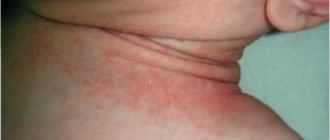
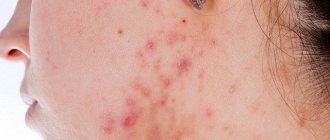
The term “diathesis” in domestic medicine refers to a feature of the body’s constitution, which is expressed in a predisposition to certain diseases. Usually, diathesis refers to allergic diathesis, the most common and easily diagnosed. According to various sources, diathesis occurs in 30-75% of children.
Unlike allergies themselves, diathesis is not associated with functional disorders of the immune system. An allergic reaction during diathesis in infants is usually explained by the characteristics of the child’s body. In children of the first year of life, the protective function of the intestine is reduced: the intestinal walls are thin, the amount of enzymes and antibodies produced is small. As a result, the child’s body may not be able to cope with a large number of highly allergenic foods and give an allergic reaction. By two to three years, the amount of enzymes becomes sufficient, and diathesis in most cases goes away.
Symptoms of diathesis
Inflammation of the skin during diathesis is the body's reaction to contact with an allergen. The main way an allergen enters a child’s body is food, but a reaction to contact with the skin of the allergen is also possible (the allergen, for example, can be components of washing powder that get on clothes during washing, plant pollen, dust, animal hair, etc.).
Diathesis in children under 3 months of age
The first manifestations of diathesis most often appear at the age of 2-3 months. This:
- diaper rash that does not disappear even with careful care;
- profuse prickly heat with mild overheating;
- sebaceous crusts of gray-yellow color on the head in the hairline area (seborrhea).
Diathesis in children aged 3 months and older
In older children, a typical manifestation of diathesis is red spots on the cheeks. As the condition worsens, the skin becomes crusty. The crusts become wet, the child experiences discomfort, itches, becomes excitable, sleep and appetite may be disturbed, and loose stools may appear.
Hemangioma in children - symptoms and treatment
Currently, there are various ways to treat infantile hemangiomas. Many of them have already lost their significance, others are successfully used at the present time. The main vector of treatment is active observation or conducting one or another type of therapy from the moment of diagnosis.
When choosing treatment tactics, you should be guided by several factors:
- age of the child (the younger the patient, the higher the risk of further growth of the hemangioma);
- type of hemangioma and its location;
- presence of complications;
- parents’ desire to conduct this or that therapy;
- doctor's experience [24].
To help doctors decide on treatment tactics for infantile hemangioma, Russian surgeons D. A. Safin and D. V. Romanov proposed a special rating scale. With its help, you can assess the need for drug treatment with beta-blockers. This scale takes into account both the age of the child and the location of the hemangioma, as well as its size, quantity and thickness (presence of pathological volume) [28].
Rating scale for determining indications for systemic drug treatment of infantile hemangiomas with beta-blockers
| Criteria | Description | Points |
| Age | 0-4 months | 4 |
| 5-8 months | 3 | |
| 9-12 months | 2 | |
| 1 year and older | 1 | |
| Localization | Orbit, nose, lips, ears | 4 |
| Perineum, buttocks, genitals | 4 | |
| Hemangiomatosis | 4 | |
| Parenchymal organs and glands | 4 | |
| Scalp and other parts of the face | 3 | |
| Neck | 3 | |
| Joint area | 2 | |
| Hands and feet | 2 | |
| Torso | 1 | |
| Limbs | 1 | |
| Size (diameter) | More than 5 cm | 2 |
| 1-5 cm | 1 | |
| Up to 1 cm | 0 | |
| Pathological volume | Eat | 1 |
| No | 0 | |
| Quantity | 5 or more elements | 1 |
| 1-4 elements | 0 | |
| Complications | Eat | 1 |
| No | 0 |
The doctor examines the patient, evaluates the specified criteria and sums up the points. When the score is from 9 to 14, systemic drug treatment is indicated, and when the score is from 4 to 8, drug therapy is not required.
When assessing the location of a hemangioma, it is necessary to take into account not only the cosmetic defect, but also the risk of various complications. These “critical zones” include the ears, nose, lips and eyelids (orbits of the eye). For example, if the cartilage of the ear is destroyed, a permanent deformation of the auricle will occur, the correction of which will require plastic surgery. When infant hemangiomas are located in the perineum and buttocks, ulcerations often appear that are difficult to heal, so this localization is also critical.
The large size of the tumor indicates an active process of proliferation, which is accompanied by the risk of further growth of the hemangioma and a high probability of various complications.
In the treatment tactics of infantile hemangioma, it is also necessary to take into account the presence of a deep (subcutaneous) component of the tumor. It is not amenable to local treatment and laser treatment, which leads to tumor progression in the deep layers of the subcutaneous fat layer. Therefore, in this case, it is recommended to resort to drug therapy.
The greater the number of hemangiomas on the skin, the more difficult it is to carry out local therapy. The presence of more than five vascular tumors significantly increases the risk of hemangiomas in the internal organs (diffuse neonatal hemangiomatosis).
All methods of treating infantile hemangiomas can be divided into two categories:
- Conservative (non-invasive) treatment : oral medication, lotions, watchful waiting (time treatment) and laser treatment.
- Surgical (invasive) treatment : injections (sclerotherapy) or surgery (removal of hemangioma).
Conservative (non-invasive) treatment
Waiting tactics
This treatment was widely practiced before the advent of beta blockers. Now this method can also be used, but it is necessary to take into account: the younger the child, the higher the risk of tumor growth. Watchful waiting requires frequent and systematic follow-up examinations to determine the possible growth of hemangioma.
Drug treatment
Beta blockers. In 2008, French dermatologist C. Leaute-Labreze discovered the effect of propranolol on infant hemangiomas. From this period began the “golden age” of beta-blockers in the treatment of infantile hemangiomas. Given the low risk of side effects and the high effectiveness of treatment, they have become the “first line” of treatment for this disease.
The exact mechanism of action of beta-blockers is still unknown. Presumably, it includes vasoconstriction, suppression of VEGF-A (vascular endothelial growth factor), stimulation of apoptosis (the natural “disassembly” of pathological tissues). Studies have revealed the presence of β2-adrenergic receptors and VEGF-A in the capillaries of expanding infantile hemangioma, which decrease when β2-adrenergic receptors are suppressed.
Beta blockers can be used topically as a lotion or systemically by administering the medication orally. For local treatment, timolol-based eye drops or eye gel are used. For systemic therapy, the drugs Propranolol or Atenolol are used. Each of them has its own characteristics in dosage, frequency of administration and the risk of side effects.
Comparison of the pharmacological activity of the drugs Propranolol and Atenolol.
| Indicators of pharmacological activity | Propranolol | Atenolol |
| Bioavailability | 20-30 % | 40-60 % |
| Half-life of the drug | 3-5 hours | 6-9 hours |
| Lipophilicity (permeability through the cell membrane) | +++ | – |
| Removing the drug from the body | Liver 100% | Kidneys 90%, liver 10% |
Steroid hormones are one of the oldest methods of drug treatment for infantile hemangiomas. This method has been used from 1960 to the present and is a “second line” of therapy. Until 2008, it was the main method of treating hemangiomas, especially with active tumor growth.
The mechanism of the effect of glucocorticosteroids on infantile hemangioma is still not completely clear. However, it is known that steroid hormones influence adipogenesis, inhibit the formation of new vessels and reduce the production of proangiogenic proteins (VEGF-A, etc.).
Steroid hormones in tablets can be used as systemic drug treatment. Given the high risk of side effects of glucocorticosteroids and the emergence of beta-blockers, this method has become much less common. The main indications for its use are complicated hemangiomas and unresponsiveness of the formation to treatment with beta-blockers. The average course of treatment is from 4 to 12 weeks (maximum dose). Sometimes steroid hormone therapy can last up to 9-12 months of the child’s life.
It is also possible to inject glucocorticoids into the tumor. Typically, this treatment uses Triamcinolone injections or a mixture of Triamcinolone and Betamethasone. As a rule, such treatment is prescribed for small volumetric formations.
Cytostatics (Cytoxan, Vinblastine and Avastin), according to foreign authors, help stop the division of tumor cells in metaphase. However, this method has not found application in Russia, since Cytoxan acts on the growth of sensitive, rapidly proliferating cells, thereby inhibiting the erythrocyte lineage of the blood and the development of the egg. There is also an opinion that after using Cytoxan there is a risk of developing a secondary malignant tumor - angiosarcoma.
Vincristine is a cytostatic drug, an alkaloid from the pink periwinkle plant (Vincarosea). It causes apoptosis (the regulated process of cell death) of endothelial cells and reduces the production of their growth factors. As a rule, treatment with Vincristine is carried out for vascular pathology, which is not a true infantile hemangioma, but is associated with kaposiform hemendothelioma or tufted angioma with Kasabach-Merritt syndrome. The medication is given weekly through a central catheter.
This treatment method may be useful if steroid hormone therapy does not respond. Its appointment is carried out with the direct participation of oncologists. Side effects of the drug include skin irritation and rash, neurotoxicity, constipation, cranial nerve palsies, bone pain, alopecia, and muscle weakness. Typically, side effects are short-lived.
Interferons (Interferon-alpha-2a, Interferon-alpha-2b and Imiquimod - 5% Aldara ointment) stimulate the secretion of interferons, which suppress endothelial and fibroblast growth factors, and also promote tumor necrosis. They are used when steroid therapy is ineffective. The effect of these drugs is noticeable only after four months of use.
Since interferons cause a lot of complications (anemia, neutropenia, hypothyroidism, fever, neuroplegia), their use in the treatment of young children is not justified.
Laser correction
To treat vascular pathology, lasers with wavelengths of 532 and 585 nm, less often 1064 nm, are used. These lasers do not damage the skin, therefore they are considered conservative treatment.
The operation of lasers is based on the theory of selective photothermolysis, which was described in 1980. Laser radiation has a constant wavelength, but is absorbed differently by tissues. This is explained by the presence of chromophores (water, melanin and hemoglobin) in the skin. The result of this energy absorption is heating of the tissue. For example, wavelengths of 532 and 585 nm are best absorbed by oxyhemoglobin, due to which isolated heating of the vessel occurs, leading to damage to its endothelium without harm to surrounding tissues. As a result, the vessel closes.
After laser treatment, there are no scars or scars.
Surgical (invasive) treatment
Sclerosis of hemangioma
This method can be used for small surface formations. To glue tumor vessels together, a special drug is injected into them, which damages the endothelium of pathological capillaries and stimulates the formation of a blood clot. As a result, a fibrous subcutaneous scar is formed [4][5][7][16].
This method requires stages - carrying out a course of treatment at certain time intervals, for example, performing sclerotherapy once every 1-1.5 months. This is due to the rapid blood flow in the hemangioma, which reduces the time of exposure of the sclerosant to the endothelium, thereby reducing its effect.
The proposed sclerosants, for example, Aethoxysclerol and Fibro-vein, are intended for sclerosis of the veins of the lower extremities. A prerequisite for their use is the introduction of the drug into the bloodstream. They can cause disruption of microcirculation around the hemangioma up to tumor necrosis, which will lead to gross cicatricial changes. Alcohol should also not be used for sclerosis of vascular formations. Although it has a pronounced sclerosing effect, its use is often accompanied by side effects.
Cryodestruction (removal with liquid nitrogen)
The tumor focus can be destroyed using liquid nitrogen at a temperature of −195.6 °C. It is a colorless and odorless liquid that is sterile, non-toxic, inert to biological tissues and non-flammable. During cauterization of the hemangioma with liquid nitrogen, the tumor focus is clearly demarcated, which is replaced by an organotypic regenerate by 21-30 days after cryotherapy.
It is impossible to stop the growth and completely eliminate extensive and deep hemangiomas that have abundant blood circulation using cryodestruction. Usually it does not bring the desired result, as it leaves cosmetic defects, and in many cases leads to increased growth of hemangioma. Therefore, this method is best used in the treatment of local, non-extensive hemangiomas [5][8][21].
Surgical method of treatment
The radicality of surgical treatment of hemangiomas lies in the complete removal of all tissue affected by the tumor. Previously, it was believed that surgical removal of a tumor was dangerous due to complications: heavy bleeding during surgery and damage to the nerves, lymph nodes, and large arterial and venous trunks involved in the tumor. Now, with the advent of modern research methods, it has become possible to simultaneously remove a vascular tumor within healthy tissues, without affecting important anatomical structures [5][7][8].
Not all hemangiomas are subject to surgical removal: it should be used only in the presence of life-threatening conditions, for example, bleeding or when the airways are blocked, but most often it is resorted to at the final stage of involution, when there is almost no blood flow in the hemangioma - most often in 4- 5 years.
The scope of the operation is determined by the ability to perform it without irreversible cosmetic defects, the formation of a rough scar and the risk of dysfunction of nearby organs. In this regard, surgical treatment has its contraindications [5][7][8][21].
Outdated treatment methods
Radiation therapy (RBRT)
The essence of this method is to irradiate an area of skin with X-rays from a short distance. Such radiation is absorbed predominantly in superficial tissues and is effective only for infantile hemangiomas located exclusively on the surface of the skin.
As a result of X-ray therapy, “scars” form in the hemangioma, and telangiectasias (spider veins) form on the surface of the skin. As a result, to obtain a good cosmetic result in the future, either plastic surgery or laser treatment of the area of close-focus therapy is required [7][10].
Methods of treating diathesis
When dealing with diathesis in a young child, the main thing is to choose the right diet, excluding foods that may cause an allergic reaction.
For a child in his first year of life, it is very important to receive breast milk.
The proteins of human milk are easily broken down by the baby's enzymes and are completely devoid of allergic properties. However, a nursing mother must also follow a diet excluding fish, poultry, tomatoes, chocolate, smoked meats, spices and other allergenic foods.
When mixed feeding, the child should not be given some juices: orange, carrot, tomato. Introduce any new product carefully - from a small amount. It is important to prevent an allergic exacerbation, and at the same time, to give the baby’s body everything it needs for its development.
Specialist consultation
The Family Doctor pediatric allergist-immunologist will help you deal with your child’s skin problems, determine the cause of allergies, and also build a rational diet that is suitable specifically for your child.
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Rate how useful the material was
thank you for rating
Does it often happen that a baby's skin peels?
Let's put it this way: if you find a baby whose skin has never peeled off in the first year of life, you will surprise not only us, but, perhaps, all pediatricians in the world. In most cases, peeling is a completely natural process that is associated with a sharp change in environmental conditions. Sometimes the baby’s skin even peels off; especially problem areas for a newborn are the feet, hands, and head.
Just think about it: over the previous nine months, the child has never encountered a situation where the temperature around him differs from his own. His skin was constantly moisturized and never came into contact with air. Finally, she did not know sunlight and was not exposed to ultraviolet radiation for a second. Now you can imagine the mess your beloved baby got into when he decided to be born
Typically, a baby's skin will peel because it needs time to adapt to life outside the womb. But there are other factors that lead to this problem.
| Our expert Polina Vasilyeva dermatologist |
| If a newborn's skin peels, this is a physiological phenomenon and is normal. This condition can occur about a day after the birth of the baby and lasts for 3–4 weeks. Despite the fact that this condition is considered normal, it is worth seeing a doctor to rule out congenital ichthyosis and other skin diseases. |
Besides this reason, why else does a newborn’s skin peel?
The skin of a baby is very delicate and thin. With the help of peeling, it can indicate a variety of problems - from uncomfortable external conditions that are easy to eliminate, to serious diseases that require competent treatment. We will tell you about the most common problems, but if you have any doubts, we recommend that you consult a doctor.
- Diapers
If ordinary clothing should simply not cause skin problems, diapers must also ensure that these problems do not arise from contact with secretions. Buy only high-quality diapers for newborns and change them at least every 3-4 hours.
Do not forget that even the best diaper will not be able to ensure the absence of flaking and redness if hygiene rules are not followed. When changing a diaper, thoroughly dry the baby's skin, lubricate the folds and let the baby's body breathe for a few minutes.
- Dry air
It is not easy for a baby’s skin to get used to the air, so it is necessary to maintain high humidity in the children’s room - about 50–70%. Buy a hygrometer (a device that measures air humidity) or a weather station with this function. If the device readings are constantly below the recommended level, install a humidifier in the child's room. You can also use traditional methods - wet towels on the radiator, basins of water near the crib, frequent wet cleaning. But with a special device, of course, it is much more convenient: you only need to periodically add water to it, the humidifier will do the rest itself.
Dry air also dries out the mucous membranes of the nose, which can cause breathing and sleep disturbances.
Our expert Polina Vasilyeva
dermatologist
Children's skin contains a large amount of moisture, many times more than that of an adult, but due to a number of physiological characteristics it loses water very easily. Drying out is fraught with the development of various dermatological problems. The baby's skin begins to peel off and becomes very sensitive to various external factors - high and low temperatures, dust, mechanical damage, sunlight and others. - Hygiene products
Some parents take their baby's hygiene very seriously. They buy various gels, shampoos, children's bubble baths and many other bathing products. All later, when the child grows up! At a tender age, these products do not help hygiene, but on the contrary, they can destroy the already fragile natural protection of the skin.
The baby should be bathed in regular tap water. Use shampoo and baby soap no more than once a week, and avoid all other products altogether. Do not add potassium permanganate to the bath - it dries it out and only aggravates the peeling problem.
Our expert Polina Vasilyeva
dermatologist
The child needs to select products specially designed for children’s skin with a good composition (without parabens, sodium lauryl sulfate, fragrances, etc.). - Improper care
The main task of caring for a child's skin is to ensure its hydration. For this, only two products are used - baby cream and baby oil; nothing else should be used. Don’t forget to thoroughly lubricate all the folds on the baby’s body, paying special attention to areas of peeling. And, of course, buy products only from reliable manufacturers and only in reputable stores.
It’s not common, but there are situations when some children’s cosmetics are not suitable for the child. When treating the baby’s skin, parents notice that the problems do not go away or even get worse. In such cases, it is recommended to change the product; in particular, you can try natural “edible” oils - olive, coconut, sesame and others.
Our expert Polina Vasilyeva
dermatologist
To moisturize the skin, it is important to ensure that the baby consumes a sufficient amount of fluid, especially if the body is actively losing it. For example, if a child experiences an intestinal disorder accompanied by vomiting, or has excessive sweating. - Wind, cold, sunlight
Does it ever happen that your face becomes chapped? Have you ever been sunburned? How does your skin feel after a long walk in the cold? Now imagine how all this affects the baby’s skin, which is several times thinner!
To prevent peeling in a newborn, protect exposed parts of his body from wind and direct sunlight. Try not to walk with him in open, windy spaces, choose a shady side of the street, use the stroller hood to protect the baby's skin. Before you start getting your baby ready for a walk in winter, lubricate his face with oil or a special cream. On sunny days, it is recommended to use sunscreen. Make sure the product is absorbed before going outside.
- Food allergies
If a baby's skin is peeling, this may be a manifestation of internal problems in the body, the most common of which is food allergies. At the complementary feeding stage, it is very important to follow the rule of sequential introduction of foods. After you have introduced the baby to a new taste, you need to wait a few days until the next menu expansion and observe possible negative reactions of the body. If you notice that your baby's skin is flaking more than before, it's most likely a new product.
How else allergies can manifest themselves, read this article.
If your baby is currently eating only mother's milk, carefully monitor your diet. Some allergens are able to pass through all the barriers of a woman’s digestive system and enter the milk, and from there into the baby’s body. Is your baby's skin peeling and the situation has suddenly gotten worse? Think about whether you've been on a diet lately.
Our expert Polina Vasilyeva
dermatologist
If the skin dries out due to an allergic reaction, the use of antihistamines is necessary (the specific drug is determined by the doctor). Parents need to ensure that the child does not have contact with the most common allergens - animal hair, dust, pollen, various chemicals, and also temporarily exclude allergenic foods from the diet. - Poor quality clothes
The baby's body is in contact with clothing almost all the time, and this can also be a source of the problem. Artificial fabrics, additives that give the material elasticity, durability and other properties, dyes - all this may not be liked by the skin of a newborn and may result in peeling.
In addition, if clothes do not allow air to pass through well, the baby may develop diaper rash. Read here how to deal with them.
It is advisable that all clothing that directly touches the baby’s body be natural. Buy it only in trusted stores - this guarantees the availability of the necessary hygiene certificates. And learn to confidently refuse an offer from your handicraft grandmother to sew a wonderful overall for your child from your old skirt.
- Detergents
Sometimes there are no harmful substances in the clothes themselves, but they come into them from washing powder, rinse aid, and stain remover. In this case, the baby's skin peels off all of his clothes at once.
If you notice that your problems have gotten worse and you've just recently switched to a new laundry detergent, don't use it anymore. And when buying in a store, choose products that say they are hypoallergenic and suitable for washing children's clothes.
Our expert Polina Vasilyeva
dermatologist
If peeling has already occurred, it is recommended, first of all, to recognize the real cause of its occurrence. If you suspect that peeling could have been caused by household chemicals or personal hygiene products, you need to replace them or eliminate them altogether. - Diapers
If ordinary clothing should simply not cause skin problems, diapers must also ensure that these problems do not arise from contact with secretions. Buy only high-quality diapers for newborns and change them at least every 3-4 hours.
Do not forget that even the best diaper will not be able to ensure the absence of flaking and redness if hygiene rules are not followed. When changing a diaper, thoroughly dry the baby's skin, lubricate the folds and let the baby's body breathe for a few minutes.
- Dry air
It is not easy for a baby’s skin to get used to the air, so it is necessary to maintain high humidity in the children’s room - about 50–70%. Buy a hygrometer (a device that measures air humidity) or a weather station with this function. If the device readings are constantly below the recommended level, install a humidifier in the child's room. You can also use traditional methods - wet towels on the radiator, basins of water near the crib, frequent wet cleaning. But with a special device, of course, it is much more convenient: you only need to periodically add water to it, the humidifier will do the rest itself.
Dry air also dries out the mucous membranes of the nose, which can cause breathing and sleep disturbances.
Our expert Polina Vasilyeva
dermatologist
Children's skin contains a large amount of moisture, many times more than that of an adult, but due to a number of physiological characteristics it loses water very easily. Drying out is fraught with the development of various dermatological problems. The baby's skin begins to peel off and becomes very sensitive to various external factors - high and low temperatures, dust, mechanical damage, sunlight and others.
What to do if your baby's skin peels?
First of all, do not forget that this is usually a natural developmental stage that the baby will outgrow over time. And take a number of measures to prevent peeling:
- Bathe your child no more than once a day. You can even less often - every other day.
- Use shampoo and baby soap no more than once a week.
- Do not dry your baby's skin after bathing, just pat dry with a towel and then let it air dry.
- After bathing and changing clothes, lubricate the folds on your body with oil.
- Change diapers as needed, but at least every 3-4 hours. After drying your baby's skin, let her breathe for a few minutes.
- Before walking in winter, apply oil to exposed skin; in summer, use sunscreen for children. Allow the product to absorb before going outside.
- Humidify the air in your baby's room.
- Use products designed for washing children's clothing.
- Choose diapers that are gentle on your baby's skin.
| Our expert Polina Vasilyeva dermatologist |
| And remember that the baby does not need to be “bundled up”, even if it seems to you that the room is cool. The accumulation of excess heat leads to sweating. Even if a child feels dry to the touch, this does not mean that his body has stopped evaporating moisture. Overwrapped children sweat, cool down, sweat again, cool down again, and this process leads to decreased immunity and various diseases. In addition, sweat dampens clothing, reducing its heat-protective properties. Therefore, it is necessary to take into account all possible individual characteristics of the child, as well as temporary situational factors that will determine the choice of optimal clothing. |
Authors: Huggies experts, dermatologist Polina Vasilyeva