July 30, 2020
To talk about local inflammation, you must first understand what lymphadenitis is in general. This is an inflammatory process in the lymph nodes, sometimes accompanied by suppuration
To talk about local inflammation, you must first understand what lymphadenitis is in general. This is an inflammatory process in the lymph nodes, sometimes accompanied by suppuration. It manifests itself through enlargement of one or more lymph nodes and can occur in several regions of the body at once. Clinical signs of the disease depend on the form and type of lymphadenitis: acute or chronic, regional (damage to lymph nodes of one anatomical group) and generalized (involvement of several groups of lymph nodes), serous, purulent, gangrenous, hemorrhagic, phlegmonous.
In the body, lymph nodes create a protective barrier against viruses, infections, cancer cells, participate in the formation of lymphocytes (special cells that destroy foreign microorganisms) and the production of phagocytes, antibodies (immune cells), participate in digestion and metabolic processes, distribute intercellular fluid between body tissues and lymph.
Normally, the lymph nodes are not palpable or are palpated in the form of elastic, small-sized formations that are not fused with adjacent tissues or with each other. Depending on the prevalence, the following types of lymphadenitis should be distinguished:
- local - enlargement of one lymph node in one of the areas (single cervical, supraclavicular lymph nodes);
- regional - enlargement of several lymph nodes in one or two adjacent areas (supraclavicular and axillary, supraclavicular and cervical, occipital and submandibular lymph nodes, etc.);
- generalized - enlargement of lymph nodes in three or more areas (cervical, supraclavicular, axillary, inguinal, etc.).
With axillary lymphadenitis, enlarged lymph nodes in the armpit are palpated. Symptoms of axillary lymphadenitis:
- Enlarged lymph nodes
- Painful sensations when palpating the affected area, turning the body, or moving
- Inflamed nodes are fused together with each other and adjacent tissues into one dense conglomerate
- The skin over the inflamed lymph nodes is hyperemic
- Symptoms of body intoxication appear - fever, weakness, headache, lack of appetite, feeling weak, muscle pain
Often the disease is accompanied by symptoms of the underlying disease; in addition, the patient may be bothered by:
- night sweats;
- weight loss;
- prolonged increase in body temperature;
- frequent recurrent upper respiratory tract infections;
- pathological changes on a chest x-ray;
- hepatomegaly;
- splenomegaly.
Causes of hidradenitis (axillary, inguinal and other localizations)
The main triggering factor for this pathology is personal untidiness. If a person ignores the rules of personal hygiene and does not take a shower or bath in a timely manner, the skin becomes a favorable environment for the rapid growth of microorganisms, including Staphylococcus aureus. In recent years, the main cause of suppuration of the sweat glands in the axillary and groin areas is shaving. Microcuts that occur during hair shaving become entry points for infection.
In addition to uncleanliness, obesity plays an important role, due to which the folds of the skin do not dry out in a timely manner (in a humid environment, microbes multiply tens of times more actively). Diaper rash and scratching also reduce the protective functions of the skin. Finally, diabetes mellitus, which impairs the nutritional function of blood vessels, is also a favorable background for the development of purulent skin infections.
The use of antiperspirants is based on blocking the function of sweat glands. Because of this, sweat does not flush their ducts, Staphylococcus aureus is not washed out and inflammation develops in the sweat gland itself.
Types of lymph nodes
Small lymph nodes are located throughout the body. Located nearby, they form groups and chains. The main groups of lymph glands are found in the neck, armpits and groin area, as well as in many other places in the body. Lymph nodes are connected to each other by lymph channels. Lymphatic fluid is formed between the cells of the body. This watery fluid travels along channels through the glands and eventually enters the bloodstream. Lymph nodes are a major part of the immune system. They contain former blood cells (lymphocytes) and antibodies that protect the body from infections.
Where does hidradenitis occur?
Typical localization is the axillary region (the same in both women and men), hidradenitis in the groin (in women more often due to shaving of the intimate area), in the areola of the nipple and under the mammary glands. Hidradenitis genitalis occurs less frequently (in men - the scrotum, in women - the labia majora), as well as on the face (mainly in men).
Such localizations are due to the fact that apocrine sweat glands located in these places are most often susceptible to inflammation. Their peculiarity is the tortuosity of the ducts, which impairs the outflow of sweat and contributes to its inflammation when Staphylococcus aureus penetrates into the gland.
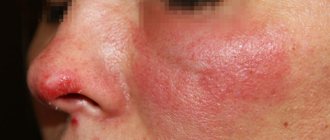
Redness of armpits after shaving
Underarm redness is most often caused by shaving, especially in people with sensitive skin or some forms of dermatitis.
Removing armpit hair with a razor is quick and cheap. A razor blade can damage the skin and make it easier for bacteria to enter, which can cause an inflammatory reaction. After shaving, you need to apply a soothing cream or gel to the skin, which relieves inflammation, softens the skin and has an anti-inflammatory effect.
If you don't have cream, you can reduce the redness caused by shaving with an aspirin tablet. It is necessary to dissolve two tablets in a small amount of water to obtain a paste consistency. Then you need to carefully apply it to the irritated areas of the armpits, let it dry, and then rinse with a small amount of water.
Be extremely careful with this and other home remedies. The active ingredient in home remedies is often a drug whose exact concentration is unknown. As a result, numerous skin lesions and irritations can occur.
Razor irritation can be reduced by cooling the affected area with cool water or an ice cube. There are also special sprays with thermal water that have an anti-inflammatory effect and help regenerate the skin.
If you frequently have problems with armpit redness after shaving, you may want to consider other hair removal methods, such as sugar paste waxing or laser hair removal.
If redness on the skin of the armpit is accompanied by pain, palpable lumps with or without a purulent tip, you should consult a doctor. Most often this is inflammation of the hair roots, but it is also possible that it is inflammation of the glandular ducts of the skin. These conditions usually lead to local or systemic antibiotic therapy.
Stages of the disease hidradenitis
There is no clear stage in the development of the disease. It all starts with the appearance of a painful small nodule under the skin in a typical location. It is not visible at first, but can be felt. After 24-48 hours, it increases significantly in size, the skin over it changes color to red, and then to purple-bluish. The pain becomes very severe and often prevents active movements of the limb.
At this moment, in the thickness of the node there is a process of tissue melting, which is manifested by the appearance of fluctuations (when you feel the node, you feel that its center seems to fall under your finger). The skin over the abscess gradually thins until a small hole appears in it, through which thick pus begins to flow. This usually occurs 7-10 days from the onset of the disease. Often, in the absence of treatment for hidradenitis suppurativa, the process ends in the formation of a fistula, through which serous-purulent contents constantly leak.
Subcutaneous tissue is penetrated by a large number of lymphatic vessels. Through them, the infection can spread to neighboring sweat glands. In this case, the general condition of the patient may also suffer. Symptoms of chronic hidradenitis: body temperature rises, fatigue, weakness appear, sleep and performance are disturbed. Due to massive infection, the subcutaneous tissue swells greatly, foci of infection protrude above the skin, which together forms a picture similar to a “bitch udder” (this has become the popular name for the disease).
Diagnostics
The difficulties of differential diagnosis for local lymphadenopathy lie in identifying a local inflammatory process of an infectious (usually) or non-infectious nature. Lymphatic vessels supplying the upper extremities of the body, the chest wall and the mammary glands pass through the axillary lymph nodes, and as a result, the inflammatory process in this part of the body can provoke enlargement of the lymph nodes. Much less often, the pathogen enters the lymph node and directly through the skin of the axillary region when its integrity is violated. Possible causes of axillary lymphadenitis:
- panaritiums;
- erysipelas of the upper limb;
- phlegmon of soft tissues of the hand, forearm and shoulder;
- osteomyelitis of the bones of the upper limb;
- boils of the same localization;
- purulent mastitis;
- cat scratch disease;
- lymphoma;
- mammary cancer;
- melanoma.
Bacterial axillary lymphadenitis is caused by the following infectious agents:
- staphylococci and streptococci;
- Proteus wand;
- coli;
- enterobacteria
In order to establish the correct diagnosis, it is necessary to take into account the anamnesis and all clinical indications. Diagnosis is usually made using puncture biopsy of lymph nodes; if necessary, lymph node excision can be performed, followed by histological analysis. Before making a diagnosis, a number of examinations are carried out:
- lymphoscintigraphy;
- computed tomography;
- radiopaque lymphography.
Often a patient has to go through several specialists at once to verify the diagnosis, from a general practitioner to an infectious disease specialist, a venereologist, an oncologist and a therapist. The examination begins with palpation (palpation) of the areas where the nodes are located. If primary signs of lymphadenitis are detected, an ultrasound examination is first prescribed. Differential diagnosis should be carried out with systemic blood diseases (leukemia, lymphogranulomatosis), storage diseases (Gaucher, Niemann-Pick), immunopathological diseases (chronic granulomatous disease, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, dermatomyositis, etc.), tumor metastases. Sometimes it is necessary to carry out a differential diagnosis with other surgical diseases, for example, breast cancer can metastasize to nearby (axillary lymph nodes) and then treatment will be aimed at the underlying disease.
Treatment of hidradenitis
At the stage of infiltration formation, the doctor may try to treat hidradenitis in the groin area, armpits and other locations conservatively. On the first or second day, the use of local remedies is recommended. Antibiotics for hidradenitis are used in the form of ointments, most often tetracycline, erythromycin ointments, and clindamycin lotions are used. Since it is most often impossible to cure acute hidradenitis with conservative methods, it is necessary to resort to surgical intervention.
Adequate outflow is a key point in the treatment of any purulent process. Hidradenitis surgery is the best way to achieve this. According to surgeons, the most appropriate method of pain relief is anesthesia. This avoids systemic effects from anesthetics that would have to be administered in too large quantities.
Progress of the operation:
- The skin above and around the abscess is treated with antiseptics.
- A small incision is made throughout the entire depth of the skin until the abscess cavity is opened.
- The cavity is treated with antiseptics, then drained with gauze turunda soaked in water-soluble antibiotic ointment.
- With multiple lesions of the sweat glands, each abscess is opened immediately. If the lesions are located very close to each other, it is better to remove the entire inflammatory conglomerate within healthy tissue. In this case, the wound is sutured. In all others, it heals on its own.
After the operation, daily dressings are performed, during which the skin around the wound is treated with antiseptics. They also wash the abscess cavity, change the turundas with ointment. At the end of the dressing, bandages with antimicrobial ointment are applied to the wound.
Turunda is removed after pus stops flowing from the wound. After this, it quickly heals on its own. Of course, until complete healing, dressings continue.
General conservative treatment is usually carried out after surgery in cases where hidradenitis recurs (some call this form of the disease chronic, which does not reflect its actual course) or many sweat glands are affected. In this case the following applies:
- courses of antibiotic therapy with cephalosporins and semisynthetic penicillins;
- transfusion of antistaphylococcal plasma;
- UV irradiation of blood;
- laser irradiation of blood;
- vitamin therapy.
For severe pain, non-narcotic analgesics are prescribed; for sleep disturbances, appropriate sleeping pills are prescribed.
Treatment of axillary lymphadenitis
Treatment tactics for axillary lymphadenitis depend on the form and cause of the disease. In most cases, lymphadenitis does not require special therapy and goes away on its own after the underlying disease is eliminated. If the process is complicated by suppuration, then the treatment tactics completely change.
General recommendations: maintain rest, immobilize the affected area (do not rub or injure the affected lymph nodes), proper nutrition, take painkillers, anti-inflammatory medications. Therapy for acute axillary lymphadenitis depends entirely on the stage of the disease. Conservative treatment is used for the initial stages: UHF therapy, sanitation of the source of infection (opening of abscesses, leaks, cellulitis, drainage of the abscess), antibiotic therapy taking into account the sensitivity of the microbial flora in the main focus.
Surgical intervention is necessary for purulent axillary lymphadenitis: adenophlegmon, abscesses are opened, pus is removed, and the wound is drained. It happens that a biopsy confirms the presence of a tumor process - benign or malignant. Treatment may include radiation and chemotherapy. In the case of lymphadenitis, as in the presence of any other diseases, it is extremely dangerous to self-medicate.
Back to articles