Barley is a harmless but unpleasant disease that usually occurs without complications and completely disappears after 7-10 days . But in rare cases, this type of inflammation can be accompanied by various complications and requires, if not urgent surgical intervention, then at least the use of medications or folk remedies.
They help relieve the symptoms of stye on the eye and speed up the healing process.
Symptoms of the disease
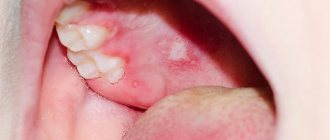
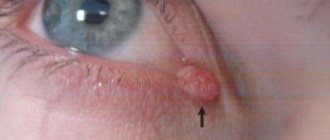
The main symptom of a chalazion is the appearance of a rounded swelling in the form of a nodule on the child’s eyelid. The formation is painless, not fused to the skin, but fits tightly to the cartilaginous plate of the eyelid. The size of the swelling usually reaches 5-7 mm. The skin on it is compacted, tense, shiny, and may be slightly hyperemic. Redness is usually more pronounced on the inner surface of the eyelid. A gray spot may appear in the center of the compaction, at the site where the excretory duct of the gland exits.
Even before the lump appears, the child may complain of discomfort, a feeling of “sand” in the eye, rapid eye fatigue, slight pain when blinking, or turning the eyeball. The swelling of the eyelid gradually increases and a nodular formation forms.
If the chalazion reaches a significant size, it puts pressure on the eyeball, which leads to visual impairment and astigmatism.
Occasionally, increased photosensitivity, lacrimation, and itching of the skin of the eyelids are noted. When a bacterial infection occurs, severe swelling of the eyelid, redness, and soreness appear; in severe inflammation, the patient’s general condition suffers and the body temperature rises.
Chalazion can be single or multiple; superficial, when inflammation is localized only in the meibomian gland itself, and deep, when inflammation affects the cartilage of the eyelid. Separately, an abscess chalazion, or pyogenic granuloma, is isolated - an acute inflammatory process as a result of the addition of a secondary infection.
Why do white spots appear under the eyes?
The main reason for the appearance of white dots under the eyes is a violation of the mechanism of exfoliation of dead skin particles. When this process fails, they accumulate on the surface of the skin, clogging the ducts of the sebaceous glands, which become clogged, and milia appear. Also, the cause may be excessive activity of the sebaceous glands - owners of excessively oily skin are well aware of this, when excess sebum does not have time to be eliminated.
Other factors that cause millet grains are disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract. Often milia are a consequence of hormonal changes in the body - for example, during puberty, pregnancy or menopause. Another version of the appearance of white spots on the skin around the eyes is exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
Milia can occur after a chemical peeling procedure, when using certain steroid drugs, as well as with frequent use of “heavy” cosmetics, in particular professional ones, which clog the pores of the skin on the face, and the process of peeling off the keratinized scales is much more difficult. In addition, doctors name allergic reactions and a lack of vitamin A in the body among the causes.
Millet is often observed in newborns in approximately 40-50% of cases. In this case, white dots can appear not only on the face, but throughout the body. In infants they disappear in the first 1-3 months of life. The cause is usually a blockage of the sebaceous glands; the child’s body adapts to a new, unusual environment for him.
Causes of chalazion in children
In children, the development of the disease is often provoked by physiological reasons - the narrowness of the ducts of the meibomian glands, the weakness of the smooth muscles of the eyelid, which are involved in the removal of secretions.
Chalazion often occurs against the background of other ophthalmological diseases - blepharitis, conjunctivitis, barley.
There are also nonspecific causes of pathology. This:
- hormonal changes and disorders (therefore, chalazion often appears in adolescence), endocrine diseases, often type I diabetes mellitus;
- skin pathologies – rosacea, seborrheic dermatitis, acne;
- diseases of the digestive system - dysbacteriosis, dyspeptic disorders, biliary dyskinesia;
- frequent colds, immunodeficiency states;
- vitamin deficiency, stress, constant hypothermia, violation of personal hygiene rules.
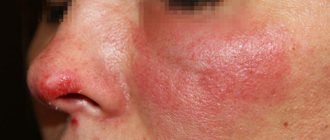
Stages of fight and prevention of xanthelasma
The only reliable way to combat xanthelasma is to eliminate it. Only the doctor will decide which method is preferable based on the specific situation. The laser beam is one of the latest achievements of high-tech medicine. Our clinic is equipped with modern equipment, and the procedure for removing xanthelasma of the eyelids is carried out by experienced professionals. Laser removal is characterized by a minimal risk of relapse, high sterility, low likelihood of injury to adjacent skin and the absence of subsequent inflammation. Contraindications for this highly effective procedure include diabetes, pregnancy, and the presence of dangerous tumor processes.
Stages of the fight against xanthelasma:
- preparation - visiting an ophthalmologist, taking tests, choosing a removal method taking into account the indications;
- destruction of education;
- restoration with the implementation of appropriate appointments and follow-up examinations.
As preventive measures, you need to choose those that are aimed at the normal functioning of the body as a whole.
To prevent xanthelasma you should:
- monitor your weight and achieve its optimal value;
- eat wisely, including fruits, vegetables, foods with beneficial properties in your diet, reduce the consumption of flour, fatty foods, and sweets;
- stabilize your drinking regime, drink at least two liters a day;
- lead a healthy lifestyle, eliminate bad habits, stress, regularly give the body adequate physical activity;
- prevent damage to the skin;
- observe personal hygiene standards;
- strengthen immunity;
- systematically undergo preventive examinations.
Diagnostics
If you suspect a chalazion, you should contact a pediatric ophthalmologist. The doctor will interview the child or parents, find out complaints, life history and illness, and also conduct a general examination. In addition to questions directly related to the disease (when did the lump occur, what preceded it, whether there were eye diseases before), the doctor will also be interested in general aspects, for example, does the child attend kindergarten, how often does he suffer from acute respiratory infections or acute respiratory viral infections, does he have chronic pathologies .
During an ophthalmological examination, the doctor will palpate the formation, examine the outer and inner edges of the eyelid, and check visual acuity.
If necessary, an additional diagnostic procedure – biomicroscopy – may be prescribed. This is an examination of the eyelid using a slit lamp in a dark room. Biomicroscopy gives the doctor the opportunity to examine the lesion enlarged in directional light. The procedure is performed for children over 4-5 years of age who are able to follow the doctor’s instructions, since during the procedure it is required to sit still and, if possible, not blink.
Treatment
Chalazion in a child can often be treated using conservative methods. For this purpose the following are assigned:
- Warm compresses - soak a towel in hot water, wring it out, cool slightly to a comfortable temperature, and apply to the affected eyelid for 5-7 minutes. When it cools down, wet the towel again in hot water and wring it out. You can also use cotton pads soaked in hot water and wrung out for this purpose. Repeat several times in one procedure, 2-4 times a day.
- Dry heat . At home, most often a hard-boiled egg wrapped in a clean, dry cloth is used for this.
- Physiotherapy.
- Massage of the edge of the eyelid . It is done with circular and perpendicular movements to the edge of the eyelid, without strong pressure. During one massage procedure, you should make 15-20 movements, repeat 2-4 times a day. Massage is contraindicated when the chalazion is suppurated.
Before compresses or massage, you should clean the edge of the eyelid and eyelashes if a large number of crusts and scales have accumulated on them. Contaminants are removed with a cotton swab moistened with warm water, if necessary, after soaking them.
If the disease is accompanied by dry eye syndrome, moisturizing drops are prescribed. If the chalazion is accompanied by blepharitis (inflammation of the edge of the eyelid), the doctor may prescribe anti-inflammatory drops and/or ointments.
When infection occurs and suppuration occurs, drops and ointments with antibiotics are indicated. When the seal is large, it is sometimes practiced to introduce hormonal injections into its cavity.
When an abscess forms, it is opened. Also, indications for surgical treatment are significant growth of the chalazion and lack of effect from conservative therapy. The excision procedure is low-traumatic and is mainly performed under local anesthesia. After opening the cavity and exfoliating the affected gland, antibacterial rinses and drops are prescribed. An alternative to excision is laser removal of the chalazion, however, the procedure has contraindications and is not performed in all clinics.
In some cases, after surgical removal of the chalazion, biomaterial is taken for histological analysis. It is not always carried out, mainly in cases of rapid growth of the tumor and frequent relapses. The study is necessary to exclude adenocarcinoma of the meibomian gland.
Any treatment methods, even such simple ones as local warm compresses, must be prescribed by a doctor; self-medication is unacceptable, as it can lead to the development of complications. In the case of frequently recurrent, multiple chalazions, one should look for a common cause of their occurrence (possible chronic diseases, reduced immunity) and eliminate it.
How to treat eyelid inflammation
Treatment of inflammatory diseases of the eyelids is carried out in accordance with their cause. Depending on the pathology, therapy includes:
- the use of ointments (with sulfonamides, antibiotics, corticosteroids), an alcohol solution of brilliant green, drops;
- general therapy (antibiotics, sulfonamides, oral antihistamines);
- massage of the eyelids with removal of the contents of the glands;
- hardware physiotherapeutic treatment with UHF, laser heating, electrophoresis;
- surgical removal of chalazion;
- vitamin therapy autohemotherapy.
Consultation with an ophthalmologist is provided at the following addresses:
- 40 years of October, 15 +7
- B. Khmelnitsky, 20 +7
- Komsomolsky Prospekt, 33 +7
- Kashirinykh Br., 131B +7
- Bluchera, 55 +7
Popular questions
How is a chalazion different from a stye?
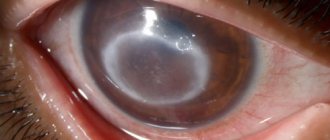
Etiology. Chalazion is a non-infectious disease, while barley (hordeolum) is caused by opportunistic bacteria that are constantly present in the human body and are activated under certain conditions. Most often, the development of barley is provoked by Staphylococcus aureus.
External signs and sensations. Barley always develops on the ciliary edge, chalazion - at some distance from it. Barley is accompanied by severe hyperemia, pain, and local fever. With chalazion, these signs are absent or slightly expressed. The stye suppurates and a yellowish spot appears in its center. Chalazion suppurates only when a secondary infection occurs.
Exodus. Barley almost always breaks through, after which relief comes. Chalazion very rarely breaks out on its own.
Is chalazion dangerous?
Timely diagnosis, medical supervision and treatment appropriate to the form and severity of the disease eliminate the danger of chalazion. However, if medical care is neglected, complications may arise, some of them quite severe.
Complications of chalazion:
- conjunctivitis, blepharitis, abscess formation due to infection;
- mucous cyst of the eyelid;
- visual impairment due to prolonged pressure on the cornea due to large formations;
- fibrosis of the cartilage of the eyelid, loss of eyelashes;
- inflammation of the subcutaneous fatty tissue of the orbit of the eye.
What to do if a child’s chalazion ruptures?
After a breakout of the chalazion capsule in a child, it is necessary to treat the breakout site and surrounding tissues with antibacterial agents to prevent infection and the development of complications. To receive qualified help, you need to see a doctor. If it is not possible to visit a pediatric ophthalmologist in the near future, you should wash the wound surface with an antiseptic solution, such as furatsilin. To do this, soak a cotton pad generously in the solution and rinse the eye moving from the outer to the inner corner. You need to rinse several times, each time using a new cotton pad. After this, you can put antibacterial drops into your eye. Before using them, you should carefully study the instructions to see if the product is suitable for use in children, and also pay attention to the expiration date, including after opening. It is better to use a freshly opened bottle.
What are the reasons for the recurrence of chalazion in a child?
Basically, relapse occurs with concomitant diseases of the body that were the cause of chalazion, other ophthalmological pathologies, as well as with incomplete enucleation of the capsule during surgical removal. Frequent recurrences of chalazion are a reason for histological examination of its contents in order to exclude adenocarcinoma of the meibomian gland.
Sources:
- Recurrent chalazions in children. Serge Doan. Service d'ophtalmologie, hôpital Bichat et Fondation Adolphe-de-Rothschild, Paris, France.https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32237654/
- A comparison of intralesional triamcinolone acetonide injection for primary chalazion in children and adults. Jacky WY Lee, Gordon SK Yau, Michelle YY Wong, Can YF Yuen. 1Department of Ophthalmology, Caritas Medical Centre, 111 Wing Hong Street, Kowloon, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region, Hong Kong.https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25386597/
- Assessment of the condition of the meibomian glands in children of different ages. Bobryshev V.A. FORCIPE, 2022. p.632-633.
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
Symptoms of stye
The appearance of stye begins with the appearance of itching, usually localized at a point on the edge of the eyelid. Then the skin in this place begins to turn red, swelling forms, and the eyelid swells. Painful sensations occur, which intensify if you touch or press on the sore spot. In some cases, stye prevents the eyelid from closing completely. The eye may become very watery. The parotid or submandibular lymph nodes are enlarged. The temperature may rise.
On the 2-3rd day, a white or yellowish head forms at the top of the barley. After some time, the barley “ripens” and breaks through. Pus flows out. After which the eye gradually returns to normal.
Prices
| Name of service (price list incomplete) | Price |
| Appointment (examination, consultation) with an ophthalmologist, primary, therapeutic and diagnostic, outpatient | 1950 rub. |
| Consultation (interpretation) with analyzes from third parties | 2250 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment regimen (for up to 1 month) | 1800 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment regimen (for a period of 1 month) | 2700 rub. |
| Consultation with a candidate of medical sciences | 2500 rub. |
| Biomicroscopy of the anterior segment of the eye | 500 rub. |
| Selection of glasses with plain lenses | 600 rub. |
| Subconjunctival injection (1 eye) | 500 rub. |
| Removal of a foreign body from the conjunctiva, from the eyelids | 800 rub. |