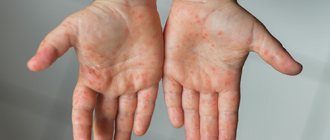
Causes and treatment
The appearance of rashes and itching is influenced by both external and internal factors.
The main causes of this problem are: A rash with itching on the palms and soles occurs in the form of pustular formations, peeling, and red spots. To find out the true cause of its occurrence, it is better to consult a doctor. After conducting a blood test and taking scrapings from the affected areas, the specialist will make a diagnosis.
Allergy
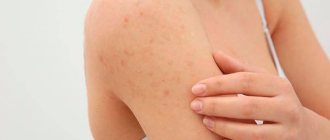
Manifestations in the form of rashes and itching usually occur on the inside of the palms, as well as on other places on the body. This happens due to the entry of substances foreign to the body into the blood. Poor quality food can also cause an allergic reaction. This is especially true for a child, with his immunity not yet fully formed. Outwardly it looks very much like urticaria.
The body's protective reaction manifests itself as dermatitis on the skin of the hands, which is accompanied by itching. Sensitization occurs, that is, the production of antibodies. Allergy manifestations have acute and chronic forms.
- The result of acute dermatitis is swelling and redness of the skin. In this case, rashes appear that resemble watery blisters, sometimes with bloody inclusions. With physical impact, the vesicles burst, leaving crusts.
- The chronic form is characterized by lichenification, which leads to cracking, keratinization and even atrophy of human skin.
Treatment begins with identifying the allergen and immediately eliminating its exposure. To do this, you must undergo a medical examination. Food allergies can be eliminated by eliminating the harmful product from the diet.
Other types of disease require the use of special ointments and antihistamines. Particularly complex cases require the use of hormonal therapy. This is why the help of a dermatologist is necessary.
Infections
A small rash with itching on the palms and soles of adults and children can be a consequence of an infectious infection, for example, rubella, meningococcus, scarlet fever, measles. All the signs of an infectious disease are also present. A rash with deadly meningococcus should be especially alarming. It bleeds and is accompanied by fever. Treatment is carried out only after consulting a doctor.
The mite that causes scabies is able to exist thanks to the microscopic passages it gnaws in thin layers of the skin. Its bites cause redness and a rash that itches a lot, especially at night. This type of problem requires immediate attention to a specialist, as the disease is contagious.
Vascular disease
Hemorrhagic rash occurs after inflammation of small capillaries and vessels. It looks like a subcutaneous hemorrhage in the form of points that can merge, occupying fairly large areas of the skin. Treatment is prescribed by a doctor.
Dyshidrosis
It manifests itself in all ages as swelling of the skin and rashes with itching in the form of serous small pustules. They occupy the sides of the fingers and toes. They are located quite deep in the thickness of the skin; you will see liquid-filled bubbles under a transparent film.
As they open, brown crusts take the place, which leads to the development of pigmentation, the appearance of itchy, flaky cracks and nodules, which provoke the penetration of infection into the wounds.
Scientists still do not understand the mechanism of occurrence of this type of rash, but there is evidence of conditions predisposing to this. It is most likely to appear during damp and cool weather. Dyshidrosis is provoked by factors such as stress, stages of exacerbation of chronic diseases, the presence of an allergen, and the influence of household chemicals.
Hormone-based ointments are used for treatment:
- elocom,
- fukartsin,
- triderm.
Traditional methods suggest applying a cabbage leaf or fresh grated potatoes to the wounds.
Stages of eczema
There are the following stages of eczema51:
- Spicy. It is characterized by the appearance of erythema, swelling, erosions with weeping, vesicles, and serous crusts. Pustules and papules rarely occur. Their contents are sterile. In addition to involution, the appearance of new elements of the rash is observed.
- Subacute. It is characterized by erythema, excoriation, formation of scales, and lichenification.
- Chronic. Infiltration occurs, the skin pattern of the affected area intensifies, and post-inflammatory hyper- and hypopigmentation is observed.
Constant signs of eczema include51:
- itching, which intensifies when the disease worsens;
- burning;
- soreness in the affected areas.
Symptoms of allergies on the palms
Since allergic reactions occur according to a single mechanism, all their signs are similar and include the following general symptoms.
Photo: An interesting case of allergy - a reaction to nickel contained in Apple computers
- Skin itching. Associated with the action of histamine and bradykinin, released from mast cells upon contact with allergens.
- Swelling and hyperemia (may lead to a local increase in temperature). Occurs under the influence of bradykinin and heparin produced by mast cells.
- Skin rashes. Also associated with the action of chemically active substances in mast cells.
This also characterizes the manifestations of allergies on the palms.
The palms itch quite severely, and bloody scratching may occur. Itching does not go away after applying moisturizer or washing hands.
Patients note that their palms are noticeably swollen, sometimes making it difficult to flex the fingers, and they become hot to the touch. Photo: Manifestations of a severe allergy to nettle on the palms of a man
The skin on the palms and back of the hand becomes red, and numerous rashes appear. Sometimes a small rash occurs in the form of blisters that tend to merge. In a chronic course, the allergic rash disappears almost completely, and the skin epidermis does not have time to peel off. This leads to the formation of so-called “crusts”, and a transverse crack occurs in the palm due to allergies.
There have been cases where blisters appear on the palms, similar to burns. Most often, this reaction develops to chemical irritants.
In contrast to systemic pathologies of the immune system, manifestations of allergies on the palms are almost always caused by contact of the skin of the hands with one or another irritant.
Situations in which allergies occur exclusively on the palms and nowhere else are not uncommon. If the allergy is caused by contact of the skin of the palms with the allergen, generalized reactions do not occur, which fully explains the strict localization of allergic manifestations.
Allergies in pregnant and lactating women
During pregnancy, a feature of allergies is their appearance in contact with those substances and objects that previously did not cause any reaction. This is due to a physiological decrease in immunity, which develops to protect the fetus from the mother’s immune aggression.
Otherwise, for the most part, pathological reactions are no different from other periods of life. Women often complain that their palms are peeling, itching and redness appear. This frightens pregnant women, because they instinctively become much more attentive to their health.
Features of allergies on the palms of children
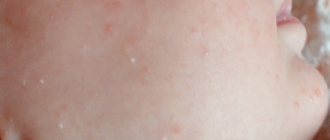
Photo: Allergic rash on a child's palm
Symptoms of allergic reactions on the palms of children are practically no different from those in other groups of the population. But the pathogenesis (the mechanism of the pathology) has a number of its own features.
The following features are characteristic of infants.
Lack of full locomotion
In other words, very young children cannot clearly explain what is bothering them. Therefore, if the allergy has no manifestations other than itching, it is difficult to give a clear answer to the question of what is wrong with the child. An allergy on the back of the hand in a child can be “calculated” in this case based on the following signs:
- restless behavior of the baby;
- the desire to constantly scratch your palms, rub your hands against each other and other objects;
- attempts to bite hands.
However, if, after contact with a certain object, food product or cosmetic substance, spots appear on the palms, peeling and cracking of the skin, redness, swelling and inflammation, an allergy should be suspected first.
Wide range of allergens
In children, the superficial epidermis is underdeveloped. Therefore, contact with almost any detergent and surfactant is dangerous for them.
It should be noted that allergies from sweat never occur in children and cannot occur.
For the development of an allergic reaction, a foreign component, an irritant, is required, in response to which the immune system “turns on” protective mechanisms.
Sweat can trigger prickly heat (learn about the differences between it and allergies) - a disease caused by the accumulation of moisture in hard-to-reach and poorly treated areas of the skin (most often, these are the buttock and groin folds, folds of the neck, abdomen and palms). This pathology is not immune in nature and is treated by careful hygiene of “dangerous” areas.
Diseases that occur with pustular rashes on the palms and soles include palmoplantar psoriasis, palmoplantar pustulosis, acrodermatitis persistent pustular Allopo, and Andrews pustular bacteridus. There are disagreements among researchers in the interpretation of the concepts palmoplantar psoriasis and pustulosis. In some sources, palmoplantar pustulosis is classified as a separate nosological form, or is considered a type of palmoplantar pustular psoriasis [1]. There are localized pustular psoriasis of the Barber type (syn.: pustulosis of the palms and soles; chronic palmoplantar pustular psoriasis; persistent palmoplantar pustulosis; pustular psoriasis of the extremities). Many domestic scientists are of the opinion that various forms of pustular psoriasis are nosologically independent [2, 3]. At the same time, the question of whether non-infectious pustular dermatoses belong to pustular psoriasis continues to be discussed. Some domestic scientists [4] believe that in terms of clinical and morphological manifestations, palmoplantar pustulosis is closer to Andrews bacterid, and not to psoriasis. Some foreign authors [5] also consider palmoplantar pustulosis as a separate nosological entity. Data from genetic, immunological, and histological studies allow dermatologists to prove these statements. Perhaps this is due to the different meanings attached to the concept of “palmoplantar pustulosis”. In the generally accepted ICD-10, the form palmoplantar pustulosis (L40.3) is distinguished, but it is considered under the heading of psoriasis (L40), as well as acrodermatitis persistent Allopeau (L 40.2). With acrodermatitis persistent Allopeau, pustular rashes of a different localization may appear, sometimes similar to generalized pustular psoriasis, which also indicates that this disease belongs to psoriasis [5]. This issue is also important in terms of differential diagnosis, since errors in diagnosis and patient management tactics often occur. Damage to the palms and soles causes a lot of physical and emotional suffering for patients, disrupting performance, interpersonal relationships, and affecting the quality of life.
Localized pustular psoriasis (Barber type), a type of pustular psoriasis characterized by erythematous-squamous and pustular elements in the palms and soles [1], is widespread throughout the world, more common than the generalized variety of pustular psoriasis [6, 7], but significantly less common than psoriasis vulgaris. The disease occurs in the period from 20 to 60 years, mainly at the age of 40-50 years, very rarely after 60 years and only in 19% of cases before the age of 20; in women 3 times more often than in men [1], while psoriasis vulgaris more often affects men [5]. A family history of this form of psoriasis is noted only in 7-24% of cases; the connection with antigens of the HLA system has not been established [1]. Analysis of some genetic studies [5] allows us to assert the nosological independence of palmoplantar pustulosis and psoriasis, but other studies [8] do not allow us to identify clear differences between these pathologies, which coincide in many aspects. According to the Tyumen Regional Dermatovenerologic Dispensary for the period 2008-2012, limited palmoplantar psoriasis accounts for only 1.4% of the total number of registered cases of vulgar psoriasis and 2% of newly diagnosed cases of psoriasis (Fig. 1, 2)
.
Figure 1. Patient V., 33 years old, with a smoking history of 20 years. Clinical manifestations of palmoplantar psoriasis. Symmetrical lesions of the skin of the hands (a, b) and feet (c) with a typical plaque located on the skin in the lower leg area (d).
Figure 2. Patient K., 51 years old, with a smoking history of 35 years.
Clinical manifestations of palmoplantar psoriasis. Symmetrical lesions of the skin of the hands (a) and feet (b). The exact cause of localized pustular psoriasis is unknown. Provoking factors are foci of focal infection, primarily odontogenic and tonsillogenic [1], Helicobacter pylori
, as well as stress, anxiety, the use of certain medications, and liver dysfunction [2]. Sometimes the disease first appeared after long-term treatment with lithium drugs. Smoking and unfavorable environmental factors (high humidity and temperature) aggravate its course, and a more pronounced association has been identified between palmoplantar pustular psoriasis and smoking, especially in women [1, 8]. Smoking cessation was an important treatment intervention given the observed abnormal response to nicotine [5].
Localized pustular psoriasis occurs with or without psoriasis vulgaris rashes, most often in patients with a personal or family history of psoriasis, although often independently [1].
A possible mechanism for the formation of pustules in pustular psoriasis is considered to be a decrease in the activity of antileukoprotease in the skin as a result of a protease/antiprotease imbalance [5]. To date, extensive material has been accumulated on the significant role of infectious agents in the occurrence, spread and activation of the psoriatic process [6]. The contents of the pustules are sterile, although some authors, in particular G.Ya. Sharapova et al. (1983) noted the presence of Staphylococcus aureus in some patients. According to numerous studies [7], microorganisms that sensitize the patient’s body against psoriasis are often streptococci and Staphylococcus aureus, as well as foci of chronic infection. Staphylococcus aureus and streptococci secrete exotoxins that play the role of superagents capable of binding to proteins of the major histocompatibility complex of tissues on antigen-presenting cells, keratinocytes, T-lymphocytes, monocytes, which leads to the formation of cytokines that enhance the proliferation of keratinocytes [5].
Subjective symptoms boil down to burning, itching and a feeling of discomfort in the palms and soles; often these sensations precede the appearance of fresh elements. Cases when in the early stages the disease is represented by single plaques or is asymmetrical in nature are rare [1]. With severe severity of rashes, the quality of life of patients is significantly reduced due to pain, inability to stand, walk, or work with their hands [5].
Clinically, on a scaly erythematous background with sharp boundaries, there are pustules, which, unlike generalized pustular psoriasis, are located deep in the epidermis, which is due to the morphological structure of the skin of the palms and soles. Localized pustular psoriasis is manifested by sterile yellow pustules with a diameter of 2-5 mm, approximately the same size, clusters of which within a few hours appear symmetrically on the apparently healthy skin of the palms, mainly in the thenar area, less often - the hypothenar, even less often - the middle and distal part of the palm and soles, mainly in the area of the arch of the foot [1]. Subsequently, a halo of hyperemia appears around individual elements. New rashes are associated with places of favorite localization and rarely spread to the back of the hand and foot, wrists, and fingers. The lesion is usually symmetrical, but a unilateral arrangement of elements may be observed. Sometimes the pustules spread to the dorsal surface of the fingers, toes, or the inside of the wrist. The skin of the terminal phalanges of the fingers is usually not affected. The disease lasts for years, with off-season exacerbations followed by remissions [9]. Episodes of new pustular eruptions occur over varying periods of time and are strictly limited to their preferred locations. Occasionally, lesions of ordinary psoriasis appear, but more often the rash remains localized [10].
Subsequently, the color of the pustules changes to yellow-brown and dark brown. Without opening, the pustules dry out to form brown crusts, which resolve within 8-10 days. The presence of pustules at different stages of evolution (evolutionary polymorphism) gives the lesion a multi-colored color. Later, the pathological process manifests itself as sharply defined erythematous-squamous plaques, within which and along the periphery there are multiple yellow and brown pustules, some of which merge to form “purulent lakes” [1]. Remission begins with a decrease in the number of new pustules, although the skin of the palms and soles may remain erythematous, erythematous-squamous, or hyperkeratotic, clinically resembling eczema. Remissions continue for weeks or even months [11]. Thus, unlike other forms of psoriasis, the course of pustular psoriasis of the palms and soles is chronic. According to W. Enfors and L. Molin [1], at the time of examination 10 years after the diagnosis of pustular psoriasis of the palms and soles, its manifestations were absent in only 28% of patients.
Localized pustular psoriasis is often associated with hyper- and hypothyroidism, diabetes mellitus, arthropathy; it is often diagnosed in patients with SAPHO syndrome (synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis, osteitis), namely with chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis, lesions included in this syndrome sternoclavicular and sternocostal joints, pustular arthroosteitis, peripheral arthritis, pseudo-infectious arthritis involving the sacroiliac joints in the pathological process [1, 5].
In the differential diagnosis, fungal, scabies, eczematous dermatitis, and Andrews pustular bacterium are excluded.
The diagnosis of pustular psoriasis of the palms and soles is established on the basis of the characteristic clinical picture and course of the disease, and in difficult cases should be confirmed histologically.
Andrew's pustular bacterium
(syn.: Lever's pustulosis of the palms and soles) is a type of pustulosis of the palms and soles, which some authors classify as localized pustular psoriasis [1, 5]. A.A. Kalamkarian et al. [12] deny the existence of this disease as a nosological form. This variant of pustulosis was isolated by G. Andrews in 1934 and is characterized by the formation of small pustules with sterile contents on the unchanged skin of the palms and soles.
The etiology and pathogenesis are not clear, but since the occurrence of the disease is facilitated by foci of chronic infection in the body, especially chronic tonsillitis [1], chronic recurrent osteomyelitis, osteoarthritis [7], an infectious-allergic origin of the process is assumed, or more precisely, a hypersensitivity reaction to streptococcal antigens.
Clinically, the disease manifests itself as multiple blisters and pustules on the palms and soles. The rashes, as a rule, are symmetrical, starting from the center, gradually covering the entire surface of the palms and soles, including the lateral parts, but the fingers are not involved in the pathological process. The blisters quickly turn into pustules, which grow rapidly. They are deeply embedded, located on apparently healthy skin or partially surrounded by a narrow rim of erythema [6]. When merging, the diameter of the elements sometimes reaches 0.5-1.0 cm. Patients are concerned about itching and soreness [1].
The course is recurrent. The process lasts 2-3 weeks, possibly 1-2 months. Remission occurs after the elimination of the factor provoking the disease, the infectious focus. Relapses are accompanied by more intense itching and pain. The process may be protracted, but atrophic changes do not occur [9].
Acrodermatitis pustularis persistent Allopo
(syn.: persistent Crocker dermatitis, persistent Setton dermatitis) is a dermatosis of unknown origin, characterized by pustular non-bacterial rashes localized in the acral zones (fingers and toes) [1]. This is a rare disease of pustular, sterile eruptions on the fingers or toes that progress slowly in a proximal direction. Subsequently, prolonged pustulization causes destruction of the nail and atrophy of the distal phalanx [5].
In 1888, H. Crocer described recurrent bullous and pustular rashes on the hands and feet, and later F. Hallopeau (1890-1897) and R. Sutton (1911) gave a detailed description. Some authors classify it as a localized form of pustular psoriasis, while others, based on the similarity of the histological picture, classify it as a localized form of Gebra's impetigo herpetiformis, Dühring's dermatitis, and enteropathic acrodermatitis. There is also an opinion about it as an independent disease [1, 10, 12]. The disease develops at any age, more often in men; provoking factors can be trauma, pyoderma, and zinc deficiency [6].
The clinical picture is characterized by lesions of the pustular, vesicular or erythematous-squamous nature of the terminal phalanges of the fingers, less often the feet, and a gradual transition to adjacent areas of the hands and feet without proximal spread. The lesion can be one-sided for a long time [7]. Initially, small pustules appear, leaving a shiny surface against an erythematous background on which new pustules develop [5]. In some cases, secondary atrophic changes in the skin are observed. Pathognomonic lesions of the nails, usually one finger, leading to involvement of the nail bed in the pathological process, to onycholysis, onychomadesis. Features of clinical manifestations mainly depend on the intensity of exudation processes. If they are insignificant, erythematous-squamous changes are found in the lesions with increased redness along the periphery, layering of dry shiny scales, and multiple superficial cracks. If pustular rashes dominate the clinical picture, the disease is more severe [6].
There are seven clinical forms of the disease [1].
In purulent form
At first, the process resembles paronychia: hyperemia and swelling of the nail folds develop, from under which pus is released when pressed. The affected areas of the fingers are red, swollen, covered with multiple pustules, merging into “purulent lakes” of a wide variety of shapes [6]. Pustules appear on the skin of the entire nail phalanx (club-shaped-thickened), turning into erosions, crusts, and scales. After opening the pustules, small erosions are formed, covered with scaly crusts; after removing the layers, new pustular elements become visible through the reddened skin. The rash is accompanied by a burning sensation and pain. Flexion and especially extension movements are limited due to severe pain, the fingers are in a half-bent position. Pustules are sterile. Radiographs sometimes reveal atrophic changes in the bones of the corresponding phalanges, osteitis, osteoporosis, and possible mutilations. At the site of regression of pustules, the skin is slightly atrophic, shiny, and has a reddish tint. The nail plates are dystrophically changed and, as a rule, are rejected.
Vesicular
(bullous) form is characterized by a similar clinical picture, but instead of pustules, vesicles or, less commonly, blisters appear; mild itching and soreness are a concern [1].
With erythematous-squamous
(abortive) form, the clinic is limited to the appearance of hyperemia, peeling, cracks.
Phlyctenulous
this variety is more malignant: conflicts spread to the palms, soles, and sometimes to the ears; the process can lead to atrophy and mutilation of the terminal phalanges.
With vegetative
form, miliary pustules are grouped into plaques with peripheral growth and a tendency to resolve in the center; The formation of semi-soft vegetation along the periphery is characteristic.
Generalized form of Аudry
distinguishes a malignant course with the spread of the process to the entire skin, primarily to the hands, groin areas, genitals, elbows and thighs. There is clinical similarity to Hebra's impetigo herpetiformis. Damage to the nails and periungual tissues is often observed. In this case, the clinical process is characterized by onycholysis, often with complete loss of the nail plate.
In Allopeau's acrodermatitis, damage to the mucous membranes (as in generalized pustular psoriasis) is characterized by migrating ring-shaped erythematous elements located in the tongue area, covered with swollen white scales (annulus migrans). With the long-term existence of the process, signs of atrophy of the skin and muscles of the fingers appear, mutating changes due to trophic disorders. The prognosis for life is favorable, but the course is long, often relapsing, resistant to therapy. Spontaneous improvement is rare, and episodes of acute pustulization appear for no apparent reason [5].
Thus, in the presence of pustular rashes on the skin of the palms and soles, it is necessary to have knowledge of differential diagnosis in order to develop management tactics for this category of patients (see table)
.
Limited palmoplantar pustulosis can be understood in the meaning of palmoplantar psoriasis, since there are no significant differences in the categories of patients and the clinical picture that make it possible to distinguish this pathology into a separate nosological group. The presence of typical psoriatic elements of a different localization in patients with palmoplantar pustulosis also confirms this. Therapeutic measures in both cases correspond to the general principles of treatment of psoriasis.
Causes of allergies on the palms
The most common reasons are the following:
Household chemicals and any surfactants
They are considered one of the most common causes of contact allergies on the palms. Rashes, itching and other symptoms appear within minutes and hours after contact.
Photo: Itchy rash on hands could be a sign of food allergy
There is an allergy to soap or other detergents, especially those with a high content of phosphates, bleaches, aromatic fragrances and other additional components.
Food
They tend to cause general manifestations - a so-called food allergy occurs. It must be said that this type of allergy appears on the palms quite rarely; it “loves” the face, neck, elbow bends, and sometimes the stomach more.
However, this cause cannot be completely ruled out: a rash caused by one or another food allergen may well appear in this area.
Water
Oddly enough, an allergic reaction can also develop to water. But we need to figure it out: is it the H2O molecule that causes the disease? Most likely no. As you know, the water flowing from the tap today is not clean, either “mechanically” (meaning various kinds of dirt, rust from the walls of pipes, etc.) or chemical.
To begin with, it is all chlorinated, no matter how hard they try to deny it. In addition to this, different regions of Russia have their own problems: in some places, for example, water is being fluoridated.
Based on these facts, we can conclude that most often allergies arise not from the water itself, but from the chemicals it contains.
Weather conditions (allergy to cold, wind)
Allergy sufferers often do not tolerate low temperatures well.
- Cold urticaria develops;
- Redness of the skin occurs;
- “Islands” of edema are formed, which is accompanied by very severe itching.
Due to the fact that hands most often remain open (and not all gloves and mittens sufficiently protect hands from cold and wind), all manifestations of allergies are noted specifically on them.
The question naturally arises: the face is also always open, but less susceptible to allergies. In this situation, the peculiarity of the structure of the epidermis, the most superficial layer of skin on the palms, is important: it has the ability to renew itself incredibly quickly.
This is easy to explain: the skin on the palms is constantly exposed to physical, chemical, mechanical and other influences, which forces it to regenerate at an extremely high speed.
This, in turn, indicates a high level of metabolic processes, which inevitably leads to activation (and often hyperactivation) of the immune system, causing allergies.
Photo: Atopic dermatitis
A reaction similar to an allergic reaction on the palms can also occur for reasons not related to allergies. First of all, we need to “remember” about skin diseases:
- dermatitis of non-allergic nature;
- psoriasis;
- skin fungus.
The differential diagnosis of allergies will be discussed in more detail below; here it is necessary to emphasize that self-diagnosis, and especially self-medication, is dangerous. As a result of an incorrect diagnosis, the situation can be aggravated, causing serious complications.
Therefore, if any manifestations of the disease appear on the palms, you should consult a doctor.
Can pimples on the palms indicate acne?
Pimples on the palms are not acne. Acne is not characterized by the appearance of a rash in this area. Contacting a dermatologist will help you find out the nature of the pathology and begin adequate treatment.
As for acne, comedones, papules, pustules, and other types of acne elements, as a rule, appear in seborrheic areas (with a high concentration of sebaceous glands): on the face, in the décolleté, on the back, etc.9. For mild to moderate acne, Azelik®5 gel can be prescribed. This is a topical drug whose main active ingredient is azelaic acid. Azelik® gel has the following effects5:
- has antimicrobial activity against Staphylococcus epidermidis and propionibacteria;
- contributes to the normalization of keratinization processes;
- helps reduce the concentration of free fatty acids in lipids;
- helps reduce inflammation, which can be explained by a decrease in the metabolism of neutrophils and their synthesis of free radical forms of oxygen.
Azelik® gel should be used twice a day, applied to dry, clean skin5.
Prevention measures
To minimize the development of an allergic reaction on the palms, you need to follow some recommendations:
- Maintain hand hygiene.
- Do not use cleaning products and detergents containing many chemical additives.
- Before using cosmetics, test your skin for sensitivity.
- Wash dishes and do laundry wearing rubber gloves.
- Change the brands of cosmetics and household chemicals you use less often.
- Protect your hands from frost and wind with mittens or gloves.
- Avoid synthetic fabrics; if you are intolerant to wool, do not wear woolen items.
To strengthen the immune system, you need to:
- Healthy food;
- treat chronic diseases in a timely manner;
- exercise;
- walk more in the fresh air.
Allergies on the palms are an unpleasant phenomenon. Any irritant can cause it. It is impossible to know in advance what will cause irritation, redness, and itching of the skin. By following preventive measures, allergic manifestations can be avoided. At the first unpleasant sensations on the palms and arms, it is better not to delay a visit to the doctor, and to take all measures to alleviate the condition and eliminate the cause of the disease.
The skin protects from a variety of external influences and performs a number of useful functions. Children, from a very early age and adults, have had allergies to their palms at least once in their lives. It can manifest itself in the form of a small rash, peeling of the skin, pustular rashes, and red spots. There are many diseases associated with skin lesions on the hands, but we will tell you about the disease allergy on the palms.
Etiology of eczema51
The development of eczema is associated with the influence of various factors: metabolic, vegetative-vascular, neuroendocrine, genetic, infectious-allergic51. The reasons for the formation of pathology can be exogenous, for example, exposure to chemicals, fungi, bacteria, the use of medications, and the consumption of certain foods. But the factors for the development of eczema can also be endogenous - antigenic determinants of bacteria from infectious foci.
Genetically determined violation of immune regulation, the functioning of the endocrine and nervous systems. An important place in the pathogenesis of eczema is given to gastrointestinal pathologies.
Prevention measures
To minimize the risk of a red rash appearing on the palms and arms, it is advisable to follow simple rules:
- Maintain hygiene, wash your hands with soap before eating and after visiting public areas.
- During periods of the year with cold weather, do not forget about gloves. During the hot season, it is advisable to limit prolonged contact with the sun's rays.
- When cleaning using household chemicals, use rubber gloves.
- If you are sensitive to certain allergens, avoid contact with them.
- Do not touch street animals.
- Use only your own personal hygiene items.
- Use protective creams with a moisturizing effect.
- Carry out regular wet cleaning in the apartment.
- Spend more time outdoors, following safety precautions for pollen allergies.
- Increase your immunity, take mineral and vitamin complexes.
- Stick to your vaccination plan, especially for children.
Prevention is one of the most important components of practical medicine, because even in ancient times it was noted that it is easier to prevent a disease than to cure it. By following simple rules you can significantly reduce the risk of various rashes. Basic preventive measures: Vaccination is an ideal method of disease prevention.
Limiting the child’s contact with possible allergens: dust, household chemicals, wool. Protecting your baby's delicate skin from ultraviolet rays and cold. You can use a special cream and wear mittens in winter.
Phased introduction of complementary feeding to infants, balanced nutrition, comprehensive skin care. If a rash does appear, you absolutely cannot fight it on your own. Only timely consultation with a doctor and implementation of the prescribed treatment can guarantee the desired result.
Eczema: causes
The main reason is immunity disorders and factors that have a depressing and destructive effect on the protective function of the skin. As a result of disruption of the immune system, the body begins to react “inappropriately” to various external stimuli. Accordingly, the causes of eczema on the hands, for example, are detergents (even soap) or cosmetics (perfumes, creams, etc.).
Also “provoking” factors include:
- hereditary predisposition;
- allergic reactions to certain external influences;
- psychosomatic reactions;
- disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine and nervous systems;
- improper functioning of the digestive system;
- external factors, etc.
Only an experienced specialist should determine the causes of eczema on the palms or hands, on the head behind the ears or on the face, in order to then prescribe an effective course of therapeutic and restorative therapy. At the first sign, it is better not to delay visiting a doctor.
Eczema: treatment (on the arms, legs, behind the ears, etc.)
The difficulty of treatment lies not only in the fact that the disease can be chronic, but also in the fact that it affects even the deep layers of the skin. Fast and effective treatment (with the prevention of relapses) is possible only with timely consultation with a doctor. a dermatovenerologist knows how and how to treat eczema on the arms, legs and other parts of the body.
. Self-medication can lead to increased skin lesions and serious complications.
Initial appointment
As a rule, at the initial appointment, the doctor immediately diagnoses eczema by simply examining the patient. During the examination, the locations of eczema lesions are also recorded (on the palms, face, neck, head, behind the ear, etc.), which makes it possible to determine the cause. Examination, examination of tests and complaints, assignment of studies for each specific clinical case are individual.
If eczema is mild, then at the first consultation the doctor will prescribe treatment, its timing and subsequent visits for monitoring. If the disease is more complex, the doctor may prescribe additional tests and examinations.
Diagnostics
General parameters for diagnosing eczema of different types (plaque, atomic, infectious, etc.):
- detailed clinical and laboratory studies to identify pathologies of internal organs;
- analyzes and studies of the functioning of the endocrine and cardiovascular systems;
- analysis for helminthic infestations;
- mycological studies.
When you know why eczema appears, it becomes clear how and with what to treat it. When prescribing a course, the doctor also takes into account the medical history (if this is not a primary infection) and the individual characteristics of the patient in order to cure eczema as quickly as possible.
Repeated appointment
This is a visit to the doctor after undergoing all examinations and tests, as well as the selection of a treatment regimen based on the results of the examinations.
A repeat appointment is also scheduled after completing the course, so that the doctor can make sure that the chosen regimen is effective. If no positive dynamics are observed, then other medications are selected and the course of treatment is adjusted. Additional examinations are possible.
Treatment of weeping or dry, microbial, allergic and varicose, plaque or coin-shaped eczema: general parameters
One of the basic rules during treatment and during periods of exacerbation is to minimize the patient’s contact with water.
As an external treatment, the doctor can prescribe various lotions and compresses to the affected areas and treat the blisters after opening with special ointments and agents. Also, for eczema, a hypoallergenic diet is necessarily indicated.
Control reception
At the initial appointment, the doctor determines the time of the follow-up visit in order to assess the patient’s health status and, if necessary, develop a plan for restorative therapy and rehabilitation after treatment.
As a rule, all measures are aimed at restoring and strengthening the immune system. The doctor already knows why eczema appears in each individual case, where the blisters appear (on the hands or face), in what form (dyshidrotic, microbial, etc.), how and with what to treat and how to recover after treatment.
Treatment results
The disease can be cured, but the timing is always strictly individual. All details are discussed at the doctor’s appointment. Also, if necessary, treatment for other existing diseases that are provoking factors for eczema is prescribed in parallel.
Prevention
To prevent eczema, diet and proper skin care are prescribed, as well as various measures to strengthen the immune system (for example, hardening) and to minimize the causes of relapses.
If possible, it is necessary to exclude any contact with allergens that cause illness, both at home and at work. It is recommended to wear clothes made from natural materials. If a relapse of eczema does occur and an exacerbation begins, then you need to consult a doctor and limit contact with water, soap and other household products.
The medical clinic provides comprehensive diagnosis and treatment of skin diseases, including eczema (wet, dry, microbial, chronic, on the lower leg or behind the ear) using various means and methods. You can make an appointment with a doctor by calling the phone number listed at the top right, or through the website using a special form.
Skin rashes in the form of blisters
For any type of rash there are 2 reasons:
- Presence of disease;
- Allergic reactions.
The difference is that the diseases of which the rash is a symptom may vary.
Blistering rashes can occur in the presence of an infectious or dermatological disease. Among the main ones: scarlet fever, rubella, measles, chicken pox.
These diseases themselves have their own reasons. For example, the chickenpox virus is transmitted by airborne droplets, but people only get it once in a lifetime, most often in childhood.
Measles has similar features to chickenpox in that it is transmitted through airborne droplets. During recovery, the patient experiences an allergic reaction to the virus, which persists for a long time.
Allergies, manifested by the presence of blistering rashes, occur due to the use of spoiled cosmetics or low-quality nail polish.
If bubbles appear in the immediate vicinity of the nails, then you should think about whether to use this varnish in the future, or whether to continue going to this salon.
The type of rash is accompanied by itching and burning of the skin.
A blistering rash may appear as a symptom of dyshidrotic eczema or athlete's foot.
To begin treatment, it is worth doing the necessary tests required by the doctor to make the correct diagnosis.
The patient should remember that the rash should not be covered with dyes such as brilliant green and iodine. You should not scratch or open the blisters, since the liquid contained in them, if it comes into contact with healthy skin, can cause the rash to spread.
Only a doctor can advise the correct treatment, and therefore you should not diagnose yourself and begin treatment with anything. Because sometimes this can only cause harm and cause serious complications.
Vascular diseases
When diseases of the cardiovascular system occur, rashes can also form. A rash in a child appears due to a decrease in the number of platelets involved in blood clotting, as well as a violation of capillary permeability.
Skin lesions on the palms and soles are caused by scabies mites. Among the main signs of scabies, it is worth highlighting a rash and itching, as there is an allergy to the scabies mite and its waste products. If you scratch the skin very hard, infection can enter the wounds, which leads to the formation of pustules.
Scabies is characterized by the presence of subcutaneous passages that are gnawed by mites. Often the lesion is observed between the fingers, on the bends of the elbows and knees, and in the lower abdomen. The scabies rash appears as small red nodules that can gradually merge with each other. The danger of this disease lies in the likelihood of a secondary infection.
Skin tuberculosis warty51
This disease is characterized by the appearance of painless red nodules with a slightly bluish tint. They merge into infiltrates, and warts covered with horny mass appear on the surface. There are no growths in the peripheral zone, which looks like a red rim. The rash is located on the feet, palms, hands, and fingers.
Principles of treating rashes on the palms
When such a negative phenomenon appears, which many people simply do not pay attention to, consultation with a specialist is necessary. After the doctor conducts an appropriate drug study and identifies the cause that provoked the formation of a rash on the palms, he will be able to select a more effective drug therapy.
In mild cases, topical agents, gels, creams or ointments that treat the itchy area of the skin are sufficient. They can have both a plant and hormonal basis. But sometimes it is impossible to do without prescribing oral or injectable antihistamines, antibacterial, antiviral or antifungal agents.
A course of physiotherapy is often necessary. Ultraviolet lamps help get rid of rashes on the hands, the rays of which eliminate acne and destroy bacteria localized in them. Don’t forget about strengthening the immune system by taking a complex of vitamins specially selected by the doctor.
First aid for babies
Only a qualified specialist can identify the true cause that provoked the appearance of a rash on children’s palms, as well as select the appropriate treatment. But before a reliable diagnosis is established, parents should take some measures to help alleviate the baby’s condition:
- If, apart from the rash, nothing else bothers the child, treating his hands with a product that effectively relieves itching will be enough. For babies in this situation, a decoction of string or chamomile added to the bathtub is sufficient, and for older children, you can purchase a special product that soothes inflamed skin.
- In addition to local treatment of the affected skin surfaces, a child affected by such a misfortune must take an antihistamine in a special dose calculated by weight.
What to pay attention to before the doctor arrives
First of all, the mother needs to examine as accurately as possible the rash that has appeared on her palms and is clearly visible to the naked eye. In young children it can vary in severity, color, location and structure of elements. Experts identify the following types of rashes:
- Specks are small elements located singly or accumulated in groups. They can have different shades of color, from pink to dark burgundy, but are always flush with the surface of the skin.
- Papules are nodules that can be felt deep in the skin.
- Pustules are swellings of the skin. They can vary in size, but they always contain pus inside.
- Bubbles are elements similar in appearance to pustules, only instead of purulent accumulations they contain clear liquid.
- Blisters are rough to the touch and rather dense swellings, rising high above the general level of the skin.
- Erosion or ulcers - accompanied by the release of ichor, a violation of the integrity of the skin in depth.
]
This information about the nature of the rash must be provided when calling the doctor, as it will help him make a presumptive diagnosis. Parents should also register and inform the doctor if their baby has other possible symptoms.
Of particular importance is the presence or absence of such signs as fever, cough or runny nose, lethargy, pain, nausea, vomiting and reluctance to eat
Treatment of allergies on the palms
First of all, treatment should be aimed at recognizing the allergen that caused the allergy. It must be remembered that making a diagnosis and prescribing treatment on your own is unacceptable, especially in the case of children. Medicines for the treatment of allergies should only be prescribed by a doctor. Everyone is individual, and it is not a fact that the medications one person takes will suit other people. Doctors prescribe medications depending on the stage of the allergic reaction, the individual characteristics of the body and the age of the patient.
If allergies on the palms are a consequence of eating allergenic foods, then doctors prescribe a diet in which there are restrictions on the following types of foods:
- flour products;
- dairy products;
- berries and fruits (all except green ones);
- eggs;
- meat of geese, ducks;
- beef;
- celery;
- cabbage;
- legumes;
- coffee and black tea;
- jelly.
If the reaction is severe, then, in addition to eliminating allergens, blood purification drips and antihistamines are prescribed to treat food allergies.
Allergy treatment is always carried out according to the following principles:
- elimination of the allergen;
- decreased histamine levels in the blood;
- use of ointments.
Doctors recommend using second- and third-generation antihistamines for allergies, since they do not cause (if taken correctly) side effects, including drowsiness. Among such products we can highlight “Fenistil”, “Loratadine”.
Ointments as a means of reducing an allergic reaction are applied directly to the palms. Of these medications, the most effective are “Skin-Cap”, “Gistan”, “Fenistil-gel”.
Particular attention has recently been paid to the product “Desitin”. It fights allergic reactions very well and is approved for use even by children
The ointment relieves inflammation, removes redness and promotes the healing of microcracks.
If the allergic reaction is severe, hormonal drugs are used.
Allergies can be accompanied by suppuration and inflammation if a person scratches their palms. Through microcracks, the infection enters the bloodstream, and pus begins to accumulate under the skin. To eliminate these conditions, a course of antibiotics and the use of various blockers of inflammatory processes (Vishnevsky ointment, ichthyol ointment) are prescribed.
Causes
A rash on the arms and legs can appear for various reasons, for example, due to infectious skin lesions, allergies, and even problems with the circulatory system. In this case, the disease may first affect the limbs and gradually spread throughout the body.
The occurrence of a rash on the palms occurs in very rare cases. In other areas of the skin, for acne to appear, simply not following personal hygiene procedures will be enough. It is very difficult to bring the skin areas of the inner part of the hand to this state.
The formation of a rash on the palms indicates that some inflammatory processes are occurring in the human body. If such rashes appear, you should immediately seek help from a dermatologist, who will determine the true cause of this disease.
A person whose palms are covered in pimples and are very itchy will feel some discomfort in front of other people. The point is not that this rash has an unpleasant itch, but the appearance itself is, to put it mildly, not very pleasant. Often this pathology has the following characteristics:
- lumps resembling warts;
- white bubbles;
- large volume formations;
- small redness in the form of dots.
In most cases, the rash affects the inner areas of the palm and the parts between the fingers. The main reasons for their appearance are diseases such as contact dermatitis, allergies and others.
Infection
A skin rash can appear as a sign of some infectious diseases, for example, chickenpox, rubella, scarlet fever, measles, meningococcus. All these diseases are considered quite dangerous if left untreated, and can not only provoke the appearance of painful ulcers on the skin, but also complications on internal organs.
Over time, the blisters burst, leaving behind painful wounds, the skin becomes rough and peels. Infectious dermatitis can affect any area of the skin, and in some diseases, red spots and painful blisters appear throughout the body. Even if the blisters are localized only on the palms and soles, and the disease does not progress, you should still not self-medicate, as there is a risk of complications.
Allergy
Often, small rashes and irritation appear on the hands and feet of young children as the body reacts to various allergens that enter it. Substances that cause the rash can be excreted in breast milk if the nursing mother does not follow a diet, and a reaction to various foods that the baby eats himself is also possible.
The fact is that the child’s body is not perfect, and until a certain time it cannot digest a large amount of substances and painlessly remove them from the body, as a result, the accumulation of substances that the small body cannot cope with manifests itself in a rash.
With allergies, the rash can be located anywhere, including on the palms and soles, usually between the fingers. In this case, small pimples can itch very much and bother the baby, he becomes capricious, sleeps poorly and constantly tries to scratch his itchy limbs.
Parasites
Children are constantly in contact with each other, get very dirty and can become infected with scabies mites; these parasites penetrate the skin, causing the appearance of a small reddish rash that itches terribly.
Itching is caused by the fluid that the mite secretes as it moves under the skin. It is also worth noting that scabies is a very contagious disease; one contact with an infected individual is enough to cause you to get sick too.
Vessels
A hemorrhagic rash on the palms and soles can appear when the circulatory system is disrupted; it does not cause inflammation, but spots and stripes of varying sizes may appear on the skin. This rash occurs when capillaries and blood vessels are destroyed, red blood cells leak through the gap and form dark spots.
A hemorrhagic rash in itself does not bring any discomfort to the child, but it may indicate that serious disturbances have occurred in the body. Therefore, if you notice such rashes in a child, you need to urgently call an ambulance or take the baby to the doctor yourself.
Poor hygiene
Children of all ages can develop rashes due to poor hygiene. Miliaria often occurs if the child is not washed in time, and if the baby crawls on the ground all day and his hands are not washed, even dangerous ulcers may appear. In addition, poor hygiene can provoke infection in the body, then dermatitis due to the disease cannot be avoided.
Eczema: what is it?
This is an inflammatory skin disease, which is non-infectious and occurs quite often in adults and children. The disease has a number of pronounced symptoms. Acutely manifesting itself at the very beginning, without proper treatment it becomes chronic, the main symptom of which is frequent relapses.
The localization of the disease varies: most often, eczema occurs on the hands and feet, affecting the area between the fingers or the entire hand and foot. But the appearance of redness and peeling is also possible in other areas: on the head (behind the ears), on the body (especially in the folds), etc.
One of the frequently asked questions to doctors is whether eczema is contagious or not?
The fact that eczema is not transmitted from person to person is an established fact, so formally there is no reason to fear infection. But it is worth keeping in mind that many infectious skin diseases are similar in appearance to eczema. Therefore, it is recommended to undergo diagnostics from specialists.
At the Energo medical clinic, dermatovenerologists provide professional medical care, relieving patients of an unpleasant disease. During treatment, the patient is given maximum attention in order to improve his quality of life as quickly as possible.
Consequences of eczema
Eczema is accompanied by severe itching, sometimes unbearable. You should not scratch the affected areas, otherwise this can lead to complications in the form of infection, as well as to longer treatment of the eczema itself. Also, disturbing itching can lead to sleep disturbances (including insomnia) and the development of neurotic disorders.
With seborrheic eczema, a common complication is inflammation of the eyelids, which is accompanied by redness and swelling of the eyes for a long time and the formation of cracks in the outer corners of the eyes.
Traditional methods
You can try to remove redness, inflammation and itching using folk remedies. You can prepare masks or creams yourself; herbal tinctures are perfect.
Cabbage leaves and potatoes will help get rid of purulent formations. Choose any remedy and use it additionally with the treatment prescribed by the doctor.
Decoctions of medicinal herbs and plants
The following herbs and plants will help relieve inflammation and redness very well:
- celandine;
- chamomile;
- series;
- chestnut;
- elder;
- nettle;
- pine branches;
- radish;
- yarrow;
- dill;
- celery.
Baked onion
This remedy will relieve swelling, redness and reduce itching.
- boil or bake an onion;
- cut and place on a cloth or gauze bandage;
- apply to inflammation 4-5 times a day.
Onion peel
For inflammation, blisters and calluses.
- put onion peels into a container;
- pour vinegar essence on top;
- leave to infuse for 2 weeks;
- squeeze and apply on palms.
Radish
Will help with eczema, ulcers, ulcers, dermatitis. You can apply grated radish to painful areas.
- pour 50 ml of vodka into a jar;
- add 50 ml radish juice;
- mix with 25 ml of honey;
- Apply to pimples three times a day.
dogwood bark
It will help with any type of dermatitis and irritation, and relieve itching.
- Grind the burnt dogwood bark;
- add boiled water and stir;
- apply to palms as needed.
Pomegranate juice with honey
Removes skin irritations.
- boil pomegranate juice for half an hour;
- cool;
- add the same amount of honey;
- Apply to affected areas twice a day.