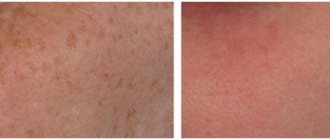
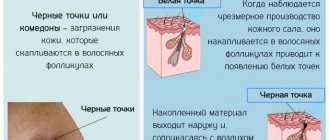
Hyperpigmentation is a focal or diffuse deposition of pigment on the skin, which leads to darkening of individual areas or the entire surface of the body. The formation of melanin, which is responsible for the appearance of pigmentation, occurs as a result of the body's protective function in response to sunlight. But excessive release of melanin is not always due to physiological processes. This is often evidence of the presence of pathologies.
Causes of hyperpigmentation
There are more than a dozen reasons for hyperpigmentation. The main reason is tanning, which causes photoaging. When the skin is irradiated with ultraviolet rays, melanin begins to be actively produced in melanocytes, which are cells in the layers of the epidermis. And excess pigment deposition leads to darkening of the skin and the appearance of spots on it.
Tanning is a relatively harmless cause of external skin changes. But besides him, there are others.
Table 1. Causes of hyperpigmentation and its pathogenesis.
| Name | Brief rationale |
| Vitamin deficiency | A lack of vitamin B12 leads to darkening of the skin. It prevents the appearance of blemishes by regulating the synthesis of the pigment melanin. Vitamin A is responsible for dark color bleaching. Vitamin E deficiency increases the risk of skin damage due to overexposure to the sun |
| Skin injuries | Damage in the form of: acne, burns, furunculosis, surgery, fungal or infectious diseases can trigger post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. The same thing sometimes happens after blepharoplasty. This is due to active cell division in the affected areas. New skin is more sensitive to direct sunlight, so it darkens quickly. And intense tanning can cause hyperpigmentation. |
| Diseases of the gallbladder, liver | In this case, lipid metabolism is disrupted. As a result, pigment spots may form on the face, stomach, back, palms and other parts of the body. |
| Age-related changes | Hyperpigmentation can appear at a young age. But for older people this is a common occurrence. External changes are associated with long-term exposure of the skin to ultraviolet rays, as well as the presence of chronic diseases |
| Housing and communal services diseases | Intestinal dysfunction provokes disruptions in the functioning of metabolic processes in the body. This may result in hyperpigmentation. |
| Hormonal disorders | Functional disturbances in the functioning of thyroid hormones and the endocrine system as a whole sometimes lead to the appearance of lesions in the form of dark pigment spots on the face (lips, eyelids, around the eyes, on the forehead near the hair, on the nose, cheeks), shoulders, chest. The same thing happens during menopause, pregnancy, puberty, when melanin synthesis increases markedly. This also applies to taking oral contraceptives |
| Kidney disease | If there are problems with the kidneys, the skin often acquires a yellow-brown tint. |
| Stress, nervous system diseases | Under stress, pigmentation may also appear due to a weakening of the body's protective functions. |
| Intoxication | When taking medications, some of the active components contained in them accumulate in the body. They are able to provoke an increase in melanin synthesis. But not only medications can cause hyperpigmentation, but also natural ingredients, herbs, and plants. |
| Heredity | The disease can manifest itself in the presence of a genetic predisposition. In this case, melanosis occurs, that is, a pathology associated with a disorder of pigment. Melanosis can be acquired, but most often it is transmitted genetically |
| Cosmetics and care | Photosensitizers included in some cosmetics provoke an increase in the skin's susceptibility to solar radiation, causing hyperpigmentation. It can also occur after depilation (unsuccessful, incorrect), including after sugaring. The use of cosmetics often causes spots on the body |
| Varicose veins | Because of this disease, a rash often appears on the lower extremities. |
Other causes of hyperpigmentation include alcohol abuse, poor diet, and smoking.
Pathogenesis of skin hyperpigmentation
The pigment-producing cells are located between the basal keratinocytes. A certain part of them are melanocytes, which enter the cells in the 3rd month of fetal development. Their function is to transfer melanin to keratinocytes in a proportion of approximately 1 to 30. The number of melanocytes depends on the location - the face and urogenital area have the most - about 1100-1300 cells/mm². The number increases with overexposure to ultraviolet light, but decreases with age.
The enzyme tyrosinase and the amino acid tyrosine are involved in the synthesis of melanin. As a result of chemical reactions in the body, 3 types of melanin are formed:
- eumelanin dark brown;
- pheomelanin yellow;
- trichrome red.
The epidermis contains a mixed type of pigmentation, but the main one is melanin, which determines the skin tone. Melanin pigmentation disorders are classified into 3 types:
- with an increased level of pigment – hyperpigmentation;
- with decreased – amelanosis or hypomelanosis;
- dyschromia – mixed type.
Normally, due to genetic factors, skin color can change and then return to its original appearance. But under some circumstances, hyperpigmentation can lead to problems.
Localization
Age spots can appear on any part of the body, regardless of the cause. There is a whole group in the international classification of diseases dedicated to different types of hyperpigmentation. The ICD disease code is L81. The group is called “Other pigmentation disorders”; it is further subdivided into subsections in accordance with the type of hyperpigmentation and its location.
On the face
Age spots most often appear on this part of the body. The face is constantly exposed to the sun's rays. They can have different sizes, colors, shapes. They appear under the eyes, on the forehead, eyelids, wings of the nose, chin, and in the upper part of the cheeks.
The location of hyperpigmentation is not associated with age. In young and old people, the predominant location of spots on certain areas of the face remains.
On the body
On the legs (thigh, lower leg), hyperpigmentation may appear as a result of:
- varicose veins;
- taking medications (as a side effect).
- hair removal, which causes irritation and ingrown hairs;
- lack of vitamins A, C or PP;
Spots on the feet appear from calluses.
On the upper extremities, the rash most often occurs due to age-related changes. The same can be said about the back and chest area. It will not be possible to completely cope with the problem, since hyperpigmentation will still make itself felt again and again. The intensity of the manifestation can be reduced through cosmetic procedures. This also applies to those with red hair.
Frequently asked questions about darkening of the skin on the legs
Could darkening of the skin be associated with varicose veins in the legs?
Yes, the most common cause of darkening (hyperpigmentation) of the skin is varicose veins. These changes occur due to the accumulation of hemosiderin (a breakdown product of hemoglobin) in the skin and subcutaneous fat.
Why does darkening of the skin occur with varicose veins?
Darkening of the skin with varicose veins occurs due to prolonged stagnation of venous blood in the distal parts of the lower extremities. One of the results of this stagnation will be chronic inflammation with red blood cells leaking outside the venous vessels. Subsequently, the hemoglobin present in these cells will provide local pigmentation of the skin.
Darkening of the skin, how to deal with it?
You can effectively combat darkening of the skin due to varicose veins with the help of timely treatment of the varicose veins themselves.
How to avoid darkening of the skin?
Hyperpigmentation (darkening of the skin) can be avoided through effective treatment and prevention of varicose veins. Periodic visits to a phlebologist with duplex ultrasound scanning of the venous bed will be the best way to avoid possible darkening of the skin.
Types and symptoms of age spots
Hyperpigmentation on the body does not cause physical discomfort. Neither itching, nor burning, nor any other unpleasant symptoms are usually observed (but not always). Only compaction, change in color of spots or their convexity should be alarming. In this case, you should consult a dermatologist to exclude the possibility of developing malignant neoplasms. For self-control, you should know about the common types of stains, their location, features, and reasons for their appearance.
Freckles
This type of pigmentation is not a pathology. Freckles are genetically determined. Their appearance is explained by a special combination of genes in the DNA of skin cells. Freckles tend to intensify in the spring and summer due to ultraviolet irradiation of the skin. In winter they are usually not so noticeable.
This kind of hyperpigmentation of the skin is expressed in the form of patches of different shades of brown. Freckles appear on the face, shoulders, arms, and back. Appearing in childhood, they can disappear without a trace with age. But this does not always happen.
It is not recommended to try to get rid of freckles on your own. This procedure requires the development of an individual program. Typically, genetic hyperpigmentation takes a long time to resolve.
Melasma
This pathology makes itself felt in the case of an excess of female sex hormones. Melasma can also occur when taking medications, using certain cosmetics, and exposure to sunlight.
Melasma is hyperpigmentation, expressed in the form of spots of different shades with uneven contours. You can get rid of it by eliminating the cause and simultaneously using bleaching compounds. As a result, melasma disappears without a trace.
Types of melasma:
- central-facial, or centrofacial. In this case, the spots are localized on the forehead, nose, chin, and above the upper lip;
- mandibular. Suggests the spread of spots on the arch of the lower jaw.
- painting With it, pigmentation mainly affects the nose and cheeks;
Melasma
With this disease, spots appear on the hands, face, neck and other open areas of the body that have an uneven color. This pathology is chronic. Subsequently, hyperpigmentation can spread to other areas of the skin.
Melasma can be acquired or hereditary. Most often it occurs during pregnancy, when taking oral contraceptives, as well as when the functionality of the ovaries is impaired and there is a lack of vitamins C and PP.
Pigmentation may also be accompanied by:
- itching;
- general malaise;
- peeling, dryness;
- progression of the disease (modification of spots, increase in their number).
Melasma passes with a change from a period of remission to exacerbation. Can be corrected.
Becker's nevus
It is characterized by the appearance of pigmented spots with hair growing on them. The pathology is shown in the photo below. Becker's nevus is characteristic of male adolescents, but it also occurs in adults. The exact cause of the disease is not known. It is assumed that the main factors are heredity, stress, and ultraviolet radiation.
The disease progresses as follows: first, a small wrinkled dark brown spot appears. Then new ones can form next to it. Over time, they either grow separately or unite, forming large pigment halos, up to 18-20 cm in diameter. Then they are evenly covered with hair. Tanning significantly accelerates pigment growth.
Secondary
The formation of spots is associated with certain damage to the layers of the epidermis.
The accumulation of melanin, which causes secondary hyperpigmentation, occurs after acne, after removal of a mole and other surgical interventions, as well as:
- psoriasis;
- peeling
- wounds, cuts;
- erosions;
- papules, pustules;
- sores;
This also applies to the use of cosmetics containing photosensitizing components.
Age
Senile (senile) lentigo usually occurs on open areas of the body. That is, those who are most often exposed to solar radiation. Age-related hyperpigmentation appears as a result of a slowdown in melanin transport and, as a result, its accumulation. The causes of the disease are also chronic diseases and a general weakening of the body's protective functions.
Age-related rashes occur on the shoulders, chest area, face, arms, and back. It is characterized by uneven color and irregular shape.
Berlocc's dermatitis
It is distinguished by the appearance of dark brown spots of different sizes after the use of perfume products. Neoplasms may be accompanied by itching, and over time disappear without a trace without any therapy. The exact cause of the disease is not known. Scientists suggest that Berlocc's dermatitis may be due to hypersensitivity to certain components of perfume.
Chloasma
The spots with this disease are usually symmetrical and dark in color. Their outlines are uneven, but always clear. Most often, chloasma forms on the inner thigh and face. Their appearance indicates liver dysfunction.
Chloasma spots are large, at least 1 cm in diameter. Formed singly or in groups. As the disease progresses, they can merge and occupy large areas of the body. Sometimes chloasma manifests itself in the form of specific stripes passing through the stomach, forehead, and cheeks.
The many faces of hyperpigmentation
Today, hyperpigmentation is considered one of the main signs of aging. Dark spots in the décolleté area, on the face and hands are perceived as an inevitable symptom of hormonal changes or liver disease. It is not surprising that women are as concerned about the appearance of characteristic spots as they are about new wrinkles.
The production of melanin (skin pigment) is a natural reaction of the skin that tries to prevent UV rays from penetrating into the nuclei of cells where DNA is located.
Hyperpigmentation occurs when, due to dysfunction of melanocytes (cells that produce melanin), melanin is synthesized many times more than necessary. This can happen for several reasons. Let's look at them in order.
Traumatic hyperpigmentation
This hyperpigmentation occurs due to the release of melanin in response to skin damage - as a kind of attempt by the body to protect itself.
This type of hyperpigmentation occurs more often in people predisposed to it, so if you have freckles on your face, be careful with peels, laser therapy, and squeezing pimples.
Help: The good news is that this type can only be treated with external remedies, i.e. ointments, creams and serums. Look for so-called “tyrosinase inhibitors” in the formulations - a protein that controls melanin synthesis: hydroquinone, arbutin, kojic acid, licorice root extract, nicotinamide, emblica extract, vitamin C, alpha-lipoic acid. As well as new products on the cosmetic market - synthetic peptides oligopeptide-34, oligopeptide-51.
Despite the fact that the mutagenic effect of hydroquinone has been actively discussed recently, cosmetologists have not yet developed a more effective whitening agent. Hydroquinone is particularly blamed for causing malignant tumors in rats. However, in the human body this substance is “neutralized” in the liver with the formation of non-toxic derivatives. Hydroquinone is approved for over-the-counter cosmetics at a concentration of 2%, but in some salons cosmetologists can make their own products containing a higher percentage. The main reason for limiting this drug for sale is various types of dermatitis due to the use of products with substance concentrations of 5% or higher.
Pigmentation in the elderly (lentigo)
Occurs in older people as a result of repeated exposure to UV radiation
The so-called “solar lentigo” are small spots 1 cm in diameter with a smooth edge, very similar to freckles. They appear on the hands and face, but unlike freckles, they do not disappear in winter and do not become paler. Lentigines occur in areas exposed to UV radiation throughout life. This is why it is important to use sunscreen on your neck, décolleté and arms at all times, especially if you spend a lot of time in the sun or like to visit a tanning salon.
Help: There are many ways to reduce the appearance of lentigo, it all depends on how quickly you want to see results. Long-term treatment includes the use of retinoids and sunscreens, as well as serums with tyrosinase inhibitor agents. The best results are obtained by combining these substances with glycolic acid, which helps them penetrate deeper into the skin. For example, a combination of glycolic acid with nicotinamide (vitamin B3) and retinol or resorcinol is good. If you want quick results, peelings with trichloroacetic acid and laser correction (Fraxel, IPL laser) are included in the treatment.
Chloasma, or “mask of pregnancy”
Chloasma (melasma) is a fairly typical skin condition during pregnancy or when using contraceptives.
This is due to an increase in estrogen levels. There are 2 types of melasma: epidermal and dermal, although the mixed type is more common.
Epidermal melasma
appears in the form of spots from light to dark brown, in some cases even black, with jagged edges. This type is more amenable to correction, since melanin is located in the upper layers of the skin, which means that the whitening components from creams and serums can achieve their goal.
Dermal melasma
appears in the form of gray-blue spots, the pigment lies in the middle layers of the dermis, where the lightening components no longer penetrate.
To make a correct diagnosis, it is best to use a Wood’s lamp (“blue lamp”) - the brighter the spots in the light of the lamp (epidermal melasma), the easier the therapy will be. However, most women do not conduct such tests, but simply randomly buy “whitening serums” in the hope that the spots will go away on their own. Alas, such a strategy does not always lead to success. Chloasma is one of the most stubborn types of hyperpigmentation. Lasts for a very long time even after the end of pregnancy or discontinuation of COCs.
Help: Hydroquinone, azelaic acid, a combination of retinoids and corticosteroids, such as fluocinolone (Fluocinoloni acetonidum), will help you in treatment. Oddly enough, but in this case, azelaic acid at a 20% concentration may be even more effective than hydroquinone at 2-4%. To speed up the effect, the so-called Jessner peel (an alcohol solution of resorcinol, salicylic and lactic acid) or peeling with salicylic and glycolic acids is performed once every two weeks. If you add medications with kojic acid to this treatment, the effectiveness increases further. In some cases, IPL laser treatment or microdermabrasion may make sense.
If you want to correct the manifestations of chloasma during pregnancy, be sure to consult your doctor!
Whatever regimen you and your dermatologist choose, the main thing is to strictly follow the regimen. To make this routine easier for consumers, manufacturing companies such as Obagi and La Roche-Posay produce products in special “numbered” packaging.
Today, cosmetic options are such that hyperpigmentation is not necessarily “forever.” Reducing unpleasant stains is possible even in the most severe cases. Of course, for skin 30+, spots will not disappear with the wave of a magic wand, and here you should no longer rely on “green” cosmetics. But the right therapy will definitely help you!
Tatiana Morrison
Photo thinkstockphotos.com
Products by topic: (retinol), [product](fluocinolone), [product](salicylic acid), [product](achromine), [product](acids), [product](peptides)
Hyperpigmentation in children
In childhood, spots on the skin appear much less frequently than in adults, and hyperpigmentation is usually a consequence of injury to the epidermis. Rash, diaper rash, inflammation in children - all this can leave behind areas of skin that are darker than the rest of the body.
You should be wary if a rash of unknown etiology appears for no reason. This may indicate the presence of serious acquired or hereditary pathologies.
As for freckles, they can appear by the age of 3-4 years and go away with age. Freckles do not pose any health risk.
Diagnosis of skin hyperpigmentation
The examination includes a number of complex procedures. To find out the cause of the disease, a dermatologist conducts a survey and examination. If necessary, the patient receives a referral for consultation with other specialists: oncologist, endocrinologist, gastroenterologist, gynecologist, and so on.
A promising and effective method for diagnosing age spots is dermatoscopy. Using an epiluminescent microscope, the doctor assesses the condition of the skin and spots - the full structure with magnification. The specialist analyzes the color, dermal, epidermal and papillary layers of the skin. This method is considered the most accurate and technically simple.
Diagnostics
Skin hyperpigmentation is treated by a dermatologist, cosmetologist, and sometimes an allergist, gastroenterologist and other specialists. It all depends on the cause of the disease. The doctor will tell you how to deal with hyperpigmentation and prescribe the appropriate treatment.
If you find suspicious spots, you should first observe them. And if they change shade and increase in number, then you should consult a doctor. If there is no specialized specialist, you can visit a therapist.
First of all, the patient is asked to undergo general blood, urine and stool tests. Sometimes it is necessary to undergo an ultrasound procedure. Based on the results of these studies, further diagnostics are predicted.
Often the patient is given a referral to visit an endocrinologist, oncologist, or gastroenterologist.
Sometimes the disease is accompanied by: itching, rash, fever, pain. It is important to inform the doctor about all the nuances in order to narrow the variability of the diagnosis as much as possible.
Classification and stages of development
The division into species is based on pathogenesis and clinical picture:
- Excessive formation of melanin. Melanocytic type - an increase in the number of melanocytes. Melanin – excessive production of pigment by melanocytes. Both types can be congenital or acquired.
- Classification by area. This is generalized diffuse and reticular, as well as limited pigmentation. Each of them has its own causes and symptoms.
Hyperpigmentation is also divided into physiological, acquired and genetic. But there is no single classification; everything depends on each individual case.
Methods for removing age spots on the face and body
Not only a dermatologist, but also a cosmetologist knows how to treat hyperpigmentation. Rashes on the surface of the skin are removed in cosmetology in several ways. You should not carry out the procedure yourself, as incorrect actions can aggravate the situation and lead to irreparable consequences. To solve the problem with the appearance of spots on the body, you need to contact professionals who have graduated from the Academy of Cosmetology.
Mesotherapy
During the procedure, the skin whitens and is also saturated with nutrients. Mesococktails contain vitamins, hyaluronic acid, minerals, medicinal compounds, and natural plant extracts.
Mesotherapy procedures are usually performed on the face. But sometimes certain parts of the body, such as the neck and shoulders, are also bleached. As a result, the skin becomes not only light and uniform, but also elastic and fresh.
The duration of treatment is determined individually by a cosmetologist. The effect of mesotherapy lasts for at least 6 months.
Chemical peeling
This is the most effective method of getting rid of pigmentation. The procedure involves applying an acidic composition to the skin tissue, which stimulates exfoliation of the upper layer of the epidermis, that is, mechanical destruction of the spot cells occurs. This is what makes hyperpigmentation disappear.
Chemical peeling can be superficial, medium, or deep. The required depth of penetration, as well as the type of product, is determined by the cosmetologist.
The most common types of peeling:
- lactic;
- peeling with calcium chloride or trichloroacetic acid.
- retinoic;
- salicylic;
- almond;
- glycolic;
Each of the products, in addition to whitening, has its own effect: lifting, narrowing pores, normalizing the functioning of the sebaceous glands.
Laser peeling
How to get rid of stains forever? Do laser peeling. The procedure is carried out by removing a significant layer of the epidermis, so after the laser the skin needs to be restored. The effectiveness of this method of removing hyperpigmentation is based on the ability of neoplasms to absorb electromagnetic radiation that destroys spot cells.
The mechanism of action of laser peeling: new cells formed at the site of laser exposure actively synthesize and accumulate the required amount of melanin. This is why the skin color of the affected area becomes lighter.
The correction procedure is carried out in at least 3 stages. The breaks between them are about 10 days.
Benefits of laser peeling:
- This method of removing pigmentation has no side effects and no patient care is required;
- no anesthesia is used during the procedure;
- laser peeling gets rid of spots relatively quickly, and, most importantly, forever;
- The first result is noticeable after the first stage of peeling.
Ozone therapy
The procedure is carried out in two ways: applications and subcutaneous injections. Ozone therapy is actively used in the treatment of foci of post-inflammatory pigmentation, as well as acne, and enlarged pores.
The procedure has an anti-inflammatory and absorbable effect. It also stimulates the active functioning of the immune system.
Reviews from patients indicate that a positive result can be achieved after just 2-3 ozone therapy procedures for primary and secondary hyperpigmentation. However, the duration of treatment, as well as its scheme, is determined by the dermatologist. Injection methods are not suitable for everyone.
Cryotherapy
The procedure involves influencing cells oversaturated with melanin using liquid nitrogen, which acts as a corrector. It destroys them and stimulates the regeneration process. As a result, new young cells with a normal content of the substance responsible for pigmentation are formed in place of the spots.
The procedure is usually well tolerated by patients. Sometimes they feel a slight burning and/or tingling sensation.
The disadvantage of cryotherapy is that after it is carried out, scars may appear, albeit slightly noticeable, on the affected areas. That is why the procedure is almost never performed to remove hyperpigmentation on the face and, especially, to eliminate periorbital spots.
Phototherapy
This is the most gentle method of getting rid of age spots. But it requires more time. To achieve results with primary hyperpigmentation, you need to undergo about a dozen procedures.
Phototherapy is based on photothermalysis, which destroys cells by exposing them to heat. In addition to removing pigment, the synthesis of elastin and collagen is stimulated during the procedure.
Definition and causes of the disease
Hyperpigmentation is most common on the face, but spots can appear all over the body. The medical term for pathology refers to the darkening of some areas of the skin compared to other areas. The pigment that creates the shade of the skin is melanin. Its amount may vary depending on race and region. But in some cases, there is an excess accumulation of melanin in different parts of the body. The main causes of hyperpigmentation:
- excessive exposure to UV – a passion for tanning, which can lead not only to darkening of skin areas, but also to photoaging;
- hormonal changes in the body - during menopause, pregnancy, puberty;
- infection and inflammatory processes;
- chronic diseases: endocrine system, gastrointestinal tract;
- metabolic disorder;
- long-term use of a number of medications: NSAIDs, antibiotics, diuretics, antihistamines, and so on;
- burns and skin injuries.
Hyperpigmentation can also be caused by a lack or excess of vitamins and minerals in the body. Products containing photosensitizing substances are another reason.
Treatment
Drug therapy is carried out after determining the root cause of hyperpigmentation. Ointments, lotions and (or) creams are prescribed by a dermatologist or dermatocosmetologist. Most of them are plant-based with the addition of modern chemicals. Self-medication is not recommended.
Pharmacy drugs
The most popular drugs whose action is aimed at whitening the skin are presented in the table.
Table 1. What to do if you have pigmentation: pharmaceutical remedies for pigmentation.
| Name | Short description |
| Belosalik | The ointment contains salicylic acid, which is involved in skin whitening. The drug has: anti-inflammatory, immunosuppressive, antifungal, hypothermic, keratolytic, antiproliferative vasoconstrictor effects. Ideal for removing post-traumatic pigmentation |
| Zinc ointment | Effectively eliminates redness and age spots, including freckles. Additionally, it has an antiseptic and softening effect. |
| Achromin | This is a whitening cream for freckles, spots, scars, pigmentation. Suitable for any skin type. Contains substances that protect against ultraviolet radiation. According to the manufacturer, the cream can eliminate hyperpigmentation completely or partially after just a month of regular use. Treatment regimen: apply the product to the affected areas 2 times a day |
| Synthomycin liniment | The active ingredients of the ointment are: castor oil, which has a cosmetic effect and saturates the skin with vitamins, and chloramphenicol. It has an anti-inflammatory, disinfecting effect. Whitening occurs precisely due to the action of castor oil. However, the effect is quite weak and is noticeable only with additional treatment. |
| Melanative | The cream fights pigment spots on any part of the body. Suitable for all skin types, safe to use. Contains components that protect the skin from UV radiation. A positive result is noticeable after a month of use |
| Retinoic ointment | The drug is able to stimulate tissue regeneration, enhance the growth of new cells, and also block enzymes that destroy elastin and collagen. The ointment promotes the disappearance of pigmentation, as well as acne and pimples. It is inexpensive, only 300 rubles. |
| Skinoren | The main component is azelaic acid, which helps get rid of stains. However, the cream has its drawbacks: · you will have to use it for a long time, a positive result can be achieved in 6 or 12 months; · when using, you sometimes experience discomfort in the form of tingling or burning; · The cream is quite expensive. Costs about 1000 rubles. for 30 years; · does not protect against UV rays, but on the contrary, enhances the effects of the sun on the skin |
| Melan | The drug blocks the active synthesis of melanin by inhibiting tyrazinase and, thereby, helps get rid of pigmentation. Melan stimulates cell renewal and has a moisturizing effect. The composition is completely natural |
Creams, ointments and other products from Asia
Hyperpigmentation on the skin can also be treated using Asian remedies, which have proven their effectiveness in practice. Reviews testify to this.
Table 2. Drugs for hyperpigmentation from Asia.
| Name (brand) | Description |
| Yoko Acne-Melasma Cream | The cream can slow down the production of melanin, has a whitening effect, and eliminates acne. Suitable for all skin types. The product protects against solar radiation. After constant use, a whitening but also a rejuvenating effect is noticeable. |
| Clear Spots Sol | Eliminates any pigmentation and post-acne. The serum is made from plant materials and is safe to use. The product blocks the production of melanin and prevents the formation of new age spots. Additional effect: the serum has a rejuvenating effect, stimulates skin regeneration, protects against UV rays |
| YOKO Under-Arm Whitening Cream and Deodorant | Designed for skin whitening in the intimate area and armpit area. The cream stimulates the normalization of melanin production and prevents increased pigmentation. Additionally moisturizes, rejuvenates the skin, promotes cell renewal |
| Kedermfa | This ointment is antifungal, its main action is aimed at treating skin diseases such as dermatitis, acne, furunculosis. However, in the fight against pigmentation, as well as prevention, the product can also be useful. Especially if hyperpigmentation is caused by trauma to the epidermis |
| Shanghai Yaozao | Soap promotes regeneration, which is necessary in the treatment of pigmentation. It has an anti-inflammatory, antiseptic effect and perfectly cleanses the skin. |
At home
Hyperpigmentation of the skin, if its manifestation is not too active, can be treated independently by using home remedies.
Plants, fruits and herbs can help with this:
- cucumber juice;
- celandine.
- parsley juice;
- lemon juice;
- fermented milk products;
They can be applied to areas affected by pigmentation several times a day. Parsley juice, for example, is especially effective. It has long been applied to the face to remove freckles. The same goes for lemon juice. But be careful with it, don't overdo it. Still, it is an acid that can cause harm by causing irritation.
Remember that folk remedies cannot completely get rid of intense pigmentation. Treatment for pigmentation can be supplemented with pharmaceutical creams and ointments, as well as products from Asian manufacturers. It is better to contact a dermatologist or cosmetologist who can prescribe the correct drug treatment.
Treatment of skin hyperpigmentation
Therapy depends on the diagnosis. In many cases, treatment can be carried out independently, at home, in accordance with the doctor’s recommendations. But more effective methods are used by aesthetic medicine centers:
- Chemical exfoliation. Application of products based on acids: lactic, fruit, glycolic, tartaric, retinoic and so on. The concentration of substances varies depending on the location and degree of color of the pigment spot. Peeling helps to lighten formations, improve skin structure, smooth out fine wrinkles, and tighten contours.
- Laser removal of hyperpigmentation. An innovative method that is used using special equipment equipped with cooling devices. The procedure is highly effective and does not cause severe pain. It also has a good effect on the skin in terms of healing and rejuvenation.
- Mesotherapy is a technique aimed at photorejuvenation of the skin. It is an injection based primarily on hyaluronic acid. It has the effect of restoring the water balance in cells and protecting them from UV exposure. Cocktails for mesotherapy also include a complex of minerals and vitamins to nourish the skin. Variety – biorevitalization. Mesotherapy is carried out after chemical exfoliation, after 10 – 15 days.
- Ozone therapy allows you to get rid of hyperpigmentation of post-traumatic and inflammatory origin.
Complex therapy and timely consultation with a doctor can improve the condition of the skin, get rid of age spots and achieve a rejuvenating effect.
Complications
Hyperpigmentation of the skin causes discomfort more because it noticeably spoils the appearance. Typically, the appearance of spots does not indicate any serious health problems that are life-threatening. But this does not mean that hyperpigmentation can be completely ignored.
Age-related rashes, progressing, can eventually turn into malignant formations. Therefore, it is better to play it safe and consult a doctor for advice.
Among the complications, it is worth highlighting the following:
- spots may begin to peel off;
- sometimes itching and intense keratinization of the epidermis appear;
- Some patients experience decreased immunity;
- the latter often leads to the development of dermatitis, infections, and inflammations.
How do I know if I have darkening of the skin associated with varicose veins?
A pathological increase in venous pressure in the legs due to varicose veins leads to the destruction of some blood cells and the accumulation of pigment in the skin. Discoloration of the skin is first noticeable in the area of the ankles or lower third of the leg.
Skin pigmentation (darkening of the skin)
Skin pigmentation (darkening of the skin), without proper treatment, progresses, the color changes from reddish to yellow-brown or reddish-brown. The skin may then become painful, hard, and scar-like in consistency and texture. These changes indicate the transition of trophic changes to the next stage, lipodermatosclerosis. And the next stage of trophic disorders will be a venous trophic ulcer. These metamorphoses can take years or several months. Finding out what processes are associated with hyperpigmentation (darkening) of the skin is quite simple. It is enough to visit a phlebologist and perform a duplex ultrasound examination of the venous vessels of the lower extremities.
Prevention or how to prevent the appearance of new spots
After getting rid of the disease, it is important to avoid direct contact with UV rays on the skin or to reduce the time spent in the sun to a minimum. You should not sunbathe or visit solariums. Wear hats and clothing that covers your arms and legs.
It is worth using protective products with SPF and creams to prevent the appearance of tumors. Maintaining the result involves the use of whitening agents such as salicylic acid, hydrogen peroxide, hydroquinone, arbutin, kojic acid, as well as folk remedies.
How to deal with hyperpigmentation
Today there are many methods that will help even out skin color, but the purpose of one or another method depends on the severity of the problem and goals.
Unfortunately, if a person is predisposed to hyperpigmentation, then making the skin look young and even in color is quite difficult.
In cosmetology they use:
- special masks and creams with whitening effect;
- in some cases, peeling or grinding (acid or laser) is indicated;
- hardware IPL procedures.
Hardware methods are the most effective way to remove the appearance of pigment on the skin.
Clinical manifestations of hyperpigmentation
The main types of skin hyperpigmentation according to clinical manifestations:
- Ephelides (freckles) are small spots of light or dark yellow color, usually localized on the face ( Fig. 1 ).
- Melasma (chloasma) is blurry spots on the face, usually arising against the background of hormonal changes ( Fig. 2 ).
- Solar elastosis is an uneven icteric hyperpigmentation with thickening of the skin, the presence of dynamic or static wrinkles.
- Solar purpura is uneven, intense hyperpigmentation with telangiectasia and wrinkles.
- Post-traumatic (secondary) hyperpigmentation - dark spots that have a slight bluish tint in the first weeks after appearance, which form at the site of skin trauma.
- Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation of the skin of the face and body is local darkening that occurs at the site of inflammation.
- Systemic hyperpigmentation is skin coloring as a result of a disease (for example, adrenal disease).
It should also be mentioned that, based on the depth of the pigment, there are 3 types of hyperpigmentation: epidermal, dermal and mixed. This is important from the point of view of further choice of treatment tactics.
Rice. 1. Freckles (Danish national service on dermato-venereology)
https://www.danderm-pdv.is.kkh.dk/atlas/7-128.html
Rice . 2. Melasma (Danish national service on dermato-venereology)
https://www.danderm-pdv.is.kkh.dk/atlas/4-161-1.html
Table of contents
- Etiology and pathogenesis
- Clinical manifestations
- Principles of treatment and hardware correction
Hyperpigmentation (dyschromia, darkening of the skin) is a condition in which certain areas of the face and/or body become darker than the surrounding skin under the influence of various factors.
In our company you can purchase the following equipment for removing hyperpigmentation:
- M22 (Lumenis)
- AcuPulse (Lumenis)
- Fraxel (Solta Medical)
- UltraPulse (Lumenis)
Causes of changes in skin pigmentation and symptoms
Changes in skin color in certain areas - in the décolleté, arms, legs or face - are associated with disorders in the reproduction of melanocytes. This mechanism has not yet been fully studied. However, it is known that there are factors that contribute to the appearance of age spots. These include:
- Hormonal imbalances associated with puberty, pregnancy, menopause.
- Exposure to sunlight, which includes photoaging.
- Lack of vitamins in the body or, on the contrary, their excess.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Improper lifestyle, alcohol abuse and smoking.
- An age factor that is associated with a natural decrease in melanin production.
- Diseases of internal organs, for example, the gallbladder and liver, in which yellowing of the skin and sclera of the eyeballs is observed.
In addition, changes in skin color can be caused by the use of certain types of medications, in particular tetracycline, antihistamines and sulfonamides.
Etiology and pathogenesis
Congenital dermal melanocytosis (Mongolian spot)
Hereditary hyperpigmentation caused by the active recruitment of melanocytes into the dermis as they migrate from the neural crest to the epidermis. The etiology of this disease is associated with a violation of the structure of G-proteins - these are GTPase proteins that act as second messengers in intracellular signaling cascades.
The prevalence of Mongolian spots varies among different ethnic groups. They occur most often in East African children with dark skin (up to 80%), somewhat less frequently in Latin American children (up to 46%), and extremely rarely in light-skinned Europeans (1–9%).
Histological examination of Mongolian spots reveals highly branched melanocytes, which are located in the deep reticular dermis and contain many pigmented melanosomes ( Fig. 1 ). Typically, melanocytes are oriented parallel to the epidermis.
Rice. 1. Histological changes in the Mongolian spot (Dermpedia)
https://www.dermpedia.org/dermpedia-textbook/mongolian-spot
Melanosis (nevus) of Becker
Its etiology and pathogenesis remain unknown to date. Androgens play a certain role, as evidenced by the presence of concomitant hypertrichosis and the predominance of this hypermelanosis in men. Thus, a study of 19,302 men aged 17–26 years found that the prevalence of Becker melanosis was 0.52%.
Microscopy reveals an increase in the amount of melanin in the basal layer of the epidermis. Melanosomes increase in keratinocytes, and giant melanosomes can be detected in both keratinocytes and melanocytes. The dermis contains melanophages—macrophages that have phagocytosed excess pigment ( Fig. 2 ).
Rice. 2. Histological changes in Becker's nevus (Parth P., et al. Sebaceus and Becker's nevus: Overview of their presentation, pathogenesis, associations, and treatment. Am J Clinic Dermatol 2015)
Lentigo
A widespread pigmentary disorder usually associated with chronic sun exposure of the skin. In the United States, lentigenic changes are observed in 90% of people with fair skin over the age of 60 years and in 20% of people under 35 years of age. The main cause of solar and senile lentigo is prolonged insolation; PUVA lentigo occurs after PUVA therapy (therapeutic effects on the skin of ultraviolet A radiation with preliminary intake of the photosensitizer psoralen); radiation lentigo - after large doses of ionizing radiation.
Solar lentigo is histologically characterized by elongation of the epidermal ridges, an increase in the number of melanocytes, which produce excess pigment, and the number of melanophages - macrophages that have absorbed the pigment and become dark in color. Atypical melanocytes are usually not detected in solar lentigo ( Fig. 3 ).
With PUVA lentigo, there is an increase in the number of hypertrophied melanocytes, often with signs of cellular atypia. Additionally, elongated epidermal ridges and increased pigmentation of cells in the basal layer of the epidermis can be seen. The same changes can be seen in lentigines after multiple visits to the solarium (tanning-bed lentigines).
Radiation lentigo is manifested by excessive deposition of melanin granules in basal keratinocytes, cellular or nuclear atypia, an increase in the number of melanocytes, and a decrease in the number of epidermal ridges.
Senile lentigo is characterized by proliferation of basal cells with the formation of cords containing excess melanin. An increase in the number of melanocytes in the area of the dermal-epidermal junction may also be detected. In general, melanocytes in senile lentigo have higher activity and longer processes than normal. By electron microscopy, large complexes of melanosomes are visible in keratinocytes.
Rice. 3. Histological changes in lentigo (Dermpedia)
https://www.dermpedia.org/dermpedia-textbook/lentigo-simplex
Melasma
Recurrent acquired dyschromia, caused by increased activity of epidermal-melanin units. Occurs in areas of the skin exposed to severe and/or regular sun exposure, more often in women of reproductive age.
Patients with melasma have an increase in the amount of melanin in the epidermis, dermis, or (most often) both of these layers of skin. Epidermal melanin is detected in keratinocytes of the basal and suprabasal region. The number of melanocytes in most cases does not increase, but the existing pigment cells are larger - they have pronounced processes and much higher activity than normal. Melanin is also detected in mecrophages of the superficial and middle dermis, which often collect around small dilated vessels ( Fig. 4 ).
Rice. 4. Histological changes in melasma (Nooshin B., et al. An overview on melasma. Pigmentary Disorders 2015; 2: 216)
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation
One of the common dermatological conditions that most often develops in people with dark phototypes (V-VI). Pathogenesis is associated with hyperproduction of sebum by the sebaceous glands and the presence of excess squalene on the skin (for example, with acne). Solar ultraviolet radiation generates singlet oxygen, which oxidizes squalene. The latter stimulates the production of prostaglandin E2, which triggers active melanogenesis.
On microscopy, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation can manifest as both epidermal and dermal increases in pigment ( Fig. 5 ). In the latter case, there is an increase in the number of melanophages in the papillary dermis. Dermal hyperpigmentation can last for many years or even last a lifetime.
Rice. 5. Histological changes in post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation secondary to systemic lupus erythematosus (Dr. Andrew Ryan, pathologist)
Histological changes in post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation