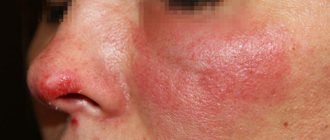
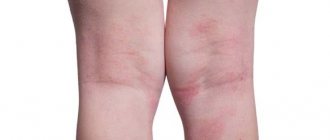
Psoriasis is a chronic, non-infectious skin disease that affects the skin, nails and joints. There are several theories of the origin of the disease - viral, psychoneurogenic, autoimmune, hereditary, etc., but none of them is generally accepted. Scientists have come to the conclusion that psoriasis has a multifactorial nature.
According to some data, more than 3% of the world's population suffer from psoriasis on the face and body, and the disease can appear for the first time at almost any age.
Until now, the disease was considered incurable, but techniques have emerged that will not only bring noticeable relief to the patient, but also ensure stable remission of psoriasis. Treatment is based on the use of innovative technologies.
Psoriasis is successfully treated in our clinic. Treatment of this and other dermatological diseases (vitiligo, atopic dermatitis, eczema) is carried out using the latest high-tech equipment. We know how to significantly reduce the manifestations of psoriasis and achieve stable remission even in the most difficult cases.
In addition, treatment with the Excilite µ excimer system allows the patient to stop taking steroid (hormonal) drugs.
1 Excilite µ system
2 Excilite µ system
3 Excilite µ system
General information about the disease
Among all dermatological diseases, the share of psoriasis in adults is approximately 7-8%, in children under 16 years of age - 4%. Even newborns, more often females, are susceptible to it.
The disease is not contagious, but the theory of its viral origin has not yet been rejected.
Psoriasis manifests itself equally at any age, but in childhood it often has uncharacteristic symptoms (atypical appearance), which can make diagnosis difficult. Thus, many dermatoses that affect the scalp and skin in the buttock area are similar to this disease. Source: Clinical guidelines “Psoriasis in children” Union of Pediatricians of Russia, 2016.
If at least one of the parents suffers from this disease, then the chance of its development in the child is 50%, if both - 60%. In the case of identical twins, if one of them is affected, the second will get sick with a 75% probability. Initially, psoriasis in a child appears in the groin area, lower back, rarely on the face, and later it is localized on the elbows, head, under the knees, spreads along the entire back, affects the armpits, and nails.
Almost half of all psoriasis sufferers acquired the disease in childhood. However, the first stage is often not detected due to the mildness of symptoms. Source: Benoit S., Hamm H. Childhood psoriasis // Clin. Dermatol. 2007. Vol. 25. P. 555–562.
The prognosis with early detection is good. In this case, local therapy is highly effective, followed by long-term remission (up to several years).
Prevention of psoriasis on the face
Preventive measures are aimed at preventing the development of the disease or the transition of psoriasis from remission to the acute stage. They imply adherence to a daily routine and rest, proper and balanced nutrition, giving up bad habits, and eliminating stress factors.
Basic criteria for caring for delicate facial skin:
- wash only with special moisturizers;
- water at a comfortable temperature (30-36°C);
- soak the remaining moisture with a soft towel;
- the use of creams that protect against cold and ultraviolet rays;
- wearing clothes (outerwear with a hood, scarf) and accessories according to the season (use an umbrella in rain and wind);
- Men are recommended to use an electric razor.
Compliance with preventive measures and timely therapy prescribed by a specialist will reduce the risk of spread and relapse of the disease.
Causes of psoriasis in children
Research continues all over the world to identify the causes of
this disease.
However, they have not yet been reliably established. The main theory is genetic predisposition
.
Scientists name the following as provoking factors:
- skin injury;
- lithium-containing medications;
- infectious diseases;
- metabolic disorders;
- dysfunction of the endocrine system;
- stress;
- smoking and drinking alcohol (applies to adults and adolescents);
- weak immunity.
Normally, skin cells mature in 30 days, but with this disease – in 4-5. As a result, papules are formed. The same abnormalities are found in apparently healthy tissues, and not just in areas of rashes.
Conclusion
Types of psoriasis vary in severity, size and distribution of patches. We looked at 6 main ones:
- psoriasis vulgaris is the most common form, in which the spots are more of a cosmetic defect. But, if left untreated, it can develop into other types;
- seborrheic psoriasis appears in areas of dandruff (hence the name) and resembles this disease in external manifestations;
- guttate psoriasis is small teardrop-shaped spots that spread throughout the body;
- pustular psoriasis is the most severe type of psoriasis, in which the papules are covered with blisters containing clear liquid;
- psoriatic arthritis is a disease that is accompanied by joint deformation. Severe form, leads to disability and death;
- erythrodermic psoriasis is a severe form of psoriasis, patches cover more than 90% of the body, and can be fatal.
The type of psoriasis determines its treatment. It is important to recognize the disease in time and make the correct diagnosis. Therefore, if you suspect psoriasis, immediately consult a dermatologist.
Symptoms of the disease
Psoriasis occurs in children in four stages: initial, progressive, stationary, regressive. Depending on this, the symptoms vary.
| Stage | Manifestations |
| Initial | Small rashes of a pinkish tint, the surface is smooth, shiny, hemispherical in shape. After some time, whitish or silver scales appear on them. |
| Progressive | The rashes grow and merge into conglomerates, the scales are located only in the center of the papules, along the edge of which there is a pink border. If the affected skin is injured, then after about a week a papule appears in this place, exactly repeating the shape of the injury (Koebner's symptom). |
| Stationary | New papules do not appear, old ones stop growing, peeling intensifies and spreads over the entire surface of the tubercle. |
| Regressive | Peeling decreases, papules become flatter in the center, gradually disappear, and in their place pigment spots or areas of skin devoid of pigmentation appear. |
Important! Psoriatic plaques have an extremely negative impact on the psychological state of children. Their peers focus on this, shy away for fear of getting infected, etc. Therefore, at the first signs, treatment should be started immediately.
As for babies, before two years of age, the first papules form in the folds of the skin, in the area where a diaper is worn. They differ from diaper dermatitis by their bright color and clear outline, with periodic mild itching.
After 10 years, children may develop psoriasis on the scalp, requiring treatment, which rarely happens at an earlier age.
Psoriatic arthritis often occurs, affecting the joints of the legs and arms. It begins with the onset of symptoms on the skin and develops approximately 10 years after the first rash.
In approximately 15% of cases, the disease affects the toenails and fingernails. Very often, the nail plates are the first to suffer, and skin rashes appear only years later.
Important! The disease has several forms and different symptoms. Any redness, peeling, or small swelling on the skin that does not go away within a week should be an alarm signal for parents. If you start treating your child in a timely manner, the process will not spread throughout the body.
Psoriasis: clinical picture and symptoms
The classic manifestation of psoriasis on the face and body is the presence of a rash in the form of papules and plaques covered with silvery-white scales.
Scraping papules leads to the following manifestations:
- the phenomenon of “stearin stain” - with slight scraping, peeling intensifies, the surface of the papules becomes similar to a crushed drop of stearin (hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis);
- the phenomenon of “terminal film” - after removing the scales, a wet, thin, shiny film appears: this is the mucous layer of the epidermis exposed;
- “blood dew ” phenomenon - scraping the film leads to the appearance of pinpoint droplets of blood (injury to the plethoric papillae of the dermis as a result of papillomatosis).
The disease is also characterized by an isomorphic reaction: rashes appear on areas of the skin that have been subjected to mechanical or chemical stress (scratching, cuts, exposure to acids, alkalis, etc.).
The most typical places for the formation of psoriatic rashes are the scalp, elbows, and knees (the so-called “duty” or “sentinel” plaques). Psoriasis often occurs on the face, psoriasis of the nails, and joints, genitals, skin folds, feet (plantar psoriasis), palms and other areas can also be affected.
There are two forms of the disease: winter (characterized by exacerbations in the autumn-winter period) and summer (a rarer form, relapses occur in the summer).
Types of disease
Simple forms:
- ordinary, or plaque – areas of redness on the skin with clear boundaries and peeling;
- film - most often diagnosed in newborns, localized on the buttocks, difficult to diagnose because it is similar to diaper dermatitis and other skin ailments.
Heavy varieties:
- psoriatic erythroderma - all skin turns red, joint pain, fever, blisters with pus may be observed;
- pustular - blisters filled with non-purulent fluid appear on the skin, causing fever if widespread;
- psoriatic arthritis - redness and blisters on the skin, asymmetric damage to the joints of the arms and legs.
Erythrodermic psoriasis
Erythrodermic psoriasis (psoriatic erythroderma) is one of the severe forms of the disease, leading to disability and death. It often develops from vulgar psoriasis, especially with abrupt discontinuation of therapy and an unstable course of the disease. This form also appears as a result of alcohol abuse, severe stress, and a severe cold.
Manifestations
- inflammation spreads to 90% of the skin or more;
- the skin becomes bright red, hot to the touch, swollen;
- large and small dry white scales that are easily separated;
- itching, burning, tight skin, painful sensations;
- weakness, loss of appetite, increased sweating;
- elevated body temperature - 38-39°;
- lymph nodes enlarge;
- hair and nails fall out.
Common sites of injury
- the entire surface of the body.
Photo
Erythrodermic psoriasis on the body
Erythrodermic psoriasis
Treatment of psoriasis
Therapy depends on the form of the disease, the person’s age, the presence of joint lesions, and previously used techniques. Severe forms often require treatment procedures in a hospital setting.
In each case, possible risks and potential benefits are assessed, especially when it comes to toxic drugs and hormonal drugs. Local treatment is most often used: moisturize the skin, soften it, relieve inflammation. Source: A.R. Umerova, I.P. Dorfman, V.V. Dumchenko, L.P. Makukhina Modern approaches to the treatment of psoriasis in children and adolescents // Russian Medical Journal, 2015, No. 19, p. 1156
In severe cases, systemic therapy may be prescribed. This is necessary when the disease significantly reduces the child’s quality of life. The consent of the child and parents must be obtained for such therapy, because it can lead to a number of side effects. Courses of treatment are usually short, each stage is carefully monitored by a doctor.
After 15 years and/or with extensive lesions, PUVA therapy is performed. The child uses a special drug containing psoralen externally or orally. After about 3 hours, his entire body or individual areas are irradiated with long-wave UV for several minutes. After several sessions every other day, formations on the skin decrease or disappear, peeling and itching are eliminated.
If other methods are ineffective, immunosuppressants are prescribed. However, they increase the risk of malignant tumors, so they are used rarely and under the strictest medical supervision.
Vitamins are prescribed together with any course of treatment: B12, ascorbic acid, A, B15, D2, pyridoxine. Only the doctor determines the dosage!
If the disease occurs in conjunction with a skin infection, antibiotics are prescribed.
Any treatment is usually long-term and is carried out to ensure that the disease is controlled and does not reduce the standard of living. Psoriasis cannot be completely eliminated.
Pustular psoriasis
Pustular psoriasis is the most severe form of psoriasis. https://kinkyads.nz. Papules can spread to the entire body or to specific areas (such as the palms and soles).
Manifestations
- rashes in the form of pustular elements (pustules), which are filled with clear liquid. The skin above and below them is red, inflamed, thickened and comes off easily;
- fever, general malaise and joint damage.
Common sites of injury
- large areas of skin, including the oral mucosa;
- sometimes only the palms and soles of the feet are affected;
- shins and forearms.
Photo
Pustular psoriasis on the foot
Pustular psoriasis on the neck
Pustular psoriasis on the arm
Advantages of SM-Clinic
Our medical center employs some of the best pediatric dermatologists in the Northern capital. There is a modern diagnostic base, its own laboratory and hospital. Children are provided with a full range of services, comfort, absence of queues and attentive treatment are guaranteed.
Call to make an appointment.
Sources:
- Clinical guidelines “Psoriasis in children.” Union of Pediatricians of Russia, 2016
- Benoit S., Hamm H. Childhood psoriasis // Clin. Dermatol. 2007. Vol. 25. P. 555–562.
- A.R. Umerova, I.P. Dorfman, V.V. Dumchenko, L.P. Makukhina. Modern approaches to the treatment of psoriasis in children and adolescents // Russian Medical Journal, 2015, No. 19, p. 1156.
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
What is selective phototherapy
This physiotherapeutic method uses mid-wave ultraviolet rays. Their effect is extremely beneficial, and is manifested in the complete disappearance of psoriasis, and the treatment has practically no contraindications.
For use, both narrow-band and broadband units are used that generate ultraviolet radiation, making it possible to act strictly on rashes without affecting healthy areas. Specialist dermatologists at the Moscow Aloderm clinic, using the latest generation technologies, achieve lasting results, eliminating the manifestations of psoriasis and will allow you to abandon the constant use of hormonal ointments.
Prices
| Name of service (price list incomplete) | Price |
| Appointment (examination, consultation) with a dermatovenerologist, primary, therapeutic and diagnostic, outpatient | 1950 rub. |
| Consultation (interpretation) with analyzes from third parties | 2250 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment regimen (for up to 1 month) | 1800 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment regimen (for a period of 1 month) | 2700 rub. |
| Consultation with a candidate of medical sciences | 2500 rub. |
| Dermatoscopy 1 element | 700 rub. |
| Setting up functional tests | 190 rub. |
| Excision/removal of cutaneous/subcutaneous elements and formations (1 element) | 2550 rub. |
| Removal of milia of one unit using electrocoagulation | 350 rub. |
How to treat psoriasis: methods and drugs
To cure psoriasis, it is better to take a comprehensive approach. It is necessary to send the patient for consultation to other specialists: therapist, endocrinologist, gastroenterologist. They will help determine the cause of the malfunction in the body.
Therapy against psoriasis involves:
- use of antiallergic and antihistamine drugs. To eliminate external symptoms, a keratolytic ointment is prescribed, as well as an anti-allergy ointment. To achieve a good result, the patient must take zinc and B vitamins;
- if psoriasis is localized on the scalp, you can use medications in the form of shampoo. For example, Skin-cap shampoo. It contains pure zinc. For some patients, this drug is a salvation. It eliminates external manifestations without the use of hormonal agents. But there are also those for whom such treatment is not suitable;
- Ultraviolet rays are used to combat psoriasis. Treatment is carried out using a PUVA unit. It contains special lamps that emit ultraviolet light.
Therapy is selected individually for each patient. The doctor must be careful in prescribing, since incorrectly selected drugs will only aggravate the course of the disease. Self-medication will not have any effect. It's better to consult a specialist.