Most frequently asked questions from patients
What causes pityriasis rosea?
There is no clear answer to this question. Research continues. Presumably, the cause may be herpes virus type 6 or 7. When immunity decreases, it becomes more active, which triggers the process of various types of rashes (plaques, vesicles, blisters). The disease can be triggered by stress, poor ecology, hormonal fluctuations, and chronic diseases.
Is pityriasis rosea contagious?
Pityriasis rosea in humans is considered non-contagious, but rare cases of the disease affecting entire families are known. Much depends on the state of the immune system and the body’s defenses, which can resist viruses, bacteria and infections.
Is it possible to sunbathe with pityriasis rosea?
One type of therapy for this dermatological disease is light therapy. Moderate exposure to ultraviolet radiation has a positive effect on the condition of the skin, stimulating its regeneration. Combustion must not be allowed. This will lead to increased itching in the area of the spots.
Eczema
Eczema is another unpleasant skin disease characterized by inflammatory processes on the human skin. In most cases, it begins in childhood, and adults usually get it only if it was treated incorrectly in childhood, and by its nature it has developed into a chronic illness.
Eczema has the following symptoms:
- at the site of inflammation, the skin becomes reddened (occasionally blue), slightly thickened;
- gradually a rash forms at the site of inflammation, often with blisters of liquid;
- the skin itches unpleasantly, up to a constant, incessant effect;
- when the blisters are damaged, the skin in their place becomes covered with wounds and cracks;
- possible increase in body temperature;
- after the inflammation has passed, the skin remains dry and very susceptible to cracks.
The disease can appear on any part of the body, but according to statistics, the arms (in particular, the palms) and legs are most often affected.
Photo showing the manifestation of eczema
We present a photo of eczema to distinguish it from other diseases.
Incorrect treatment of pityriasis rosea
- Lubrication with iodine, brilliant green
. These antiseptic drugs do not provide results in the treatment of pink dandruff. The virus is located deep in the skin, so iodine or brilliant green cannot affect it, but at the same time they dry out the skin, causing a burn. - Celandine
. The poisonous sap of the plant leads to damage and inflammation of the skin. Celandine causes burns, increasing the risk of complications. - Zinc ointment
. Causes skin tightness. - Salicylic acid, alcohol
. Ineffective against the virus. Dries and irritates the skin, increasing peeling. Leads to hyperpigmentation. - Vinegar
. Dries out the skin and increases peeling.
To treat Gibert's disease, you can only use products prescribed by a dermatologist.
Description of the disease
Depending on the type of lichen, the rash may be dry or weeping, pale pink or bright red.
Most often, the disease affects the back, face and chest of the child (it is in these areas that the largest number of sweat glands are located). The disease is infectious in origin and is caused by viruses or fungi. The disease most often manifests itself in the spring-summer season, when it is warm and humid outside. At the moment, a large number of varieties of lichen are known. Many of them are highly contagious and potentially dangerous to the child’s immediate environment. That is why, if there is any suspicion of an infectious disease, it is necessary to immediately show the patient to a qualified specialist.