The article was prepared by a specialist for informational purposes only. We urge you not to self-medicate. When the first symptoms appear, consult a doctor.
An acute inflammatory process occurring in the sweat glands of the armpit is called hidradenitis or udder knot. The disease is characterized by the collection of pus in the ducts responsible for the removal of sweat.
Sometimes in some cases the disease is localized in the navel, in the perineum, near the labia, scrotum and anus. These are the places that sweat the most.
What it is?
The medical term “hidradenitis” means inflammation of the apocrine sweat glands of a purulent nature and is a subtype of pyoderma.
Apocrine glands, unlike eccrine glands, are not located throughout the body; they have a specific localization.
The sweat they produce is thicker than usual, has a specific odor, and its reaction is neutral or alkaline. Such an environment is not dangerous for pathogens, so the “bitch udder” develops precisely in the apocrine glands.
Hidradenitis is caused by bacteria, most often staphylococci; a much smaller percentage of the disease is associated with exposure to streptococci and bacilli.
Harmful microorganisms can enter the sweat glands through microtraumas of the skin and through the lymphatic tract. Another implementation option is through the mouth of the hair follicle.
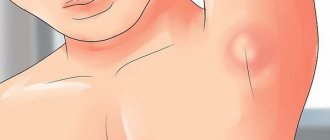
Purulent abscesses, mainly in the armpits, are shaped like the nipples of a dog nursing its offspring. Hence the colorful name of the disease among the people.
Hidradenitis does not occur in children before puberty, due to the fact that the function of the sweat glands is not sufficiently developed. The disease can affect adolescents and is often diagnosed in women.
But people of mature age, whose activity of the apocrine glands is fading, are no longer threatened by this disease.
The inflammatory process of the ducts of the sweat glands is also observed during hormonal surges in the body - during menopause, in pregnant women.
Hidradenitis has its own ICD-10 code - in the International Classification of Diseases, “bitch udder” is listed under number L 73.2.
Hidradenitis should be differentiated from furunculosis. With some similar symptoms, the difference is that with the disease “bitch udder” there is no necrotic core, which is separated during the opening of the boils.
Diagnostic procedures
Diagnosis for knotted udders includes:
- external examination by a dermatologist;
- visiting an infectious disease specialist;
- taking a blood test for bacteriological culture;
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland;
- urine collection;
- histological analysis (for complicated purulent form).
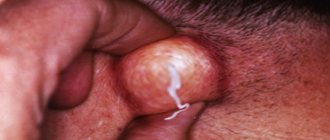
in the photo, hidradenitis (bitch udder) under the armpit.
In a chronic course, diagnosis includes a series of tests to identify the causes of weakened immunity.
This series of diagnostic procedures is aimed at excluding pathologies with similar symptoms. Wolf udders are often confused with mycoses, manifestations of sexually transmitted diseases, carbuncles, boils, tularemia and pathologies of the lymphatic system.
Causes
Pathogenic microorganisms live on human skin, but provoke disease only under certain conditions.
One of the main causes of hidradenitis is considered to be a weakened immune system, when the body is unable to resist the harmful effects of bacteria.
Why do the body’s protective properties decrease:
- as a result of chronic diseases, as well as against the background of infectious pathologies, when hidradenitis manifests itself as a secondary infection;
- due to operations and injuries;
- due to excessive stress (both physical and emotional);
- with frequent stress, insomnia - the psychosomatics of the disease is such that constant worries and negativity provoke the development of pathology;
- as a result of autoimmune diseases;
- due to diseases associated with metabolic disorders;
- due to hormonal changes during pregnancy, puberty and menopause.
There are a number of other factors that can contribute to hidradenitis:
- excessive sweating associated with the physiological characteristics of the body and dysfunction of the secretory glands;
- hyperhidrosis due to heavy physical activity, hot climate and high humidity;
- poor choice of clothing - if it is too narrow, tight, and not breathable, it rubs the skin and causes diaper rash;
- insufficient body hygiene, especially in the armpits, genitals, and anus;
- the use of cosmetics that disrupt the pH of the skin (at normal rates, the growth of pathogenic microorganisms does not occur); the use of antiperspirants, deodorants and powders that clog skin pores;
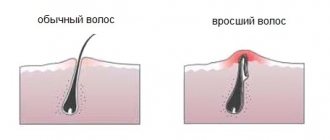
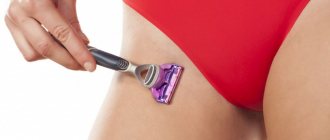
- injuries and damage to the skin - cuts, scratching with itching, scratches from shaving, abrasions from wearing clothes, ingrown hairs after hair removal;
- poor nutrition – passion for diets, lack of sufficient amounts of microelements necessary for the body, excess carbohydrates (they serve as a breeding ground for pathogenic microflora).
We invite you to get acquainted with the doctor’s opinion about the causes and pathogens of hidradenitis in the following video:
Prevention
In order to avoid hidradenitis, you must also follow a few simple preventive rules:
- Maintaining cleanliness and personal hygiene.
- Experts strongly recommend not wearing tight clothes. Tight clothing often causes irritation on the skin.
- The armpits should be kept clean at all times.
- If any deodorants or cosmetics cause inflammation on the skin, then it is better not to use it. It is these preventive norms that can prevent the occurrence of the disease.
Localization of hidradenitis: under the arm, in the groin, etc.
“Bitch udder” is localized in places where apocrine glands accumulate. They are most abundant in the armpit area, which is why axillary hidradenitis is the most common disease.
In addition, these areas of the body are constantly exposed to negative effects - this includes traumatic depilation, friction from tight clothing, and inappropriate deodorants.
Some people simply neglect basic hygiene in places where there is increased sweating.
Where else is hidradenitis localized:
- in the groin area;
- in the perineal area, around the anus;
- in men - on the scrotum;
- in women - on the labia;
- in the folds under the breasts;
- on the mammary gland - in the area of pigmentation around the nipples;
- Rarely, hidradenitis appears in the scalp.
To prevent the infection from spreading throughout the body, when a single lesion appears, for example, a lump on the pubis, you should immediately begin antiseptic treatment of this area.
Signs of hidradenitis or how to distinguish knot udder from other skin diseases
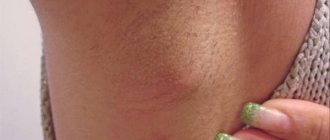
photo of the formation of hidradenitis
Hidradenitis of the armpit is localized mainly in the area of only one armpit. In some cases (complicated by concomitant chronic diseases), lesions appear on two armpits and in the folds of the mammary glands.
At the infection stage, the nodules have the red shape of inflamed pimples. They itch when sweating and are painful on palpation. Unlike furunculosis, hidradenitis extremely rarely appears on the face and in the shoulder girdle. In places where there are no sweat glands or hair, hidradenitis appears as a concomitant dermatological phenomenon.
The udder is pea-shaped and has a blue-red hue for a long time (with furunculosis, pimples with a purulent cap, small). Unlike folliculitis, hidradenitis does not affect the scalp. At the second stage, the knotted udder has a pronounced round shape and is very painful. Several lesions can merge into one.
At the maturation stage, the patient experiences general weakness, pain at the site of inflammation, fever and other signs of infection. At the third stage, the nodules begin to soften, become less painful and open. Opened lesions can fester for several days, and serous fluid with blood fragments may be released. Thick purulent masses have an unpleasant, pungent putrefactive odor. As soon as the discharge from the wound ends, it heals. In patients with the chronic form, new lesions and ulcers appear next to the scars, which later heal.
Symptoms
More often, hidradenitis is one-sided, for example, in the left armpit; inflammation on both sides is very rare.
The initial stage of “bitch udder” is the appearance under the skin of one, and more often than not several, nodules of a dense structure, the size of a pea.
Gradually, painful lumps reach 1.5–2 cm in diameter; they protrude above the surface of the skin, becoming similar to a dog’s udder.
The surrounding skin turns red, itches, then swelling occurs, the nodes merge, forming an area of a large inflamed infiltrate of a bluish-burgundy color.
These characteristic symptoms are accompanied by signs of general malaise:
- Weakness, weakness.
- Hyperthermia, increased temperature.
- Headache (cephalgia).
- Nausea, lack of appetite.
- Constant pain in the affected area, not only upon palpation, but even at rest.
When a hard node gradually becomes soft, then when pressure is applied to the wall of the cavity, vibrations are formed - fluctuation. This serves as a sign by which one can distinguish a “bitch udder” from a boil.
After the infiltrate has matured, it is opened, during which the purulent contents come out. Then a scar forms in this place.
The process can take from 10 days to a month - the fact is that while some abscesses are healing, others appear.
After the pus is released, the patient usually feels better. During this period, it is important to prevent contents with a large number of staphylococci from getting into neighboring areas.
Otherwise, the involvement of new sweat glands in the process threatens recurrent hidradenitis. The disease can take a chronic, relapsing form.
This video is about the types and symptoms of hidradenitis:
Treatment of hidradenitis with conservative therapy
In order to prevent surgery for hidradenitis, you can resort to conservative therapy. It involves treating inflammation with an antiseptic. It can be salicylic or boric alcohol, bigluconate, chlorohexide, octenesept. If you don’t have them on hand, you can use calendula tincture. Before treating the “bitch’s udder” with it, dilute the product in boiled water in a 1:1 ratio.
After treating the inflammation with an antiseptic, apply Vishnevsky ointment or levomekol to it. It is necessary that it completely covers the “bitch’s udder” with a thick layer. Then apply cotton wool and secure it with adhesive tape. This procedure must be carried out 2 times a day. Along with this, lubricate the affected areas with iodine or brilliant green.
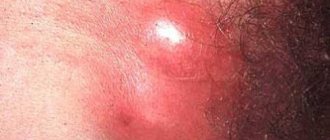
What does a bitch's udder look like (photo)
Causes of hidradenitis: what causes hidradenitis?
Hidradenitis does not occur out of the blue. The appearance and development of inflammation of the sweat glands is facilitated by factors such as:
- Staphylococcus aureus infection
- decline in immunity
- thyroid diseases
- diabetes
- insufficient hygiene of the affected area
- abuse of deodorants or other cosmetics
- increased sweating (often as a result of being overweight)
- skin prone to rashes
- hormonal imbalance
- decreased skin barrier function
IMPORTANT: Hidradenitis never occurs in older people or young children. This disease most often affects women and men aged 18 to 50 years.
Types and forms
The generally accepted classification of hidradenitis is based on its various manifestations.
Based on location, “bitch udders” are divided into one-sided (more common) and two-sided.
Also, the disease at the place of origin can be axillary, inguinal, located in the anus, scrotum, labia, navel, mammary glands.
There are several stages of the disease:
- Initial – when the sweat gland has just become blocked. Accompanied by swelling, redness of the skin, itching, pain.
- Medium – proliferation of inflamed nodes and increased pain.
- Severe - the formation of purulent abscesses mixed with blood.
Depending on the nature of the development of the pathology, there are 2 types of hidradenitis: acute purulent and chronic.
Suppurative (acute) hidradenitis
The reason for the development of this form of the disease is blockage of the apocrine glands, mainly due to poor body hygiene.
It is important to notice in time the formation of a lump, which quickly becomes inflamed and turns into a purulent abscess.
The disease is accompanied by typical symptoms - fever, weakness, pain in places where abscesses form.
Untimely treatment of the pathology is dangerous due to intoxication of the body and complications in the form of abscesses and phlegmons.
Recurrent
The chronic form of hidradenitis is also called recurrent. The inflammatory process lasts quite a long time, appearing at certain intervals.
Extensive inflammation of the sweat glands is considered the most complex form of hidradenitis. For successful treatment, it is necessary to find out the causes of the long-term pathological process.
The disease is dangerous by increasing the area of inflamed apocrine glands and the formation of abscesses.
Adequate comprehensive treatment with the use of antibiotics is required, it is necessary to avoid alcohol and follow a diet, and careful personal hygiene.
Suppurative
The suppurative form of hidradenitis is also called acne inversa. It most often affects adolescents during puberty.
The peculiarity of the disease is that various forms of acne are combined with an inflammatory process in the sweat glands.
Hidradenitis suppurativa of the armpit or other area of skin occurs due to blockage and rupture of the hair follicle.
The disease is characterized by the formation of an inflammatory process that affects the sweat glands.
The pathology can be localized in the groin, perineum, armpits, and less often on the face. Factors predisposing to the development of the disease are excessive sweating, obesity, and uncomfortable clothing.
Therapy methods
Hidradenitis is treated with a wide range of therapeutic measures. This complex includes: antibacterial therapy depending on the causative agent of the infection, local therapy (painkillers, drugs that accelerate wound healing), surgical excision of ulcers. In the chronic form, treatment of concomitant diseases and triggers is prescribed.
The treatment method is developed individually depending on the stage of the disease. At an early stage, it is necessary to get rid of hair in the focal area, but without damaging the skin. It is best to use nail scissors. Wipe the infiltration area with a disinfectant (calendula tincture, hydrogen peroxide, brilliant green). Do not use drugs that can cause burns (concentrated alcohol, pepper and iodine tinctures).
Afterwards, you need to apply a bandage or patch soaked in chlorophyllipt or dioxylin. This procedure must be repeated every 4-6 hours. If after 5 days the infiltrate does not resolve on its own, increases in size and becomes purulent, it is necessary to apply antibacterial therapy. Antibiotics are prescribed only when the udder reaches the stage of abscess formation.
During self-diagnosis and self-medication, antibiotic therapy is often useless due to the resistance of pathogens to the active component of the drug.
For successful antibacterial therapy, the discharge is collected for bacteriological culture to establish the exact type of bacteria and determine the most effective means to eliminate it. Taking the medication lasts no more than 10 days. For hidradenitis, tetracycline antibiotics are prescribed (if Staphylococcus aureus is detected). Tetracyclines also prevent the spread of the disease and its transition to other skin infections (furunculosis, sycosis and others). Tetracyclines are prescribed to adult patients with unimpaired renal and hepatic function.
Macrolides are new generation antibiotics, allowed from the second trimester of pregnancy.
Cephalosporin antibiotics are prescribed in case of severe infection. Act on pathogenic streptococcal microorganisms. They are used primarily for the groin form of the disease to prevent infection of the urinary tract. Cephalosporins are nephrotoxic and are not recommended for chronic kidney pathologies.
Lincomesin preparations are ointments with an antibacterial effect and have no side effects. They can cause allergies only in case of individual intolerance.
The complex takes vitamins, corticosteroids and antihistamine ointments. In the chronic stage, the formation of fistulas and scars, surgical excision of foci of infection is used for effective treatment. The operation is performed under local anesthesia and lasts no more than 45 minutes for large affected areas.
Which doctor should I contact?
At the very beginning of the onset of the disease, a dermatologist can prescribe adequate treatment.
Conservative therapy is not always effective, so you may need to seek help from a surgeon.
Hidradenitis in the suppuration stage is treated with surgery. The doctor opens the abscess and inserts a drain to remove the contents of the cavity.
If you notice signs of hidradenitis in children, you should contact your pediatrician. The pediatrician will decide what treatment to prescribe and which specialist to refer the child to for consultation and subsequent therapy.
Symptoms of hidradenitis in pregnant women are a reason to visit a gynecologist, who will determine a treatment regimen and the need to see a surgeon for surgical intervention.
The development of “bitch udders” during lactation in nursing mothers is especially undesirable. The disease causes discomfort and interferes with normal feeding of infants.
In the case of a chronic form of the disease, you may need to consult an immunologist, nutritionist, or endocrinologist.
Diagnosis of hidradenitis
A bitch udder is quite easy to identify. The specialist must first visually examine the patient and evaluate the location of the inflammatory process, as well as the clinical picture that is characteristic of this disease.
Very often people confuse a knotted udder with a regular boil. However, these diseases have one distinctive feature - necrotic core . Such a rod is typical only for a boil. A bitch's udder can still be very similar to collicative tuberculosis. This disease is characterized by the appearance of severe inflammation of the lymph nodes and the absence of pain.
To visually assess the difference between a boil and a knotted udder, look at the photo of the boil in an article on the topic.
The basis for diagnosing a bitch's udder is a general blood test. If an acceleration of ESR and an increased number of leukocytes are detected in the blood, then this indicates the development of a bitch udder.
If a decision has been made to take antibiotics, then a culture is performed to determine the body’s susceptibility to drugs that are aimed at antibacterial therapy. If the disease has been going on for a long time or appears again, then it is necessary to conduct an immunogram that examines the entire immune system.
Diagnostic methods
A correct diagnosis is important in order to begin appropriate treatment for the patient in a timely manner and prevent the development of complications.
Hidradenitis should be differentiated from diseases with similar symptoms - phlegmon, furunculosis, skin tuberculosis, sebaceous cysts, atheroma, lymphadenitis.
The doctor’s task is to interview the patient. It is important to find out:
- when the compaction formed, how quickly it began to increase in size;
- what symptoms accompanied the appearance of the lump - did the patient feel itching and pain;
- what was the general condition of the patient - the presence of fever, weakness, pain;
- whether there have been previous cases of hidradenitis in the patient himself and his family members;
- What chronic diseases does the patient suffer from?
During the examination, the doctor pays attention to the presence of swelling, changes in skin color, the shape of the seals, and skin fluctuations.
A blood test is often required - an increase in ESR and leukocytes, a decrease in the number of red blood cells indicates the presence of an inflammatory process.
Bacteriological examination is usually prescribed for recurrent forms of hidradenitis.
A test sample of material is taken from the abscess to determine the microorganism that caused the disease and its sensitivity to antibiotics.
People often ask: CMV infection in children - what is it? Our publication will tell you in detail about the disease.
What does Advantan ointment help with? This article will answer the question.
Read about how to treat a cold in the nose here: https://udermatologa.com/zabol/gerp/chem-lechit-prostudu-v-nosu-foto-gerpesa-simptomy-profilaktika/
Symptoms and causes of the disease
Hidradenitis begins with the appearance of small compactions, which over time enlarge and merge into one whole in the thickness of the skin. The disease can develop not only under the armpit, but also in other places where there are sweat glands (groin, perineal area, etc.). As the disease progresses, the skin in the area of the seals becomes bluish, swollen, and painful to the touch. Then it begins to sag down. Outwardly, it resembles the nipples of a dog that feeds puppies with milk. This is where the popular name for the disease comes from.
How to treat bitch udders in men and women
There are two ways to get rid of “bitch udders” – conservative and operational.
Treatment without surgery is successful only in the first 3 days from the moment the lump forms.
Drug therapy
The doctor prescribes topical and oral medications. Typically, patients have to take antibiotics:
- Doxycycline;
- Ampicillin;
- Erythromycin;
- Amoxiclav;
- Lincomycin;
- Ciprofloxacin;
- Tsiprolet.
Antibiotics can effectively fight pathogenic bacteria. They can be taken as tablets or as injections.
Taking medications is combined with external therapy. Local preparations are quickly absorbed and begin to act immediately after application.
To treat affected areas use:
- Ichthyol ointment and Vishnevsky ointment are used to speed up the release of purulent contents;
- Ilon - this ointment helps to liquefy pus and remove it out, also has an anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect;
- Levomekol - an antiseptic with antimicrobial and wound-healing effects is applied to the area of the abscess after it has opened;
- lotions with a solution of the antibiotic Clindamycin are applied to the wound;
- the affected area must be smeared with brilliant green, iodine, Synthomycin ointment, and a swab soaked with diluted Dimexide must be applied to kill bacteria;
- apply bandages soaked in calendula tincture, Chlorophyllipt (alcohol solution);
- the skin surrounding the abscess should be wiped with alcohol solutions (salicylic or boric acid) to destroy pathogenic microorganisms.
Additional measures
Additional methods of therapy can help cure hidradenitis - taking medications and physiotherapeutic procedures:
- preparations for stimulating the immune system - based on Interferon, echinacea, ginseng;
- antihistamines – Claritin, Suprastin, Tavegil;
- in some cases, the prescription of hormonal drugs, for example, corticosteroids, is required;
- the disease goes away faster if additional physiotherapeutic procedures are used - electrophoresis, UHF (ultra-high frequency therapy), Ural irradiation (ultraviolet irradiation);
- X-ray therapy is used for recurrent hidradenitis. Its purpose is to destroy the inflamed sweat gland;
- an appropriate diet helps treat hidradenitis - it consists of excluding fried, spicy, fatty foods, sweets, and alcohol from the diet.
Surgical intervention
It is not always possible to successfully treat “bitch udders” at home. Often it is necessary to remove the abscess surgically. If the abscess is single, then surgical intervention is performed under local anesthesia.
Once the hidradenitis is opened, the wound is cleaned and a drain is installed to remove the fluid. The surgeon prescribes postoperative treatment, which usually takes about a week.
One operation is not enough to remove hidradenitis, which consists of multiple micro-abscesses. The surgical intervention is performed in stages:
- First, an autopsy is performed with drainage to remove pus, then the inflamed tissue is removed and a healing bandage is applied.
- The patient is prescribed antibiotics, and after scarring the wound and relieving inflammation, the affected area of skin and remaining subcutaneous tissue are removed.
- At the end of the surgical treatment, autodermoplasty is performed - the operated area is covered with a flap of skin from another part of the patient’s body.
This operation is indicated for repeated relapses of hidradenitis, when other treatment methods do not produce results.
During the recovery period, various procedures are prescribed - laser therapy, infrared irradiation, magnetic therapy, ultrasound, phototherapy, and chemotherapy.
A specialist’s opinion on the surgical method of treating the disease:
Treatment of hidradenitis with folk remedies
It is unlikely to cure hidradenitis with folk remedies alone. But in complex therapy with medications, such treatment is quite acceptable.
Onions, cabbage and aloe are the most popular ingredients in folk recipes. These medications are easy to prepare at home:
- in order to “pull out” pus from a wound, you need to apply half an onion baked in the oven to the sore spot and secure it with a bandage. This compress should be left overnight;
- as a means of drawing out pus, use a well-beaten cabbage leaf, which is also applied to the abscess and kept for at least 6 - 8 hours;
- the aloe leaf must be cleared of thorns, cut lengthwise and applied to the affected area several times during the day;
- a medicine from onions and soap is prepared as follows: chopped onion is fried in melted butter, mixed with grated laundry soap (2 spoons are enough) and a compress is applied overnight;
- You can treat the affected areas with a herbal decoction or take a mixture of herbs internally. To do this, take a mixture of plantain, eucalyptus and sweet clover leaves, chamomile, sage and calendula flowers (1 tablespoon each), pour a liter of boiling water, cook over low heat for 4 - 5 minutes.
Treatment at home
There are many “folk” recommendations on how to get rid of a bitch’s udder, but some of them may contradict common sense and aggravate the pathology.
If you decide to get rid of a bitch udder without the help of a doctor, you need to know a few basic rules of therapy, and only then resort to folk recipes.
- If a growth with purulent discharge appears, warm bandages should not be applied under any circumstances.
- You cannot open boils and try to sanitize them yourself.
- You cannot apply ointments and masks directly to open ulcers.
An effective and absolutely safe method of treating hidradenitis without drugs is sunbathing. Just clean your armpit of hair and lie in the sun. Unfortunately, this method only helps at the early stage of the disease.
You can wipe the inflammation with decoctions and tinctures of herbs that have antiseptic properties (calendula, chamomile, St. John's wort, celandine).
In some sources you can read that you can cure a bitch udder with the help of an onion or curd compress. However, there is no confirmed data on the effectiveness of such methods.
How to cure illness in children
Hidradenitis in children develops in adolescence, when the process of puberty occurs with changes in hormonal levels.
Provoking factors are also long-term infectious diseases, excessive sweating, skin rash, and insufficient personal hygiene.
You should not self-medicate, exposing children to the risk of severe hidradenitis and possible complications.
The teenager needs to be shown to a pediatrician, who will decide whether further action is necessary:
- if the process is at the very beginning and there are no signs of general malaise, local therapy can help. The patient is prescribed antibiotics and external agents;
- Perhaps the doctor will refer the child to a surgeon for removal of abscesses and further rehabilitation therapy.
During the recovery period, the patient needs rest, peace, a balanced diet, and taking vitamins. If necessary, the teenager is prescribed physiotherapeutic procedures.
In general, the treatment regimen is similar to that used in adults. But the use of medications is required according to the age of the child and in the appropriate dosage.
If frequent relapses of hidradenitis are observed, the teenager should undergo a full examination to identify the causes of this pathology - these could be chronic diseases or metabolic disorders in the body.
Are you interested in how to treat cheilitis on the lips? What causes the disease, how to prevent it? Our publication will tell you in detail about the disease.
Do you think it is possible for a child with chickenpox to wash and bathe? You will find advice and recommendations from pediatricians in this material.
How to treat?
Therapy for hidradenitis is complex. Patients need:
- Follow the general recommendations of the doctor, in particular regarding diet, body care and strengthening the body.
- Treat the skin at the affected area with medications prescribed by your doctor.
- Use medications for internal use that neutralize the unpleasant symptoms of the disease and fight pathogenic pathogens.
- Seek medical help if necessary.
Complications
The disease is fraught with complications as a result of the generalization of the inflammatory process, that is, its spread beyond the sweat glands to the surrounding tissues. As a result, foci of disease appear throughout the body.
Complications of hidradenitis include:
- lymphadenitis is the name given to inflammation of the lymph nodes and vessels located close to the lesion. Usually the groin and axillary areas are affected;
- phlegmon is a pathology consisting in the spread of the inflammatory process to the subcutaneous fatty tissue; We wrote more about the types and treatment of phlegmon here;
- scars (keloid and hypertrophic) - can form mainly in the armpits as a result of severe hidradenitis;
- osteomyelitis - a fistulous form of damage to the periosteum and bone tissue as a result of the development of a purulent process;
- sepsis - a purulent process can develop into blood poisoning in the absence of appropriate treatment.
Nutrition for hidradenitis
Adjusting the diet for hidradenitis is indicated for patients with a chronic form of the disease who have endocrine disorders.
For overweight people, calorie restriction and a low-carbohydrate diet are recommended. In addition, it is advised to avoid fatty and spicy foods. A diet rich in vitamins and fiber helps speed up recovery.
In case of hidradenitis suppurativa, you need to give up sweets and baked goods, since such products provoke the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria and fungi. It is undesirable to eat hot and spicy foods, which provoke increased sweating.
Disease prevention
To prevent the occurrence of purulent inflammation of the sweat glands, you must first of all maintain personal hygiene and take care of strengthening the immune system .
And since chronic infections serve as risk factors that can provoke the development of hidradenitis, it is necessary to eliminate the foci of such diseases - pharyngitis, otitis, herpes, tuberculosis, hepatitis.
To avoid getting hidradenitis, it is important to follow the rules of personal hygiene:
- wear clothes made from natural, breathable fabrics, change underwear daily;
- Take a shower regularly, thoroughly washing problem areas of the body;
- once a week, replace the shower gel with Nizoral medicated shampoo or Citeal antiseptic solution, and for daily use, gels containing lactic acid are suitable (the acidic environment protects the skin from the growth of bacteria);
- wash areas of the body prone to excessive sweating with tar or laundry soap (no more than 2 times a week);
- for hygiene of the intimate area, use Lactacid gel (Epigen, Tamiful);
- eliminate the use of antiperspirants or at least reduce the frequency of their use. Instead, it is recommended to use powders with a bactericidal effect;
- Be careful when shaving; after removing hair, treat the skin with disinfectants, for example, salicylic, boric and camphor alcohol. It is better to entrust the hair removal procedure to specialists at a beauty salon;
- Wipe problem areas of the skin with decoctions of medicinal herbs - calendula, string, oak bark, chamomile or a solution of potassium permanganate;
- avoid injuring the skin, do not scratch it if you have allergies or dermatoses;
- carefully choose cosmetics - avoid those that irritate the skin structure or clog the ducts of the sweat and sebaceous glands.
Treatment of bitch udder
Treatment of bitch udders is carried out under the supervision of a doctor using antibiotic therapy, sulfonamides, autohemotherapy and nitrofurans. For repeated, recurrent forms of the disease, individual immunotherapy is used, and various modern means are used to generally strengthen the body.
For higher efficiency, local treatment of the bitch's udder is used: dry heat, irradiation with ultraviolet and solar rays, UHF, ultraviolet therapy, laser therapy and magnetic therapy.
When an abscess (abscess) forms, it is advisable to open it. A surgeon can do this. To protect the wound from infection, it must be covered with a special bandage or bactericidal patch.
For the first 3 to 5 days, when the udder disease is just beginning to progress, it is necessary to warm up the areas where the pain is felt with dry heat. It is advisable to do this every 3 to 5 hours. Warming up can be done independently by heating a clean towel, preferably terry, with a hot iron, and applying it to the inflamed area, holding it until it cools down. This needs to be repeated several times. For the same purposes, you can use bags of salt or sand, which are preheated.
To prevent the spread of infection to the glands that are adjacent to the ulcers, the skin around them must be treated with camphor, boric or salicylic alcohol three or four times a day.
Treatment with compresses is contraindicated. It increases infiltration and accelerates suppuration.
To localize the disease and prevent spread to other sweat glands, and shorten the recovery time, it is recommended to carefully remove hair, preferably with manicure scissors, that grows in the inflamed area and nearby.
When treatment is completed, it is not recommended to take baths for another week. It is better to take a shower, first covering the inflamed area with a plaster (simple or bactericidal) so that water does not get under it, which contributes to the spread of infection.
Diet
For a speedy recovery, special dietary nutrition is prescribed from the first day of illness and for at least three months. The diet means eliminating alcoholic drinks, spicy foods, and reducing the consumption of sweets. People who smoke should give up this habit.
The diet should be rich in foods containing vitamins A, C, B1, B2, B6, iron, phosphorus. Therefore, it is recommended to create a menu that includes eggs, dairy products, butter, liver, tomatoes, green peas, vegetable oil, cabbage, carrots, apples, citrus fruits, berries, black currants, rose hips, almonds, peanuts, walnuts.
To prevent the occurrence of udder disease, it is recommended to always adhere to special personal hygiene, try not to wear clothes made of synthetic fabrics that impede movement, and also not to overcool or overheat. If you have problems with excess weight, any low-calorie diet is recommended to normalize weight. You should also avoid perfumes and cosmetics, since in most cases they provoke the development of udder disease.
Author of the article:
Mochalov Pavel Alexandrovich |
Doctor of Medical Sciences therapist Education: Moscow Medical Institute named after. I. M. Sechenov, specialty - “General Medicine” in 1991, in 1993 “Occupational diseases”, in 1996 “Therapy”. Our authors
Hidradenitis inguinalis: causes and symptoms
Inguinal hidradenitis, as well as axillary hidradenitis, develops quite often due to the location of many sweat glands in the designated area. Purulent cones of hidradenitis ripen in the groin according to the same scenario as in the armpits. The reasons for the appearance are usually:
- poor hygiene
- heavy sweating
- sloppy shaving
- ingrown hairs
- hormonal imbalances
- wearing tight synthetic panties
IMPORTANT: Hidradenitis inguinalis often takes on chronic, recurrent forms. Due to the “intimacy” of the disease, not everyone goes to the doctor, wasting precious time and contributing to the further development and spread of hidradenitis.
Hidradenitis inguinalis is one of the most painful. It is very difficult to independently carry out proper treatment and skin care in this delicate area. In most cases, the only way to get rid of hidradenitis inguinalis is through surgery.