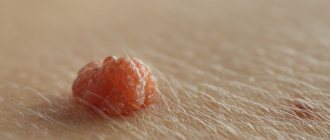
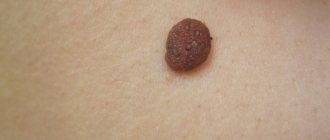
Every person has slightly noticeable dark spots on his body. These are so-called black moles. Experts explain this phenomenon as a non-oncological formation.
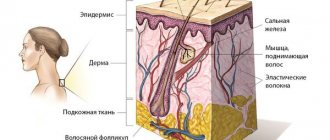
It is difficult to understand when they appeared. The main explanation is that pigmented skin cells grow too quickly.
Causes of moles
Most moles form in childhood and adolescence. Heredity and genetic predisposition play a key role. In adulthood, the appearance of new formations is facilitated by external and endogenous factors. The most important is hyperinsolation - regular and prolonged exposure of the skin to ultraviolet radiation.
Ultraviolet light is the main catalyst for the formation of melanin pigment in skin cells, and it is melanin that determines the color of the entire skin and its elements. The appearance of a black mole may be a consequence of too frequent and long exposure to the sun. Fans of artificial tanning are at risk, since solarium lamps are a source of intense ultraviolet radiation.
Changes in hormonal balance can contribute to the appearance of new nevi. For women, a risk factor is ovarian dysfunction (imbalance of sex hormones). Changes in hormonal levels can be triggered by taking oral contraceptives and hormone replacement therapy during menopause. The formation of black moles is possible during pregnancy and lactation.
Dangerous symptoms
Only a very few black moles pose a potential threat. The risk of malignant transformation to melanoma is low, but caution should be maintained. In any case, it is advisable to show the skin lesion to a specialist. You definitely need to see a dermatologist or oncologist if you have the following symptoms:
- The black mole increases in size. Even small growth should be alarming; a rapid increase in size is an unfavorable sign.
- The surface has changed (becomes “glossy” or loose).
- The formation peels off or bleeds.
- Unpleasant sensations appear in the form of pain, burning or itching.
- The shape has changed, the edge has become striated, uneven, asymmetrical.
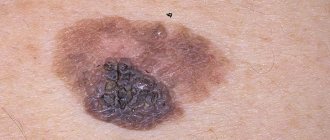
- The color changes: an ordinary mole becomes black, bluish or dark brown.
Any dynamics should be alarming. There is no need to panic, but you need to make an appointment with a specialist. What you definitely cannot do is try to remove the tumor yourself using traditional medicine. Injury by mechanical or chemical influence is one of the main causes of malignant degeneration.
Melanoma-dangerous nevi
Listed below are specific types of black moles that are melanoma-dangerous. This means that when exposed to unfavorable factors, they can degenerate into melanoma; the risk of malignant transformation is higher than in the case of ordinary nevi.
Dysplastic nevi. This type of nevi is characterized by the presence of melanocytic dysplasia, an atypical arrangement of melanocytes. Only a dermatologist can diagnose melanocyte dysplasia. The patient needs to know that a dysplastic nevus has a smooth surface. It does not rise above the skin, or only its central part rises. The shape is irregular, with uneven edges. The coloring is uneven, with black areas located in the center.
Blue nevus. Despite the name, the formation can be not only blue, but also black. Usually has the shape of a regular hemisphere and rises above the surface of the skin. The surface is smooth, the edges are even. Typical localization is the scalp, feet and hands, and gluteal region. The risk of malignancy increases after injury, including independent attempts at removal.
Nevus Ota. This type of tumor appears only on the face. Characteristic mainly for representatives of the Mongoloid race. The color is black or bluish. The differential sign is the presence of pigmentation of the sclera, iris or conjunctiva of the eye.
Borderline pigmented nevus. The neoplasm is formed in childhood. Subsequently, birthmarks increase in size throughout life, reaching one and a half to two centimeters in diameter. The differential feature is an uneven ring-shaped coloration, with a decrease in color intensity from the center to the periphery. The color is brown, darker in the central part.
Giant pigmented nevus. Refers to congenital. Increasing in size, such birthmarks reach gigantic sizes, up to 15 centimeters or more. A characteristic feature is an uneven surface with “potholes”, nodules and cracks. Hair growth from the nevus may occur.
For melanoma-dangerous moles, the risk of malignancy is higher than for ordinary skin tumors. Such nevi and birthmarks require observation by a dermatologist or oncologist. Malignant degeneration can be caused by exposure to external factors - mechanical or chemical damage, ultraviolet irradiation.
Congenital nevi (moles)
Balybina Yulia Gennadievna
Dermatologist
April 24, 2021
Congenital nevi (moles) are considered to be those with which a child is born, or those that appear in the first year of life. They differ from the usual dark spots that appear in all people later, as they are quite active. If the baby has skin lesions, they should be examined by a dermatologist.
The cells of such nevi can be located deep - in the lower third of the reticular layer of the dermis, sometimes in the subcutaneous fat, muscles, and even bones. Or they may have a superficial location. Superficial nevi often have dark shades of brown. This may contribute to the appearance of melanocytic dysplasia (malignancy).
This process occurs due to the influence of internal factors, such as hormonal stimulation, or external ones, for example, under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, due to trauma.
The risk of dangerous behavior of congenital nevi directly depends on:
- size
- heredity, cases of melanoma in family history
- skin phototype (1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6)
- harmful environmental factors
- hormonal stimulation
- traumatization
For each child with a congenital nevus, management tactics are selected individually by a dermatologist/dermato-oncologist, taking into account all the data.
The size of the education matters most. Therefore, let’s look at the classification by size and the risks within each group:
— Congenital nevus is small. Has a size of less than 15 mm. The risk of developing a malignant process in this group, according to one data, is less than 1%; according to others, from 1 to 4% throughout life. When present, melanoma most often appears after age 20. In childhood, it is characterized by a calm course, so routine observation by a dermatologist is usually sufficient.
— Congenital nevus averages from 15 to 100 mm. Before the onset of hormonal changes in puberty, on average up to 12 years, the risk of malignancy is low. Further, during life, according to various sources, from values less than 1% to 5%.
The tactics for managing such nevi, removal or observation, are determined by the doctor, taking into account the presence or absence of severe somatic diseases, skin characteristics, for example, a tendency to form scars, and aesthetic goals.
In general, I consider it safer to remove it at the age of 7 to 12 years in the absence of contraindications. Contraindications may be, for example, for the use of general anesthesia or in the form of severe skin pathology.
It is also important to consider the location of the nevus. After removal of the nevus, a scar remains; if it is on the face, you need to make a very balanced decision about the operation. On the scalp, if located deeply, removal may leave a hairless area.
— A special place in the classification is occupied by large formations, from 100 to 200 mm, and giant, more than 200 mm formations. They can occupy an entire anatomical region. They have the greatest risk of malignancy compared to those indicated above. The main distinctive feature of large nevi is that against their background, melanoma can form in the first years of a child’s life. The average risk of developing malignant cells during the first 20 years of life is about 5%. Therefore, I consider the main tactic to be removal.
Such nevi are observed when removal is impossible. This may be due to the complexity of the location, or due to excessively large sizes, when there are not enough skin grafting options.
In cases where the nevus is located on the scalp and spine, it is additionally recommended to do an MRI to exclude nerve damage. In some of these cases, neurocutaneous melanosis must be excluded. This pathology is a separate topic.
It must be borne in mind that even in cases where a difficult decision is made to remove large and giant nevi, this will not be a guaranteed fact that melanoma will not appear in other areas.
The main thing parents need to remember:
- If a newborn baby or a baby under one year old has moles, an examination by a dermatologist/dermato-oncologist is mandatory.
- Small congenital nevi should be observed by a specialist until the age of 20 (unless there are reasons to remove them earlier). In cases where the characteristics of the nevus change after 20 years, it may need to be removed.
- Medium congenital nevi are routinely removed between the ages of 7 and 12 years, in the absence of contraindications. Earlier removal may be recommended based on the results of follow-up examinations.
- Large and giant nevi should be removed, if possible, with the participation of a plastic surgeon under general anesthesia. If removal is impossible - observation and inspection once every 3-6 months. When a suspicious area appears, a fragmentary histological examination is performed.
- For skin with congenital nevi, it is necessary to adhere to general measures of protection from ultraviolet radiation: avoid direct sunlight, do not be in the open sun from 11 am to 5 pm, use photoprotection products with SPF 50+ and mechanical protection with clothing and hats.
- Try not to injure moles.
- When prescribing stimulant medications, discuss with a dermatologist the feasibility and safety of taking them, taking into account the presence of a congenital nevus.
Fortunately, large nevi are rare. Moles can be beautiful and even piquant, giving your appearance a special twist. The main thing is to have information about possible risks and keep them under the supervision of a competent specialist. At our center, doctors are ready to provide qualified assistance and answer all your questions.
Diagnostics
If you have a black mole on your body, it is not at all necessary to remove it, but you need to contact a specialist. The dermatologist will conduct a diagnosis, which consists of examining the neoplasm and studying it using optical or digital dermatoscopy (under magnification).
During the examination, the doctor evaluates the size of the tumor, its density, structure, consistency, surface character, symmetry, edge, color and other signs. As a rule, examination and dermatoscopy are sufficient to make a diagnosis. Biopsy and histological examination are carried out only before removal. In other situations, dermatologists prefer not to injure black moles unnecessarily.
A reasonable approach to the problem
You shouldn’t immediately panic when you discover a black mole on your body. First, it’s worth understanding the reason for its appearance. It is also important for general peace of mind to be able to distinguish between skin birthmarks and cancerous tumors.
Those involved in this topic can often even determine from a photo of black moles that they belong to a certain type. The topic is quite interesting and useful for general development.
Treatment: removal or observation?
Benign neoplasms of the skin do not require removal, but surgery can be performed for aesthetic reasons, as well as in situations where the nevus is located in an open area of the body, is exposed to ultraviolet radiation, or is injured by parts of clothing or jewelry.
Removal of benign black moles that are not melanoma-dangerous is carried out in the following ways:
- Surgical removal;
- cryodestruction;
- electrocoagulation;
- radio wave removal;
- laser removal.
Melanoma-dangerous nevi can only be removed surgically. The operation is performed in the presence of an oncologist and involves healthy skin. The removed tissues are necessarily sent for histological examination. Melanoma-dangerous nevi can also be removed in aesthetic medicine clinics if the medical institution has a dermatologist oncologist on staff. The operation is performed in a classical way; cryodestruction and other modern technologies are not used.
If malignant degeneration of the neoplasm is diagnosed, complex antitumor therapy is indicated, which includes surgical removal with wide coverage of adjacent tissues, radiation and chemotherapy.
Changes in black mole
If a black mole on the body does not change and does not cause aesthetic or physiological discomfort to its owner, such a neoplasm usually does not require removal or any therapeutic intervention. If the nevus intensively changes its external signs, this is most often considered a symptom of oncological degeneration. First of all, you should evaluate the color characteristics of the mole. If black dots or red spots appear on the mole, we can talk about the accumulation of melanomocytes, which can lead to further division of epidermal cells.
Changes in black moles that you should pay attention to include the following processes:
- Growth of pigmented formation;
- Changing the shape and structure of the mole, forming an asymmetrical edge;
- The appearance of itching and burning in the area where the pigmented structure is located;
- Ulceration of the surface and discharge of blood or ichor;
- The appearance of crusts and growths on the surface of a black mole.
Since black moles quite often form in areas of dense hair, another sign of malignant transformation of a nevus may be loss of hair growing in the area where such a formation is located, which is a consequence of destruction of the hair follicle.
After the procedure
After removing a nevus, it is extremely important to protect the skin from ultraviolet radiation. You can’t sunbathe in a solarium; you should be in the sun as little as possible. It is recommended to refrain from thermal procedures. It is impossible to remove crusts at the site of the surgical wound; the skin should be provided with maximum rest. After removing a mole on the face, it is not advisable to use decorative cosmetics.
You can learn more about the diagnosis of skin tumors and methods of their treatment at a consultation with a dermatologist at the Galaktika clinic (Moscow).