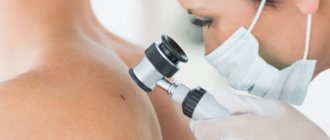
Eyelid melanoma is an aggressive malignant tumor that develops from melanin-producing cells and is located on the upper or lower eyelid. However, this is not the only neoplasm that develops in this area, but it is the most malignant and, fortunately, the rarest. Melanoma of the eyelid is diagnosed in approximately 5-7% of all melanomas. It develops mainly in people of the older age group. The peak incidence occurs at 50-60 years of age.
- Types of eyelid tumors
- Causes of development of melanoma of the eyelid
- How is eyelid melanoma diagnosed?
- Methods for treating eyelid melanoma
- Prognosis for recovery from melanoma of the eyelid
Types and causes of moles
Among the most common nevi that occur near the eyes or on the eyelids themselves, there are four types:
- Intradermal. They form in the deep layers of the skin and visually resemble a small ball. The color is dark (brown or black).
- Vascular. They appear as pinkish or reddish bumps (consisting of a collection of blood vessels). Often appear as a result of abnormalities in the functioning of the capillaries.
- Epidermal (hanging). The most common neoplasms are flesh-colored or dark brown.
- Mixed (flat). They are located between the epidermis and dermis and are light brown or dark brown in color.
A mole near the eye can appear for various reasons. Their growth is facilitated by a number of factors, including: genetic predisposition, hormonal imbalance, puberty, pregnancy, uncontrolled use of certain medications, prolonged exposure to direct sunlight.
Causes of development of melanoma of the eyelid
Why melanoma occurs in the eyelid area is not completely known. As with most cancers, this tumor develops due to mutations that have occurred in melanocytes. As a result, they gain the ability to reproduce uncontrollably and spread to neighboring tissues.
Several risk factors have been identified, the presence of which increases the likelihood of developing eyelid melanoma:
- Belonging to the white race. The risk of developing melanoma is especially high in people with light skin color.
- Age over 50-60 years.
- The presence of dysplastic nevi in the eyelid area.
- Excessive insolation.
- Sunburn.
- The presence of melanoma in close blood relatives (hereditary predisposition).
Advantages of laser technique
The tumor can be removed in different ways: cryodestruction, using a scalpel, radio knife or laser. The latter method is most preferable when working with nevi located on the face. The laser acts on the tumor with high precision, evaporating its cells layer by layer. Its main advantages include:
- minimal trauma;
- complete security;
- eliminating the appearance of new formations in the area of mole removal;
- no risk of bleeding;
- saving time (the procedure lasts about 5-10 minutes);
- short postoperative period;
- absence of scars and cicatrices.
Are there any restrictions after deletion?
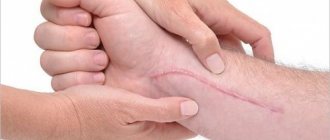
When removing small moles on the eyelids, contrary to popular belief, I do not recommend limiting yourself in water procedures. This is due to the fact that the operation is performed without completely cutting the skin and without suturing. In order for patients to understand the scope of the operation more clearly, I usually give an analogy with a small scratch on the skin.
Unfortunately, there is still one limitation. Direct sunlight should be avoided at the extraction site for 2 months from the date of surgery. This is necessary to obtain a good cosmetic result.
Indications and contraindications for tumor removal
A specialist may recommend removing a nevus near the eye if it causes severe discomfort, has uneven edges, bleeds, quickly increases in size, or changes color. Some moles are prone to malignancy, which is also an indication for removal. Doctors often advise getting rid of tumors that can easily be damaged mechanically, for example, with a comb. Patients themselves often resort to surgical intervention due to the unaesthetic appearance.
Despite the safety of the laser technique, its implementation is not always possible. Absolute and relative contraindications include:
- infectious diseases;
- severe cardiovascular diseases;
- abnormalities of the endocrine system (diabetes mellitus);
- pregnancy and lactation;
- exacerbation of chronic pathology.
Also, it is prohibited to remove tumors on the eyelids if there is inflammation and redness. You must first consult an ophthalmologist who will draw up a treatment plan. After recovery, there are no restrictions on the laser technique.
Types of eyelid tumors
Eyelid tumors can be benign or malignant.
Benign neoplasms
Benign eyelid tumors grow slowly, superficially, and do not affect the underlying tissue. Their course is favorable and the reason for visiting a doctor, as a rule, is a cosmetic defect. Most often, benign neoplasms develop from epithelial tissue, but the source can be hair follicles and other skin elements (trichoepithelioma, Malert epithelioma, fibromas, lipomas).
The most common benign eyelid tumors are:
- Papillomas are nodular neoplasms of a dirty yellow or dirty gray color. They can be located on a leg or a wide base. The neoplasm resembles a villous mushroom or cauliflower in appearance. Sometimes it can spread widely throughout the tissue of the eyelid, affecting the tear ducts, conjunctiva of the eyelid and even the paranasal sinuses. May become malignant.
- Senile warts (senile warts) are similar in appearance to papillomatous nevus. It looks like a brown, yellow or grayish nodule, dense to the touch, does not cause pain. Compared to papilloma, they have more pronounced keratinization. Does not malignize.
- Keratoacanthosis - manifests itself as white spots covered with scales. If left untreated, it may become malignant (risk 20%).
- Trichoepithelioma - a neoplasm arises from hair follicles, has the appearance of a dense nodule, 1-3 mm in size, rarely 1 cm. It can be multiple. In some patients, the number of tumors exceeds a dozen. Mostly young people suffer. If left untreated, they can malignize into basal cell carcinoma.
- Syringoadenoma is a tumor growing from the epithelium of the sweat glands. The tumor is a multilocular neoplasm. It grows very slowly.
- Fibroma - has the appearance of a node on a wide base or on a narrow stalk. It grows from mesodermal tissue and can reach several centimeters.
Malignant tumors of the eyelids
Malignant tumors of the eyelids have infiltrative growth and tend to destroy underlying tissues and metastasize. Basal cell carcinoma progresses most favorably. It is also called a semi-malignant tumor. The most aggressive growth is in melanoma. It not only infiltrates the underlying tissues, but also gives distant metastases.
- Basalioma is a type of skin cancer. It looks like a nodule with a ridge-like surrounding. It grows slowly, germinating into the underlying tissue. In advanced cases, it can spread to the structures of the eyeball and even the orbit. Metastases are casuistically rare. Most often, basal cell carcinoma is located on the outer side of the eye, a little less often - on the lower and upper eyelids, and very rarely in the area of the inner corner. When located in the lower eyelid area, the neoplasm proceeds more favorably. The most aggressive growth is in basal cell carcinoma of the inner corner of the eye.
- Skin cancer of the eyelids. Usually this disease is represented by squamous cell skin cancer. At the initial stage, the tumor has the appearance of redness, which eventually thickens and ulcerates. The tumor is prone to infiltrative growth and metastasis.
- Meibomian gland cancer is a very rare type of cancer and has an extremely aggressive course. The tumor is localized in the upper eyelid, looks like a basal cell carcinoma, but grows quickly and metastasizes.
- Melanoma of the eyelids is the most malignant neoplasm localized in this area. The first signs are the formation of a spot with blurry contours, surrounded by an area of increased pigmentation and redness. The stain quickly spreads over the surface of the skin. Also, melanoma of the eyelid can be presented in a nodular form. In this case, it will be a node with vague contours, which is prone to bleeding. It grows rapidly, infiltrating the underlying tissue.
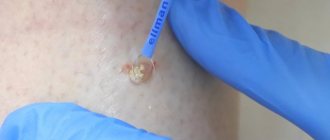
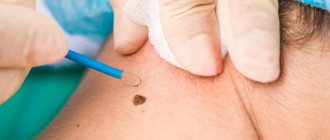
How to remove a mole near the eye using a laser
No special preparation is required for the procedure. In one session it is possible to completely get rid of one or more tumors. The skin is pre-treated with an antiseptic. To prevent the patient from experiencing discomfort, he is injected with an anesthetic substance. Special glasses are used to protect the eyes. If the mole is located on the eyelid itself, during laser technology the eyeball is covered with a soft shield that reliably protects it from external influences.
Next, using the device, the doctor acts on the tumor in a targeted manner. During the procedure, the doctor is able to control the penetration of the laser beam deep into the epidermis (healthy nearby tissues are not injured). Thanks to its sterilizing properties, it is possible to avoid infection or inflammation in the treated areas. After the procedure, a small depression remains, which completely levels out within 10 days.
How to safely and quickly remove a mole on the eyelid?
In my opinion, the simplest and most convenient way to remove small (up to 6mm) moles on the eyelids is the method of radio wave surgery. It allows you to take into account all the features of this anatomical area, perform the removal in 1 visit and achieve an excellent cosmetic result within 1-2 months after the operation:
- The minimal size and shape of the instrument allows you to remove moles of any size, even the smallest, with minimal damage to healthy tissue
- Syringes with a needle thickness of 0.33 mm allow you to inject an anesthetic into the skin without damaging blood vessels
- Special plastic cornea shields reliably protect the eye during surgery
If you follow all the care instructions, you will soon forget about where the mole was that you lived with for so many years.
Thanks to Svetlana for the photographs provided.
Svetlana also liked the result: A pleasant feature of this method of removal is that after the procedure there is no need for repeated examination, dressings and removal of sutures. The operation itself takes no more than 10 minutes.
Where to have the procedure done in Moscow
Due to the thin and delicate skin, the eyelids are recognized as one of the most difficult areas to eliminate tumors. Therefore, you should entrust your health only to an experienced specialist. Certified surgeon Kirill Viktorovich Listratenkov can safely remove a mole using laser technology. Thanks to extensive experience, a positive result is guaranteed. Other advantages of seeking help from Kirill Viktorovich include:
- competitive prices for services provided (the price list is presented on the website);
- confidentiality (patient data never leaves the medical institution);
- individual approach;
- convenient work schedule;
- free online consultations (you can ask a question online, the doctor will give a detailed answer to it in the near future).
To make an appointment for an initial consultation, just call the number provided or fill out a standard form on the website (leaving your contact information).
Methods for treating eyelid melanoma
The standard treatment for melanoma is surgical removal within healthy tissue. However, with such a complex localization, it is not always possible to carry out a full-fledged surgical intervention, since a large defect is formed that disfigures the person’s appearance. In addition, the anatomy of the eyelid is disrupted, which leads to various consequences for the eye - constant lacrimation, inflammation, eye injury, etc. Therefore, when melanoma is localized on the eyelids, other treatment methods are used, including radiation therapy and minimally invasive surgery.
Close focus radiotherapy in the treatment of melanoma of the eyelid
The essence of the technique is to irradiate the tumor from a short distance with low voltage values. Due to this, radiation is mainly absorbed by tumor cells and minimally affects other tissues. This treatment method is effective only for small, superficial tumors. Irradiation is carried out daily up to a total focal dose of 60-80 Gy.
Radiation therapy for eyelid melanoma
Radiation therapy is the exposure of a tumor to a concentrated stream of ionizing radiation. In the treatment of melanoma of the eyelid, contact radiation therapy has become widespread. For this purpose, a special plate containing radioactive material is used. In appearance it resembles a bottle cap. It is attached to the eye and left for 4-5 days, after which it is removed. As part of radiation therapy for eyelid melanoma, external irradiation can also be used, in which ionizing radiation is generated by special devices.
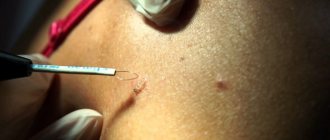
Excision of melanoma with a laser scalpel
A laser scalpel involves dissecting biological tissues due to a sharp increase in temperature in a small area. This leads to the fact that the irradiated area instantly burns, coagulating proteins and “sealing” the wound. A cut 2-3 mm deep appears. To completely remove the tumor, the tissue is cut in layers. The advantage of a laser scalpel is:
- Low morbidity.
- Simultaneous sealing of vessels. This not only eliminates bleeding, but also prevents the spread of melanoma cells.
- Cells are dissected in a non-contact manner, and heating the tissue leads to the death of possible microorganisms in the wound. Thanks to this, the risks of infectious complications are reduced.
The use of electric knife in the treatment of melanoma
When using an electric knife, high voltage alternating current is supplied to the tissue. Because of this, it is locally heated and charred, which leads to the formation of a cut. At the same time, coagulation of blood vessels occurs, which reduces the risks of bleeding and hematogenous spread of melanoma cells. The advantages of this removal method are similar to those of a laser scalpel, but there are a number of disadvantages:
- Trauma to tissue during removal process. This not only leads to the development of an inflammatory response in the dissection area, but also damage to the tumor being removed, which complicates its morphological and molecular genetic testing.
- There is a high risk of keloid scar formation, which in itself is not desirable, especially if it is in the eyelid area.
- Risk of permanent scar formation.
In this regard, the use of electric knife when removing melanoma is limited.
How to protect yourself and your loved ones
You should always remember that any birthmark contains danger within itself. It is impossible to say with certainty that this or that mole cannot develop into a malignant tumor, since there is always a risk. Therefore, such a rare phenomenon as a nevus in the eye should be kept under constant medical supervision.
If the mole is stable and does not bother the patient, then most likely surgical intervention will not be required. In such cases, ophthalmologists usually give simple recommendations to avoid further modification of the growth. The mole must be protected from the harmful effects of ultraviolet radiation, especially during the seasons of solar activity; dark sunglasses will help you with this. Children are recommended to wear hats with a visor.
Possible danger
For a long time, a mole may never bother you, as it happens in most cases, but there are a number of factors, if identified, you should immediately contact an ophthalmologist:
- Changes in the color and size of the nevus;
- Feeling of a foreign body in the eye;
- Decreased quality of vision;
- Limitation of field of view.
All these reasons are characteristic of progressive nevi. Therefore, exhibiting such symptoms is a danger to your vision and overall health. Therefore, you should not try to remove a mole yourself. Remember, the earlier the doctor diagnoses the disease, the easier the treatment will be.
Clinical manifestations
A nevus on the eye can be located on the outer or inner part of the tunica albuginea, the lacrimal caruncle, the limbus, and sometimes on the retina. True, in the latter case it is not visible to the naked eye and is detected only during ophthalmoscopy (examination of the fundus). An ocular nevus can have different colors (pinkish, black, brown, yellow), shape and size.
As statistics show, the more melanin a person has in his skin, the lower the likelihood of developing a nevus on his eye. That is why pathology is more often observed in fair-skinned and blue-eyed people, in particular residents of Scandinavian countries.
Useful video
Causes of birthmarks on the choroid of the eye. Effective treatment of this type of nevus.
Author's rating
Author of the article
Alexandrova O.M.
Articles written
2100
about the author
Was the article helpful?
Rate the material on a five-point scale!
( 5 ratings, average: 3.20 out of 5)
If you have any questions or want to share your opinion or experience, write a comment below.
How to remove a nevus on the eye?
Until recently, the only safe treatment for nevus on the eye was its surgical removal. The operation was performed under a special microscope using a radioscalpel or microscalpel.
The use of a laser beam was considered dangerous by many experts, since it could damage neighboring eye tissues.
Currently, the development of modern laser technologies has made it possible to develop new methods of surgical treatment of nevus. And now it is increasingly being removed from the eye using laser radiation.
The main advantages of using laser technologies to remove a nevus are that they are painless, bloodless, and most importantly, the absence of a rough postoperative scar.