Causes of polyps and papillomas of the anus
The anus is an area in which the growth of tumors is quite often observed. Polyps may form inside the rectum. Condylomas (a type of papillomas that resemble cauliflower in appearance) may appear in the perianal area (around the anus). In some cases, condylomas can also occur inside the anal canal.
Sometimes you may not even suspect the existence of such formations in yourself. A common situation is when their presence is established during an examination (or during an endoscopic examination) when treating for other diseases.
Polyp
- This is the growth of the mucous membrane in the form of a mushroom body. With its thin stalk, the polyp maintains contact with the wall of the rectum, and the body itself hangs freely inside the canal.
Papillomas (genital warts)
are caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). HPV is a widespread disease; according to various sources, from 70 to 90% of people carry this infection. However, in most cases, the virus “sleeps” and becomes active when immunity decreases. This is when active growth of papillomas occurs.
In the perianal area, HPV manifests itself in the form of genital warts, which usually also affect the human genitals. Often condylomas become injured and bleed. The virus can be transmitted through blood from damaged condylomas.
1.General information
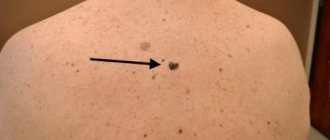
Papilloma is a benign superficial growth, usually flesh-colored or white-pink in color. The specification “benign” means that at the cellular level such neoplasia retains a certain structural similarity to the tissue that served as its soil; grows relatively slowly; does not grow into surrounding tissues and organs; does not have a pronounced tendency to metastasize, i.e. the spread of pathological cells with blood or lymph to other parts of the body, where similar tumors form. These are the main differences between benign neoplasms and malignant, cancerous ones. It must immediately be emphasized that in most cases, under unfavorable conditions, malignancy is possible, i.e. the appearance and rapid multiplication of immature mutant cells capable of only dividing and nothing more - in other words, the degeneration of a benign formation into a malignant one. That is why warts, “hanging” moles, polyps, condylomas, papillomas are not absolutely safe neoplasias, even if they remain “in the same pore” for decades and do not cause much discomfort.
Papillomas can develop on any part of the body, but more often they affect the most intimate areas, which are constantly hidden under clothing and therefore rarely come into contact with open air and the sun. Such areas are characterized, at the same time, by increased secretory activity and, as a consequence, humidity, as well as participation in excretion (removal of waste, waste and harmful substances from the body) and sexual activity. Taken together, all this creates a very high probability (confirmed by medical statistics) of all kinds of infectious and inflammatory processes, irritations, diaper rash and many other problems that are not only extremely unpleasant hygienically and aesthetically, but also really dangerous.
If such problems arise during defecation or, in general, in the anus, one can, of course, consider them “shameful” and, embarrassed by one’s own anatomy, suffer for years in categorically rejecting the very idea of going to a proctologist. However, for a modern civilized person, such a position is not just obscurantist and unreasonable; in many cases it poses a direct risk to life. And therefore, it is necessary, at a minimum, to understand what papillomas of the anal area are in order to consult a doctor in time and have time to prevent much more serious clinical situations.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Symptoms of polyps and papillomas of the anus
Polyps, genital anal condylomas and other benign neoplasms that arise in the rectum and perineum can transform into malignant ones. The likelihood of degeneration increases if the formation is constantly injured, as is often the case with this localization.
It should be taken into account that in the initial stage of development such formations may not manifest themselves in any way, and they can only be identified endoscopically (during recothoromanoscopy or colonoscopy). It is all the more important to pay attention to symptoms that may indicate the presence of formations.
Painful sensations
Subjectively, a large polyp may feel like a foreign body in the anus. There may be pain with different localization in the lower abdomen.
Diarrhea
The presence of a polyp in the intestinal lumen disrupts its functioning. The intestines are constantly trying to free themselves from contents - this is how diarrhea is stimulated.
Constipation
A large polyp obstructs the passage of stool and causes constipation.
Bleeding from the anus
If you detect even minor bleeding from the anus, you should definitely consult a proctologist.
Methods of treating pathologies
To treat all types of papillomas and polyps, medical or surgical methods are used. In some cases, removal of growths is mandatory. Sometimes dynamic observation and monitoring of tumor growth is recommended. Drugs that strengthen the immune system are also prescribed.
Polyp
For small polyps, a wait-and-see approach is used. The patient is recommended to undergo ultrasound and endoscopic examination twice a year.
If there is a tendency for growth or the appearance of new formations, surgical intervention is performed.
If the growth is localized in the intestines or stomach, the polyp is removed with an endoscope during colonoscopy or fibrogastroscopy.
When a polyp is located in the uterine cavity, therapeutic curettage and cauterization are performed. If a tumor occurs in the mouth or nose, endoscopic surgery is performed. After removal of the polyp, it must be sent for histological examination.
Papilloma
For papillomas, antiviral drugs and immunomodulators are prescribed. Local treatment is also carried out. The following methods are used for this:
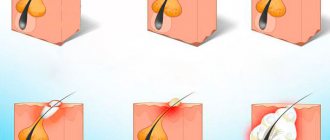
- Electrocoagulation. This method involves cauterizing the papilloma with an electric current.
- Laser therapy. It is performed without anesthesia. Crusts form and fall off on their own after a few days.
- Cryodestruction. Liquid nitrogen is used for this treatment option.
- Chemical destruction. Chemical acids are applied to the surface of the wart.
Cryodestruction is a method of treating papillomas
Isoprinosine, Lavomax, cycloferon or interferon are used as antiviral drugs. They are taken in the form of tablets or intramuscular injections.
If neoplasms are detected, you must contact the clinic. For small polyps and papillomas without clinical manifestations, observation is usually recommended. Large formations are removed surgically.
Thus, polyp and papilloma have nothing in common. Their differences are due to different etiological and pathogenetic factors. These neoplasms do not pose a threat to human life. However, both polyps and papillomas require regular monitoring and examination. This will prevent malignancy and other complications of these diseases.
Methods for diagnosing polyps and papillomas of the anus
It is important to pay attention to symptoms that may indicate the presence of formations: a feeling of discomfort or a foreign body in the rectum, burning, mucus-like discharge from the anus - this is a serious reason to consult a proctologist.
Endoscopy
It should be taken into account that in the initial stage of development such formations may not manifest themselves in any way, and they can only be identified endoscopically (during recothoromanoscopy or colonoscopy).
More information about the diagnostic method
Sign up for diagnostics To accurately diagnose the disease, make an appointment with specialists from the Family Doctor network.
Modern methods of removing warts, moles, condylomas, papillomas, polyps
There are only 2 such methods so far - removal of tumors by laser and radio wave method.
Laser method for tumor removal
Laser -
is based on the use of a laser that “evaporates” the formation with a light beam. The method has many advantages:
- Selectivity.
Each tissue reacts to certain parameters of the waves, so the device affects the affected tissues without affecting healthy ones. During the procedure, the doctor can change the tinctures, reducing or increasing the strength and depth of effect. - Low trauma
- the method does not cause extensive tissue damage, chemical and thermal burns, swelling, blisters and severe pain. - Healing times after laser treatment
are shorter than when using electricity, scalpel or liquid nitrogen. A brownish crust forms at the site of exposure, under which new skin forms. After the procedure, there are no scars, scars or areas without pigmentation. - The laser has an antimicrobial and antiviral effect, eliminating the occurrence of relapses. By acting on blood vessels, it prevents bleeding.
- The procedure takes only 5-10 minutes, and the injected anesthetics make it painless. In one session you can get rid of all formations at once.
Radio wave method for removing any tumors
The radio wave method is the most modern method for removing any tumors —
papillomas, condylomas, warts, polyps, moles, etc.
Formations are removed using high-frequency waves. Radio radiation heats the cells of the tumor, the water in them boils, tearing the tissue of the growth. A hot radio knife “cuts off” a wart, mole, etc., cauterizing tissue and blood vessels and preventing bleeding. Removal takes 5-10 minutes.
The treatment site is treated with an anesthetic and the procedure does not cause pain. There are no burns, scars, or blisters left on the skin. Fine adjustment of the operation of the radio knife allows minimal trauma to neighboring tissues, reducing healing time.
After exposure to radio wave radiation, a crust remains on the skin, under which healthy tissue is formed. There is no skin treatment after the procedure. After the crust falls off, smooth skin without scars or areas of disturbed pigmentation remains.
The gentle effect of the radio knife allows you to remove formations even in delicate places - on the genitals, face, mammary glands. Relapse is completely excluded.
Outdated traumatic methods for removing formations on the skin and mucous membranes are disappearing, giving way to modern techniques - laser and high-frequency waves.
Treatment methods for polyps and papillomas of the anus
Treatment of polyps and condylomas usually involves their removal.
Removal of polyps and condylomas of the rectum
Removal of condylomas in the “Family Doctor” is carried out using a laser or a radio wave device “Surgitron”. Removal of rectal polyps can be done during endoscopy if the location and size of the polyp allows it. In difficult cases, planned hospitalization in a surgical hospital is performed to remove the polyp.
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Rate how useful the material was
thank you for rating
The main differences between polyp and papilloma
Polyp and papilloma have many differences. Their main difference is that it is impossible to see the polyp on your own. The disease can be diagnosed only by conducting an instrumental examination. Typically, such a growth is detected during rhinoscopy, laryngoscopy, hysteroscopy or endoscopic examination.
Papillomas can be seen even with the naked eye. They are located on the skin or mucous membranes of the nose, mouth or genitals. These neoplasms represent an overgrowth of the epidermal layer. Papilloma can be flat, pointed or filiform.
External features
First of all, the difference between a polyp and a papilloma is that they have different appearances. Even with a visual examination, a specialist will be able to make the correct diagnosis. The main differences between these neoplasms are presented in the table.
| Differences | Polyp | Papilloma |
| Appearance. | They have a round, ellipsoid or oval shape. The surface of the tumor is usually smooth, pale pink, gray or white. There are polyps with a thin base (pedicle), with which they are attached to the surface. There are also growths on a broad base. | There are small (from 1 to 5 mm), medium (5 – 10 mm), large (10 – 30 mm) and giant (more than 30 mm) neoplasms. In appearance, papillomas resemble cauliflower or have a thread-like shape. They can be light, brown, black, purple or bluish in color. |
Thus, ordinary papillomas rise above the surface of the skin and look like small moles. Polyps are convex formations that tend to merge.
Localization
Such growths can be located in various places. However, a characteristic feature of polyps is their localization only in internal organs. Papillomas can occur both on the surface of the skin and on any mucous membranes.
| Differences | Polyp | Papilloma |
| Localization | Most often, such anomalies develop in the intestines (small or large), uterine cavity, stomach, gall bladder or bladder. Polyps can also occur in the paranasal sinuses, nasopharynx and oropharynx. | They are located on the skin of the back, chest, face, neck, upper or lower extremities. In some cases, hanging papillomas can be localized in the armpits, under the breasts, on the skin or mucous membrane of the genital organs. Sometimes growths (vulgar warts) appear on the fingers, toes, and skin of the feet. |
What do these diseases have in common?
Both endometriosis and cervical papilloma are accompanied by changes in the structure of its tissues, and upon examination, the doctor discovers areas of unusual color on the cervix and an uneven surface of the mucous membrane. He can establish a specific diagnosis only after colposcopy and additional examinations, and at the stage of diagnostic search he only assumes the presence of papilloma or proliferation of endometrioid tissue.
What unites these two pathologies is the fact that they often cause intermenstrual spotting, bloody vaginal discharge, including those that appear after sexual intercourse, and a feeling of pain during it. That is, there is a certain similarity in symptoms.
When should you sound the alarm?
You should definitely visit a doctor if you have:
Painful sensations, the intensity of which often increases as menstruation approaches or during menstruation, as well as during sexual intercourse.
Intermenstrual bleeding. If they become bleeding, you should seek help immediately.
It is necessary to visit a doctor if you cannot conceive a child for a long time, since infertility, when the affected ovaries cease to function fully, can be a complication of endometriosis. The most common concomitant pathology of internal endometriosis (in more than 80% of cases) is uterine fibroids. The diseases are similar in their pronounced dependence on hormonal levels and excessive proliferation - tissue growth.
Pathological tissue in endometriosis can be localized outside the cervix: in the area of the ovaries, pelvic peritoneum, fallopian tubes, and vagina. In the case of deep invasive endometriosis, the intestines, bladder, urethra, etc. may be involved in the process.
Against the background of endometriosis, there is a high risk of hypoxia and underdevelopment of the fetus, and subsequently, inhibition of its development.
Cervical papilloma has an equally dangerous complication - it increases the risk of developing cancer. Therefore, you should visit a gynecologist even in the absence of complaints, for the timely detection of asymptomatic pathologies.
This is why early diagnosis is so important in clinical practice. Ineffective treatment of these conditions can lead to serious consequences for women:
- formation of pain;
- psycho-emotional disorders;
- decreased quality of life.
Types of tumors
Benign:
- cysts;
- nevi or moles;
- nodules whose name has the oma suffix: fibroma, myoma, adenoma, papilloma - depending on the specific tissue.
Malignant:
- formations whose name is appended with the word carcinoma, sarcoma, blastoma, blastosis (fibroblastoma, myosarcoma, adenocarcinoma);
- oncological diseases of the blood - lymphogranulomatosis, leukemia and others;
- skin cancer - melanoma, basal cell carcinoma.
The differences are not always obvious. A thorough diagnosis is needed to look for atypical cells.