Symptoms of melanoma are a set of indicators according to which ordinary moles on the body, which everyone has, are beginning to degenerate or have already degenerated into a malignant tumor. The appearance of melanoma depends on its type and stage; superficial spreading, acral lentiginous, nodular melanomas and lentigo are known.
More than 20% of melanomas belong to the superficial spreading variety. However, patients rarely live more than 5 years. However, with timely and high-quality treatment, life expectancy can be significantly increased, and for this it is important to know what melanoma itself looks like in order to recognize it in time.
General information
Melanoma (other designations used are melanoblastoma , melanosarcoma ) is a malignant disease, one of the types of skin cancer, which is formed as a result of mutational changes in cells that accumulate the pigment melanin .
This formation develops, as a rule, in open areas of the skin - on the skin of the extremities, back, etc., less often on the mucous membrane (oral cavity, rectum, vagina), and the retina of the eye. The ICD-10 code is C43 (malignant melanoma of the skin). Melanoblastoma is an aggressive formation that metastasizes . Experts note that this tumor can demonstrate a very wide variety of clinical courses. According to statistics, 89% of patients with this disease die in the first years after diagnosis. A favorable prognosis is observed only at the first stage of the disease. However, the outcome and prognosis of the disease largely depends on the condition of the patient’s body and the characteristics of the tumor. A pre-melanoma condition can be Dubreuil melanosis, as well as a number of other diseases - melanosis of the colon, sclera, etc.
The human melanoma gene was discovered in 1965 by US doctor R. Tuckington. But there are still many points regarding this disease that require further research.
Speaking about what skin melanoma is, it should be noted that this is a very serious disease that progresses rapidly. As evidenced by Wikipedia and other sources, how quickly this malignant process develops depends on a number of factors. This article will discuss how to recognize the symptoms of this terrible disease and what methods of treatment are currently practiced.
Survival Projections
According to WHO, more than 132 thousand cases of melanoma are diagnosed every year worldwide. Women get sick more often than men. Melanoma can be inherited - about 10% of cases. However, thanks to early diagnosis and new developments in the field of medicine, the overall survival rate (up to 5 years) of patients has increased in the last 10 years. Melanoma at an early stage is characterized by a positive prognosis in treatment and stable remission in more than 90% of patients. Statistical data on five-year survival rate: I degree (up to 92%), II degree (53–81%), III degree (40–78%), IV degree (15–20%).
Sometimes the prognosis for grade IV melanoma is even better than, for example, grade II or III, since cancer cells metastasize to distant areas of the skin and lymph nodes, “bypassing” important organs and systems. In addition, the prognosis must take into account the level of LDH - if it is normal, then the chances that the disease will recede increase even more.
The survival prognosis is influenced by the age of the patients. Thus, older people have slightly less chances than young people, regardless of the stage of melanoma. White-skinned people are more likely to suffer from skin cancer, but if the disease is diagnosed in a dark-skinned person, their chances of survival are lower. Those who have undergone organ transplants, have HIV, or have serious chronic diseases also have worse prognoses for recovery.
Pathogenesis
The pathogenesis of melanoma is a very complex process, characterized by significant metabolic and molecular abnormalities. Many aspects of pathogenesis still remain unclear to scientists.
Melanoma develops from melanocytes, pigment cells that produce melanin. In order for a tumor to appear and begin to develop, a certain effect on normal tissues or cells is necessary. Their damage provokes proliferative reactions. necrosis of cells or tissues occurs But if proliferation is delayed under the influence of certain carcinogenic factors, cell differentiation may be disrupted, as a result of which the change in the membrane antigenic structure is disrupted and hyporesponsiveness to the influences of regulatory factors of the body is noted.
As a result of these processes, undifferentiated proliferating cells can escape the body's control.
Speaking about the pathogenesis of melanoma, scientists do not exclude that changes in the DNA of the cell with disruption of its protein structure and differentiation in the future may occur due to primary damage.
More than half of primary skin melanomas develop against the background of previous pigmented nevi . Therefore, such nevi are regarded as optional precancer. The most important exogenous factors influencing the development of this tumor are trauma to nevi and UV radiation. The mechanism for the harmful effects of UV radiation may be the formation of highly active free chemical radicals in healthy cells. A tumor occurs when these radicals damage the cell's DNA and interfere with its normal repair.
If we describe the sequence of development of skin melanoma due to the influence of UV radiation, it is as follows: UV radiation affects melanoblasts, melanocytes or nevus cells, cell DNA is damaged, cell differentiation is disrupted, the protein structure changes and new membrane antigens appear. Hyporesponsiveness and tumor growth are noted. The possibility of this mechanism of carcinogenesis is confirmed by the fact that melanomas often develop after a single and strong influence of UV radiation (with a sunburn).
The essence of the mechanism of the carcinogenic effect of injury to pre-existing pigmented nevi is tissue proliferation in response to damage. However, trauma does not provoke tumor development. Cells in a state of proliferation are more sensitive to carcinogenic effects. They are especially vulnerable during the mitotic cycle. Consequently, proliferation (active reproduction) of cells can provoke their neoplastic transformation.
If we describe the sequence of development of skin melanoma due to trauma to pre-existing pigmented nevi, it is as follows: nevus cells are damaged, inflammation and proliferation of the damaged tissue occurs. Long-term proliferation is observed, and under the influence of endogenous carcinogenic factors, the structure of the cell's DNA is disrupted. As a result, cell differentiation is disrupted, its protein structure changes, and new membrane antigens . Hyporesponsiveness and tumor growth are noted.
How long will the patient live after diagnosis?
The prognosis for this cancer depends on several factors, one of which is tumor metastasis.
If melanoma has metastasized, the patient’s lifespan depends on the number of affected organs:
- one – seven months;
- two – up to four months;
- more than two organs – less than two months.
One of the factors influencing the patient's life expectancy is the location of the tumor process. The prognosis is more favorable when melanoma is located on the forearm and lower leg, less so on the scalp, hand, foot and mucous membranes.
Melanoma recurs very often. Scientists have found that the malignant process can start again even ten years after complete recovery.
However, when stage I melanoma is detected and this formation is removed in a timely manner, the prognosis is more than favorable (97% of patients survive).
Classification
In total, depending on the characteristics of the process, four types of melanoma are distinguished:
- Superficially spreading - according to statistics, approximately 70% of developing melanomas are of this type. Most often, this tumor is asymptomatic and develops on the skin of the legs in women and on the torso in men. The formation has irregular outlines, brown or light brown color, and there may be spots on the surface - red, white, blue or brown. It may also have small blue-black nodules. In some cases, small tooth-like notches appear along the edges, the size increases, and the color changes.
- Nodular melanoma – 15-30% of melanomas are of this type. It can appear on any part of the skin and looks like a black papule or gray-black plaque. It may be amelanoma (non-pigmented, meaning that it has no pigment at all) or it may contain little pigment. Nodular melanoma can also look like a vascular tumor.
- Lentigo malignant melanoma - up to 5% of such formations belong to this type. Most often develops in older people. Formed from lentigo maligna (Hutchinson's freckle or melanoma in situ). Typically, this melanoma appears on the face, but it can also form on other areas of the skin that have been exposed to sunlight. An asymptomatic flat spot or light brown or brown plaque appears on the face or other areas of the skin, having irregular outlines and unevenly located on the surface.
- Acral - 2-10% of formations belong to this type. This type of melanoma is most often diagnosed in people with dark skin color. It develops on the soles, skin of the palms, under the nails. Its symptoms and histological features are similar to lentigo melanoma.
- Amelanotic melanoma - any of the varieties listed above can be non-pigmented. Most often, small formations are non-pigmented (spitzoid, desmoplastic, neurotropic melanomas, etc.). This type occurs in less than 10% of cases. The color of this formation is pink, red or brownish. Since such a tumor can easily be mistaken for benign, late diagnosis often worsens the prognosis.
- Lentiginous melanoma of the mucous membranes is a rare form of the disease, occurring in approximately 1% of cases. Formed on the mucous membranes - in the nasal cavity, mouth, perianal and vulvovaginal areas. It is characterized by pronounced uneven pigmentation.
- Malignant melanoma of soft tissues - forms on ligaments and aponeuroses.
- Melanoma of the eye (uveal) - affects the eyelid, conjunctiva or choroid. Choroidal melanoma is also diagnosed, a tumor of the retina that develops from choroidal melanocytes. A tumor of the choroid of the eye is a lesion of its choroid. As a rule, it progresses rapidly. The prognosis is unfavorable - due to the aggressive development of the process, death is recorded in approximately 70% of cases.
- Subungual melanoma is a very dangerous type, as it can develop rapidly and at first unnoticed by the patient. Initially, a pigment spot develops under the nail, usually dark in color. The nail plate becomes brittle and sometimes deformed.
The types of the disease are also determined depending on the development of metastases during tumor progression. Melanoma of the central nervous system is a condition in which damage to the central nervous system develops. We are talking about secondary tumors of the central nervous system.
Morbidity statistics
Detection rate
Melanoma is quite rare - from 3% to 6% of the total number of malignant tumors. It is considered the most aggressive type of skin cancer, characterized by rapid growth and early metastasis. Of all deaths due to malignant skin tumors, it accounts for 80%. The average annual increase in the incidence of the disease in Russia is 3.9%.
Age and gender of patients
The tumor is mainly detected between the ages of 30 and 60 years, and also occurs in older people. Recently, the disease has become “younger” and is increasingly diagnosed in patients aged 24 to 40 years. The average age of patients is 52 years, more than a quarter of cases are detected in people under the age of 45.
Under the age of 40, neoplasms are more common in women. After 40 years, the incidence is higher in men and, as age increases, this trend becomes more pronounced - at the age of 65, men get sick twice as often, and at 80, three times more often than women.
Dependence on race and skin color
The risk of melanoma is highest in Caucasian people with fair skin. Hispanics, Asians and African Americans are less susceptible to the disease. At the same time, African Americans have the lowest survival rate.
Survival
The average mortality rate from melanoma in Russia is 2.13-2.52 per 100 thousand population. The average annual increase in the mortality rate is about 1.5%. Detecting a tumor in the early stages allows you to achieve almost 100% survival within 5-10 years.
Causes
Skin melanoma develops due to a combination of the influence of the underlying cause and environmental conditions, as well as the internal environment of a person. Today, scientists do not have data on the main etiological factor in the development of skin melanomas. There is a theory that melanoma is a polyetiological disease.
Factors influencing the development of this disease are divided into exogenous and endogenous .
The following exogenous factors :
- Place of residence of a person (geographical latitude) and associated solar radiation activity. The influence of the ultraviolet spectrum is one of the most important factors affecting the development of skin melanomas. Its negative impact is also determined by the fact that ozone decreases in the stratosphere, which leads to an increase in the carcinogenicity of solar radiation. There is confirmed evidence that what is more dangerous in this context is not the chronic influence of ultraviolet radiation, but its sudden and very strong influence, sometimes one-time. Sunburns received in childhood and adolescence are important.
- Injuries to pre-existing nevi - bruises, cuts, abrasions, as well as chronic injury from clothing or shoes.
- The influence of chemical carcinogens.
- Fluorescent lighting – a negative effect is observed with intense exposure to fluorescent lighting sources.
- Ionizing radiation.
- Electromagnetic radiation.
- Socio-economic factors also play a role. In particular, it is noted that the incidence is higher among the urban population; that patients tend to have a higher social status. It is also noted that melanomas occur more often in people working in the rubber, electronics, petrochemical, and coal industries; in contact with polyvinyl chloride, plastics, benzene, pesticides, radiation.
- Biological - dietary habits (large amounts of proteins and fats in the diet), bad habits (alcohol abuse), and taking certain medications have a certain influence.
The development of the disease is also influenced by the following endogenous factors :
- Precancerosis – there are a number of conditions against which a tumor can develop. These are xeroderma pigmentosum (hereditary, recessively transmitted photodermatosis), Dubreuil melanosis (lentigo - areas of skin pigmentation).
- Nevus plays a certain role in the etiology of skin melanomas. It should be noted that in addition to pigmented ones, there are non-pigmented nevi. In addition, there are so-called acquired nevi that appear during life, and which a person may not notice until they transform into a malignant formation. Nevi are a morphologically unstable population of cells, since their localization in the layers of the skin changes throughout life. The number of nevi depends on the hormonal background of the body. Nevi should be considered a phenotypically unstable population of cells. The fact that melanomas develop from nevi is generally accepted, but still, research and observation data do not allow us to state that nevi are the cause of absolutely all melanomas.
- Biological - researchers note that the tumor develops more often in people of the white race. A pigmentation disorder in the body, in which the skin reacts inadequately to ultraviolet radiation, also plays a role. Melanoma most often develops in people with weak skin pigmentation and high sensitivity to UV radiation. Those who are prone to sunburn are more likely to get sick. Heredity also plays a certain role. It has been established that melanoma is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. Hormonal fluctuations also influence the development of the disease ( estrogens and androgens ). Certain importance is attached to immune factors - the risk of disease is increased by immunosuppression and immunodeficiency states.
Types and symptoms of age spots
Hyperpigmentation on the body does not cause physical discomfort. Neither itching, nor burning, nor any other unpleasant symptoms are usually observed (but not always). Only compaction, change in color of spots or their convexity should be alarming. In this case, you should consult a dermatologist to exclude the possibility of developing malignant neoplasms. For self-control, you should know about the common types of stains, their location, features, and reasons for their appearance.
Freckles
This type of pigmentation is not a pathology. Freckles are genetically determined. Their appearance is explained by a special combination of genes in the DNA of skin cells. Freckles tend to intensify in the spring and summer due to ultraviolet irradiation of the skin. In winter they are usually not so noticeable.
This kind of hyperpigmentation of the skin is expressed in the form of patches of different shades of brown. Freckles appear on the face, shoulders, arms, and back. Appearing in childhood, they can disappear without a trace with age. But this does not always happen.
It is not recommended to try to get rid of freckles on your own. This procedure requires the development of an individual program. Typically, genetic hyperpigmentation takes a long time to resolve.
Melasma
This pathology makes itself felt in the case of an excess of female sex hormones. Melasma can also occur when taking medications, using certain cosmetics, and exposure to sunlight.
Melasma is hyperpigmentation, expressed in the form of spots of different shades with uneven contours. You can get rid of it by eliminating the cause and simultaneously using bleaching compounds. As a result, melasma disappears without a trace.
Types of melasma:
- central-facial, or centrofacial. In this case, the spots are localized on the forehead, nose, chin, and above the upper lip;
- mandibular. Suggests the spread of spots on the arch of the lower jaw.
- painting With it, pigmentation mainly affects the nose and cheeks;
Melasma
With this disease, spots appear on the hands, face, neck and other open areas of the body that have an uneven color. This pathology is chronic. Subsequently, hyperpigmentation can spread to other areas of the skin.
Melasma can be acquired or hereditary. Most often it occurs during pregnancy, when taking oral contraceptives, as well as when the functionality of the ovaries is impaired and there is a lack of vitamins C and PP.
Pigmentation may also be accompanied by:
- itching;
- general malaise;
- peeling, dryness;
- progression of the disease (modification of spots, increase in their number).
Melasma passes with a change from a period of remission to exacerbation. Can be corrected.
Becker's nevus
It is characterized by the appearance of pigmented spots with hair growing on them. The pathology is shown in the photo below. Becker's nevus is characteristic of male adolescents, but it also occurs in adults. The exact cause of the disease is not known. It is assumed that the main factors are heredity, stress, and ultraviolet radiation.
The disease progresses as follows: first, a small wrinkled dark brown spot appears. Then new ones can form next to it. Over time, they either grow separately or unite, forming large pigment halos, up to 18-20 cm in diameter. Then they are evenly covered with hair. Tanning significantly accelerates pigment growth.
Secondary
The formation of spots is associated with certain damage to the layers of the epidermis.
The accumulation of melanin, which causes secondary hyperpigmentation, occurs after acne, after removal of a mole and other surgical interventions, as well as:
- psoriasis;
- peeling
- wounds, cuts;
- erosions;
- papules, pustules;
- sores;
This also applies to the use of cosmetics containing photosensitizing components.
Age
Senile (senile) lentigo usually occurs on open areas of the body. That is, those who are most often exposed to solar radiation. Age-related hyperpigmentation appears as a result of a slowdown in melanin transport and, as a result, its accumulation. The causes of the disease are also chronic diseases and a general weakening of the body's protective functions.
Age-related rashes occur on the shoulders, chest area, face, arms, and back. It is characterized by uneven color and irregular shape.
Berlocc's dermatitis
It is distinguished by the appearance of dark brown spots of different sizes after the use of perfume products. Neoplasms may be accompanied by itching, and over time disappear without a trace without any therapy. The exact cause of the disease is not known. Scientists suggest that Berlocc's dermatitis may be due to hypersensitivity to certain components of perfume.
Chloasma
The spots with this disease are usually symmetrical and dark in color. Their outlines are uneven, but always clear. Most often, chloasma forms on the inner thigh and face. Their appearance indicates liver dysfunction.
Chloasma spots are large, at least 1 cm in diameter. Formed singly or in groups. As the disease progresses, they can merge and occupy large areas of the body. Sometimes chloasma manifests itself in the form of specific stripes passing through the stomach, forehead, and cheeks.
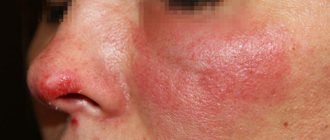
Skin melanoma symptoms
Photo of the initial stage of skin melanoma
The clinical picture of pigmented malignant tumors can be very diverse. Therefore, the symptoms of skin melanoma can manifest in different ways. The tumor can have different shapes, colors, sizes, etc.
Since this tumor is formed from melanocytes (pigment-forming cells), it can develop in almost any organ or tissue. But still, melanoma most often appears on the skin.
The question of how to recognize melanoma is quite complex. After all, its clinical picture has high variability. Melanoma develops predominantly on congenital or acquired nevi. However, a tumor can also appear if the patient has Dubreuil melanosis, as well as on skin where there are no signs of a nevus or other formation.
Due to the fact that the degeneration of a mole into melanoma is a fairly common phenomenon, it is necessary to clearly know the clinical manifestations of malignancy of nevi. Simply put, you need to understand how to distinguish a mole from a melanoma, what melanoma looks like, and identify which birthmarks are potentially dangerous.
The following signs should alert a person:
- growth, induration or ulceration of the nevus;
- weakening or strengthening of the color of the birthmark;
- the appearance of radiant growths around the nevus - they can be either pigmented or non-pigmented;
- hyperemia or stagnant halo around the birthmark;
- the appearance of an exophytic component on its surface;
- frequent development of bleeding;
- enlargement of regional lymph nodes;
- the appearance of satellites near the nevus - pigmented or non-pigmented nodules.
It is important to consider that the symptoms of the initial stage of melanoma are difficult to determine, since the first signs of malignancy are often similar to the symptoms of a normal inflammatory process.
Photo of skin melanoma
In typical cases, the initial stage of skin melanoma manifests itself as follows: a birthmark for no apparent reason or after an injury begins to grow. Its color changes, and an exophytic tumor appears in one of the areas of the nevus. The initial stage is not always determined in a timely manner, since melanoma during this period can have a small diameter: as a rule, it is no more than 1-2 cm. Large tumor nodes form in the later stages.
During the development of the tumor, the signs of skin melanoma can be varied: it can be a flat spot, a formation with a slight protrusion, papilloma growth, mushroom-shaped formation, etc.
The shape of the tumor can be round, oval, or irregular. As a rule, melanoma is a solitary formation. But often additional outbreaks appear near it. They can either merge with the main tumor (multicyclic form), or be located nearby and separated from the tumor by areas of healthy skin.
The surface of the tumor may initially be shiny and smooth, but later irregularities and ulcerations appear on it. The tumor site may bleed even with minor trauma. As the tumor grows, tissue infiltration and disintegration of the tumor node often appear on it, as a result of which the surface resembles cauliflower. Sometimes there are no signs of ulceration, and thin skin covers the tumor. In rare cases, early stage melanoma begins as localized redness and gradually develops into an ulcer that does not heal.
The consistency of the tumor can also be different - it can be either soft or hard or dense. One tumor can form areas of varying consistency.
The color of the tumor depends on the amount of melanin. It can be purple, red, blue-black, brown, black. Pigmentation may be uniform or uneven. In the center the tumor appears more pigmented.
When benign nevi become malignant, their color often changes. This is one of the warning signs. Pigmentless tumors develop to form secondary tumors containing pigment. In the later stages of melanoma, the patient’s general well-being also worsens.
Thus, the signs of nevus malignancy are the following symptoms:
- nevus growth along the plane and above the skin;
- bleeding from its surface;
- asymmetry of its edges;
- peeling of the surface;
- change;
- burning sensation in the area of the nevus;
- hair loss from its surface;
- formation of nodes.
Signs of metastasis in the final stages
Melanoma metastases usually occur in the following cases:
- if the patient is elderly;
- with complications of melanoma by chronic diseases;
- when melanoma cells grow into the walls of other organs;
- with a large size of primary melanoma.
Signs of liver metastases
When metastases are localized in the liver structures, black melanin accumulations form in them, representing the affected areas. In this case, functional or physical disorders occur in the liver, the consequences of which are felt by the entire body.
The main signs that melanoma has metastasized to the liver are:
- tuberosity of the organ;
- increase in liver size;
- sudden weight loss;
- presence of jaundice or ascites;
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- nausea and vomiting;
- enlarged spleen;
- frequent nosebleeds.
Metastases in the lungs
The initial phase of pulmonary metastases does not have pronounced symptoms. In this case, there will be general signs of cancer problems in the body such as apathy, anemia, weakness, weight loss, decreased appetite, hyperthermia. Signs of metastases may initially include various colds - bronchitis, flu, pneumonia. Sometimes symptoms of lung metastases in melanoma occur only at the final stage of the disease, when nothing can be done to alleviate the patient’s condition. In this case, multiple nodular formations with involvement of the pleura and bronchi are diagnosed in the lungs.
If a large part of the lung is affected or the bronchi are compressed due to metastases, the patient experiences shortness of breath. The cough with metastases is predominantly nocturnal and dry, then gives way to ulcerations of mucopurulent sputum, odorless, but often with traces of blood. As metastases grow, the bronchi narrow and the sputum thickens, becoming purulent. Pulmonary hemorrhage may occur.
Pulmonary metastases, which affect the pleura, spine and ribs, cause pain. If metastases reach the lymph nodes of the left part of the mediastinum, hoarseness and aphonia appear, and with right-sided damage to the lymph nodes, the upper part of the body may swell due to compression of the superior vena cava.
Metastases in lymph nodes
Metastases in melanoma most often occur at stages 2-3 of the disease. The most common site for metastasis is the lymph nodes. Moreover, if a patient has a single metastasis to a lymph node, then, according to doctors’ forecasts, he will live another 5 years in 51% of cases. With 4 metastases in this area, only 17% of patients will overcome the five-year mark.
Signs of lymph node metastasis in melanoma are:
- sudden loss of body weight;
- causeless enlargement of lymph nodes;
- visual impairment;
- constant fatigue and chronic feeling of tiredness.
Metastases in bones
Metastasis to the bones is considered a very common phenomenon in melanoma in medicine, which gives severe pain to patients. The main manifestations of this process can be hypercalcemia, bone fragility, neurological changes, and compression of the bone marrow. Metastases to the bone come from the primary site, but other tumors can also be the cause, such as soft tissue sarcoma, ovarian tumors, etc. Melanoma most often affects the bones of the pelvis, hips, vertebrae, and ribs. Metastases follow from melanoma to the bones of the skull along the venous vertebral plexuses.
Nature has protected the skull bones with the ability to constantly renew themselves through osteoclasts and osteoblasts, but the entry of melanoma cells through the bloodstream into the bone marrow destroys these structures. The result of this is constant fractures of the skeleton in different parts, even under small loads.
Metastasis in the brain
Melanoma causes metastases to the human brain more often than other cancer pathologies. After this, there is no need to wait for a complete cure of the disease. The chances of survival for a patient with such metastases are significantly reduced. However, sometimes modern therapy with monoclonal antibodies helps to stop this process if there are individual characteristics of the human body.
Metastases to the brain area occur in 45% of all patients suffering from late-stage melanoma. This ultimately leads to the death of the patient. The symptoms of such metastasis will depend on the location of the lesion, necessarily including incoordination of the patient’s own body, emotional instability, headaches, fever and fever, memory loss, personality changes, lethargy, changes in pupil size, general weakness and difficulty in speech skills.
If the metastases have affected the frontal part of the brain, then the patient may experience sudden changes in rudeness, he begins to swear, and experience disturbances in visual functions and the musculoskeletal system. The symptoms of such metastases are very individual and sometimes they can completely change the patient’s personality.
When the patient's brain stem metastasizes, bursting or dull intracranial pain occurs in the head, which leads to dizziness and impairs visual functions. Also, such metastasis causes constant nausea and vomiting in the patient, convulsions, which in manifestations resemble epileptic seizures.
Tests and diagnostics
It is very important to see a doctor as soon as possible, because the success of treatment depends on how quickly the diagnosis is made.
Dermatoscopy is a method for early diagnosis of melanoma. To carry it out, a magnifying glass or a dermatoscope (epiluminescence microscope) is used. During the diagnostic process, it is possible to determine whether a nevus is dangerous. The doctor makes conclusions using the so-called ABCDE system . It has been used since 1985, analyzing nevi and determining the presence of such changes:
- A - asymmetry, that is, asymmetry;
- B - border irregularity, the presence of an uneven edge
- C - color, different parts of the mole have different colors;
- D — diameter, diameter greater than 6 ml;
- E - evolving, variability.
In modern medicine, a number of research methods are used when the development of melanoma is suspected.
- Indication of a tumor with radioactive phosphorus is based on the fact that selective accumulation of radioactive phosphorus occurs in the tissue of a growing malignant tumor. This test has not only diagnostic value, but also allows you to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment.
- Thermal differential test - it is based on the temperature difference between the tumor site and healthy skin. An electric thermometer is used to carry out the test.
- Cytological diagnosis is the only morphological method for verifying a clinical diagnosis. a biopsy be performed if melanoma is suspected because of the danger of stimulating the growth of the tumor. To conduct the study, smears and scrapings are taken from the surface of the tumor. If melanin pigment is present in the cytoplasm of tumor cells, this is a significant sign of the development of melanoma. For different types of tumor, distinctive features are determined during a cytological examination.
The final diagnosis is established after a histological examination, which is carried out after total removal of the nevus. If necessary, additional research is carried out.
Classification and stages of melanoma development
In clinical practice, the international classification of melanomas according to the TNM system of the American Joint Commission on Malignant Neoplasms is used. It is used for many malignant tumors. The assessment takes into account the prevalence of the tumor and the presence of metastases:
- T—primary tumor. Classified depending on the thickness of the germination, the presence or absence of ulceration. It is determined after histological examination of a tumor tissue sample.
- pT—primary tumor.
- pTX—the primary tumor cannot be assessed.
- pT0—no data on the primary tumor.
- pTis - melanoma in situ (I level of invasion according to Clark) (atypical melanocytic hyperplasia, severe melanocytic dysplasia, non-invasive malignant lesion).
- pT1 is a melanoma 1 mm thick or less (pT1a is Clark grade II or III without ulceration, pT1b is Clark grade IV or V or with ulceration).
- pT2 - melanoma with a thickness of more than 1 mm, but not more than 2 mm (pT2a - without ulceration, pT2b - with ulceration).
- pT3 - melanoma more than 2 mm thick, but not exceeding 4 mm (pT3a - without ulceration, pT3b - with ulceration).
- pT4 - melanoma more than 4 mm thick (pT4a - without ulceration, pT4b - with ulceration).
- N - reflects the involvement of lymph nodes in the pathological process.
- Nx - there is no reliable data for a correct assessment.
- N0 - there are no signs of lymph node damage.
- N1 - metastases in lymph nodes up to 3 cm in size.
- N2a - metastases more than 3 cm.
- N2b - the presence of metastases in the skin or subcutaneous fat, located at a distance of more than 2 cm from the main tumor (transit metastases).
- N2c - the presence of metastases in lymph nodes larger than 3 cm in combination with transit metastases.
- M - presence of distant metastases (extending beyond the anatomical area).
- Mx - there is no data to determine the presence of distant metastases.
- M0 - distant metastases are not detected.
- M1a - distant metastases in the lymph nodes, skin or subcutaneous fat.
- M1b - presence of metastases to internal organs.
The depth of ingrowth (vertical growth) of melanoma is divided into 5 levels of invasion according to Clark:
- Level I - non-invasive tumor limited to the epidermis;
- Level II - tumor cells are located in the papillary layer of the dermis;
- Level III - tumor cells are located between the papillary and reticular layers;
- Level IV - tumor cells are found in the reticular layer of the dermis.
- Level V - tumor cells are found in subcutaneous fat.
Based on the above criteria, the clinical stage of melanoma is determined (Fig. 2).
Figure 2. Stages of melanoma development. Source: Alexilus / Depositphotos
Treatment with folk remedies
Under no circumstances should you use unverified sources regarding any traditional methods of treating melanoma. Treatment with herbal preparations, soda or other methods can lead to short-term relief of the condition, but in the end the person will miss precious time, and the outcome will be sad.
Many similar reviews and stories can be found on thematic forums: “Melanoma Fight”, “Life Forum”, etc. If you read any patient forum or VKontakte discussions, you can find out a lot of evidence that treatment with traditional methods can become a fatal mistake.
How we treat
In addition to the enormous experience and professionalism of doctors, in addition to the latest technical base and the current range of drugs used, one of the significant advantages of treating melanoma in Euroonko clinics is the personal attitude of specialists towards this disease. Why for Andrei Lvovich Pylev the treatment of melanoma is an area of special scientific interest - in the following video:
Prevention
To prevent the development of a malignant tumor, important rules of prevention should be taken into account:
- Conduct self-diagnosis, paying attention to all changes in nevi. At the first suspicion, consult a doctor. If a specialist advises removing the nevus, you must do so.
- Avoid exposure to harsh sunlight. Do not be in the sun from 10 am to 4 pm, do not overuse sunbathing, and do not visit solariums. When exposed to sunlight, wear clothing that protects exposed skin.
- Use sunscreens with a protection factor (SPF) of 30 or more. Follow the instructions when using such products.
What are the recommendations after treatment for melanoma?
For patients who have survived skin cancer, there is a list of mandatory rules that must be followed in order to avoid or promptly detect recurrence of the disease.
First of all, every month the patient should independently or with the help of relatives examine their skin for the presence of suspicious formations and the first alarming symptoms of relapse.
The patient must adhere to a schedule of visiting a specialist for consultation and examinations (as indicated).
Patients with cured first stage of the disease are recommended to visit the doctor once every three months for the next few years. With the second, third and fourth stages - once every month for four years.
It is also very important to avoid sunlight and stop visiting solariums if the patient used these services before illness.
Such patients must qualitatively change their lifestyle. Exercise, adequate sleep, and proper and balanced nutrition are encouraged. Quitting bad habits (drinking alcohol, nicotine) is an important measure in preventing relapse.
Playing sports does not involve intense physical activity. This could be walking, aerobics, fitness.
This disease is extremely stressful for the psyche. And even if the disease was overcome, unpleasant memories can still haunt the mind of such a person. Therefore, it is important to use stress prevention methods (meditation, relaxation). It is recommended to visit a psychotherapist if the patient cannot independently cope with the negative emotional background of the disease.
The participation of family and loved ones in rehabilitation after treatment for melanoma is also important. Regular communication, support, and spending time together will only have a beneficial effect on the psychological state of the patient.
Diet
Diet for cancer
- Efficacy: no data
- Duration: until recovery or lifelong
- Groceries cost: 2500 - 4800 per week
The diet of patients with melanoma should be light, low in calories, but still contain a sufficient amount of protein. The menu must include the following products:
- Lean meat - chicken, turkey, rabbit, beef, veal.
- Eggs – preferably quail.
- Vegetables – carrots, pumpkin, avocado, broccoli.
- Fruits – apples, citrus fruits.
- Cereals – buckwheat, lentils, wheat.
- Legumes - peas, beans.
- Dairy – cheese, milk, curds.
- Fish, seafood.
- Sesame seeds, flax.
- Nuts.
- Green tea.
It is better to cook by steaming, in the oven, using natural seasonings and spices. It is better to avoid fried foods. It is recommended to replace side dishes with boiled vegetables.
The following foods should be excluded from the diet:
- Margarine.
- Lard, animal fats.
- Sweets.
- Alcohol.
- Smoked meats, canned food.
- Pickles.
Hyperpigmentation in children
In childhood, spots on the skin appear much less frequently than in adults, and hyperpigmentation is usually a consequence of injury to the epidermis. Rash, diaper rash, inflammation in children - all this can leave behind areas of skin that are darker than the rest of the body.
You should be wary if a rash of unknown etiology appears for no reason. This may indicate the presence of serious acquired or hereditary pathologies.
As for freckles, they can appear by the age of 3-4 years and go away with age. Freckles do not pose any health risk.
Prognosis for melanoma
This tumor spreads very quickly, so the prognosis depends on how early the disease is diagnosed and treatment started.
- In the first stage, the 5-year survival rate is 95-97%, the 10-year survival rate is 95%.
- Prognosis for stage 2 melanoma: 5-year survival rate is 70-86%, 10-year survival rate is 57-67%.
- At the third stage: 5-year survival rate – 40-78%; 10-year survival rate – 24-68%.
- Life expectancy at stage 4: 5-year survival rate - 15-20%. 10-year survival rate is 10-15%.
Melanoma on the hand. Photo.
- Mole removed without histology
- After two months, a black spot appears at the removal site
- Removal and histology - melanoma Breslow 1.1, Clark IV, 1 mitosis sq/mm
- Wide excision in Israel and sentinel lymph node biopsy
History: Why do we need histology of a benign mole?
Methods for removing age spots on the face and body
Not only a dermatologist, but also a cosmetologist knows how to treat hyperpigmentation. Rashes on the surface of the skin are removed in cosmetology in several ways. You should not carry out the procedure yourself, as incorrect actions can aggravate the situation and lead to irreparable consequences. To solve the problem with the appearance of spots on the body, you need to contact professionals who have graduated from the Academy of Cosmetology.
Mesotherapy
During the procedure, the skin whitens and is also saturated with nutrients. Mesococktails contain vitamins, hyaluronic acid, minerals, medicinal compounds, and natural plant extracts.
Mesotherapy procedures are usually performed on the face. But sometimes certain parts of the body, such as the neck and shoulders, are also bleached. As a result, the skin becomes not only light and uniform, but also elastic and fresh.
The duration of treatment is determined individually by a cosmetologist. The effect of mesotherapy lasts for at least 6 months.
Chemical peeling
This is the most effective method of getting rid of pigmentation. The procedure involves applying an acidic composition to the skin tissue, which stimulates exfoliation of the upper layer of the epidermis, that is, mechanical destruction of the spot cells occurs. This is what makes hyperpigmentation disappear.
Chemical peeling can be superficial, medium, or deep. The required depth of penetration, as well as the type of product, is determined by the cosmetologist.
The most common types of peeling:
- lactic;
- peeling with calcium chloride or trichloroacetic acid.
- retinoic;
- salicylic;
- almond;
- glycolic;
Each of the products, in addition to whitening, has its own effect: lifting, narrowing pores, normalizing the functioning of the sebaceous glands.
Laser peeling
How to get rid of stains forever? Do laser peeling. The procedure is carried out by removing a significant layer of the epidermis, so after the laser the skin needs to be restored. The effectiveness of this method of removing hyperpigmentation is based on the ability of neoplasms to absorb electromagnetic radiation that destroys spot cells.
The mechanism of action of laser peeling: new cells formed at the site of laser exposure actively synthesize and accumulate the required amount of melanin. This is why the skin color of the affected area becomes lighter.
The correction procedure is carried out in at least 3 stages. The breaks between them are about 10 days.
Benefits of laser peeling:
- This method of removing pigmentation has no side effects and no patient care is required;
- no anesthesia is used during the procedure;
- laser peeling gets rid of spots relatively quickly, and, most importantly, forever;
- The first result is noticeable after the first stage of peeling.
Ozone therapy
The procedure is carried out in two ways: applications and subcutaneous injections. Ozone therapy is actively used in the treatment of foci of post-inflammatory pigmentation, as well as acne, and enlarged pores.
The procedure has an anti-inflammatory and absorbable effect. It also stimulates the active functioning of the immune system.
Reviews from patients indicate that a positive result can be achieved after just 2-3 ozone therapy procedures for primary and secondary hyperpigmentation. However, the duration of treatment, as well as its scheme, is determined by the dermatologist. Injection methods are not suitable for everyone.
Cryotherapy
The procedure involves influencing cells oversaturated with melanin using liquid nitrogen, which acts as a corrector. It destroys them and stimulates the regeneration process. As a result, new young cells with a normal content of the substance responsible for pigmentation are formed in place of the spots.
The procedure is usually well tolerated by patients. Sometimes they feel a slight burning and/or tingling sensation.
The disadvantage of cryotherapy is that after it is carried out, scars may appear, albeit slightly noticeable, on the affected areas. That is why the procedure is almost never performed to remove hyperpigmentation on the face and, especially, to eliminate periorbital spots.
Phototherapy
This is the most gentle method of getting rid of age spots. But it requires more time. To achieve results with primary hyperpigmentation, you need to undergo about a dozen procedures.
Phototherapy is based on photothermalysis, which destroys cells by exposing them to heat. In addition to removing pigment, the synthesis of elastin and collagen is stimulated during the procedure.