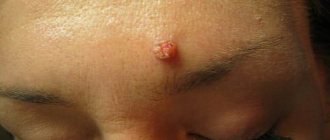
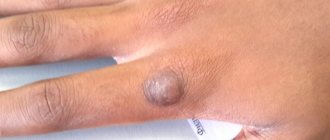
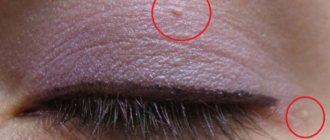
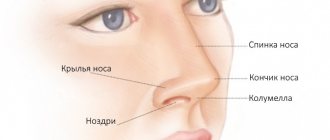
Polyp
is a pathological proliferation of the mucous membrane. By its nature, this is a benign formation, however, there is a risk of the polyp degenerating into a malignant tumor.
The mucous membrane lines the inside of the hollow organs of those systems of our body that communicate with the external environment, in particular the respiratory, urinary, reproductive and digestive systems. The functions of the mucous membrane are varied - this includes a protective function, absorption (typical of the gastrointestinal tract), hydration, and some others.
As a result of various reasons, the mucous membrane may become weakened, and then it begins to grow. So the body tries to compensate for the loss of properties of the mucous membrane by increasing its area. The result is a polyp that looks like a mushroom-shaped body on a stalk or on a thick base. Polyps can be either single or multiple (in this case the disease is called polyposis
).
Nasal hemangioma and other benign tumors of the nose
Benign nasal tumors are formed from various tissues present in the nose and paranasal sinuses. Hemangioma is a benign tumor that most often develops in the first days of a child’s life and actively grows in the first six months of his life. After the child is one year old, the tumor begins to involute; most of the hemangiomas disappear by the age of seven, the rest by the age of twelve. More often, hemangiomas form in girls. The cause of the disease is a disturbance in the development of blood vessels in the embryonic period. Nasal hemangioma can grow deep into the skin, tissues of the organ and to the sides, destroy tissues, provoke bleeding, and disrupt the functions of the organ.
Nasal fibroma is a benign formation that can spread to the orbit. Nasal fibroma is rare, characterized by active growth and quickly grows into the orbit and paranasal sinuses. The tumor causes nosebleeds and nasal congestion. Fibroma that has grown into the orbit and nasal sinuses causes various complications: constant lacrimation, decreased visual acuity, exophthalmos, and can cause deformation of the skull bones. Fibroids rarely develop in the paranasal sinuses, most often developing in the maxillary sinus.
Adenomas in the nose can be true adenomas, a papilloma-like tumor, or a malignant destructive adenoma. Adenomas do not produce secretions, despite the fact that the tumor contains glandular epithelium. Adenomas in the nose are rare and are characterized by nosebleeds, nasal congestion, and can lead to the development of exophthalmos, purulent dacryocystitis and other complications.
Benign neoplasms of the nose are osteoma, chondroma, angioma, papilloma, chordoma, lipoma, myxoma, bleeding polyp, ganglioneuroma, dermoid cyst and other neoplasms. Tumors are formed during intrauterine development of the fetus with a negative impact on the woman’s body during pregnancy. They can appear in chronic diseases of the nasopharynx; the appearance of tumors is influenced by poor environmental conditions, injuries, and infections.
Causes of boils in adults
The main cause of the disease is the activation of staphylococci and streptococci. These same pathogens cause tonsillitis, chronic tonsillitis and sinusitis. In most adults, these microorganisms are constantly present on the mucous membranes, but diseases do not always develop. For inflammation to occur, predisposing factors must occur:
- injuries and mechanical damage to the nasal cavity, including pulling out hairs from the nasal passages - infection can easily get into the wounds; This category also includes surgical reasons: rhinoplasty, installation of implants, etc.;
- a chronic source of infection in the body - chronic tonsillitis, chronic sinusitis, caries, etc.;
- purulent skin diseases of the nasal cavity;
- reduced immunity: the cause of the appearance of an abscess in adults can be simple hypothermia, lack of vitamins, stress, diabetes, HIV, oncology and other factors that “hit” the body’s own defenses;
- violation of basic hygiene rules (neglecting water procedures, constantly touching the face with dirty hands, squeezing pimples are common causes of chirp);
- unfavorable working conditions, work in hazardous industries with polluted air, constant contact with fuel oil and other fuels and lubricants;
- Hormonal imbalance is a common cause of ulcers in pregnant and adult women during menopause.
Treatment of an external abscess and treatment of a boil inside the nose will be most effective if its cause is correctly identified. Finding out the cause of the disease and prescribing a competent treatment regimen is the profile of an otorhinolaryngologist.
Cancer of the nose and paranasal sinuses: symptoms
A tumor in the nose develops in the maxillary sinus (maxillary sinus cancer), and cancer also affects the nasal cavity. Nasal cancer, the symptoms and signs of which become pronounced at a late stage, accounts for 1.5% of all cancers; men are more often affected. The reasons for the development of the disease are not fully known; most often, nasal cancer develops in workers of nickel production enterprises, woodworking and leather industries, in people who smoke and who often suffer from nasal infections. Symptoms and signs of nasal and sinus cancer vary. At the initial stage of development, the symptoms are similar to those of various diseases - rhinitis, sinusitis and other disorders.
Then the patient begins to experience headaches, discomfort, pain in the sinuses, and a change in sense of smell. The nose is constantly stuffy, mucous discharge from the nose bothers me. The pain can radiate to the upper jaw, temple, and a constant severe headache - such symptoms develop with cancer of the maxillary sinuses.
Cancer of the posterior external part of the maxillary sinus is manifested by difficulty while eating, difficulty opening the mouth - the cancer grows into the masticatory muscles. Cancer of the anterior lower part of the maxillary sinus often affects the hard palate and upper jaw, leading to tooth loss and the appearance of wounds on the gums. Cancer of the nose and paranasal sinuses can lead to displacement and loss of the eye, and facial deformation.
Squamous cell carcinoma is the most common type of cancer; adenoid cystic carcinoma, adenocarcinoma, poorly differentiated transitional cell carcinoma, olfactory esthesioneuroblastoma and melanoma are less common. Carcinoma of the nose is not as dangerous as cancer of the paranasal sinuses, which has a less favorable prognosis. If early stage cancer is detected on the nose, then the five-year survival rate of patients is more than 50%, for cancer of the paranasal sinuses it is no more than 25%. Sinosanal poorly differentiated carcinoma has an aggressive course - the tumor affects the paranasal sinuses and nose, and is characterized by the appearance of ulcers and a tendency to necrosis.
Cancer of the nose and paranasal sinuses has clinical manifestations depending on the location of the tumor. Often a tumor in the thickness of the alveolar process is mistaken for an inflammatory process. It manifests itself in growth after tooth extraction. It is very difficult to differentiate tumors from the upper internal sinus. A tumor of the upper outer part of the maxillary sinus can remain unrecognized for a long time and manifest clinical symptoms in the form of pain. A tumor that has grown into the orbital area is manifested by swelling of the lower eyelid. A tumor that affects the infratemporal fossa, pterygopalatine fossa leads to swelling of the eyelid, the development of chemosis with exophthalmos.
Types of boils in adults
Like any other disease, ulcers inside, on the tip or wing of the nose can have their own varieties. A purulent formation consisting of several ulcers fused together is called a carbuncle. Typically, up to ten pimples form a carbuncle.
Multiple abscesses that appear simultaneously in different parts of the new cavity - on the tip, wings or inside - are called furunculosis.
Furunculosis is the most dangerous manifestation of ulcers. This condition must be treated urgently.
The disease usually occurs in an acute form. But in the absence of proper treatment and neglect of hygienic measures, recurrent boils can occur. This means that the disease has become chronic.
At the location of the abscess, an internal boil or boil on the tip or wings of the nose is isolated.
Based on the stage of the disease, boils inside, on the wings or on the tip of the nose are infiltrative (inside which exudate accumulates), purulent (with the formation of purulent masses) and necrotic (when a necrotic rod with dead cells forms inside the abscess).
Nasopharyngeal cancer
With a tumor of the nasopharynx, the symptoms of the disease can be widespread and less common. Early manifestations of nasopharyngeal cancer are nasal congestion, a burning sensation in the throat, swollen lymph nodes, and ear congestion. The symptoms are similar to those of a cold. The tumor begins to progress rapidly and is manifested by the following symptoms: nosebleeds, hearing loss, sore throat, nasal congestion, frequent headaches, enlarged cervical lymph nodes, squint on one side, a feeling of numbness in the face, difficulty opening the mouth, non-healing in the nasopharynx. wounds.
Nasopharyngeal cancer is dangerous because the disease is asymptomatic in the early stages of development. Very often, the symptoms of cancer resemble the symptoms of colds. When oncology of the nasopharynx is detected, the symptoms most often indicate a late stage of cancer - an unpleasant putrid odor appears from the mouth, the patient feels an unpleasant odor that comes from the nasal sinuses, headaches are tormented, the vocal cords swell, the voice changes, the patient has difficulty swallowing, opening the mouth.
Nosebleeds are a constant concern, the body temperature periodically rises, tachycardia worries, speech becomes incoherent, strabismus and paralysis of the facial nerves may develop. Stage 4 nasopharyngeal cancer is characterized by general weakness, severe symptoms, severe pain in the nasopharynx, neck, and headaches.
Nasal polyps: diagnosis
When examined by an ENT doctor, nasal polyps can be identified visually.
Additional methods, such as computed tomography, provide additional information about the extent of the pathological process. Examination by an ENT doctor.
First, the specialist asks about the patient’s complaints and previous diseases (allergies, sinusitis, etc.). Symptoms such as problems with nasal breathing, impaired sense of smell or frequent sinusitis already raise suspicions about polyposis rhinosinusitis.
Then the doctor carefully examines the ENT organs. Large nasal polyps that protrude into the nasal cavity may already be visible to the naked eye. With the help of speculums and a nasal endoscope, the doctor often finds smaller polyps located more deeply.
Radiation diagnostics.
To obtain accuracy in diagnosis, it is necessary to understand the extent of the spread of polyps in the paranasal region; imaging methods, in particular computed tomography (CT), are suitable for this purpose. Conventional x-rays of the sinuses are considered obsolete. Ultrasound and MRI can be used in the diagnosis of nasal polyps only in rare cases.
Nasal polyps: treatment
To treat nasal polyps, the first stage is drug therapy, for example, in the form of nasal sprays. If the prescribed treatment does not improve the patient's condition, surgical methods are considered in which polyps are removed.
Drugs for the treatment of nasal polyps.
To treat nasal polyps, hormonal drugs based on glucocorticosteroids are used.
Hormonal medications are usually prescribed first in the form of a nasal spray. Advantage: It only works locally, possible side effects are limited to the site of use.
Unlike vasoconstrictor decongestant nasal sprays (xylometazoline, oxymetazoline), the effect of a hormonal spray appears only after a few days.
Correct use of the drug is important; the spray should not be sprayed into the nasal cavity towards the nasal septum!
If treatment with hormonal sprays is ineffective, tablets may be prescribed; this therapy sometimes causes side effects. Therefore, you should carefully monitor your condition.
If an allergy is a provoking factor for nasal polyps, then you first need to pay attention to its treatment. Medicines for allergic reactions, so-called antihistamines, are recommended. The patient should avoid contact with the allergen if possible. Specific immunotherapy (hyposensitization) is also acceptable in this situation.
Surgery for nasal polyps.
If drug treatment fails or the polyps are already very large, surgical treatment options should be considered.
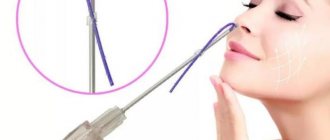
Removal of single polyps (polypectomy) can be performed on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia. However, nasal polyps are usually just the tip of the iceberg because the polyps originate from the paranasal sinuses.
Advanced interventions are usually performed under general anesthesia in an inpatient setting.
During the operation, the doctor removes the polyps “minimally invasively,” that is, without large incisions. Surgery can almost always be done directly through the nose - endoscopic intranasal surgery (FESS) using a shaver is the most optimal treatment for nasal polyps.
Correction of intranasal structures is often performed simultaneously. Sometimes it is advisable to straighten the nasal septum (septoplasty) or reduce enlarged nasal turbinates (vasotomy), or expand the anastomosis of the paranasal sinuses (sinusotomy) to normalize ventilation.
All measures should be aimed at normalizing aerodynamics and ensuring normal passage of discharge from the sinuses through the anastomosis into the nasal cavity. On the one hand, this should eliminate symptoms such as difficulty breathing through the nose and sinus pain, and on the other, prevent the appearance of new polyps.