- Rehabilitation after edema
- Guasha massage on the face
- Microcurrent therapy
Morning swelling sometimes changes the face beyond recognition. Almost everyone is familiar with the problem of edema, but few know why it appears, how swelling on the face can be prevented and what methods of eliminating edema are offered by cosmetology.
Why does the face swell?
Physiological reasons
In the absence of allergies, intoxication and chronic diseases of internal organs, the symptom may be associated with constant lack of sleep, adherence to strict diets, and fasting.
In some cases, swelling of soft tissues is caused by improper selection of decorative cosmetics and skin care products. Puffiness can occur after crying, or be observed against the background of chronic stressful situations. Sometimes morning swelling of the face is explained by sleeping on a pillow that is too high, since the non-physiological position of the head provokes a narrowing of the cervical vessels. Other possible causes of puffiness in the morning include eating salty, fried foods, or drinking large amounts of liquid in the evening.
Hormonal changes in women
Cyclical fluctuations in hormone levels in women are not a disease, but a normal condition. However, such fluctuations sometimes cause facial swelling. In some women, this symptom is part of premenstrual syndrome. The symptom often appears during pregnancy and is caused by impaired renal function or physiological changes in the body. Many patients complain of facial pastiness during menopause.
Endocrine diseases
Swelling of the face is observed with persistent deficiency of thyroid hormones. The following forms of hypothyroidism cause the development of symptoms:
- congenital hypothyroidism;
- hypothyroidism during pregnancy;
- peripheral hypothyroidism;
- hypothyroid phase of autoimmune thyroiditis;
- the final stage of cytokine-induced thyropathy.
The symptom is observed constantly, combined with a yellowish or peachy skin tone, dry and brittle hair, and slowed mental processes. It is most severely manifested in myxedema - due to pronounced mucous edema of the skin and subcutaneous tissue, facial features become coarser, the chin enlarges, the palpebral fissures narrow, facial expressions become poor, and the face takes on a mask-like appearance.
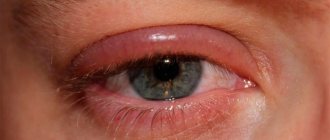
Facial swelling
Allergic reactions
Allergic swelling of the face develops acutely due to contact with certain substances: medications, food products, pollen, animal hair. It is observed with insect bites and cold allergies. There are several allergic reactions accompanied by the appearance of this symptom:
- Hives.
Swelling is combined with rashes, hyperemia, and skin itching. - Contact dermatitis.
Swelling and hyperemia appear in the area of contact with the allergen, giving way to the formation of papules, which open, forming erosions. - Atopic dermatitis.
Develops in early childhood and is manifested by edema and erythema, against which blisters appear. - Bronchial asthma.
Puffiness of the face is detected during an attack, combined with breathing problems and forced body position.
The most severe forms of allergies, accompanied by swelling of the face, are acute allergic reactions - Quincke's edema and anaphylactic shock. With Quincke's edema, the contours of the face change over the course of several minutes, less often - several hours. The symptom is pronounced, especially in the middle and lower parts of the face, and persists for 2-3 days. Quincke's edema can develop independently or occur at stage 2 of anaphylactic shock, accompanied by swelling of the respiratory tract.
Kidney diseases
Watery, soft, mobile swelling of the face after a night's sleep, combined with a yellowish tint to the skin, is characteristic of kidney disease. The following pathologies are the cause:
- Glomerulonephritis.
In the acute form of the disease, edema persists for 2-3 weeks; when the process becomes chronic, it appears during periods of exacerbation. - Amyloidosis of the kidneys.
The symptom occurs in stage 2 (proteinuric) and progresses as renal function deteriorates. - Membranous nephropathy.
Develops after drug therapy, treatment of oncological pathologies, acute infections. It occurs in waves with episodes of complete or almost complete disappearance of edema. - Lesions in systemic pathologies
. Facial edema is detected in diabetic nephropathy and SLE. Appear against the background of symptoms of the underlying disease. - Chronic renal failure.
Swelling increases gradually over several years.
Diseases of the cardiovascular system
In diseases of the blood vessels and heart, edema is more pronounced in the area of the lower extremities, but can also be detected on the face, especially in the evening. They differ from renal edema in their higher density, decreased local temperature and bluish tint of the skin, slower formation and resorption. Caused by the development of chronic heart failure, detected in the following diseases:
- cardiomyopathy;
- cardiosclerosis;
- amyloidosis;
- constrictive pericarditis;
- some arrhythmias;
- heart defects;
- heart damage due to rheumatism;
- arterial hypertension.
Poisoning and intoxication
In people who smoke, morning puffiness of the face is more pronounced than in non-smokers due to the negative impact of toxins on the condition of the lymphatic system. Episodic swelling of the face can occur the morning after consuming large amounts of alcohol, especially noticeable when drinking beer or impaired renal function.
In patients with alcoholism, swelling becomes constant, the face takes on a characteristic appearance, and the skin is often yellowish or with a purplish tint. Edema is aggravated with the development of alcoholic nephropathy. In addition, swelling of the face and body can be observed when substances that have a nephrotoxic effect are absorbed, for example, in case of vinegar poisoning.
Other reasons
Minor swelling is quite typical for the manifestation of acute respiratory diseases; it is more pronounced in children, but can be detected in people of any age. The appearance of soft tissue swelling is possible with ENT pathologies: sinusitis, frontal sinusitis, tonsillitis. Facial swelling is accompanied by some hypo- and hypervitaminosis.
Stress
When a person encounters stress, a number of processes controlled by the endocrine system are activated in the body.
At the first stage, appetite decreases, and energy levels increase due to the rapid breakdown of fats. When the reaction subsides, the hormone cortisol is released, which increases appetite - the body needs to restore blood glucose levels and replenish fat reserves.
| If a person is in a state of chronic stress, cortisol levels are always slightly elevated. This also leads to swelling. |
Diagnostics
At the initial stage, patients with swelling on the face often go to therapists, who, depending on the clinical picture, diagnose themselves or refer patients to other specialists: allergists, endocrinologists, nephrologists, etc. To establish a diagnosis, the following methods are used:
- Questioning, external examination
. The doctor finds out the circumstances, frequency and time of swelling, the dynamics of changes during the day, throughout the menstrual cycle. Evaluates the severity and extent of edema, skin temperature, and tissue density. - Lab tests
. During laboratory tests, signs of inflammation are identified, kidney function is studied, and hormone levels are determined. According to indications, tests are done to identify allergies. - Ultrasound methods
. Taking into account the characteristics of clinical symptoms, ultrasound of the kidneys, thyroid gland, echocardiography, and other types of sonography are prescribed. - Other visualization techniques
. To clarify the diagnosis and detail pathological changes, CT and MRI, including those with contrast, can be used.
Skincare treatments help get rid of morning puffiness of the face
Passive lifestyle
A sedentary lifestyle leads to stagnation of lymph and water retention in tissues; physical activity helps improve this situation.
The lymphatic system does not have its own pump, like the circulatory system. Therefore, the movement of lymph and the return of fluid to the blood depends on the functioning of skeletal muscles.
When you sit for a long time, the pressure in the capillaries increases and fluid begins to accumulate. Get up at least once an hour and stretch your legs , ankles, rise on your toes and wiggle your toes.
Treatment
Pre-hospital assistance
To eliminate the physiological causes of facial swelling, it is necessary to adjust the diet, normalize the daily routine, avoid stress, and select suitable cosmetic preparations. Mild allergic edema in the absence of signs of breathing difficulties and the presence of a previously established diagnosis can be eliminated with the help of antiallergic drugs.
In other cases, self-medication is not recommended. It should be borne in mind that self-administration of diuretics can lead to the development of serious side effects and disorders of the body.
Specialized treatment
Many patients require adjustments to their diet and eating regimen. The tactics of conservative treatment are determined by the etiology of the disease or condition that provoked facial swelling:
- Hormonal fluctuations in women
. Hormonal medications and sedatives are used. - Hypothyroidism
. Replacement therapy with levothyroxine is carried out. If there is a lack of iodine, iodine-containing medications are prescribed. - Allergic reactions
. Antihistamines and glucocorticosteroids are effective. In severe cases, resuscitation measures are necessary. - Kidney diseases
. For glomerulonephritis, antibacterial agents and drugs to correct immunity are indicated. For systemic diseases, treatment of the underlying pathology is required. In all cases, medications with symptomatic effects are used. - Diseases of the heart and blood vessels
. Cardiac glycosides, nitrates, vasodilators, B-blockers, anticoagulants, and drugs to improve cardiac muscle metabolism may be recommended. - Intoxication
. If edema is associated with smoking and drinking alcohol, the patient is advised to give up the bad habit and is given medicinal and non-medicinal treatment to eliminate the addiction. - Poisoning
. In some cases, gastric lavage is possible. Carry out detoxification measures.
For hypovitaminosis, vitamin preparations are prescribed, for acute infections, symptomatic therapy is carried out, for ENT diseases, antibiotics and symptomatic drugs are used, and sinus punctures are performed. Surgical treatment is rarely required. In case of heart defects, surgical correction is performed. Tonsillitis and sinusitis can be considered as indications for tonsillectomy, maxillary sinusotomy, and frontotomy.
Causes of edema: not enough water
If a person drinks too much fluid in one day, this will not affect the long-term balance of water in the body - the kidneys will remove the excess through urine.
If there is too little water, the kidneys will excrete less fluid. Chronic lack of water can lead to the launch of adaptation mechanisms in the body: swelling, increased thirst, and rare urination. This is how the body will try to prevent dehydration.
| To reduce or relieve swelling, drink more water. |
How to quickly relieve facial swelling at home
Swelling can be removed using very simple methods at home.
Contrast wash
- alternately wash your face with cold and warm water. This procedure refreshes, tones and improves skin color. Be sure to try it! There's no need for any preparation or extra expenses - just open the tap and adjust the temperature.
Massage
- improves blood flow and lymph movement. You can even do a massage using your hands (hands are the best tool to always have with you). Watch the video and repeat simple exercises to get rid of swelling.
- Use your fists to walk along the side and back surfaces of the neck (do not touch the front surface of the neck), moving from top to bottom from the jaw to the collarbones.
- Press your chin from below with your fist, and lower your head to meet the fist.
- Use the back of your hand to rub your chin with pressure.
- Between two fingers folded into the Victoria sign, three ears up and down.
- Place your palms tightly with the edges towards your nose and press your thumbs to your chin. Slowly, without lifting the ribs from the skin, open your palms and, as it were, squeeze everything out of your face towards your ears.
- Using your fingertips, run over the area under your eyes. This will not only remove swelling, but also save you from unsightly bags.
As a result, the skin should turn red and burn a little.
Allergies and sensitivity to products
Sensitivity, or food intolerance, is a symptomatic reaction without the participation of the immune system. This is how it differs from allergic. Sensitivity is more common than allergies.
The effect of individual reactions to foods has been noted in a number of diseases and symptoms, including irritable bowel syndrome, weight gain, chronic headaches, skin conditions, autoimmune diseases and even depression. Swelling can also be a symptom of food sensitivity.
While the most common allergens are eggs, milk, nuts, wheat, soy, fish and shellfish, sensitivity can occur to unexpected foods.
For example, among arthritis sufferers, sensitivity to citrus fruits, pork, corn, oatmeal, coffee, cheeses, tomatoes, sugar, chocolate, wheat was found, and among migraine sufferers, food additives, preservatives, tea, potatoes and salt were added to the list.
| To find out what food causes swelling, you need to give up potentially problematic foods for several weeks one at a time. If the symptoms weaken or disappear, you have found a product that should be excluded from the diet. |
Another approach is to switch to a diet consisting of a minimum amount of foods for the same period of time, then gradually return them, observing the changes.
Potentially problematic foods: allergenic foods, fruits, alcohol, gluten-containing foods, milk and dairy products, food chemicals, spices and sugar.
Can dairy products, fruit, stress or too intense exercise cause swelling? Yes they can. But you shouldn’t limit yourself in food or physical activity - first, find out what exactly your reason is.
Author: Elena Degtyar, PhD, nutrition psychology coach and nutritionist
LITERATURE:
1. Maughan, R. J. “Impact of mild dehydration on wellness and on exercise performance.” European journal of clinical nutrition 57.S2 (2003): S19. 2. Xie, Lulu, et al. “Sleep drives metabolite clearance from the adult brain.” science 342.6156 (2013): 373-377. 3. Kannan, Arun, et al. "Renal sympathetic nervous system and the effects of denervation on renal arteries." World journal of cardiology 6.8 (2014): 814. 4. Gallen, Ian W., et al. "On the mechanism of the effects of potassium restriction on blood pressure and renal sodium retention". American journal of kidney diseases 31.1 (1998): 19-27. 5. Kreydiyyeh, Sawsan Ibrahim, and Julnar Usta. "Diuretic effect and mechanism of action of parsley". Journal of ethnopharmacology 79.3 (2002): 353-357. 6. Horita, Shoko, et al. "Insulin resistance, obesity, hypertension, and renal sodium transport." International journal of hypertension 2011 (2011). 7. Light, Kathleen C., et al. "Psychological stress induces sodium and fluid retention in men at high risk for hypertension." Science 220.4595 (1983): 429-431. 8. Espiner, Eric A. “The effects of stress on salt and water balance.” Best Practice & Research Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 1.2 (1987): 375-390. 9. Riebl, Shaun K., and Brenda M. Davy. “The hydration equation: Update on water balance and cognitive performance.” ACSM's health & fitness journal 17.6 (2013): 21. 10. Hong, Seung Min, et al. "Changes in Body Water Caused by Sleep Deprivation in Taeeum and Soyang Types in Sasang Medicine: Prospective Intervention Study." Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2022 (2017). 11. Gerth van Wijk R, van Cauwenberge PB, Johansson SG. Revised terminology for allergies and related conditions. Ned Tijdschr Tandheelkd. 2003, 110: 328-331. 12. Gaby AR. The Role of Hidden Food Allergy/Intolerance in Chronic Disease. Alternative Medicine Review. 1998, 3: 90-100. 13. Tarasova, I. V. “Food intolerance, true food allergy and food pseudo-allergic reactions: presentation and diagnostic methods.” Allergology and Immunology in Pediatrics 3 (2008): 24-28.