White ulcer on the oral mucosa: how to deal with the problem
White sores in the mouth appear quite often. Although the problem cannot be called critical, it causes significant discomfort. Difficulty talking, chewing, swallowing and smiling. In some cases there is pain. Therefore, everyone who has ulcerative formations wants to get rid of them as quickly as possible. In this case, you cannot self-medicate. To determine the cause of the ulcers and prescribe effective therapy, it is necessary to undergo examination by a specialist.
Causes of sores in the mouth
Purulent ulcers in the mouth can appear for various reasons. They are often the result of dental diseases.
The list of reasons may include the following:
- viral infections (herpes simplex or herpes zoster);
- fungal and bacterial infections;
- irritation of the mucous membranes from smoking and certain foods (nuts, cheese, citrus fruits);
- ulcerative stomatitis;
- chemotherapy drugs;
- frequent stress and nervous tension;
- oral injuries;
- hormonal changes.
Symptoms of ulcerative lesions of the oral mucosa
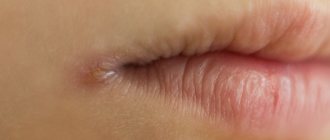
An oral ulcer is a sign of pathological processes occurring in the body. It looks like a round or oval wound with uneven, soft edges and a loose bottom. The tissues swell. Such lesions can be single or multiple. The localization locations are different: under the tongue or on it (especially at the edges), on the cheek, palate, in the throat, on the inside of the lower or upper lip, on the mucous gingival tissues. Symptoms that may accompany the formation of ulcers:
- itching felt in the affected area;
- bad breath;
- pain when eating;
- increased body temperature;
- increased salivation.
Mouth ulcers can occur in adults and children. When they form, the layer that is responsible for restoring the integrity of the gums is affected. In most cases, the ulcers do not reach large sizes and disappear after 2 weeks. Improvement should be observed within 7 days. If unpleasant symptoms do not go away, or their severity increases, you should consult a doctor.
The occurrence of ulcers due to diseases/damage to the soft tissues of the mouth and tongue
1. Recurrent
aphthous stomatitis is a chronic inflammatory disease that is characterized by periodic eruptions of aphthae (small ulcerations) on the oral mucosa. Aphthae can be localized on the tongue, buccal mucosa, hard and soft palate, and also on the mucous membrane of the lips. They are painful. In some cases, with constant injury, aphtha can turn into a long-term non-healing ulcer, after epithelization of which a scar is formed.
Patients with recurrent aphthous stomatitis usually suffer from colitis. Nervous strain, minor injuries to the mucous membrane, for example, when brushing teeth, as well as menstruation, can also predispose to the onset of the disease. The aphtha heals within 7 - 10 days. In case of complications of the disease, the number of ulcerations may increase, then the healing period is extended by 2 - 4 weeks.
2. Herpetiform stomatitis
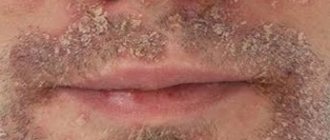
characterized by the appearance of numerous small ulcers. In appearance they resemble the sores of herpes simplex. As a rule, they occur in women under 30 years of age. They are localized mainly on the lower surface of the tongue and in the area of the floor of the mouth. They do not have clear boundaries, the base is gray. The healing process is completed largely without scarring within 7 to 10 days. In simple forms of stomatitis, white ulcers in the mouth are observed (or rather, the center of the ulcer is covered with a thin, loosely fitting white or grayish film). Also, a white ulcer in the mouth can form in children in cases where there is candidal, or fungal, stomatitis.
As for the treatment of stomatitis, in this case the form of the disease and the severity of the lesion are taken into account. General and local treatment depends on this. But for almost all forms of stomatitis, vitamin C is prescribed to improve immunity.
3. Recurrent necrotizing peryadenitis
(Setton's aphthae) is characterized by the formation of a compaction in the submucosa, then painful ulcers with raised and compacted edges form in this place, as well as the presence of an inflammatory infiltrate (accumulation of cellular elements mixed with blood and lymph). Ulcers are localized on the upper and lower lips, cheeks, and lateral surfaces of the tongue. Eating food becomes extremely difficult for many patients, even to the point of giving it up. The same severe pain can be observed when talking. The ulcers do not heal until several months, and the disease lasts for years.
4. Afty Bednar
occur exclusively in children and are defined as traumatic erosions (ulcerations). The cause is poor oral hygiene or rough mechanical rubbing of the mucous membrane of the palate (this is where they are located). Covered with a whitish-yellow coating.
5. Traumatic ulcer
in the mouth is most often the result of physical impact, hence its name. As a rule, such an ulcer occurs as a result of an accidental or intentional bite of the mucous membrane, damage by a toothbrush. The presence of a traumatic ulcer in the oral cavity can provoke dental treatment (with careless use of dental instruments or, for example, with pointed temporary crowns).
Also among traumatic ulcers are the so-called prosthetic ulcers, which arise from exposure to complete or partial removable dentures, the dimensions of which are larger than necessary, or their surface is poorly processed and has sharp edges. Such ulcers can be located directly under the prosthetic structure. As a rule, healing takes place within 10 - 14 days, provided that the traumatic factor is eliminated. Treatment may not be necessary, since traumatic ulcers are often painless and small in size. In the case of the opposite, antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed, and the use of an ultrasonic brush is recommended, which not only cleans, but also has an antibacterial effect.
Also, the presence of ulcers can be caused by the effects of alkalis, acids, and certain medications on the oral mucosa.
Causes of lesions in the mouth
To determine how to treat a pathology, you must first find out why it appeared. In most cases, ulcerative lesions occur against the background of reduced immunity, lack of vitamins and microelements, in particular iron and folic acid. The most common causes of ulcers:
- Different types of stomatitis. The aphthous form of the disease is accompanied by the appearance of white or yellow lesions in the center with a red border. Such wounds are 0.3–1 cm in diameter. Pain during the disease is often moderate, in some cases it is severe. If large wounds form, a careful approach to treatment is needed. With candidal stomatitis, caused by fungi of the genus Candida, the ulcers are covered with a characteristic cheesy coating.
- Injury to the mucous membrane. Various factors can provoke a pathogenic process: mechanical influence (with an incorrectly installed filling, caries, improper fitting of dentures, etc.) or thermal (eating hot food), chemical (smoking, exposure to caustic drugs). Even a simple bite of the cheek or tongue injures the tissue. In a child who frequently sucks his thumb, ulceration may occur on the soft palate. The habit of biting nails and pencils also provokes the formation of microtraumas. When they get infected, inflammation develops.
- General diseases of a systemic or chronic nature (disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, tuberculosis, syphilis and HIV, blood diseases). In rare cases, the cause of their formation is oral cancer. Viral diseases also provoke ulcers. Sore throat and tonsillitis can cause lesions on the tonsils.
White sores on the oral mucosa are sometimes a consequence of taking certain medications. They are also formed when there is insufficient saliva production. The problem can be provoked by the use of toothpastes containing sodium lauryl sulfate and triclosan.
Ulcers caused by trauma
The main reason for the appearance of ulcers when the mucous membrane is injured is infection in the wound. Most often, white rashes occur due to the habit of biting nails or the tip of a pencil or pen.
Fans of seeds and hard toothbrushes may also be at risk. Many people believe that hard bristles remove plaque better. Actually this is not true. If you carefully brush your teeth with such a brush, you can damage the enamel, gums and cause inflammation.
Other causes of mucosal injury:
- uncomfortable dentures;
- braces or other orthodontic structures;
- habit of unconsciously biting your cheek or tongue;
- exposure to mucous membranes with drugs or acids.
How to treat?
It is enough to remove the irritating factor and wait 1 - 2 weeks. Usually the ulcers go away on their own. If this does not happen, it is recommended to consult a doctor.
What to do if a white sore appears in your mouth
If ulcerations are detected, you should contact your dentist, especially if they do not heal on their own. The doctor will tell you how to treat the wounds, comparing the problem with the causative factor. The following drugs are most often prescribed:
- Antiseptic solutions for rinsing: “Chlorhexidine” 0.05%, “Miramistin” 0.01%, “Furacilin” (a prepared preparation that does not require dilution). It is important to take into account the concentration of the active substance so as not to get a burn to the oral cavity.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs. To eliminate white ulcers in the mouth, alcohol tinctures from medicinal plants are used. For example, “Chlorophyllipt”, “Stomatophyte”. If a white sore appears in a child, gels (Metrogil Denta, Cholisal) are prescribed, which also have an analgesic effect.
- Antibacterial agents. Prescribed if ulcers are caused by bacteria (tuberculosis bacillus, streptococci, etc.).
- Antifungal agents. Fluconazole and Ketoconazole effectively combat fungi.
Any medications can be taken only as prescribed by a doctor. Self-medication can cause complications! To speed up the action of drugs, electrophoresis, phonophoresis or laser treatment methods are prescribed.
In addition to the complex of drug therapy, you can rinse using decoctions based on medicinal herbs (chamomile, oak bark, sage, calendula). Sometimes a course of vitamins and immunostimulating drugs is also prescribed, especially if the ulcers are chronic.
Special recommendations for the treatment of white ulcers on the oral mucosa
To quickly get rid of unpleasant ulcerations in the mouth, you need to follow a diet. Your diet should include vegetables, fruits, red meat, and fish. It is important to avoid spicy and sour foods, such as citrus fruits, until complete recovery. Any rough food (nuts, etc.) that can injure the mucous membrane is also excluded. Sweets (cakes, jam, chocolate), crackers, chips, coffee are also prohibited.
It is important to pay attention to the quality of the water consumed. The heavy metal salts and other impurities it contains can cause constant bleeding from the gums and contribute to infection. If the pathology is provoked by some disease, it is necessary to eliminate it.