A purulent coccyx cyst is an inflammatory process under the skin in the sacrococcygeal region, most often found in young men. A cyst in the sacrococcygeal region appears as a result of exposure to various factors:
- A congenital anomaly that occurs when embryonic development is disrupted in the early stages of pregnancy.
- The anomaly is formed during growing up due to improper escalation of hair.
- It can develop with a sedentary lifestyle.
- Weak immunity can cause illness.
- Hereditary predisposition, trauma and other factors.
Treatment of pathologies of the sacrococcygeal region is carried out in the coloproctology department of the Yusupov Hospital. Yusupov Hospital is a multidisciplinary medical center, which includes several clinics, a clinical laboratory, diagnostic and rehabilitation centers, and a hospital. The hospital performs surgical operations in operating rooms equipped with innovative equipment. The latest world developments in the field of medicine and medications certified in Russia are used to treat patients. Consultations and treatment of patients are carried out by experienced doctors: doctors of science, professors, highly qualified doctors, patients are provided with various types of medical care.
Delicate and complex problem
Coccyx cyst (epithelial coccygeal duct) is one of the most delicate and complex health problems.
Those who have dealt with her understand what we are talking about. Coccyx cyst occurs in both men and women. According to statistics, the stronger sex suffers three times more often. The delicacy lies in the localization of the pathological focus. The formation is located in a fairly intimate place (the area of the coccyx, sacrum and intergluteal fold) not far from the anus. Not everyone will easily want to share this with others, even with relatives and loved ones. Not everyone is ready to immediately show the sore spot, discuss their complaints and discomfort, even with doctors. When an epithelial cyst of the coccyx becomes complicated (abscess formation, suppuration, relapse), a person in most cases is deprived of the opportunity to maintain his usual lifestyle and quality of life. Irritating pain, excruciating discomfort, serous or purulent discharge, an unpleasant odor appear, laundry gets dirty, and additional hygiene procedures become necessary. Often it is simply impossible to sit normally. And this is not the whole list of inconveniences.
Many in this situation are forced to give up their usual activities, sports, and even intimate life. All this is depressing. Adding to the delicacy is that a coccyx cyst clinically manifests itself more often in adolescence or puberty. Teenagers are known to be especially sensitive to such problems, although they will try their best not to show it. Wise advice, understanding, help and timely consultation from a surgeon are especially important for them.
The complexity of this pathology lies in the fact that very often there are relapses (repeats) after improper preparation for surgery, an insufficiently radical operation (incomplete removal of cysts, fistulas and leaks), inattentive management in the postoperative period, failure to follow doctor’s recommendations, ignoring basic hygienic procedures and other reasons. Some people have to undergo surgery for coccyx cysts not once, not twice, but multiple times. You won’t believe it, but there are still people who suffer all their lives due to relapses. This reduces the quality of life and is certainly a tragedy. It shouldn't be like this!!!
It is necessary to initially take this disease and the initial operation very seriously. Agree, no one wants to have multiple surgeries. However, repeated surgical intervention should be taken no less seriously, and perhaps more seriously, if the clinical situation has recurred. It is very important to prevent chronicity and continuation of the sluggish process. A coccyx cyst is not a very common and not at all an ordinary problem. The choice of clinic and doctor is extremely important to minimize the risk of relapse. Consultation and surgery with a qualified surgeon who has experience in treating this pathology is necessary.
Application of Vishnevsky ointment
How to quickly cure a boil on the tailbone in men or women? It’s worth trying Vishnevsky’s ointment (the full name is “Balsamic Liniment according to Vishnevsky”). This product contains tar and xeroform. These components help relieve swelling, provide a slight anti-edematous effect, and accelerate the maturation of the boil, regardless of its location.
Dermatologists recommend applying a thin layer of ointment to the affected area around the boil two to three times a day. In this case, it is not necessary to make a compress or bandage; the ointment is absorbed quite quickly by the tissues. Contraindication for use: allergies or intolerance to tar.
Coccyx cyst. What is this? What is the reason? Classification
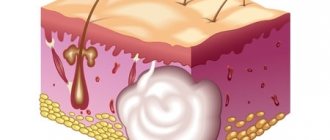
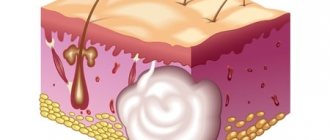
Coccyx cyst (epithelial coccygeal duct, pilonidal cyst, ECC) is a closed small cavity (tube-shaped canal), which is located subcutaneously in the area of the upper part of the intergluteal fold. It does not have a direct connection with the coccyx and sacrum. The inside of the cyst cavity is covered with a special epithelial lining, which contains ordinary hair follicles, hair, sweat and sebaceous glands.
According to the main generally accepted version, a coccyx cyst is a type of congenital pathology. An unusual defect (anomaly) in the area of the intergluteal fold is formed in the prenatal period. As a result, a person has a cavity (canal or passage) with a special internal epithelial lining under the skin in the upper part of the intergluteal fold in the coccyx area. According to another version, a cyst (epithelial tract) is formed as a result of hair ingrowth into the skin due to improper inward growth with intussusception (immersion). The appearance of the formation is often associated with injury to the sacrococcygeal region or prolonged sitting (professional drivers often suffer). The cause of suppuration is most often the addition of a specific infection (present in the anus).
In childhood, a coccygeal cyst practically does not make itself felt, since there is no infection in the formation cavity, there is no active hair growth and gland secretion. Clinical manifestations of the disease usually occur between 13 and 30 years of age. As a rule, during these years of life there is increased hair growth, active secretion of sweat and sebaceous glands, including inside the cyst. The hair in the cyst grows, and the glands secrete their secretions inside the formation. It all adds up.
When the cavity becomes full, unpleasant discomfort appears, excruciating pain, weeping, itching and other symptoms may appear. Then one or more primary serous holes (serous fistulas) open between the buttocks in the coccyx area. The contents of the formation (serous discharge, tufts of hair) are released. When holes appear, microorganisms actively colonize the cavity (infection) in which they were not previously present. If for some reason the connection with the external environment is closed, there is a delay in the evacuation (removal) of the discharge from the formation. Overflow, tension, acute inflammation and abscess formation (suppuration) occur.
It so happens that this pathology has many different names. This can sometimes be confusing or misleading. If there is no inflammation, the formation is called an uncomplicated coccyx cyst, dermoid cyst, or epithelial coccygeal duct. In the English literature, a pilonidal cyst or pilonidal sinus (pilonidal cyst, pylonidal sinus, hairy or hairy cyst, “hair nest”) is more common due to the presence of hair inside. Holes or holes that occur primarily or secondary are called fistulas in the coccyx region. When acute inflammation and exacerbation of chronic inflammation occurs, suppuration occurs and abscess formation, the diagnosis sounds like an abscess, a festering coccyx cyst or a festering epithelial coccygeal tract. All these names describe different stages or features of the same process.
However, the following classification is most often used in clinical practice:
- Coccyx cyst uncomplicated by inflammation (without clinical manifestations)
- Acute or exacerbation of chronic inflammation of the coccyx cyst
- Chronic inflammation (sluggish process) of coccyx cysts
- Remission of the inflammatory process (cold period)
Baked onions as a means to draw out the purulent core of a boil
Peel the onion, cut off a piece and bake over the fire, stringing it onto the tip of a knife. If your apartment has an electric stove, it’s no problem; you can bake a piece of onion in the oven.
When the onion has cooled a little, apply it to the boil and secure it with a bandage and adhesive plaster. After half an hour, change the bandage to a fresh one. This method, judging by patient reviews, helps to pull the boil root out as quickly as possible. This method was used by our great-great-great-grandfathers at a time when there was no talk of any ointments or products containing antibiotics.
Basic preventive measures:
- Observe all rules of personal and intimate hygiene
- Rinse the intergluteal fold
- Wear loose, clean, eco-friendly clothing (avoid tight, tight, synthetic clothing)
- Avoid trauma to the coccyx area
- Avoid prolonged sitting
- Epilation and/or depilation in the tailbone area
- Promptly treat and sanitize primary holes, wounds and microtraumas in the coccyx area.
- Immediately contact a surgeon if the first signs of discomfort and inflammation appear
If clinical manifestations or relapse appear, then the only correct preventive measure will be surgical treatment.
"Levomekol" - ointment with antibiotic action
“Levomekol” is a cheap (about 90 rubles) and effective drawing ointment for boils with an antibiotic. This is a drug for external use and has a complex effect. Effectively fights inflammation, destroys pathogenic microflora, quickly pulls out the root of the boil, and promotes better wound healing (thanks to the content of methyluracil).
“Levomekol” is optimally used two to three times a day, under a compress. You can use a medical bandage for this purpose, or a cotton pad. You can secure the compress with an adhesive plaster.
What worries you about a coccyx cyst? Symptoms
If the coccyx cyst is not complicated or is in the “cold period” after inflammation, then in the vast majority of cases it does not manifest itself and is asymptomatic. From time to time there may be some discomfort in the coccyx area, serous discharge or moisture above and between the buttocks. Sometimes anal itching can be disturbing. Small points (retractions) of the skin in the area of the coccyx and intergluteal fold are visually determined.
When an infection enters the cavity, discomfort increases significantly, inflammation and pain occur in the area of the coccyx and sacrum. Primary openings (holes, fistulas) may appear from which serous, sanguineous or purulent discharge is released. With suppuration and abscess formation, secondary purulent fistulas can form.
In the absence or delay of discharge from the cyst, a painful infiltrate (swelling, edema, tumor, lump) appears through the holes with clear contours in the area of the coccyx and intergluteal fold, which interferes with movements and walking. When the contents of the cyst become infected, acute inflammation develops. Pain, swelling, and redness appear in the area of infiltration. Increased body temperature (fever). Abscess formation occurs (formation of a cavity with suppuration).
After the abscess of the coccyx cyst is drained independently or as a result of surgery (outflow of pus), relief occurs. Pain, swelling and redness disappear, inflammation subsides. The fistula gradually closes, and the postoperative incision wound heals. A period of imaginary well-being begins (the cold period). There is no point in waiting for a complete cure, since there remains a focus of dormant chronic infection (the substrate of chronic inflammation), which becomes aggravated or becomes re-inflamed under certain favorable conditions.
If radical surgery is not performed, then periods of exacerbations and remissions (the interval between exacerbations) can alternate for months and sometimes years. During remission, there is usually no edema or hyperemia. Periodic dull pain or discomfort in the tailbone area may be bothersome. Inconvenience occurs when sitting and in the presence of scanty discharge from holes or fistulas. Fistulas can function, open and close. With prolonged remission, pigmentation and scar tissue changes appear around the holes.
Tetracycline ointment
The antibiotic tetracycline included in the ointment actively fights pathogenic bacteria and prevents inflammatory processes in the boil hole. In dermatology, it is customary to use tetracycline ointment after the root has come out. The purpose of use is to prevent the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria in the hole and avoid relapse of furunculosis.
If the hole from the boil is large, then the dermatologist puts on a surgical “blotter” soaked in a product containing tetracycline. It is quite difficult to carry out such a procedure at home.
Treatment of coccyx cyst (preoperative examination, preparation, operations)
Treatment of coccyx cyst is surgical.
To clarify the diagnosis and exclude other pathologies (rectal fistulas, presacral teratoma, osteomyelitis), an examination of the rectum is necessary; in some cases, radiography, colonoscopy or irrigoscopy may be required. Before surgery, thorough depilation of the surgical field is very important and cleansing enemas are required. In case of abscess of a coccyx cyst (festering epithelial coccygeal duct), acute inflammatory phenomena or exacerbation of a chronic process, the first stage is to drain the purulent contents of the cyst (open, drain). The abscess is opened urgently with a small incision under local anesthesia. The cavity is emptied, sanitized with antiseptic solutions and drained. After the drainage of pus, relief occurs. Bandages with water-soluble ointments (levomekol) are applied. The pain goes away, the inflammation subsides, and the postoperative incision wound heals. A period of imaginary well-being begins (full recovery does not occur). A focus of dormant chronic infection remains. Without the second stage - radical surgery (complete excision or removal of the coccyx cyst), as a rule, suppuration is repeated again and again. With a long delay of radical intervention, inflammation can become chronic with the formation of new infiltrates and secondary fistulas.
Primary radical surgery (uncomplicated coccyx cyst) or the second stage of treatment after the subsidence of acute inflammatory phenomena during the period of remission (“cold period”) is carried out as planned. The operation is performed under local infiltration, spinal anesthesia or intravenous anesthesia. Surgical intervention consists of removing (excision) the pathological formation (cyst, canal, tract) along with the internal lining, the contents of the cavity, the surrounding tissues that have changed after repeated inflammatory processes to the fascia. All primary and secondary holes (holes, fistulas) are also excised. To minimize the risk of relapse, all passages and fistulas must be painted with a special dye. After excision of the coccyx cyst, the postoperative wound is usually sutured tightly. Donati sutures are applied to ensure good bleeding control and accurate alignment of the wound edges.
In a number of clinics, the postoperative wound is left open or the edges of the wound are sutured to its bottom for secondary healing (marsupilization). In our opinion, this tactic of postoperative wound management has many disadvantages:
- traumatic
- decrease in the patient's quality of life
- possible secondary infection
- high probability of relapse
- vicious postoperative scars after secondary healing
Ointment "Gyoksizon" with a hormonal component
"Gyoksizon" is an ointment with a combined effect, which includes the hormone hydrocortisone and the tetracycline antibiotic oxytetracycline. The ointment should be applied to the area of the boil up to 3 times a day, in a thin layer. The duration of treatment is individual for each patient. As a rule, the root of the boil comes out within two to three days from the start of using the ointment. It is not necessary to put it under a compress - it is quite enough to simply apply a thin layer on the boil and the area of skin around it.
Contraindications to the use of “Gyoksizona” are during pregnancy and breastfeeding. It is also undesirable to use the ointment for people with chronic liver diseases, especially in the acute stage.
Postoperative period. Dressings after surgery
In the postoperative period, bed rest must be observed during the first day after surgery.
You can get up and walk the day after surgery. You can sit down on days 5-6-7. Fully sit for 8-9 days. It is very important to avoid stress on the seams. It is necessary to avoid traumatizing the postoperative wound, and subsequently the scar. In the postoperative period, antibacterial therapy is prescribed if the process was accompanied by acute inflammation and abscess formation. Painkillers are used in the presence of pain. A modern breathable aseptic dressing with an absorbent pad is applied to the sutures. Dressings are done daily. On days 4-5, if there is no discharge from the wound, you can bandage it every other day. During primary healing, the sutures are removed 12-14 days after surgery. If the postoperative wound is treated openly, then secondary healing takes a fairly long period. In such a situation, it is best to use modern medical dressings and fixation means for dressing and care. In the postoperative period, the patient's quality of life should not suffer. We can select special dressings to care for an open wound, even if you had surgery in another clinic.
Compresses for boils with Dimexide
"Dimexide" is a solution that is used for burns, festering wounds, and boils. It provides a local warming effect and also promotes deeper penetration of the therapeutic components of the compress into the tissue. Step-by-step instructions for using the product:
- Wash your hands before applying the compress. Prepare honey, Dimexide and a clean cotton pad, as well as a piece of adhesive plaster.
- Blot a cotton pad with Dimexide. Wipe the area of skin on the tailbone with the boil. Apply a thin layer of honey - this will help reduce the degree of inflammation, reduce the severity of pain and burning, and also speed up the process of removing the purulent root out.
- Cover the boil with a soaked cotton pad and secure with adhesive tape.
- Leave the compress for half an hour. Monitor your well-being: in some patients, the solution provokes a burn. If the skin gets sore, it is better to immediately wash off the remaining compress with warm water and not try this method again.
Complications and consequences
If the process is severe, the following complications may develop:
- relapse
- coccyx osteomyelitis (purulent bone lesion)
- fistulous pyoderma (purulent skin lesion)
- fungal infection
- multiple communicating purulent fistulas and pathological tracts with epithelial lining (sacrococcygeal region, perineum, scrotum, inguinal folds, anterior abdominal wall, anus)
Complications require painstaking, lengthy, often multi-stage treatment. Competent prevention, the right choice of clinic and doctor, timely treatment, radical surgery, and compliance with all recommendations will help you avoid such problems.
Traditional methods of fighting boils
If a boil appears on the tailbone, what should you do? Try using folk remedies that have proven themselves to be the best. They will help the rod with suppuration come out in just a couple of days. You can alternate traditional methods of treatment with the use of pharmaceutical ointments. After the course of treatment, you should drink a vitamin-mineral complex and think about strengthening your immune system.
The two most popular methods of combating boils are a compress with baked onions and salt heating at home. Details of their use are described below. Before use, consult a specialist.
Warming a boil with salt at home
Warming up with a salt compress will help reduce pain and relieve swelling. True, not all patient reviews are positive. Some people note that the boil on the tailbone began to hurt more intensely after warming up. So this method is quite individual. Step-by-step instruction:
- Heat a small amount of salt in a frying pan.
- After the salt has cooled slightly, pour it into a bag made of natural fabric. It is important that there are no holes in the bag, otherwise you can burn your hands.
- Place the bag on the lumbar area so that the tailbone and the boil on it are completely covered.
- After the salt has cooled, remove the bag and lubricate the boil with any of the ointments described above. You can also alternate heating with compresses of baked onions.
Prevention
Purulent skin diseases are a common pathology. It is especially relevant in cases of excessive sweating and oily skin. Patients with hormonal disorders and diabetes need to be especially careful. They belong to the risk group for furunculosis. Wound healing in such people also occurs with difficulty. Therefore, the prevention of boils is to keep the skin of the tailbone clean. Treating oily or sweaty skin areas with various antiseptic wipes also helps prevent the formation of boils. It is possible to cure an abscess, but it is easier to prevent it.
When working in contaminated areas, maintain hygiene. To prevent an abscess on the tailbone, you should clean the skin of this area in between work. This is necessary because the lumbar area is easily rubbed during physical labor, and the skin is injured. When it becomes contaminated, conditions arise for the occurrence of a boil.
Furunculosis