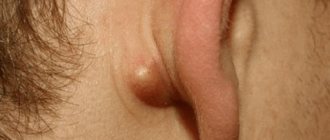
Atheromas are cysts of the sebaceous glands that are often found under the skin behind the ears and look like small whitish balls.
Atheromatous sebaceous cyst is not an oncological disease. Often atheromas go unnoticed, but sometimes they can be felt and cause discomfort upon palpation.
Rice. 1. Atheroma behind the ear
Atheromas that occur behind the ears can be located in other places: for example, on the head, back, face, chest, etc.
The most common location for atheromas is the face, neck and torso.
Atheromas can be of different sizes, large and small.
Very often, atheroma does not bother you at all, but sometimes, as a result of friction of atheroma on clothing, rupture due to pressure or injury, or infection, discomfort and pain appear. In this case, the atheroma must be removed.
Atheroma or cyst of the sebaceous gland in the postauricular area
Atheroma is a cyst filled with dead skin cells and sebum.
Behind the ears there are countless sebaceous glands, so it is in this area that atheromas are found very often. However, atheromas can often be found in the ear canal itself.
Rice. 2. Suppurating atheroma behind the ear
Although atheromas do not become malignant (such cases are described extremely rarely), they can become complicated. First of all, atheroma, in the absence of timely treatment, can become infected. When infected, the atheroma becomes inflamed.
If the atheroma is located in the genital area, then when it becomes inflamed, pain may occur during urination and sexual intercourse.
What do they look like on the ear?
A medical examination begins with clarification of complaints, anamnestic information, and determination of objective signs of pathology. It is precisely by the features of the clinical picture that a diagnosis can be assumed at the initial stage.
Small on the cartilage
When a lump grows on the cartilage of the ear, one can think of chondrodermatitis nodosa, which occurs due to excessive pressure, or preauricular papilloma, which is a defect in embryogenesis. In the first case, a dense painful nodule appears, usually in the area of the helix or antihelix of the concha. The skin around it may be normal or reddened, sometimes ulcerated. Preauricular papillomas are a small growth on the tragus that is present from birth and does not cause subjective discomfort. If there is mechanical damage to the cartilage, for example, after piercing, there is a possibility of scar formation, which also appears in the form of a lump.
Why do atheromas appear behind the ears?
Research into the mechanism of atheroma formation is still ongoing.
Today it is known that the epidermis (the surface layer of the skin) consists of layers of cells that constantly peel off from the surface during the process of growth. In the case when skin cells stop exfoliating and, accumulating and multiplying, begin to move into the tissues - a cyst wall is formed - atheroma. Inside the formed cavity, dead skin cells rich in proteins - keratin, and sebum accumulate. This is how atheroma is formed.
On the surface of the atheroma you can always find an enlarged pore through which the cyst can drain. In this case, we may notice yellowish masses with an unpleasant odor of decomposing sebum.
Other cysts, called epidermal, are very similar in appearance to atheromas. However, epidermal cysts are formed from sweat glands and their contents are very different in composition from the contents of atheromas.
Causes of tumor formation in the soft tissues of the ears
The most common sources of the disease, as a result of which a wen may appear in the skin tissues of the ear:
- hormonal disorders;
- diabetes;
- oily seborrhea;
- metabolic disease;
- influence of radiation;
- abnormal development of hearing organs;
- injuries (for example, unsuccessful piercing);
- insect bites;
- heredity;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- smoking;
- bad ecology.
Individually or together, all of these factors cause the formation of tumors in the earlobe.
Symptoms and signs of atheroma
Many patients, having atheromas behind the ears, do not even pay attention to them. However, sometimes atheromas become a serious concern.
It is worth paying attention to the following signs indicating the need to seek medical help:
- There is a small round ball under the skin;
- There is redness, swelling, thickening;
- There are signs of inflammation and infection;
- On the surface of the atheroma there is a small pinhole closed with a black plug;
- It is possible to extract thick yellow contents with an unpleasant odor from the atheroma.
You should consult a doctor immediately if the atheroma:
- Suddenly it began to grow quickly;
- Suddenly burst;
- Inflamed;
- It became sharply painful.
What is a lipoma?
Benign tumors located directly under our skin, consisting primarily of adipose tissue, are called lipomas (colloquially a lipoma is called a “fat”).
A classic lipoma (fat) is a lump located directly under the skin, elastic, painless when touched, and displaces with light pressure. Typically, a lipoma is visible to the naked eye because it forms a lump on the skin. The size of lipomas usually does not exceed the size of a bean grain, but in “advanced cases” the tumor can reach significant sizes. The localization of lipomas can be very diverse. This tumor can develop in any part of the body where there is fatty tissue. Once formed, the wen gradually grows, increasing in size.
Removal of atheromas behind the ears.
Atheroma behind the ear can be removed in two ways:
- Laser;
- With a scalpel.
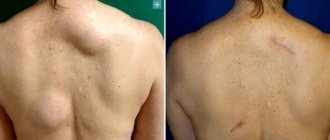
With traditional removal with a scalpel, after injection anesthesia, a skin incision is made to expose the atheroma. Then the cyst is removed along with its contents. The skin wound is sutured.
Rice. 3. Bursting atheroma behind the ear
It is clear that when working with a scalpel, a scar is left on the skin, comparable in size to the atheroma itself, and sometimes larger.
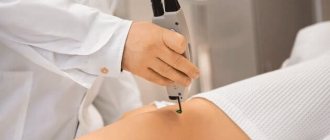
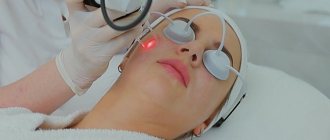
Laser technologies make it possible to remove atheroma entirely without a single drop of blood from a small puncture in the skin, which allows for the best possible cosmetic result.
Folk remedies against wen
In the fight against tumors, one must be careful when using traditional and non-traditional methods of treatment. They will give results only in the beginning. You shouldn’t count on a complete recovery, but traditional medicine will come in handy as a deterrent.
To the question of how to get rid of wen, healers answer differently: they recommend making compresses from aloe juice, rubbing heated lamb fat, cauterizing the tumor with celandine juice, applying chopped garlic, making lotions from pepper tincture.
However, before starting treatment with folk remedies, you must consult your doctor. Without laboratory tests, it is extremely undesirable to manipulate subcutaneous formations: there is a high probability of causing infection or causing degeneration. In addition, squeezing out the wen at home will not allow you to remove the capsule. And this will lead to the formation of a new tumor in the old place.
Advantages of laser removal of atheroma behind the ear:
- Speed (removal is possible on the day of treatment in just 15-20 minutes);
- Atheromas of any size and in any condition can be removed (even festering atheromas can be removed, since the laser has a sterilizing effect on tissue);
- Bloodlessness (the laser seals the vessels that feed atheromas and removal takes place in a dry field);
- Fast recovery;
- Almost complete absence of relapses and complications in the postoperative period.
If you have atheroma, we suggest seeking help from laser medicine specialists at the ATLANTIC Laser Surgery Center.
Classic methods of treating atheroma
In classical medicine, there are several approaches to treating wen. The most loyal is the introduction of a special liquid into the sebaceous duct. Under its action, the fat “plug” is gradually reabsorbed.
This procedure can be carried out either by an otolaryngologist or by a qualified cosmetologist. The method is suitable for removing tumors up to 2 cm in diameter.
A more radical method involves surgical removal of the wen, when the cyst is “husked” out of its shell, under local anesthesia. Also used:
- radio wave therapy;
- laser burning of tissues;
- liquid nitrogen treatment;
- endoscopy;
- liposuction.
The choice of technique is made by the doctor, based on the type of tumor and the individual characteristics of the patient’s body.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of wen behind the ear is rarely difficult. Usually, examination and palpation are enough for an experienced doctor to make a preliminary diagnosis. Additional research is prescribed to differentiate from other tumors with a similar course and structure.
A number of such measures are prescribed as diagnostics.:
- X-ray;
- Ultrasound;
- MRI or CT examination.
Laboratory tests are prescribed to identify or exclude possible concomitant pathologies and the inflammatory process. If there are atypical symptoms indicating the development of complications, then extensive diagnostics is required.
Wen behind the ear belongs to the field of surgery, oncology, and dermatology. If surgery is necessary, a consultation with an anesthesiologist-resuscitator is possible.
How is it detected?
Diagnosis of tumor-like formations in the area of the auricle is a responsible and important task. It is possible to determine the nature of the pathological process and its cause only through the results of a comprehensive examination. Depending on the clinical situation, its structure may include:
- Complete blood count (leukocyte count, ESR).
- Analysis of discharge (cytology, culture).
- Biopsy with histological examination.
Several specialists are involved in the diagnostic process. The patient needs to be examined by a dermatologist or ENT doctor. If the lump on the ear is of a tumor nature, then consultation with an oncologist is required.
Wen or lymph node?
Often the wen looks like a hardened, inflamed lymph node. However, fatty tissue is easy to distinguish from a lymph node, since the appearance of a lymph node is often associated with an increase in body temperature or some kind of infectious or inflammatory disease. Lymph nodes are located in certain places of the human body, while a wen (lipoma) can be localized in any part of the body where there is subcutaneous fatty tissue. The lymph node can often be painful when pressed (a lipoma will be painless).
What to do if a ball appears in your earlobe?
Don’t immediately start getting rid of the unpleasant lump. No one will like the sight of earlobes festering from an infection. But stop assuming the worst and making dire diagnoses for yourself.
Symptoms that distinguish lipoma from other types of tumors:
- the skin does not change color;
- the fat globule under the skin is mobile, which is easy to check by pressing with your finger;
- pain and discomfort are not felt until the wen is injured and inflamed.
If the tumor is smaller than a pea, its size is constant - there is no danger. You can simply make sure that it is really a wen at an appointment with a therapist. There are several signs that you urgently need to consult a surgeon:
- The wen grows quickly (about 1 cm in 6 months).
- The swelling became painful.
- Inflammation began and pus appeared.
- Lipoma is noticeable and affects appearance and self-esteem.
When a wen appears behind the ear, it is difficult to prevent it from being injured. Combing hair and wearing hats constantly disturbs the swollen area. In this case, it is also appropriate to visit a surgeon.
To clarify the diagnosis, a more complete examination will be required. Depending on the symptoms, these may be the following procedures:
- a detailed blood test to determine the number of lymphocytes that increase in cancer;
- puncture to check the tumor tissue or the contents of the wen for pathology;
- Computed tomography with a contrast agent gives a more complete picture of the lipoma, but it is done mainly when examining internal organs.
The doctor will draw conclusions based on the results obtained and recommend the best treatment. To date, lipoma has been little studied. The only way to cure a wen is to remove it completely.
Traditional and modern methods of surgical treatment
There are several ways to remove a wen.
1. The simplest, proven method is surgery. It is prescribed for lipomas of any size and is performed under local (less often general) anesthesia. Through the incision, the doctor removes the entire fat capsule, so there are practically no relapses. The disadvantage of this technique is noticeable scars and long healing times.
Causes of painful bumps
Pain is a universal response to injury. Volumetric formations on the auricle are accompanied by the development of such a symptom in several cases. First of all, it is necessary to exclude an acute inflammatory process:
- Furuncle.
- Lymphadenitis.
- Sialadenitis.
- Mastoiditis.
A reddened ball on the lobe may be a suppurating atheroma, and a black (dark blue) swelling may be an inflamed hematoma. Pain is also accompanied by chondrodermatitis nodosa, injuries, insect bites, and destructive malignant tumors.
The variety of causes of ear bumps creates the need for a thorough differential diagnosis, excluding the most dangerous conditions.
How to get rid of the defect?
After establishing the diagnosis, the doctor begins therapeutic correction. In some cases, it is optional - for example, with small lipomas, atheromas, preauricular papillomas or scars after piercing. The exception is cases when there are medical indications or the patient wants to get rid of a cosmetic defect.
Conservative treatment
Conservative methods occupy key positions in the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Furuncle, purulent lymphadenitis, inflamed atheroma are treated according to general principles - during the period of infiltration, anti-inflammatory ointments (ichthyol) are prescribed, the surface is treated with antiseptics. After opening, drugs with an adsorbing effect (Levomekol, Dioxykol) are used. At the same time, systemic antibacterial therapy, antipyretics, and immunomodulators and vitamins are prescribed to increase the body’s defenses.
Conservative treatment is sufficient for bruises, insect bites, and inflammatory diseases. In other cases, you have to resort to more radical correction.