June 29, 2020
Psoriasis with its entire appearance speaks of its “contagiousness”. Pink raised plaques all over the body, flaky skin, unsightly cloudy nails with grooves involuntarily instill fear of infection in others. Sometimes ordinary people confuse the disease with eczema or lichen, and ignorance in any case raises many questions and fears.
Causes of psoriasis on the face
Psoriasis on the face is rarely isolated; usually, similar rashes are present on the skin of the upper and/or lower extremities and torso.
It has been statistically proven that facial skin lesions in people diagnosed with psoriasis occur in 42% of patients. Such indicators indicate a fairly widespread change. Before the problem began to be closely studied, it was believed that psoriasis on the face was characteristic of the Caucasian race, as it manifests itself several times more often. This assumption is explained by weak exposure to sunlight and cold, in contrast to the population of African countries, the South American continent, Eskimos and Japanese.
How and from what causes psoriasis on the face has not been precisely established; we can talk about several combined causes or one associated with a malfunction of the immune system, a change in a section of a chromosome, etc. Reasons for the development of psoriatic rashes:
- Hereditary and genetic predisposition. It has been established that the likelihood of developing a skin disease is higher in people whose immediate relatives suffer from psoriasis. Several genes have also been identified that are responsible for the formation of a predisposition to the development of psoriasis (PSORS 1-13). Changes in the functioning of these genes lead to the development of an inflammatory response, disruption of the cell cycle, defects in the barrier function of the skin, etc.
- Immune system dysfunction. In psoriasis, there is also a malfunction in the functioning of a number of immune cells (T-lymphocytes, antigen-presenting cells and others) and signaling molecules (in particular, interleukins and interferons) involved in the development of the inflammatory process.
- Prolonged exposure to a stress factor or severe nervous shock.
- Severe and moderate course of infectious diseases.
- Skin injuries, especially professional injuries affecting the same area of the body (Koebner phenomenon).
- Taking a number of medications.
- Smoking and drug abuse, unhealthy diet.
There are different classifications of psoriasis; a number of researchers divide the disease into 2 types depending on the age when the rash first appeared:
- Patients under 40 years of age, peak detection period is 16-22 years. Characterized by rapid spread of the rash, generalized nature, difficult to control course and frequent relapses.
- Patients are over 40 years old, peak – 57-60 years. There are mild symptoms, a sluggish process, and is easily amenable to pathogenetic therapy.
Is psoriasis contagious?
The external manifestations of the disease in this case are deceptive; doctors know for sure that psoriasis is not contagious, it is not transmitted from person to person either by airborne droplets, or by household or sexual contact.
That is, even if you hug a person with psoriasis or touch the plaques with your hands, it is impossible to become infected. If someone who has been in contact with the patient ever develops psoriasis, then this will be an independent event.
Psoriasis is not transmitted through clothing; it is impossible to become infected with it in a store fitting room. There is also no household route of transmission. If you meet a person who has manifestations of psoriasis in the pool, in the bathhouse, not on the beach, in the gym, rest assured, there is no danger of infection in this case.
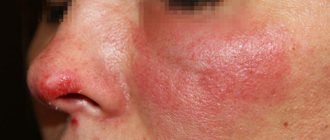
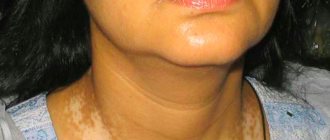
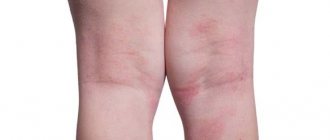
Photo of psoriasis on the face, what psoriasis looks like on the face
Photo 1. Psoriasis on the face.
Photo 2. Psoriasis of the scalp.
Photo 3. Seborrheic psoriasis of the face.
Photo 4. Psoriasis on the skin of the face.
Psoriasis on the face in the initial stage may resemble simple dermatitis; for comparison, just look at the photo on a medical website. In order to get acquainted with what classic psoriasis looks like on the face, it is recommended to familiarize yourself with the photo.
Is psoriasis inherited?
Psoriasis is transmitted to another person only when it comes to heredity. In other words, the disease can pass from parents to children. But even here there are some subtleties. For example, the disease occurs due to certain mutations and disorders in genes. However, this does not mean that parents with psoriasis will necessarily have children with this problem. We are talking only about predisposition to the disease.
The chances of inheriting psoriasis increase in children who have both parents with the disease. But even here, to start the mechanism, certain catalysts or triggers are needed that can activate this autoimmune process.
Symptoms of psoriasis on the face
The intensity of the manifestation of skin symptoms on the face differs from how and at what age psoriasis begins. At a young age, the rashes are typical, they are difficult to confuse with other types of dermatitis, unlike in older patients.
Psoriatic rashes are flat papules or plaques that rise above the skin, have clear outlines and a rounded shape. The rashes are usually bright pink in color and tend to merge. On the surface of the elements, multiple white scales are dotted, which easily fall off when rubbed and scraped.
The rash may spontaneously regress, leaving slight pigmentation on the skin.
The rash can be located on any part of the face, the most typical areas being the border with the scalp, the skin of the eyelids, nasolabial folds, and the area of the beard and mustache.
The formation of plaques occurs in several stages; first, new pink elements appear, which are partially covered with scales. The plaques unite and white-silver scales are observed over the entire surface, which is characteristic of stopping the growth of the rash. Regression of rashes is accompanied by a decrease in local redness, infiltration, and peeling.
In dermatological practice, there are specific clinically significant symptoms characteristic only of psoriasis. Psoriatic triad:
- Symptom of a stearin stain: when scraping with a glass slide over the rash, the peeling intensifies.
- The appearance of the terminal film: when the scales are removed, the skin is bright red, smooth, and shiny.
- Auspitz's sign (blood dew): scraping the terminal film leads to pinpoint bleeding due to closely spaced capillaries.
Is it possible to cure psoriasis: modern methods
Unfortunately, it is impossible to completely get rid of psoriasis. But modern treatment methods can significantly reduce the manifestation of symptoms, avoid the exacerbation stage, and reduce the likelihood of its occurrence to a minimum. Therapy is usually complex. It is developed by a dermatologist taking into account the patient’s age, gender, concomitant diseases and other factors.
Typically, drugs such as corticosteroid ointments and non-hormonal agents are used. Certain procedures are also indicated: plasmapheresis and physiotherapy (ultraviolet irradiation).
During treatment, it is necessary to adjust your lifestyle and establish a balanced, nutritious diet. It is noted that psoriasis in the head, legs and elbows can be controlled through a certain diet. The menu must include products that create an alkaline environment:
- apples;
- melons;
- bananas;
- citrus.
Moreover, they need to be consumed on their own, i.e. as a separate meal. On the other hand, foods with an acidic environment also help, for example:
- meat of different types;
- legumes;
- cereals;
- dairy cream;
- sugar (in moderation).
The menu also regularly includes such healthy products as:
- fresh vegetables (green;
- milk;
- fish;
- kefir;
- buckwheat;
- broccoli;
- lamb and others.
Treatment of psoriasis on the face
Before you begin to treat psoriasis on the face, you will need to collect a full history of the patient’s life and illness, perform laboratory and instrumental diagnostic procedures, it is important to establish the degree of activity, type and presence of complications for individual selection of therapy.
Treatment of psoriasis on the face with oral and parenteral medications is prescribed in the case of a generalized, long-term or advanced form. For such treatment, cytostatics and immunosuppressants are mainly used,
Topical remedies for psoriasis on the face are divided into hormonal and non-hormonal. It is important to note that hormonal liniment drugs have a quick, but not always long-lasting effect. In addition, long-term application of active and highly active corticosteroids can cause skin atrophy and decreased visual acuity in psoriasis on the eyelids.
Corticosteroid ointments and creams are prescribed in a short course in combination with a vitamin D3 analogue or salicylic acid, which enhances the therapeutic effect.
Non-hormonal ointments and creams for the treatment of psoriasis on the face:
- Salicylic ointment in low concentration (2-5%) relieves inflammation and peeling.
- Tar-based preparations help reduce inflammation and itching and affect the rate of cell division.
- Kartalin has an antiphlogistic effect, regulates the division and maturation of epidermal cells.
- Drugs containing grease in their composition also have similar effects.
In what cases do they consult a doctor: diagnosis
To diagnose the disease, contact a dermatologist. It is better to do this when the first signs of the disease appear. Moreover, you should not diagnose it yourself - there is a high probability of making a mistake. Moreover, you should not self-medicate, including using hormonal drugs, which can be harmful to health.
During the appointment, the doctor analyzes complaints and conducts a visual examination, prescribes blood tests, urine tests and, if necessary, other procedures (for example, taking a fragment of the skin - biopsy). No special preparation is required to visit a dermatologist. It is only important to ensure that the skin is clean and not to use ointments the day before.
Losterine in the treatment of psoriasis on the face
For patients suffering from psoriasis on the face, the manufacturer of the Losterin line has created special care products based on deresined naphthalan:
- Cream.
- Shampoo.
- Shower gel.
- Cream soap
The peculiarity of the Losterin line is the possibility of use during periods of exacerbation and remission as complex therapy. The drugs are characterized by a balanced composition. The ingredients are selected so that the action of one component is potentiated and complemented by another. Gently soothe the skin, relieve signs of inflammation, moisturize, and promote rapid healing.
Conclusion
Types of psoriasis vary in severity, size and distribution of patches. We looked at 6 main ones:
- psoriasis vulgaris is the most common form, in which the spots are more of a cosmetic defect. But, if left untreated, it can develop into other types;
- seborrheic psoriasis appears in areas of dandruff (hence the name) and resembles this disease in external manifestations;
- guttate psoriasis is small teardrop-shaped spots that spread throughout the body;
- pustular psoriasis is the most severe type of psoriasis, in which the papules are covered with blisters containing clear liquid;
- psoriatic arthritis is a disease that is accompanied by joint deformation. Severe form, leads to disability and death;
- erythrodermic psoriasis is a severe form of psoriasis, patches cover more than 90% of the body, and can be fatal.
The type of psoriasis determines its treatment. It is important to recognize the disease in time and make the correct diagnosis. Therefore, if you suspect psoriasis, immediately consult a dermatologist.
Prevention of psoriasis on the face
Preventive measures are aimed at preventing the development of the disease or the transition of psoriasis from remission to the acute stage. They imply adherence to a daily routine and rest, proper and balanced nutrition, giving up bad habits, and eliminating stress factors.
Basic criteria for caring for delicate facial skin:
- wash only with special moisturizers;
- water at a comfortable temperature (30-36°C);
- soak the remaining moisture with a soft towel;
- the use of creams that protect against cold and ultraviolet rays;
- wearing clothes (outerwear with a hood, scarf) and accessories according to the season (use an umbrella in rain and wind);
- Men are recommended to use an electric razor.
Compliance with preventive measures and timely therapy prescribed by a specialist will reduce the risk of spread and relapse of the disease.
Where does psoriasis come from and how does it arise?
We found that psoriasis:
- not sexually transmitted;
- not contagious by shaking hands, hugging, touching or other bodily contact;
- not transmitted through household contact;
- does not threaten healthy people in the bathhouse, fitting room, or swimming pool;
- It is not transmitted through the air, through water or dirty hands, as it is not infectious in nature.
Why then do people get sick? Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease, that is, caused exclusively by internal characteristics of the body. Autoimmune diseases are the result of the fact that cells that are supposed to protect the body from a variety of external threats, for some reason, begin to destroy the tissues of their own body, seeing them as a threat. Such diseases are never contagious.
External treatment
Particular attention in the treatment of psoriasis is paid to the choice of external medications, since among patients there are predominantly people with mild and moderately severe disease, which are characterized mainly by skin manifestations.
These products are designed to cope with skin symptoms:
- reduce and eliminate itching;
- relieve inflammation;
- reduce the volume of lesions;
- promote regression of plaques;
- reduce skin peeling;
- moisturize dry areas.
Stages and types of psoriasis
Doctors distinguish 4 stages of disease development:
1) progressive
2) stationary
3) regressing
4) remission
The development of psoriasis, as a rule, corresponds to the stages of psoriasis and occurs sequentially, subject to a properly selected treatment plan.
The initial stage of psoriasis is characterized by severe itching. The patient constantly scratches the skin, as a result of which the growth and fusion of psoriasis plaques occurs, as well as the appearance of new lesions. Thus, in the first stage of psoriasis, the lesions rapidly increase, and it is at the progressive stage that a visit to a dermatologist will help stop the area affected by ordinary psoriasis. The main goal of treatment at the progressive stage is to eliminate itching of the skin and relieve acute inflammation.
Characteristic signs of the stationary stage: new rashes do not appear, and the affected areas of the skin are covered with white scales. From this stage, under unfavorable conditions, a transition back to the progressive stage is possible, and with successful treatment, to the regressive stage. In the stationary stage, treatment is often prescribed with products with an exfoliating effect and drugs with anti-inflammatory effects that do not contain hormones.
In the regressing stage, the rashes turn pale and resolve from the center to the edges. The patient can remain in this stage for a long time, and with constant skin care with moisturizers and on-demand treatment with non-hormonal drugs, it is possible to achieve remission.