What is breast atheroma?
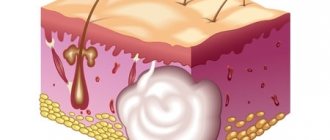
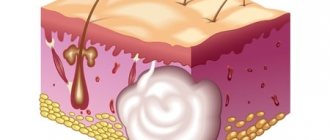
An epidermal cyst, or atheroma, is formed due to blockage of the sebaceous gland in any area where hair grows, including on the mammary gland. On the skin of the latter there are quite a lot of glands that have increased activity. Under certain conditions, the excretion of sebum through the ducts may be impaired: it is this obstruction that causes the formation of a cystic cavity.
Over time, a capsule with a putty-like mass forms in the cystic cavity. The size of the formation can be very different - from microscopic to gigantic, but this does not mean that it is worth finding out prices for atheroma removal only in case of large growths.
Preparations for topical use
Cleansers for certain skin conditions are considered an essential part of the therapeutic plan. In recent years, as a result of chemical synthesis, surfactants called detergents or “syndets” have been obtained, i.e. "synthetic detergents". The fundamental difference between syndets and soaps is that the pH value can be chosen more or less freely. For severe seborrhea, special acne soap is often used, but excessive facial hygiene with frequent washing should be avoided, since overhydration of the follicle leads to the accumulation of sebaceous gland secretions and can cause increased inflammation. Various creams, gels, emulsions, and solutions are used as hygiene and care products for oily skin with a tendency to acne. Shampoos can be divided into cosmetic and medical. Cosmetic shampoos can be liquid, creamy, aerosol, or oil-like. Medical shampoos are used to treat diseases of the scalp and contain antiseptics, active substances, and antifungal agents. For dandruff, the drug of choice is the frequent use of mild detergent shampoos, which are usually used 1-2 times a week. This procedure cleanses the scalp of scales, but in itself does not have a therapeutic effect. Shampoos containing the following components have a beneficial effect (for example: coal tar, ichthyol, piroctone olamine, zinc pyrithione, ciclopiroxalamine, plant extracts, selenium sulfide, AHA, BHA, ketoconazole - an antifungal component). At the multidisciplinary clinic CELT
We take a comprehensive approach to solving problems associated with impaired sebum secretion, using the most modern methods of treating this disease. Remember that self-medication is unsafe, as there is a risk of worsening the problem, therefore, at the first sign of acne, consult a dermatologist! If necessary, the dermatologist will refer you to another specialist (endocrinologist or gynecologist). Our clinic provides excellent laboratory diagnostics, where you can always take hormone tests with a referral from an endocrinologist to prescribe individual treatment. Be healthy, beautiful and cheerful! Make your face a source of pride!
Is it dangerous?
At the initial stage, in the absence of inflammation, atheroma does not cause pain and reminds itself only of a soft-elastic consistency under the skin. As the cyst increases in size, it causes discomfort, including psychological discomfort. If inflammation occurs, the skin turns red, and palpation reveals an infiltrate that surrounds the capsule.
The mammary gland swells and hurts. In severe cases, an abscess forms, and all this is accompanied by an increase in body temperature with intoxication. With this development of events, even a small atheroma can cause significant harm to health.
Function of the sebaceous glands
Sebaceous glands are found on the skin of the entire body, except the soles and palms.
Their secretion (sebum) serves as a lubricant for hair and skin.
There are so-called “seborrheic zones”, in which the density of the sebaceous glands is much higher. These include: forehead, central part of the face, ears, scalp, interscapular region, chest, shoulders. The sebaceous glands of these areas are involved in the inflammatory process, which leads to the formation of acne.
They lie under the skin at a level of 0.5 mm, at the root of the hair, forming the so-called pilosebaceous follicle. It opens on the surface of the skin as a pore.
Over the course of life, the depth, number and size of the sebaceous glands change. In a child, they are located more densely and work more actively. But over the years, their activity weakens, and some of the sebaceous glands die off altogether.
Before puberty, the consistency and chemical composition of sebum changes. During puberty, hormones (androgens) act on the sebaceous glands, under the influence of which the secretory activity of the sebaceous glands increases. The maximum is reached by 18-25 years.
Significantly more sebum is produced, but in addition it becomes denser. When the follicles of the pilosebaceous ducts are clogged with a “plug” of a mixture of sebum and dead skin flakes, acne vulgaris develops (another name is comedones, acne).
If the follicles are open, the plugs look like blackheads on the face and are called open comedones. Comedones can also be closed (they do not communicate with the surface of the skin). These comedones are called whiteheads, or whiteheads.
If the cause is not eliminated and excess sebum is not removed, then favorable conditions are created inside the follicle for the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria and microorganisms. The bacteria Propionibacterium acnes (P.acnes) are constantly present on our skin, which, under unfavorable conditions, begin to actively multiply and cause inflammation in the pilosebaceous follicle.
If an infection occurs:
- pain syndrome appears;
- the chest swells;
- the skin turns red or blue;
- pus or blood is released from the cyst.
It is this condition that causes the greatest concern for a specialist, because an infection can penetrate into the cavity, and during a consultation with a surgeon, the patient will be prescribed surgical intervention. And this is always fraught with scars and cosmetic defects. If the cyst is located in a place where it is not possible to completely remove it, there is a high probability of relapse. Degeneration into a malignant formation is very rare, but this is not a reason not to pay attention to atheroma, which even without this risk is fraught with many dangers.
Causes of acne
There are many causes of acne, but the main ones are:
- increased blood levels of male sex hormones (androgens)
- action of propionic bacteria (Propionibacterium acnes)
- follicular hyperkeratosis
- excess sebum production, changes in its composition
* Sebaceous gland cells have a high affinity for the male sex hormone - testosterone. They also contain an enzyme (5-alpha reductase), which converts testosterone into its active form (dihydrotestosterone). It is he who is involved in the formation of rashes and increases the secretion of sebum.
Therefore, to identify the causes of acne, it is recommended to study the amount of sex hormones.
* The appearance of rashes in the second phase of the menstrual cycle (“before menstruation”) is most likely associated with the effect of progesterone, the level of which increases. This hormone has the ability to somewhat suppress the immune system and retain fluid in the body. All this leads to increased activity of bacterial flora and the development of inflammation in the sebaceous gland.
Often, increased sebum production is the result of increased sensitivity of the sebaceous glands to sex hormones, and not a consequence of their high levels. In this case, a genetic predisposition to acne comes to the fore.
* Hyperkeratosis is an increase in the upper, stratum corneum layer of the skin. Lack of vitamin A, occupational intoxication, prolonged pressure or friction of the skin, exposure to petroleum products (for example, lubricating oil) on the skin are the main causes of hyperkeratosis. Hyperkeratosis of the sebaceous glands also develops under the influence of hormones. It is the cause of acne. With hyperkeratosis, the sebaceous glands become overcrowded with epidermal scales and bacteria, causing acne.
* Rashes may appear or increase in number under stress, since sebum production is regulated by the nervous system.
* Often patients note the appearance of rashes while eating certain foods. These include nuts and chocolate. But these are rather individual characteristics of the body and there is no clear diet for this disease. However, animal fats (lamb fat and lard), vegetable oils, nuts, hot cheeses, and spices can affect the composition of sebum and lead to blockage of the sebaceous glands.
* Comedogenic cosmetics can lead to acne formation.
Acne-provoking cosmetics (creams, lotions, powders, blushes, sunscreens for tanning) contain lanolin and its derivatives, squalene, sulfur, D and C red pigments (used to give a red tint and are extremely comedogenic). Acne-aggravating cosmetics contain mineral and vegetable oils. As a rule, with acne, cosmetics are used to disguise pimples and acne, aggravating the course of acne. A vicious circle is formed. Pay attention to the non-comedogenic label on the packaging of both decorative and care products.
* Some medications may cause rashes (medicinal acne). Drug acne is characterized by the sudden appearance of pus-filled pimples or pimples in people taking corticosteroid medications. After stopping oral contraceptives, many women also experience moderate acne.
How to treat
You can get rid of the problem through surgery, laser or radio wave method. The operation is usually planned and does not cause complications. If the formation is small and not infected, it is quite possible to use a laser or radio waves, after which there will be no scars or scars.
The inflamed cyst is first opened, the contents are removed, and after the inflammatory process subsides, the capsule is removed. Patients with a tendency to form atheromas are prescribed a special course of treatment, and in the presence of infection, antibiotic therapy.
Features of treatment
It is impossible to treat atheroma in such an acute condition. As soon as the inflammatory process can be stopped, the patient will be offered one of the removal methods. Large formations are removed surgically under local anesthesia. By cutting the skin, the doctor removes the capsule, applies cosmetic sutures, after which a scar remains on the skin.
If the cyst is small, a laser will be offered - without contact with the patient's blood. After this procedure, no traces remain. Sometimes it is advisable to combine these two methods - perform surgical excision and treat the capsule with a laser.
If an abscess has formed inside, the surgeon opens the atheroma under local anesthesia, removes the pus and rinses it. To prevent repeated suppuration, a special drainage is inserted into the cavity for several days, and antibiotics are also prescribed. In this case, the formation can be removed no earlier than three months after the wound has completely healed.
Bartholin gland cyst - symptoms and treatment
Small asymptomatic cysts do not need to be treated. They are usually removed only for cosmetic purposes. Only large cysts - from 3 cm or more, which not only disrupt the aesthetic appearance of the external genitalia, but also interfere with everyday activities and sexual life - are subject to surgical treatment.
There is no point in simply opening or puncturing a cyst or abscess. This can lead to relapse, since the edges of the tissues, when punctured or incised, very quickly close again due to the rapid healing process [6].
The main goal of surgical treatment is to preserve the Bartholin gland and its functionality, and to form a channel for the outflow of secretions. There are several treatment options. Let's look at each of them.
Installation of Word catheter
This is a modern method of surgical treatment of cysts. This is especially relevant for its relapses.
Under local anesthesia, the cystic area is opened with a small incision of about 5 mm, after which its contents are removed and sent for bacteriological examination, and then the cyst cavity is washed and a Word catheter is installed into it. It is a silicone tube 55 mm long and 5 mm in diameter, inside of which there is a channel with thinner walls at the end. By inflating its rubber tip to 3 ml with saline solution of 0.9% sodium chloride, the doctor fixes the catheter in the cavity of the cyst. For better fixation and prevention of loss during movements, it is recommended to apply 2-3 absorbable interrupted sutures along the contour of the exiting part of the catheter. The second end of the catheter is inserted into the vagina.
The catheter remains in the cyst cavity for six weeks. This is necessary to form a channel for the passage of secretions, the walls of which will not grow together. The study shows that the Word catheter is easy to use, inexpensive to install, and has acceptable short-term relapse rates [7].
While the catheter is in the cyst cavity, the patient is advised to have sexual rest to avoid its loss. In some countries, there is no such restriction, since studies have shown that the pain symptom caused by both the cyst itself and the presence of a catheter in its cavity completely disappears by the sixth day [8].
As an alternative, a Jacobi ring . This catheter is more solid, it does not have a channel and is presented in the shape of a ring. It is installed through two punctures in the mucosa and capsule of the cyst, and then the two ends of the catheter are secured to each other.
Opening and draining the cyst
Under local infiltration or intravenous anesthesia, the cyst is opened, the cavity is washed with antiseptic solutions, then a rubber drainage is installed in it to drain the secretions. The effect of such an operation is low due to the rapid healing of the incision site and the cessation of outflow from the gland. It can be used only if there is no other method of treatment available or if the cyst has transformed into a Bartholin gland abscess.
Puncture of the cyst
It is performed by puncturing the cyst itself with a needle and then suctioning out its contents. This method of manipulation is carried out in pregnant women or when surgery is impossible.
Marsupialization of the cyst
This type of treatment involves opening the cyst, removing the secretion and creating a new duct. It is used in the following cases:
- if the cyst reappears despite treatment using a Word catheter;
- with a small cyst size;
- if the cyst has several chambers;
- if it is impossible to install a Word catheter.
Marsupialization of a cyst is a simple outpatient procedure. It is performed under local anesthesia for 20-30 minutes. An oval flap 1.5 cm long is cut out in the most convex part. The cyst itself is dissected in the same way, after which it is cleaned and washed. Then the cyst wall is sutured to the labial mucosa so that an artificial duct is formed [13]. The wound does not need to be sutured, as it will heal on its own.
On the second day after surgery, the patient is shown warm sitz baths, and on the third day, stool softeners are prescribed. They are necessary for the prevention of constipation, since hard stool increases pain in the postoperative area, and its stagnation in the colon contributes to the accumulation of harmful microbes that can penetrate through the tissues into the postoperative area. Sometimes antibiotics are prescribed based on the results of a microbiological study. Sexual activity can be resumed in the fourth week after surgery.
The likelihood of relapse after marsupialization is extremely low - about 10%. The operation itself can be performed several times, as it is simple and less traumatic compared to complete removal of the Bartholin gland.
CO2 laser
CO2 laser surgery is also an effective way to treat cysts and can be performed on an outpatient basis. A skin incision is made with a focused laser beam, then the capsule is opened to remove the contents of the cyst, followed by internal evaporation of the damaged capsule [9].
Carbon dioxide provides complete healing in an average of 22 days, with no scars, hematomas or wound infections. You can return to everyday life in about two days. Patients undergoing traditional surgery require 14 days to return to daily activities and 28 days for the surgical wound to heal completely [10]. Due to this, and the minimal risk of complications that may occur during or after surgery, CO2 laser surgery is more cost-effective than traditional treatment [10].
Gland removal
If the cyst recurs frequently with the formation of an abscess, doctors recommend removing the cyst along with the gland [13]. The operation requires great experience and accuracy of the surgeon. It is performed under intravenous anesthesia. Most often performed in a hospital setting.
The incision is made outward from the labia minora, since the opposite side of the mucosa is usually thin, which is why the cyst capsule can be accidentally cut. The cyst is carefully removed using gauze pads while moving away the incised tissue. The gland is also removed. The wound is sutured in layers with absorbable sutures. It is very important to remove the entire gland. Incomplete removal may cause recurrence of the cyst or abscess. If the other Bartholin gland functions normally, then there will be no problems with secretion after this operation.
It should be understood that during the operation the cyst capsule may rupture. This can slow down the duration of the operation and lead to contamination of the wound. Also, the operator may encounter bleeding from the vessels of the cyst bed, but it is easily stopped by applying submersible sutures.
After removal of the Bartholin gland, a rectovaginal fistula may occur - a pathological canal between the rectum and vagina. It appears as a result of ongoing inflammation and “melting” of surrounding tissues.
In this case, patients may complain of pain in the perineal area, which occurs during sexual intercourse and bowel movements. To establish and confirm the diagnosis, you need to contact a coloproctologist, undergo a gynecological and rectovaginal examination, as well as additional examinations. The tissue defect is eliminated using an autograft, a biological collagen plug or a titanium clip. If a fistula is detected during pregnancy, then natural childbirth is prohibited.