In the clinical practice of pediatric cardiologists, the shade of the skin is often one of the defining signs during diagnosis. For example, a bluish color indicates a lack of oxygen in the blood. Blue skin in certain areas in children should make parents wary, because this symptom most often signals hidden heart pathologies. It is not at all necessary to wait for the appearance of other disorders that will act more convincingly than a change in the shade of the skin.
Adults should understand that many congenital anomalies, including heart defects, can be asymptomatic in children. But the loyalty of cardiac pathologies does not last long, since impaired oxygen metabolism affects the vital functions of all organs. As the little person grows, the situation only gets worse. Therefore, the prognosis depends largely on the actions of adults: the sooner they show the child to a pediatric cardiologist, the greater the chance of a full recovery.
Cyanosis: main types and their features
In medicine, there is a special classification used to determine the degree of cyanosis, which doctors use in diagnosis. This sign is divided into several groups according to different parameters.
Depending on the location of distribution, cyanosis is of two types:
- Total cyanosis covers all skin.
- Local or regional cyanosis spreads to certain areas of the skin. Based on this characteristic, blueness, in turn, is divided into two subspecies:
- central cyanosis is usually located near the mouth and around the eyes.
- peripheral cyanosis (acrocyanosis) is noted in distant areas: fingers and nails of the extremities, earlobes.
Cyanosis is characterized by different levels of severity. For example, with a rapid increase in oxygen starvation, it manifests itself acutely, while the chronic type develops gradually over many years.
The main causes of cyanosis in children
Before listing the possible factors that can affect the change in skin color, you should find out how the creation of an individual shade is formed. This process involves the coloring pigment (melanin) and a network of capillaries. In other words, the skin color of each person depends on the level of this natural dye, as well as on the location of the peripheral blood vessels that nourish the dermis.
The composition of the blood itself also plays an important role. It is known that the main function of this biological fluid is to transport oxygen. This process occurs with the involvement of the hemoglobin protein, which is part of erythrocytes, that is, red blood cells.
Blood enriched in the lungs (arterial) has a bright scarlet color. But as it passes through the blood vessels, the amount of oxygen decreases, so the scarlet hue changes to a dark cherry color. And this is already venous blood. When oxygen exchange is disturbed, it is venous blood that accumulates in the tissues, which determines the bluish color of the skin.
Stagnation of such blood is explained by two reasons:
- Poor circulation with insufficient venous outflow. This disorder is more typical for pathologies of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems.
- Impaired gas exchange in the lungs. This type of disorder is associated exclusively with diseases of the respiratory system, or it develops when the center that regulates respiratory functions is damaged.
The skin of climbers takes on a bluish tint because the oxygen content in the atmosphere at high altitudes is catastrophically reduced.
How does a tumor occur?
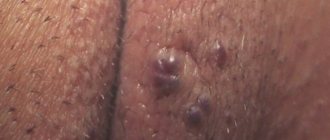
Statistically, hemangioma appears in ten percent of infants. The percentage is not so small if you think about it. Most often, formations found on the baby’s skin are located at such points that the tumor does not pose a danger to vital organs and does not cause damage to the mucous membranes. The only problems that education can cause are aesthetic ones. But they are precisely the most significant. Agree, a rough red “blot” in the middle of the forehead or on the child’s face, reminiscent of an exaggerated wart or depression, will bring few parents into a relaxed state.
Hemangioma on the forehead. Unsightly stain
By the way. Not every formation found on the skin of a baby is a hemangioma. Therefore, those parents who, at the sight of a spot, begin to sound the alarm and go to the doctor are right.
Signs of hemangioma.
- The most common type of tumor among newborns.
- Benign education.
- Appears only in children from age zero (immediately after birth) to the age of 60 days.
- Affects every tenth child on the planet.
- It is three times more common in girls (for every three newborn girls with this type of tumor, there is one male child).
- May appear as a flat spot.
- May resemble a depression (grow deep).
- Forms a bulge (most often).
- It has any size - from a “grain” to a large spot.
- There may be several or even many formations.
- If more than three hemangiomas are found on the skin, they are also present inside the body.
- Goes away on its own (in the vast majority of episodes).
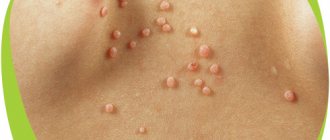
Hemangiomas
Combined hemangioma in the breast area
Important! The most important sign that this is not a malignant formation, but a “harmless” benign hemangioma is that it contains elements of endothelial cells (the inner surface of blood vessels).
Of course, we are talking about “harmlessness” only when the formation is located outside, does not block physiological openings, does not damage the mucous membranes and does not increase in size.
There are several types of hemangiomas based on their location and structure.
Table. Types of hemangiomas.
| Variety | Description |
| It is formed from dilated vessels and cavities filled with venous or arterial blood. Does not penetrate deep into the skin, is located on the surface. It has the softest structure of all varieties. Amenable to basic therapy. |
| Located in internal organs, the blood supply to which is enhanced. These are the spleen and liver, adrenal glands, kidneys and brain. Diagnosed using ultrasound. It is considered dangerous, especially if localized in the liver, spleen and brain. Education is asymptomatic, and this poses the greatest danger. In case of injury, the spleen and liver rupture, filling the abdominal cavity or liver capsule with blood, which in more than 80% can be fatal. Rupture of a cerebral hemangioma leads to hemorrhage in the brain, which plunges the patient into a coma or causes death. |
| It consists of a combination of simple capillary and cavernous parts. And this is the greatest danger. The formation can go deep into the skin, and it is often mistaken for capillary, while the hidden cavernous part is capable of ruptures and hemorrhages. |
| Mixed | This is no longer quite a hemangioma, since, along with the vascular formation, in parallel with it, a tumor of other tissues develops - nervous, connective, and so on. |
| Capillary | It is considered the simplest formation consisting of blood vessels of the dermis. Does not enter the lower skin layers, usually has a convex shape. These are capillary vessels intertwined with each other, which in very rare cases are capable of hemorrhage. As a rule, its size is no more than a centimeter, and its color is light, which indicates its involutionary development. |
What pathologies cause cyanosis?
Most often, a bluish tint to the skin is a companion to cardiovascular diseases in children. But in some pathologies of the respiratory system, this symptom is also clearly expressed. We list the most common diseases:
- congenital heart defects;
- arrhythmias;
- cardiomyopathy;
- myocarditis;
- heart valve defects;
- ischemia;
- bronchial asthma;
- bronchiolitis;
- pneumonia.
In young children, cyanosis in most cases is caused by a congenital heart defect formed during fetal development. Therefore, a newborn baby develops cyanosis characteristic of this pathology already in the first minutes after birth. Thanks to modern technologies, today it is possible to identify such abnormalities in the fetus during pregnancy.
Acquired heart defects often develop as a complication of other pathological processes. For example, endocrine diseases affect blood circulation. Damages to the central nervous system can also negatively affect cardiac activity and blood supply to internal organs.
What does a mother need to know about her newborn baby?
The questions are answered by the chief freelance neonatologist of the Ministry of Health of the Amur Region, assistant of the Department of Childhood Diseases of the Faculty of Pedagogical Training and Pedagogical Training of the AGMA, Ph.D. Kharchenko Maria Vitalievna.
Any question you have, you can ask through our {rokbox text=|form|}index2.php?option=com_contact&view=contact&id=2{/rokbox} feedback.
My baby was born weighing 3 kg 600 grams, and in the maternity hospital he lost 250 grams. Is this normal or not? After all, I breastfed him at the “child’s request,” as recommended by the pediatrician. Maybe I should have supplemented him with formula. ?
Don't worry, everything is fine! During the first 5 days of life, a newborn may lose up to 10% of its birth weight.
Your baby has lost 7% of his original weight. This weight loss is normal and is called physiological weight loss . It can be caused by several reasons: the passage of meconium, quite significant losses of fluid through the skin and lungs (during the baby’s breathing) and insufficient nutrition in the very first days of life. Colostrum, which a child receives in the first days of life, cannot fully compensate for the child’s energy costs. However, if mother and baby are in the same room, then she will be able to put him to the breast every time he demands it (free feeding mode). In this case, the mother’s milk comes in much faster and the newborn’s weight loss is unlikely to exceed 5-7%. Most babies, with this type of feeding, regain their original weight by the time they are discharged from the maternity hospital or during the first days (week) of being at home.
What is colostrum and why is everyone so in favor of early breastfeeding?
Colostrum is a secretion of the mammary gland, which is a yellowish thick liquid with a salty taste and a specific odor. Colostrum production begins a few days before birth (with the exception of premature birth) and continues for 3-4 days after birth. Colostrum differs from milk in its increased acidity, higher content of proteins (mainly albumins and globulins), fats, minerals and vitamins and less sugar.
In terms of the set and combination of nutrients, colostrum is an indispensable food for newborns. It contains a large number of immune bodies and antioxidants that protect the baby from various infections that his immune system does not yet produce. Colostrum also stimulates normal intestinal activity, helps cleanse the newborn’s digestive system of meconium and fills it with bifid flora, thereby facilitating the baby’s adaptation to extrauterine existence.
Early latching is the latching of the baby to the mother's breast in the delivery room 20-30 minutes after birth. The first contact between mother and child is extremely important. It is believed that the sooner a mother can touch her baby, hold him close, the better for establishing emotional connections between her and the child, the sooner the mother’s maternal instinct awakens, and the child’s love for his mother. It is at this moment that the child begins to recognize you by your voice, absorbing the warmth of your body with his whole being, learns that you are a source of food for him, his protection, and begins to love you. The first, so early application of a child to the breast can be considered the first vaccination, because Colostrum contains a large amount of antibodies (immunoglobulins) that protect the baby from various infectious agents of the surrounding world. Breastfeeding a baby in the delivery room is also very beneficial for the mother, because... When a baby sucks at the breast, the mother's body actively produces a hormone - oxytocin, which causes contractions of the uterus and helps prevent postpartum uterine bleeding.
Please tell us about birthmarks, and which ones should we be “afraid of”?
Quite often, birthmarks of various colors and types can be observed on the skin of a newborn baby. Some birthmarks remain with a person for life, while others disappear after a while.
Congenital age spots can vary in color: from barely noticeable light brown to dark brown and even black. The shape, size and number of pigment spots are different. It happens that pigmented birthmarks have the same shape and are located in the same places on the body as those of the child’s parents. Pigmented moles (nevi) rise above the surface of the skin.
In addition to pigmented birthmarks, there are vascular birthmarks - hemangiomas . They can be of different color saturation: from pale pink to dark crimson, sometimes with a purple tint. Hemangiomas are quite common, but at birth they can be very pale and flat, and therefore almost invisible. Some time after birth, the spots may increase in size and rise above the surface of the skin. With age, some hemangiomas disappear on their own, but more often “port-wine stains” remain for life.
Most newborns with yellow and dark skin (having Asian and/or Negroid blood) have rather large gray-blue spots that never rise above the surface of the skin between the shoulder blades, along the spine or in the sacrum, buttocks. These are “Mongolian blue spots”. Most of these spots disappear by 5-6 years, but some “Mongolian” spots remain.
In addition to birthmarks, which remain on a person’s skin for life, newborns may also experience spots or stripes that will disappear after a short time. Thus, between 2-8 weeks of life, some children may develop a thin pigment strip along the midline of the abdomen, which will disappear after 2-3 months.
On the head (on the back of the head, forehead, bridge of the nose, eyelids or lips), some babies can observe reddish vascular spots (telangiectasia ). Old obstetricians call them “Stork Slivers.” These are the remains of embryonic vessels that disappear by 12-15 months.
You should pay close attention to birthmarks on your baby’s body. Usually they do not require any care or treatment, but you must remember that the doctor will monitor children who have more than 5 age spots on their body or have port-wine stains on the face, or protruding moles. And be sure to tell your doctor if you notice that a birthmark on your child’s body is increasing in size or changing color!
Please tell us what is newborn jaundice?
1-2 days after birth, most newborns experience yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes. Yellowing begins on the face and then spreads to the entire body. This is physiological jaundice of the newborn. The cause of this condition is enzymatic immaturity of the liver. A newborn baby's blood contains a large number of erythrocytes (red blood cells), which are highly unstable and easily destroyed. When red blood cells break down in a person's blood, hemoglobin (a substance that binds and transports oxygen) is released, which in turn is destroyed, turning into the yellow pigment bilirubin. Having entered the liver, bilirubin, under the influence of liver enzymes, is converted into a component of bile and excreted into the intestine. The newborn's liver cannot cope with large amounts of bilirubin, and it is released into the blood. In an adult, bacteria live in the intestines that continue the process of breaking down bilirubin. Newborn babies do not have such bacteria, but they do have an enzyme that allows bilirubin to be reabsorbed into the blood. As a result, the baby’s skin, mucous membranes and whites of the eyes acquire a yellowish tint. Such jaundice is observed in almost all children in the first days of life. It does not require treatment because the blood clears itself within a few days. If jaundice persists for more than a week, a blood test is taken from the child to determine the amount of bilirubin, after which treatment (phototherapy) is prescribed.
What should a newborn baby be able to do?
A healthy full-term baby should be able to:
- briefly raise his head when lying on his stomach (but the child still cannot hold his head while in an upright position!);
- reflexively move legs and arms (almost all the time when not sleeping);
- move your head from side to side;
- respond to sudden stimuli with active movements of the whole body;
- demonstrate the normal development of unconditioned reflexes: “searching for the breast”, sucking, grasping, crawling (lying on the stomach, if you place your palms on the baby’s piles), etc.;
- close your eyes to bright light and focus your vision at a distance of 20-30 cm from the eyes. The eyes may “squint” slightly at this time;
- respond to sounds: to loud ones - by shuddering or freezing, to a quiet voice - by “listening”;
- ask to eat every 2-2.5 hours;
- frequently empty the intestines (at every feeding and sometimes up to 12 times a day) and the bladder (from 6 to 20 times a day);
- maintain normal body temperature (from 36.50 to 37.30).
Please tell us what free swaddling is?
Swaddling still remains the most popular way of dressing children in our country, at least during the newborn period. Conventionally, swaddling is divided into tight and loose.
Tight swaddling is when the baby is wrapped in a swaddle up to the neck, covering both arms and legs, after which he resembles an ancient Egyptian mummy. It is believed that this option is optimal for the first week of a child’s life - the baby does not disturb himself with restless and unconscious movements of his hands and sleeps better. Whether this is true, you can check in practice.
Free swaddling is when the child is dressed in a vest on top, and you wrap the lower part of the body with a diaper, while the arms remain free, and the legs are not swaddled tightly (the diaper is fixed under the baby’s chest, and the legs move freely in the resulting bag). At the same time, you need to remember that if you use loose swaddling for a newborn baby at night, you need to use baby undershirts with sleeves sewn at the ends (because the baby may get scratched or be afraid of his sharp nails). In the second month of life, such precautions are usually not required.
When can you dress your baby in real clothes?
Whenever you want, even upon discharge from the maternity hospital! The manner of dressing newborns in blouses and pants is more typical for Europeans, because The textile industry abroad has been producing clothes marked “from 0 to 6 months” for many years. Our compatriots, rather, are committed to tradition, in the sense that they prefer to swaddle the baby at home, albeit in a free way, and leave beautiful things that resemble adult clothes for ceremonial occasions at the clinic, for guests, or for walks. And yet, if you are categorically against turning a little person into a cocoon, today there are ample opportunities to dress him “for real” from the first days of life (and even premature babies). The most important thing is that children's clothing is comfortable for the baby, easy and quick to put on, take off and wash.
Benefits of diapers:
- easy to wash and iron;
- more affordable.
Flaws:
- almost inaccessible to dads (in the sense of mastering the swaddling technique!);
- Tight swaddling restricts the baby's movements.
Advantages of “real” dressing:
- available for dads;
- amuses mother and others.
Flaws:
- more difficult for “sanitization”
- double-sided ironing of eight pairs of sliders “at speed” can affect mother’s nervous system.
Remember that a newborn baby, regardless of gender, does not like to dress, resists this in every possible way, and you will have to carry out this procedure in record time with the least amount of effort!
Attention! Hats, caps and scarves on the head of a child in the house are not needed. They are used after bathing to protect the baby’s wet head from hypothermia (for a short time, until the head dries out) or during walks.
Please tell us how to tell if your baby is warm or cold?
When dressing your baby, always remember the basic principle - dress like yourself! If you walk around the house wearing a hat, go ahead! But this is rare. With all responsibility, we can say that a baby wrapped up to the brim, crowned with a flannel cap, will instantly catch a cold and get sick if you unwrap him. Give your baby's body a chance to fight the environment and activate its natural powers.
How to determine if your baby is warm? A fairly accurate criterion is the condition of the skin: normally the skin is light pink and pleasantly warm to the touch. If the baby is red, the skin is hot, and even damp, and diaper rash and heat rash appear - there is no doubt that you are dressing him too zealously. Reduce the amount of clothing you wear and don't stress! If the baby begins to freeze, his nose will first turn red and become cold, then his arms and legs will become cold. They may even acquire a bluish tint, but you should not allow this to happen. There must be a limit to everything, even testing your child’s safety margin. Warm him up as soon as possible and dress him a little warmer, and remember, not a single healthy child will stoically endure the cold. If the baby is really cold and frozen, you will be the first to know about it - by angry crying, active movements and restlessness.
Please tell me what temperature should be in the room where a newborn baby is?
The temperature in the room where the newborn is located should be 22-240. In modern apartments, during the heating season, the air not only has a higher temperature, but also is dry. This leads to drying out of the nasal mucosa in the newborn and the formation of crusts. That's why babies sneeze often. It is necessary to regularly ventilate the room and humidify the air using modern climate systems or wet diapers that can be hung near the radiators.
How to correctly measure body temperature in a newborn baby?
First, you should know that a healthy newborn has fluctuating body temperatures, especially in the first week of life. Only by one and a half to three months the temperature becomes fairly constant. The amplitude of temperature fluctuations during the day depends on age, air temperature, physical activity, emotional state (screaming, prolonged crying lead to an increase in t0), the quality and quantity of food taken (overfeeding, underfeeding can lead to an increase in t0), the state of the endocrine system and others factors.
Secondly, temperature measurement must be carried out while the child is calmly awake. Temperature measured during sleep or during feeding may be 0.3-0.5 degrees higher.
Thirdly, the normal temperature in newborns is considered to be a temperature in the range of 36.5-37.30 (rectal temperature is 0.3-0.50 higher).
The temperature can be measured in the usual way (as in adults) in the armpit or in the anus.
When measuring the temperature in the armpit, make sure it is dry, press the handle tightly against your body and hold the thermometer for 5-10 minutes. You can place a thermometer rectally. In this case, the temperature measurement time is reduced to 3-4 minutes. Nowadays, modern digital infrared thermometers have appeared in pharmacies, allowing you to measure body temperature in just 1-2 seconds. This thermometer allows you to measure the temperature by only briefly touching the baby’s forehead or inserting it into the ear. In standby mode, such a thermometer shows the air temperature in the room. Infrared thermometers “pacifiers” are also sold in pharmacies, with the help of which it is convenient to measure the baby’s temperature in the mouth. By the way, this method is quite widely used by mothers in many foreign countries. All this is quite convenient, although such pleasure is quite expensive. {rokbox text=|interactive form|}index2.php?option=com_contact&view=contact&id=2{/rokbox}
When to see a doctor
Even the slightest change in the color of the skin or mucous membranes is an alarm bell. Parents should be wary of the marbled skin tone not only on the face, but also on other parts of the child’s body. For example, in infants in the first months of life with heart problems, intense cyanosis is observed on the heels and nails. In addition to the changed color of the skin, you should pay attention to the following features:
- causeless anxiety of the baby;
- lethargy;
- cold sweat;
- poor breastfeeding;
- shortness of breath (in infants it manifests itself clearly during feeding).
Children in the first year of life experience poor weight gain. The presence of cardiac pathologies in a child is eloquently indicated by a lag in physical development.
All the symptoms listed here may have varying degrees of severity, but observant parents will not miss changes in skin color in the child.
What is the essence of the disease?
Hemangioma is a benign vascular neoplasm, the formation of which begins during embryogenesis. Externally, it appears as a flat bluish, red or burgundy spot that rises above healthy tissue. The tumor does not have a capsule, and therefore, as it grows, it damages nearby tissues and organs. Characteristic is rapid, progressive growth and a tendency to bleed.
The presence of more than 3 hemangiomas on the skin may indicate their presence on the internal organs of the child.
The factors causing the disease are poorly understood and completely unknown. At the same time, there are a number of reasons that could serve as a predisposing factor to the development of the disease. These include:
- Genetic predisposition. According to statistics, children born into a family prone to the formation of vascular moles have a much higher chance of developing hemangiomas.
- Presence of estrogen receptors in tumor tissue. The hormone acts as a growth stimulator.
- Taking certain groups of medications by the mother during pregnancy.
Contributing factors are also unfavorable environmental conditions suffered by the mother during pregnancy, infectious diseases, and multiple pregnancies.
The neoplasm is not prone to malignancy and, if all the recommendations of the attending physician are followed, with positive dynamics of the pathology, it completely disappears by about 5-7 years. They are not dangerous and do not lead to cancer. At the same time, large vascular growths can lead to organ dysfunction or cause improper development of the body as a whole. Hemangiomas are very easily injured, and therefore there is a risk of infection of the child through an open wound. They also help reduce blood clotting.
Main services of Dr. Zavalishin’s clinic:
- consultation with a neurosurgeon
- treatment of spinal hernia
- brain surgery
- spine surgery
Which doctor will help you cope with the problem?
In most cases, respiratory and cardiovascular problems in children are treated by several specialists at the same time. But consultation with a cardiologist is necessary in any development of events. Parents should contact this specialist if their child becomes cyanotic.
The Kaliningrad private clinic "Edkarik" employs pediatric cardiologists with many years of practical experience. Timely implementation of diagnostic measures will make it possible to accurately determine the cause of bluish discoloration of the skin in children of different ages. Our clinic uses the most advanced diagnostic methods:
- ECG;
- Echocardiography;
- Ultrasound;
- CT and MRI;
- X-ray of the chest organs.
Diagnosis of cardiac pathologies includes laboratory tests. Parents can also make a significant contribution to this important process. After all, young children, due to their age, cannot describe the symptoms that bother them. Attentive mothers and fathers will notice when cyanosis appeared, and what other pathological phenomena were accompanied by this symptom at different times.
It remains to add that the multidisciplinary children's center is known not only in Kaliningrad. Young patients from other regions of the Russian Federation and even from neighboring countries come to us for consultation and treatment. Comfortable conditions and high service will be the key to a quick recovery.