Herpes on the pubis appears as a result of infection with the corresponding virus.
There are types 1 and 2 of herpes simplex.
Herpetic lesions on the pubis are usually caused by the second type.
The source of infection is a virus carrier or a person with herpes.
It is transmitted sexually.
There are also other methods of transmission.
Infection is possible through close household contact.
However, if the elements of the rash are located predominantly on the pubis, infection most likely occurred during sexual intercourse.
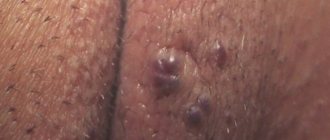
Genital herpes on the pubis
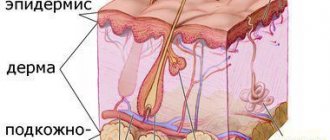
Initially, the herpes virus, penetrating the body, begins to multiply exactly where it penetrated the skin.
Bubbles form there.
These are vesicles - morphological elements that are small cavities with clear liquid.
The virus subsequently enters the circulatory system.
It invades nerve endings and ganglia.
The herpes virus will persist for life in autonomic nerve cells and can cause exacerbations.
It leads to a decrease in immunity, as it affects immunocompetent cells.
If herpes is localized on the pubis and genitals, then the main reservoir of the virus is the ganglia of the lumbosacral spine.
The infection can have a different clinical course.
Sometimes a person who has had genital herpes never suffers from it again.
But in 40% of cases recurrent herpes develops.
It can occur at any age.
Pubic herpes may appear again after a few months or years.
The causes are provoking factors:
- insolation (tanning)
- hypothermia
- injury
- serious disease
- drinking alcohol
- hormonal disorders
Most often, recurrent herpes develops as a local process.
That is, rashes appear on the pubis again and again.
But the rash does not spread to other parts of the body.
Sometimes genital herpes becomes generalized.
It can affect different areas of the skin, organs, including the brain.
Tumor formations
Lumps in the groin area and labia can be a sign of a tumor process in the body. Fortunately, genital tumors are often benign.
- Fibroma is a neoplasm of benign etiology, which is localized in the connective tissue, less often in the fascia of the parametric tissue. As a rule, it is located on the labia majora. Treatment of the tumor is exclusively surgical. Our doctors effectively treat this disease, guaranteeing a further favorable prognosis.
- Fibromyoma is a tumor that does not entail tissue destruction and metastasis (also benign). It is formed from muscle fibers and appears as a lump on the labia majora. Surgical excision is mandatory.
- Lipoma is a more severe tumor that does not have a malignant etiology. It is formed from adipose tissue and is located near the vulva. It is a nodule or several overgrown small neoplasms. Located on a dense, stable leg. The size of the nodule is usually small, but tends to grow. Such a tumor is always accessible during a traditional examination without additional diagnostic procedures. You may also be able to detect a lipoma by feeling your genitals or washing your face. If the disease is not treated, various complications are possible: hemorrhage, infection, swelling and even tissue necrosis. Our surgeons excise the lipoma and prescribe further supportive therapy.
- Hidradenoma is a rare type of tumor in the genital area. It develops due to the active activity of the sweat glands and some other abnormalities. In the case of this disease, hardening in the form of nodules forms on the labia, sometimes they are localized over the entire area of the organ or are single. Hidradenoma must be treated in a timely manner, otherwise it may develop into a malignant tumor.
- Oncology. (Cancer or sarcoma of the vagina, cancer of the vulva). It appears in the form of nodes and dense tubercles in the genital area. If benign tumors practically do not cause additional symptoms, oncology is always accompanied by copious discharge of pus or mucus with a pungent odor, bleeding, and diffuse infiltrates. Unfortunately, in this case, no one can give an unambiguous favorable prognosis, even with timely treatment.
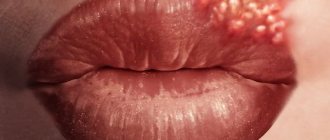
What does pubic herpes look like?
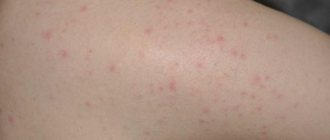
Classic herpes consists of blisters with liquid on the skin.
They often appear not only on the pubis, but also on other areas of the skin and mucous membranes.
Vesicles are formed in groups.
They are located asymmetrically.
Appear on hyperemic skin.
The vesicles resolve spontaneously after an average of 3 days.
In their place, either erosions or ulcers form.
More often these are erosions, and they are more favorable.
Because ulcers leave behind scars, because they are associated with damage to the deeper layers of the skin.
Main patient complaints:
- burning sensation on the pubis
- pain
- edema
- enlarged lymph nodes
Local and general symptoms of herpes on the pubis
After the initial infection, as well as with each relapse, rashes appear on the pubic area.
Herpes also gives general symptoms.
They are as follows:
- hyperthermia
- weakness
- enlarged lymph nodes
- their soreness
This condition occurs with general viremia.
That is, it is caused by the herpes virus entering the circulatory and lymphatic system.
This occurs when the human immune system is unable to localize the process.
Herpes on the pubis can be primary or recurrent.
Primary is the one that arose for the first time.
It is caused by a fresh infection from another person (sexual partner).
Recurrent is a form of the disease that develops as a result of activation of herpes.
The virus remains latent for a long time.
Then it “wakes up” and causes an exacerbation with the re-formation of a rash on the pubis.
Recurrence of herpes occurs without previous sexual contact with the source of infection.
Since the virus is already in the patient’s body.
Based on the symptoms, genital herpes can be:
- typical
- atypical
- asymptomatic
After infection, two scenarios are possible.
The first is that the person does not feel symptoms.
He becomes a carrier of the virus, but is unaware of it.
Second, a stormy clinical picture arises.
Herpes is much more severe than subsequent relapses, if any.
The shorter the incubation period, the stronger the symptoms.
Its duration is up to 10 days.
Sometimes the incubation period lasts only 2-3 days.
Then an acute herpetic infection can last up to 1 month or more.
The typical form of genital herpes is characterized by:
- formation of erythema (red spots)
- the appearance of vesicles
- their resolution with the formation of erosions
- epithelialization
With recurrent herpes, subjective sensations appear a day or two before the next relapse.
The patient suffers from itching of the pubic skin, pain, and the skin may turn red.
Sometimes general symptoms such as fever and malaise appear.
Lymph nodes may enlarge before the rash appears.
How to treat
Therapy depends on the disease and the type of pathogen. Initially, you need to seek help from a doctor - a dermatologist, gynecologist or venereologist. The doctor conducts a visual examination, collects anamnesis, and prescribes the necessary laboratory tests. Once the results are received, a diagnosis will be made.
- Treatment of genital herpes lasts from two weeks to two months. Patients are prescribed antiviral drugs - Acyclovir, Valacyclovir. Additionally, you need to take a vitamin complex and immunomodulators. In parallel with the use of tablets, you need to use local ointments - Zovirax, Panavir. Complex treatment helps to cope with ulcers, and the disease goes into remission for a long time.
- Sebaceous cysts and boils are usually removed surgically. The doctor gives an injection, opens the cavity of the abscess under local anesthesia and cleans it. Then stitches are applied if the pimple is large. The patient is recommended to take a five or seven-day course of antibiotics, this will avoid complications. Surgery allows you to get rid of the blister permanently.
- When diagnosing scabies, it is necessary to use local remedies. Usually these are ointments that cause the death of parasites. They are produced on the basis of benzyl benzoate. Sulfur ointment and products with pyrethroids also help in therapy. Additionally, it is necessary to maintain personal hygiene and change underwear regularly. Before starting treatment, it is necessary to disinfect bedding and clothing to destroy all larvae.
- For head lice, topical preparations based on permethrin or phenothrin are used. Additionally, household items are treated with special sprays to kill lice.
- If blisters in women or men are caused by allergies, then it is necessary to limit contact with irritants and take antihistamines: Zodak, Zyrtec, Suprastin. The duration of the course and dosage are prescribed by the attending physician.
- Psoriasis requires regular comprehensive treatment. Tablets for oral administration and ointments for topical use (they are used to lubricate plaques) are prescribed as medications.
It is not recommended to treat acne with traditional methods, since they will not be able to influence the causative agent of the disease. If necessary, it is allowed to use folk advice as an additional treatment, but after consulting a doctor.
Conclusion
Pubic ulcers in men and women cause unpleasant symptoms, they depend on the specific disease. The ulcers hurt, itch, and cause discomfort when walking. Treatment is prescribed depending on the disease and the microorganisms that caused the blisters.
For bacterial infections, antibiotics are used, for viral infections, antiviral agents are used. If we are talking about fungal diseases, then antimycotic ointments are prescribed.
Enlarged lymph nodes due to herpes pubis
With herpes, the inguinal lymph nodes increase in size.
This occurs after the initial infection.
And also whenever the infection recurs.
Enlarged lymph nodes are often unilateral.
They may be painful when palpated.
Swelling of the skin and redness over the lymph nodes and blood vessels are often noted.
Contagious diseases that cause itching in the groin
First of all, these may be.
Scabies
It is characterized by two-point rashes all over the body. There are most of them in the skin folds, including the inguinal folds. A special symptom is that the skin itches more at night.
Pubic lice
Even a condom does not protect against them, since these insects live in the hair surrounding the genitals. With a careful examination through a magnifying glass, a urologist-venereologist can see them.
Fungi
Most often these are fungi of the genus Candida, transmitted through sexual intercourse. Along with redness and itching in the groin, the man will have inflammation and plaque on the head of the penis, and white discharge from the urethra.
Sometimes irritation in the inguinal folds is caused by ordinary saprophytic skin fungi. The spots in a man's groin will be in the shape of a ring, with swelling of the skin around the edge.
Other sexually transmitted diseases
Chlamydia, ureaplasmosis, and genital herpes occur after sexual intercourse with a sick partner. Unpleasant sensations in the groin are accompanied by pain when urinating and discharge from the urinary canal. The inguinal lymph nodes become denser.
In the photo: fungal rashes
Atypical forms of herpes on the pubis
It is much more difficult to diagnose herpes on the pubis if there is an atypical form of the disease.
Atypical is a form in which:
- the cycle of formation of morphological elements changes
- non-standard location of lesions
- subjective sensations prevail over objective symptoms of herpetic infection
Abortive form - characterized by rapid regression of rashes immediately after their appearance.
It often occurs in patients who receive antiherpetic therapy in a timely manner.
The next exacerbation is usually preceded by a prodromal period.
Over time, patients learn to recognize it.
As soon as the condition worsens, the body temperature rises, the pubis itches, they take medications.
As a result, a classic exacerbation does not develop.
The rash may present as:
- papules
- red spot on swollen skin
- microerosions
Quite quickly the skin clears up and the exacerbation passes without really starting.
Edema form - there are no rashes, but only hyperemia and swelling.
Itchy form - the leading symptom is itching.
In the hemorrhagic form, blisters containing blood rather than clear liquid appear.
In the subclinical form, there are no rashes, but only cracks in the skin.
Non-communicable causes
Other reasons can also cause itching and redness in the groin in men.
Allergies
The thin skin of the inguinal folds and scrotum is susceptible to many allergens. It can be:
- food products;
- detergent components;
- linen fabrics;
- lubricant for sex;
- condom material.
When the factor that caused the allergy is eliminated, improvement occurs. Tests for immunoglobulins and the immune status of the blood help to identify allergies.
More often, allergies occur in the form of atopic dermatitis - dry redness and peeling in the groin in men; If small blisters appear against a background of redness, they speak of eczema.
Prickly heat
A groin rash in men and itching can be caused by wearing tight or synthetic underwear. The condition is aggravated by staying in a hot atmosphere, long trips, when there is no opportunity to wash with soap and allow the body to breathe.
The essence of prickly heat is that sweat is actively secreted, and the sweat glands are clogged with sebaceous secretions and skin flakes. White nodules and red spots appear in the inguinal folds.
Systemic diseases
Diabetes mellitus, liver and gallbladder diseases, kidney failure, and psoriasis can provoke itching. In all such cases, there are other important symptoms of these ailments, and itching all over the body, and not just in the groin. With iron deficiency anemia, itching intensifies during contact with water.
Psychological reasons
In some cases, the cause of severe itching in the groin in a man may be general nervousness or obsessive-compulsive disorder. Scratching injures the skin, a streptococcal infection gets into the scratches, and inflammation begins.
Pubic herpes and pregnancy
Herpes is dangerous during pregnancy.
Although external manifestations may be localized only on the pubis, in fact, pathological processes also affect the internal reproductive organs.
According to some studies, herpes provokes up to 30% of all cases of spontaneous abortions in the early stages of gestation.
This is the cause of half of late miscarriages.
In terms of the degree of negative impact on the fetus, herpes ranks second after rubella.
In addition, a mother can infect her child with this virus.
Infection occurs both in utero and during childbirth.
Any relapse of herpetic infection in pregnant women is subject to treatment.
If herpes occurs on the pubis before 34 weeks, drug prevention is indicated.
It is necessary to prevent the child from becoming infected.
Acyclovir is prescribed in the last 4 weeks before birth.
If infection or exacerbation occurs after 34 weeks, this is an indication for cesarean section.
Complications of herpes on the pubis
Herpes in most cases has a mild or moderate clinical course.
But sometimes seemingly harmless pubic rashes ultimately lead to serious complications.
At risk are elderly and weakened patients, people with immunodeficiencies.
Herpes can cause:
- inflammation of the ENT organs and bronchitis
- meningoencephalitis
- myocarditis and coronary heart disease
- inflammation of the digestive tract
Therapy in our clinic
If you notice lumps on your genitals, we recommend that you do not hesitate to contact our qualified specialists. You will be examined by our gynecologists, after which, if necessary, they will be referred to a surgeon. We will carry out the appropriate treatment, choosing the best option for you. We always strive to choose gentle techniques, but if this is not possible, our surgeon will eliminate your tumor quickly, painlessly, with a guarantee of no complications.
Many years of practice and extensive experience of our specialists allow us to vouch for the health of each patient. We recommend that you consult a doctor in a timely manner to avoid serious complications and relapses of the disease.
Treatment of herpes on the pubis
The principles of herpes therapy are as follows:
- Destroying the virus with antiviral drugs
- Normalization of the immune system
Treatment goals may vary.
Usually they are as follows:
- stopping another exacerbation of infection
- relapse prevention
- preventing infection of sexual partners or a child (from a pregnant woman)
- prevention of complications
Treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis.
Rarely, hospitalization is required.
Indications for it:
- complications of the brain or spinal cord
- generalized herpetic infection
- individual intolerance to antiviral drugs against the background of severe herpes
Drugs that are used for herpes pubis:
- acyclovir
- famciclovir
- valacyclovir
Studies do not show benefits for any drugs.
They all have the same mechanism of action.
The efficiency is comparable.
The differences relate mainly to cost and ease of use.
The most convenient to use is valacyclovir.
It can be taken less frequently than other drugs of this pharmacological group.
The doctor chooses the treatment regimen.
It depends mainly on the clinical course, form and severity of herpes pubis.
Treatment takes the longest for primary infection.
The course of therapy for relapse may be somewhat shorter, since it usually proceeds more easily.
Drug prevention of herpes
Drug prophylaxis can be emergency or planned.
Emergency is performed after unprotected sexual intercourse.
Planned - in advance.
Emergency drug prevention for herpes is ineffective.
Even if a person receives medications immediately after coitus, this will not reduce the risk of infection.
The symptoms of herpes will be much less pronounced.
Perhaps they won't appear at all.
But the pathogen will still penetrate the body.
It will persist in the nerve ganglia and may cause exacerbation in the future.
Planned prevention is effective.
The source of the infection should receive the drugs, not the person who may become infected.
Prevention of herpes infection in the family
It happens that one spouse suffers from herpes on the pubis, and the second is healthy.
Naturally, he does not want to get infected.
In such cases, planned drug prophylaxis can be used.
Valaciclovir can be used for this.
It is prescribed 0.5 g, once a day.
Two schemes are possible.
The first is used for constant, the second - for occasional sexual intercourse.
The patient chooses the regimen.
The decision depends on how often sex is practiced in the family.
If it is regular, then the drugs must be taken constantly and continuously.
If sex is episodic, then valacyclovir should be used 3 days before planned contact.
This use of the drug allows you to protect your healthy partner from infection.
Herpes pubis: why do you need a vaccine?
We are all accustomed to the fact that vaccines against viral infections are administered for preventive purposes.
The body develops immunity, and a person does not become infected with a particular disease.
But the herpes vaccine is curative.
It has been used for decades.
Although the drugs are constantly being improved.
The vaccine is a killed virus.
The use of vaccinations is indicated for recurrent genital herpes.
Vaccination helps to form specific immunity due to antigenic stimulation of the body.
Antibodies are produced that prevent relapses.
Indications for use of the vaccine:
- elderly age
- concomitant HIV infection
- severe exacerbations of herpes
- frequency of exacerbations more than 3 times a year
- established immunodeficiency conditions
Complications
If left untreated, the disease can lead to complications. Genital herpes and psoriasis will constantly recur. Dermatological or fungal skin lesions gradually affect large areas of the skin. With lice or scabies, parasites can spread throughout the body.
In addition, the skin becomes more vulnerable, and secondary infections are possible. In this case, the integument swells and hurts greatly. In case of an abscess, surgical intervention, opening of the abscess and taking antibiotics are urgently required.
Maintenance therapy for herpes
Suppressive or maintenance therapy is continuous antiviral treatment.
It is used in severe cases when relapses occur too often.
The essence of this treatment is the continuous use of antiviral drugs.
Can be used:
- acyclovir – twice a day, 0.2 g
- famciclovir – 0.25 g once daily
- valacyclovir – once a day 0.5 g
The duration of suppressive therapy is determined individually.
The number and severity of relapses are taken into account.
Patients may receive this treatment for years.
If the doctor cancels it, the further clinical course of herpes is assessed by two relapses.
If the disease worsens, suppressive therapy can be resumed.
Immune drugs for herpes
As we have already found out, there are drugs that destroy the herpes virus.
Despite this, immunomodulatory therapy is used for this disease.
Why is it needed?
Firstly, in order to reduce the number of relapses.
Few people want to receive antiviral drugs constantly and continuously.
It is much easier to normalize the immune system so that it can resist viruses on its own.
Secondly, herpes itself causes secondary immunodeficiency.
Therefore, patients who present with pubic rashes often complain of frequent respiratory infections.
They may develop ulcers.
The following changes are found in the blood:
- decrease in the number of T-lymphocytes
- decrease in CD4 count - both during exacerbation and during remission
- increased CD8
- in severe cases, the level of IgA (immunoglobulins of the mucous membranes) decreases
The number of circulating immune complexes increases significantly during an exacerbation.
Subsequently, the body’s defense response is exhausted.
If you have recurrent herpes, patients should:
- take an immunogram
- consult an immunologist
- receive immunomodulatory therapy
In this case, the relapse rate will be lower.
Exacerbations of herpes on the pubis with normal immunity are much easier.
Bartholinitis
Very often, bumps on the labia appear due to inflammation of the Bartholin glands. They are localized at the entrance to the vagina and are located in the subcutaneous fatty tissue of the labia majora. The Bartholin gland synthesizes a mucous secretion that forms in the vagina on the eve of sexual intercourse. Blockage of the excretory ducts of these glands leads to an inflammatory process in the organ, resulting in neoplasms in the form of small bumps. This disease often occurs in women who do not pay due attention to personal hygiene.
How do symptoms develop?
- The specificity of the disease is such that symptoms do not appear immediately;
- 1-2 weeks after the onset of the inflammatory process, a seal forms on the inside of the labia majora;
- The ball begins to hurt and cause discomfort, especially when wearing tight underwear;
- The large lips swell, there is a burning sensation and pain in the perineum;
- Suppuration and effusion of exudate are possible, but more often this does not happen.
Bartholinitis does not require specific treatment, however, in its complete absence, women experience frequent relapses of the inflammatory process. At the same time, a new disease begins - a Bartholin gland cyst. In this case, surgical treatment is used, since alternative therapeutic methods become powerless. If the lump begins to suppurate during bartholinitis, there is a sharp deterioration in general well-being, pain during sexual intercourse, and an increase in body temperature up to 40 degrees. It should be emphasized that bartholinitis during pregnancy can provoke spontaneous abortion.
If you have been diagnosed with bartholinitis, our experienced specialists will select a course of gentle antibiotic treatment for you or use surgical tactics to excise the cyst. Do not forget to maintain your health after treatment, maintain good personal hygiene and use contraceptives when changing partners. Know that bartholinitis can also develop due to parasitism of pathogenic microorganisms in your individual microflora. Often the disease is a consequence of trichomoniasis, gonorrhea and chlamydia.