general characteristics
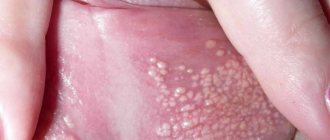
A rash on the head of the penis is one of the external symptoms of a number of pathological processes provoked by endogenous factors or infectious agents. White or red rashes have a different character (tubercles, watery blisters, erosions). In addition to structural changes in the skin, hyperemia, itching, and pain appear.
Rash on the head can make it difficult to urinate and ejaculate.
Primary pathological elements of the rash occur in patches and are localized in the following areas:
- head;
- whisk;
- coronal sulcus;
- foreskin;
- external opening of the urethra.
As the activity of provoking factors worsens, secondary morphological elements appear, which grow and form continuous conglomerates, covering the entire surface of the penis.
Swelling of the labia.
In women, swelling is often combined with itching and burning, discomfort, redness of the mucous membranes, the appearance of erosions, pathological watery discharge mixed with pus or blood, and inflammation of the inguinal lymph nodes. Pain may occur when walking, playing sports, or having sexual intercourse.
Swelling often occurs as a result of abrasions or wearing synthetic underwear, due to insufficient hygiene, allergies and sexual intercourse. But there are also more serious problems.
Why do the labia swell? Causes of swelling of the genital organs.
Various factors can cause swelling of the labia:
Candidiasis (thrush).
A characteristic symptom of the disease is white curd-like discharge, a sour smell, possible itching and burning, swelling, pain during urination and sexual intercourse. Yeast infections most often occur when the immune system is weakened and during pregnancy.
Bacterial vaginosis.
The result of an imbalance in the vagina. Green or gray discharge often appears, a fishy odor is felt, and swelling is possible. But asymptomatic progression of the disease also occurs.
Genital infections. Quite often, the labia become swollen due to irritation from pathological vaginal discharge caused by sexually transmitted diseases (trichomoniasis, ureaplasmosis, chlamydia, mycoplasmosis, gonorrhea). Other signs may appear: itching, irritation, unpleasant odor, painful urination.
Vulvodynia.
Accompanied by pain of varying intensity in the vulva area. It occurs suddenly, worries for a long time and often goes away just as abruptly. May sometimes cause swelling.
Vulvitis.
The main symptoms are swelling of the genitals, redness of the skin and burning. Inflammation of the vulva can occur due to poor hygiene and frequent changes of sexual partners, as a result of allergies, long-term use of medications and certain diseases.
Vulvovaginitis.
The main symptoms are skin flushing, abnormal discharge, pain when urinating, severe itching, causing the desire to scratch, which can lead to swelling. Often, inflammation of the labia develops due to poor hygiene and active masturbation, as a result of allergies or infections.
Bartholinitis.
Bartholin's glands are located in the vestibule of the vagina. When infected, they become inflamed, which is accompanied by redness and swelling of the genitals. If the gland duct is blocked, pus accumulates inside, which contributes to the formation of a cyst. In this case, discomfort and pain occur, which intensifies with movement.
Allergic reactions.
An allergy to fragrances contained in soap or intimate hygiene gel, components of washing powder, spermicides, latex condoms, tampons, low-quality pads, linen fabric, certain foods or medications can cause irritation. In addition to swelling, rashes are often found.
Contact and atopic dermatitis.
It develops with hypothermia, severe depilation of the bikini area, wearing tight synthetic underwear, and exposure to allergens. In the acute form, edema appears unexpectedly and grows rapidly, while in the chronic form it can periodically disappear and then reappear.
Sexual contact.
As a result of rough friction during sexual intercourse due to lack of lubrication (natural or artificial), damage to the labia and vagina is possible, which is accompanied by discomfort and swelling. In some cases, wounds and hematomas may form.
Stressful state.
Sometimes severe stress can cause itching of varying intensity and swelling in the genital area, which makes a woman distracted from the problems that have arisen.
Phthiriasis. (Pubic lice, lice)
You can become infected with lice not only through sexual intercourse, but also through everyday contact. The problem can be diagnosed quite easily by identifying bite marks or parasites. Lice cause severe itching, causing scratching, which causes swelling of the labia and pubis.
In addition to lice, swelling can be caused by mosquito bites, wasps, and bed bugs. In this case, bite marks are clearly visible, and the skin color may be red or bluish.
Hormonal disorders.
During the premenopausal period, the synthesis of estrogen decreases, which is why the woman feels dryness and burning, and possibly swelling of the genitals.
During pregnancy and the premenstrual period, blood flow to the tissues increases, which can lead to increased sensitivity of the mucous membrane. As a result, even the usual gel causes itching, burning and swelling.
Genital herpes.
The virus may not manifest itself in any way until favorable conditions arise (hypothermia, colds, vitamin deficiency, weakened immunity). The main signs are watery blisters, erosions, itching, swelling, twitching.
Tumor.
Quite often, in the initial stages, malignant neoplasms do not cause any symptoms. Occasionally, mild itching and slight swelling may occur, to which women do not attach much importance.
Additional factors.
With dermatological diseases, various parts of the body itch. The genitals are no exception. The woman begins to itch, causing swelling.
Diabetes mellitus causes increased dryness of the labia, which causes cracks and swelling. The wounds are irritated by urine, increasing the itching.
In rare cases, edema can occur due to diseases of the internal organs (heart, kidneys, liver, intestinal dysbiosis).
Treatment methods.
If swelling does not decrease within 24 hours and other symptoms become noticeable, you should visit a gynecologist. He will conduct a diagnosis, determine the cause of the pathology and select an effective treatment method. If necessary, he can refer you for consultation to other specialists (endocrinologist, cardiologist, gastroenterologist, nephrologist, allergist, venereologist).
Most often, local antiseptic treatment is carried out, and antibacterial or antifungal medications are prescribed. For candidiasis, suppositories containing antifungal substances, immunostimulating drugs, and a special diet are used.
For allergies, antihistamines will be helpful. For vulvitis, analgesics are used, and sometimes antihistamines and antidepressants may be needed. Herpes is treated with antiherpetic and immunomodulatory medications.
Timely consultation with a doctor helps to quickly get rid of problems. Self-medication can aggravate the situation, leading to the development of serious diseases and infertility.
Treatment of the rash
A rash on the penis, regardless of origin, needs treatment. Rashes can be treated in several ways, which are selected depending on the nature of the disease. The main methods include:
- hygiene procedures;
- drug treatment;
- surgical intervention.
Prevention of provoking diseases can reduce the likelihood of recurrence of rashes.
Hygiene procedures
To prevent irritation caused by stagnation of smegma from developing into a chronic inflammatory process, it is necessary to carefully remove the lubricant. The essence of hygiene procedures is to wash away the smegma that has accumulated between the head and foreskin. If the foreskin fits tightly, it must be pulled back until the head and coronal groove are completely exposed.
A minor rash caused by uncomfortable clothing or hot weather does not require treatment.
Hygienic procedures are performed daily, using intimate hygiene products. Obese people can additionally use antiseptic and drying agents.
Underwear plays an important role, which also needs to be changed daily for fresh ones. It is recommended to wear loose panties made from natural fabrics.
Treatment of phimosis
Phimosis and paraphimosis, which are characterized by a tight fit of the foreskin, make hygiene procedures difficult. Phimosis is treated using several methods:
- Limited masturbation
. Stretching the foreskin is performed manually by exposing the head during incomplete masturbation and urination. Stretching of the foreskin can be done by spreading fingers inserted into the preputial sac or by using a silicone retractor ring that fixes the glans in an exposed state. - Drug treatment
. Treatment of phimosis is performed locally, using glucocorticosteroid ointments (clobetasol, betamethasone). Glucocorticoids relieve swelling, inflammation and rashes, facilitating gentle stretching. Antiseptics are also used that destroy microbes on the surface of the skin. - Surgical intervention
. Pathological formation or growth of the foreskin requires surgery for complete or partial excision of the foreskin. The operation is known as circumcision.
Phimosis is a reversible pathology and responds well to treatment. In case of relapse, a repeated treatment complex is carried out.
Treatment of venereal rash
Rashes caused by sexually transmitted diseases are treated only in accordance with the recommendations of a venereologist. The doctor makes a diagnosis, establishes the type of pathology and selects the appropriate type of conservative treatment. The therapeutic plan for the treatment of infectious and viral STDs contains a number of drugs:
- antibiotics (antimicrobial) drugs for oral, intramuscular, intravenous or infusion administration (Ciprofloxacin, Azithromycin, Ofloxacin);
- antiviral drugs (Acyclovir, Interferon);
- antiseptics and disinfectants for external use (Chlorhexidine, Betadine);
- glucocorticoids for systemic therapy (Advantan, Sinaflan).
It is prohibited to use medications on your own if you have sexually transmitted diseases, since some of them can not suppress bacteria, but cause the development of superinfection.
Medicines for rashes
Treatment of male candidiasis is carried out through the complex use of antifungal drugs. For oral administration, Fluconazole, Pimafucin or other antifungal tablets that are effective against Candida fungi are prescribed. Clotrimazole ointment is prescribed externally. To successfully suppress thrush, treatment must be completed together with your partner.
For allergic rashes, the treatment plan consists of taking antihistamines.
Depending on the degree of sensitization, a rash on the genitals is treated as follows:
- a single oral dose of an antihistamine;
- course intake of antiallergic drugs or glucocorticoids.
External application of anti-inflammatory or corticoid ointments helps to localize morphological elements.
Consultation with a doctor is required
If the cause of the development of itching and rash lies in the action of one or another microorganism, complex treatment is prescribed, consisting of taking an antihistamine and an antibiotic or antiviral agent.
Antihistamines (tavegil, suprastin) are used to relieve discomfort during therapy, since sometimes identifying the type of microorganism and its elimination take quite a long time. Antibacterial drugs are used both topically (for example, using clotrimazole cream to treat candidiasis) and orally or intramuscularly. For some diseases, douching of an antibiotic solution directly into the urethra is prescribed. Sometimes, when treating some other diseases not related to the reproductive system, if a rash occurs, including on the genitals, stopping the drug is enough to improve the condition.
In some cases, especially when condylomas develop on the surface of the penis, their surgical removal is required. If assistance is not provided, there is a significant risk of these condylomas degenerating into cancer (human papillomavirus infection is considered a precancerous disease). If you delay in providing help, in the most severe cases, amputation of the penis may be required. If surgical intervention is not advisable (old age or serious condition of the patient), you can limit yourself to courses of radiation and chemotherapy in parallel with taking antiviral drugs.
If the cause of the development of itching and rash is of an allergic nature, typical antiallergic therapy is prescribed - most often antihistamines, some infusion solutions, and vitamin complexes are used.
Each of them has its own role - antihistamines promote competitive binding to histamine receptors, preventing it from causing all allergic manifestations; the role of infusion solutions (sodium chloride, Ringer's solution, Trisol, Acesol) is to dilute the blood plasma and reduce the concentrations of circulating antigens; vitamin preparations are intended to normalize the immune system and the normal course of its reactions (since when an allergy develops, the immune response is usually excessively strong). Most often, several sessions of such treatment are enough to eliminate all existing symptoms.
The use of glucocorticoids for the treatment of these diseases is advisable only in the case of local application and their effect. When glucocorticoids are administered systemically, the benefits of their use are often much less than the consequences that may occur while taking them.
The use of physiotherapeutic methods has not particularly justified itself. More or less effective methods used to strengthen local immunity are UHF therapy and the use of a bioptron. These procedures contribute to the activation of local immunity and its correction in case of possible violations. Most often they are used during the rehabilitation period to quickly restore all body functions.
Diagnosis of the disease
The appearance of a rash on the penis in most cases indicates the presence of a pathological process occurring in the body. There are several types of rashes:
- non-pathological rash, often appears with insufficient hygiene of the genital organs;
- pathological rashes occur as a concomitant symptom of inflammatory, infectious and fungal diseases;
- vmorphological elements can also be a consequence of an allergic reaction.
A pathological rash localized in the urethra and accompanied by discharge allows partial diagnosis of the presence of an infectious disease. Most often, the provoking factors of such symptoms are sexually transmitted diseases. If there is a rash, burning and itching in the perineum, mandatory specialized treatment is required.
White coating on the penis after sex
Usually these are remnants of female genital lubricant. Discharge is suitable food for bacteria, so after sexual intercourse, be sure to wash the male organs and wipe dry.
Failure to comply with hygiene provokes the addition of infection and the onset of diseases:
- balanitis - inflammation of the skin;
- balanoposthitis - damage to the head and inner part of the foreskin;
- phimosis is a condition when, due to tissue swelling, it is difficult or impossible to expose the head of the genital organ;
- urethritis is the penetration of infection into the urinary canal, causing pain when urinating.
The transition to disease is caused by a decrease in immunity due to chronic diseases, hormonal problems, and diabetes. Urologists are often the first to detect hidden diabetes.
Treatment depends on the cause of the plaque and is prescribed after smear tests, PCR, and drug sensitivity cultures.