Throughout life, each person can observe the appearance of various neoplasms on the skin: moles, warts (or papillomas) .
They can be either benign or malignant.
A mole or wart (papilloma) are similar in that they can pose a danger in terms of malignancy - degeneration into a cancerous tumor, but their difference is in the reasons for their appearance, external manifestations, properties and locations.
To avoid dangerous health consequences, you should understand the difference between these neoplasms.
What is a mole
Moles or nevi (medical term) differ in shape, color and size.
They can be brown, black, purple and red.
They are located on the surface of the skin or slightly rise above the skin.
After six months of age, the first nevi may already form on the child’s body.
They can appear throughout life with varying intensity.
The formation of nevi is associated with the accumulation of melanocytes in certain areas of the skin surface.
A mole is a benign formation and does not pose a danger, but under the influence of negative factors it can degenerate into a malignant form - melanoma.
The neoplasm carries a mortal danger to humans, as it has the ability to very quickly metastasize throughout the body.
Other types of skin lesions
- Another formation is atheroma , which appears at the site of blockage of the sebaceous gland, most often on the scalp, neck, and back. The formation is painless and not dangerous; when pressed with a finger, it slips away.
- Hemangioma is a tumor that occurs on blood vessels. If the hemangioma has grown on capillaries (vessels located in the superficial layers of the skin), then it looks like a reddish spot. Benign.
- Lipoma or wen - grows in the fat layer. When it reaches a large size and causes discomfort, the wen is removed. However, in some cases, a lipoma can degenerate into a cancerous tumor.
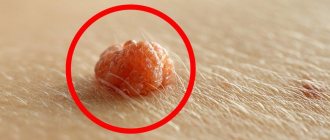
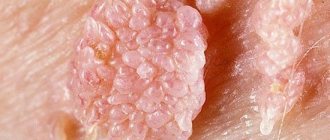
- Papillomas or warts are formations of viral origin, often very similar to moles. Occurs with reduced immunity. They come in different colors and shapes. They can appear unnoticed and disappear without a trace. But sometimes they degenerate into cancerous formations.
There are many other types of neoplasms that cannot be distinguished from each other, much less understand their nature and danger to health. Without tormenting yourself with doubts, it is better to trust your doctor.
Reasons for the appearance of a mole
Among the reasons for the formation of nevi are: genetic predisposition, prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation on the skin, hormonal pathology and other factors.
Most often, the formation of moles on the body is observed during puberty and in women with the onset of pregnancy.
This is explained by an increase in pituitary activity during this period of a person’s life.
Often people tend to consider any formation on the skin as moles, however, this is a big misconception.
Therefore, any neoplasm on the skin must be identified by a specialist.
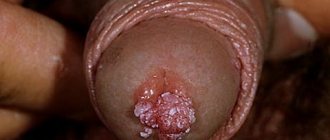
What is papilloma
Papilloma (wart) is a benign formation caused by papillomavirus (HPV).
Growths can appear on various parts of the body, both on the skin and on the mucous membranes, including the surfaces of internal organs.
Favorite places for warts to be localized are the groin and axillary areas, feet, and neck area.
Some types of the virus are highly oncogenic, causing cancer formation.
The tendency to malignancy is more typical for hanging and large papillomas.
Infection with the human papillomavirus can occur not only through sexual contact, but also through household contact.
Papillomas can vary in shape and size, and sometimes remain completely invisible.
HPV is able to penetrate the body through the skin and mucous membranes.
The pathogen immediately begins to reproduce, causing organ damage.
Signs of infection do not appear immediately, so the patient may find out that he has an infection months or even years later.
Why do papillomas appear?
The main reason for the formation of papillomas is infection of the body with HPV, which most often occurs through casual sexual contact.
Factors that can trigger the growth of warts include:
- decreased immune defense of the body
- alcohol abuse
- presence of chronic, regularly recurring infections
- pathology of the digestive system
- stress conditions and depression
- long-term antibiotic treatment
- visiting the swimming pool, public bath, sauna
The distinctive features of papillomas are:
- rapid appearance of growth
- spread of papillomas due to rapid growth
- increased risk of cancer
- high contagiousness of papillomas
- merging of warts into one large growth
When multiple neoplasms appear on the surface of the skin, this should be the reason for a full diagnosis for HPV infection and urgent treatment.
Molluscum contagiosum
What it looks like: single painless dense nodules of a round shape, sometimes the skin acquires a pink tint or a pearlescent sheen. The size of the rashes ranges from a millet grain to a pea. Causes of appearance : caused by a parasite - a saprophyte, which is activated when immunity decreases. What is dangerous: growth, increase in size of rashes. How to fight : mechanical squeezing of nodules followed by treatment of the affected surface with antiviral ointments and immunomodulators.
What is the difference between a mole and a papilloma
The main distinguishing feature of neoplasms is the cause of origin.
Papillomas are formed as a result of infection of the body with papillomavirus, and nevi are formed as a result of the accumulation of melanocytes.
To understand what kind of tumor this is, you need to pay attention to the following signs:
- Localization location. Warts form in places where skin friction and sweating most often occur, as well as on mucous membranes. A nevus can form on any part of the skin surface. No factors can influence the location of the mole.
- The edge of a healthy mole is always smooth, the formation has a symmetrical shape.
- The size of the wart is small; if damaged, it can rapidly increase in size. Nevus can have different sizes: from small to very large.
- Presence of pigmentation. The mole can have a color: black, brown, red, purple. Papilloma always has a light pink tint.
- Warts are characterized by a loose structure, while nevi are dense, hard formations. It should be noted that these formations do not always meet these criteria.
- The mole does not contain any vessels. Papilloma is equipped with capillaries.
- Nevi can be inherited, but papillomas cannot.
Moles and papillomas: what must be removed and when
Experts do not recommend removing moles if they behave calmly and do not cause discomfort to their owner.
If any complications arise from the nevus, and doctors strongly recommend removing it, then it is advisable to do this as soon as possible.
It is strictly not recommended to do this yourself at home.
It is necessary to get rid of unwanted moles only in a medical facility.
Before removing the tumor, the specialist will conduct the necessary examination, after which he will suggest one of the methods for removing the tumor.
Doctors are well versed in which nevus removal methods are the most effective and safe.
As for papillomas, you will also need to consult a doctor.
After an examination and a series of diagnostic tests, the doctor will prescribe removal of growths using the most gentle method and antiviral therapy.
Treatment of papillomas and warts comes down to their removal; the difference is that for each type of tumor, the doctor selects the method that will be most optimal for each specific case.
If it is necessary to send biomaterial for diagnostics, radio wave therapy or surgery will most likely be used.
In order to remove tumors, the following techniques are used:
- Cryodestruction . The technique is based on the use of low temperatures. Liquid nitrogen is used to freeze papillomas, which provokes necrosis of pathological tissues.
- Chemical removal method . Medications containing high concentrations of substances that cause chemical burns are used. The formations dry out and subsequently fall off.
- Electrocoagulation. High frequency current is used for removal. The tumors are burned out.
- Laser therapy. This technique is the most preferable, since after removal of papillomas there are no traces left on the skin. After the procedure, the recovery period is short.
- The radio wave technique is based on the use of radio waves, which promotes excision of the growth.
- Surgical method of removal . A scalpel is used to cut out the affected tissue, after which the material is sent to the laboratory for histological analysis. The technique is indicated for suspected malignancy of the process.
For small papillomas, conservative therapy is carried out using antiviral drugs.
Diagnosis of moles and papilloma
If a neoplasm is detected on the skin or mucous membrane, you should not wait for it to resolve on its own.
This will not happen.
To dispel all doubts regarding the oncogenic activity of the growth, you should immediately go to a specialist, preferably an oncologist-dermatologist.
The doctor will examine the tumor and decide what tests need to be taken.
What is the difference in tests and histology for papillomas and moles?
It all depends on what kind of neoplasm it is.
- 1. If it is a nevus that does not show signs of degeneration, then it will be removed, and the biomaterial will be sent to the laboratory to determine the nature of the neoplasm. If malignancy is present, histological analysis will show a positive result.
- 2. If HPV is suspected, the patient will be examined for the presence of papillomavirus and its type. After removing the growth, a histoanalysis will be performed to determine the presence of cancer cells.
There is no difference in performing dermatoscopy and the initial examination of moles and papillomas.
The use of a dermatoscope is necessary so that the doctor can evaluate the structure of the skin formation and identify possible changes.
Diagnostics
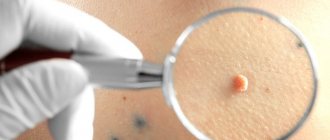
In the process of diagnosing nevi, the doctor uses both standard methods (history collection, visual examination) and instrumental diagnostic methods. In this case, studies such as dermatoscopy, biopsy and histological analysis of the mole are highly informative.
Dermatoscopy
The essence of the dermatoscopy method is to examine the skin under magnification. During the examination, the doctor evaluates the color and structure of the epidermis, identifies the main characteristics of skin rashes, examines the epidermal-dermal junction and the papillary layer of the dermis.
To perform the study, a special device is used - a dermatoscope. This device may resemble a small magnifying glass (manual dermatoscopy) or be a special device that can be equipped with a digital photography function with the possibility of subsequent detailed, even computerized, analysis of various skin structures.
The dermatoscopy method is simple and accessible, but at the same time very informative. Examination of moles by a doctor using a dermatoscope significantly increases the chance of detecting malignant skin tumors, primarily melanoma.
Treatment of moles and papillomas
Therapy will depend on the type of tumor.
- 1. After removal of a mole, as a rule, no treatment is required, unless it is malignant. In case of degeneration, the patient will continue to be treated by the oncologist.
- 2. If the PCR analysis confirms the presence of the virus, this means that the neoplasms were provoked by papillomavirus. After they are removed, the patient will be prescribed antiviral therapy. The results of the analysis will also answer the question regarding the possibility of degeneration into an oncological disease.
The use of medications to remove papillomas is possible only with the approval of a doctor.
Since the prognosis of the disease with unauthorized removal of growths can be sad.
Of the products that are sold in the pharmacy chain for the removal of papillomas, the following are very popular: Salicylic acid, Podophyllin, Feresol, Superclean.
If there is no effect, more radical methods are used to remove growths.
When growths degenerate into a malignant neoplasm, the method of surgical excision is used.
Transformation into a malignant tumor
Under certain conditions, moles can degenerate into malignant formations - melanoma. Such factors include ultraviolet radiation, trauma to the mole, and genetic characteristics. During degeneration, the appearance of the mole changes - it increases in size, becomes ugly, multi-colored. The condition of the formation can be assessed using dermatoscopy and visual examination by a dermatovenerologist or oncologist.
You should constantly monitor moles and see a dermatologist at least once a year. This is especially true for those whose relatives had malignant skin diseases.