| "Before and after" | Prices | Question answer | Doctors | Sign up |
Modern advances in dermatocosmetology make it possible to effectively get rid of acne on the face and body. Acne is a disease that causes many aesthetic problems. In addition, quite noticeable scars may remain in place of the inflammatory elements on the skin. Therefore, timely treatment of acne not only helps eliminate acne, but also prevents the appearance of post-acne scars.
The first step is to conduct an examination to identify the main cause and factors supporting the occurrence of acne. These may be hormonal changes, the spread of subcutaneous mites (Demodex), gynecological diseases, and disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract.
There are several methods for treating acne, the use of which depends on the results of the examination and the extent of the disease.
- Drug treatment: drugs that reduce the secretion of sebaceous glands, antibacterial agents, correction of underlying diseases.
- Laser treatment of acne allows you to effectively clean the mouths of the skin glands and disinfect acne lesions.
- Laser carbon peeling - cleanses the openings of the sebaceous glands, tightens pores, eliminates inflammation, stimulates blood circulation, significantly reduces the severity of age spots
- Cosmetology procedures – various types of cleaning (mechanical, ultrasonic). They are performed mainly to remove comedones - horny plugs that cover the mouths of the skin glands. Additionally, special medicinal cosmetics can be used.
- Laser treatment of post-acne scars. The result of acne is often multiple retracted scars scattered across the face. Various types of laser resurfacing are used to treat them. Polishing is performed only after all rashes have resolved, making the skin of the face more even and smooth.
What is the cost of treating problem skin?
The cost of treating acne, post-acne, pimples, problem skin depends on the set of procedures used. A regimen may be prescribed for home medicinal treatment, as well as hardware and aesthetic cosmetology procedures for cleaning and disinfecting inflammation, and later to eliminate the consequences in the form of remaining scars and pigmentation.
You will find all prices for the treatment of problem skin in the price list. The exact cost of treatment will be determined by a cosmetologist after an initial examination and identification of the existing problem.
What is acne?
Acne
– this is the result of chronic inflammation of the sebaceous glands, caused by:
- genetically predetermined level of secretory activity of the sebaceous glands;
- hormonal imbalance;
- hyperkeratosis.
Why does this unpleasant disease most often first make itself felt in adolescence? The fact is that during this period in the blood the content of sex hormones and adrenal androgens increases many times over, enhancing the work of the sebaceous glands. The sebum they produce is the most important element of the hydrolipid mantle of the dermis, which contains complex compounds of fatty acids, polyhydric alcohols, glycerin, cholesterol, and wax esters.
In itself, the increased secretion of skin secretion does not pose a danger, however, at the same time, at the mouths of the sebaceous ducts, the layer of corneocytes, dead epidermal cells, thickens, that is, hyperkeratosis occurs, making it difficult for sebum to come to the surface. Gradually, it accumulates more and more, and in this environment rich in lipids (fat-like substances), ropionibacterium acnes, bacteria that live in the microflora of the sebaceous glands, begin to actively multiply. They intensively produce lipase - an enzyme that breaks down glycerol into free fatty acids, the abundance of which further clogs the ducts, which ultimately leads to the formation of a plug - a comedon. Under comedones, staphylococci, streptococci and other pathogens of purulent infections thrive, easily penetrating the dermis when the protective barrier of the epidermis and its normal microflora is disrupted, as well as when immunity is reduced.
Manifestations of acne on the face and body
- Increased sebum secretion, mainly in the so-called T-zone (forehead, nose, chin).
- Primary non-inflammatory elements are various types of comedones: (whiteheads or milia, blackheads, microcysts, etc.).
- Inflammatory lesions such as red bumps or papules and pustules (red around the periphery with a white head in the center).
- Deep nodular skin lesions, stagnant spots and scars.
Our clinic is a multidisciplinary medical institution. The Endocrinological Research Center is the leading clinic in Russia, where diagnostics and comprehensive treatment of acne in adolescents and adults is carried out within the framework of world standards.
Treatment methods for acne (whiteheads on the face and body, blackheads)
Experienced dermatologists and cosmetologists at our clinic in Moscow, after examination, medical history and mandatory examination, prescribe an individual course of acne treatment, choosing the optimal method.
Taking into account the degree of skin damage and the spread of the process, before performing the planned course of external procedures, it is possible to prescribe oral medications with a detoxifying effect, antibiotics, systemic retinoids, antiandrogens in women, and external pharmaceuticals for home care. When endocrine disorders are detected, their mandatory adequate hormonal correction is carried out.
Acne (acne disease) has various forms of manifestation and severity. Occurring in adolescence, the disease can drag on for several years and continue into adulthood. Scars and scars, age spots and congestive spots, as accompanying destructive elements in the outcome of the disease, remaining for life, create serious psychological discomfort.
A professional integrated approach to the problem, modern equipment and methods proven by many years of experience used in our clinic are the components of effective treatment not only for acne. Our doctors also successfully eliminate their consequences - post-acne (age spots, scars, stagnant bluish spots).
Treatments for acne
- a comprehensive procedure for manual atraumatic facial cleansing using certified cosmeceuticals from the world's leading manufacturers;
- chemical and enzymatic peels for the treatment of acne using various active ingredients;
- injection methods of treatment - mesotherapy, biorevitalization and bioreparation with anti-inflammatory, vascular components, microelements and vitamins;
- microcurrent therapy;
- injection carboxytherapy – microinjections of sterile CO2
- comprehensive treatment programs for the care of problem skin;
- acne laser treatment.
Treatment of acne (acne) on the face, back and other parts of the body with laser is one of the most modern, versatile and effective procedures in the complex dermatological treatment of acne in adult men and women at any stage.
Laser beam against acne
Acne is one of the most annoying problems of adolescence. To the numerous complexes characteristic of this age is added deep dissatisfaction with one’s appearance, sometimes reaching the point of self-loathing. Acne (various forms of acne), which do not pose an immediate threat to life and do not cause severe health problems, nevertheless often leave long-lasting scars on the skin and soul. The severity of the consequences of acne makes us think about the fact that the largest number of suicide attempts occur among dermatological patients. Dermatology patients make more suicide attempts than patients with any other disease, including cancer.
Acne is the most common disease in the world: according to various sources, acne affects 85–90% of adolescents and up to 25% of adults. The scale of this disease is evidenced, for example, by the fact that in the United States alone, more than $1.4 billion is spent annually on the treatment of acne.
Unfortunately, treating acne is not easy. Traditional therapy includes the following components:
- antibiotics for topical use;
- oral antibiotics;
- topical retinoids;
- diet.
Without denying the need for traditional types of treatment, we note their serious shortcomings. This is, firstly, the resistance of a fairly large number of patients to these methods of therapy, especially in the case of severe forms of acne (i.e. treatment is carried out, but improvement does not occur). Moreover, resistance to antibiotic therapy is increasing every year. Secondly, the long period of therapy: the first signs of improvement occur weeks or months after the start of treatment. Thirdly, the need for multiple courses of treatment. What's especially troubling is that all of these methods (except diet) are associated with side effects, such as irritation, redness, or dryness of the skin when topical antibiotics or retinoids (vitamin A derivatives) are used, or gastrointestinal irritation when used orally. In addition, some synthetic retinoids, especially popular in the treatment of acne, negatively affect the emotional and mental state of patients, causing depression. The list of disadvantages of these methods goes on.
However, acne must be treated, and treatment should begin as early as possible. Therefore, while continuing to use traditional methods, doctors are looking for new possibilities for treating acne.
Among the new treatments that have emerged over the past few years are various methods of skin resurfacing. These are microdermoabrasion (mechanical skin resurfacing), chemical peels, and laser skin resurfacing. All of them are a procedure for removing the thin top layer of skin in different ways and in some cases they can achieve quick and impressive results. However, all three methods are very painful, are performed under anesthesia and require a long period of recovery treatment. However, the advantages of these methods include rapid removal of acne, which certainly improves the quality of life of patients, as well as the possibility of removing acne scars.
Other methods that have gained popularity in recent years include various types of light therapy and laser treatments. Both methods are based on exposure to light. A simple example of the positive effects of light on acne is exposure to the sun, after which, as a rule, improvement occurs. Therefore, in recent years, various artificial light sources, the impact of which is based on certain mechanisms, have gained popularity. As a rule, the effects of these light sources are well tolerated, the procedure takes about 10–30 minutes, after the procedure the skin looks no worse than before, and improvement of varying degrees of severity occurs after several procedures. Therefore, all these methods based on the use of artificial light sources have the right to exist.
However, the search for a well-tolerated treatment method that gives quick and lasting results after one or two procedures, especially for severe forms of acne, is still relevant. Therefore, in recent years, laser treatment methods have attracted particular interest, the therapeutic effect of which is presumably associated with the effect on propionibacteria and the porphyrin they contain.
Lasers are used on their own, and also as part of the photodynamic therapy method. Photodynamic therapy was created to treat cancer. It consists of using a certain dye substance (photosensitizer), which accumulates in the cells intended for destruction, then, under the influence of laser light of a certain wavelength, is activated and releases free oxygen, which kills these cells. Recently, reports have appeared that this method has begun to be used to treat not only cancer, but also other dermatological diseases, in particular severe forms of acne.
However, according to various sources, for the treatment of a wide range of dermatological diseases, including acne, lasers are in most cases successfully used as monotherapy, i.e., without the simultaneous use of other methods. Various types of lasers are used to treat acne.
Blue light sources with a wavelength of 405–420 nm (for example, ClearLight) are intended for the treatment of mild to moderate acne. Treatment should be carried out twice a week for 4 weeks (total 8 sessions), after which most acne disappears. The method is painless and does not cause complications.
Infrared diode lasers with a wavelength of 1450 nm (for example, Smooth Beam Laser, Candella Corporation, Wayland, USA) are used in a course of four procedures performed at intervals of 1 month. Once treatment is completed, most acne disappears and remission is observed for at least six months after treatment. Treatment with this laser is painful, so local anesthetics are used to reduce pain, and a cooling spray must be prescribed to prevent side effects such as hyperpigmentation and scars.
A pulsed dye laser emitting yellow light at a wavelength of 585 nm (eg: Nlite system, EUPhotonics, Swansea, Wales, UK), operating at low powers, is almost painless and provides significant improvement in papular lesions in most patients after a single treatment. A copper bromide vapor laser (for example, Pro Yellow), which emits yellow light with a wavelength of 578 nm, is also used to treat acne.
The latter two types of lasers, emitting yellow light and operating in a pulsed mode, are used to treat a wide range of dermatological diseases, especially for the treatment of various vascular disorders of the skin, and therefore these lasers are called “vascular lasers”.
The considered treatment methods are used only for mild forms of acne. It is also necessary to consider the pathogenesis and treatment of severe forms of acne, since this pathology causes the greatest difficulties in the practice of a dermatocosmetologist.
Acne vulgaris is a chronic disease that has a clearly traceable genetic predisposition, one of the manifestations of dense or mixed forms of seborrhea, or a disease of the hair follicles and sebaceous glands.
Early manifestations of acne consist of pathological hyperkeratosis of the follicular epithelium, which leads to blockage of the follicular duct with horny masses and the formation of microcomedones. Comedones, like plugs, clog the mouths of dilated hair follicles. Excessive production of sebum and disruption of the outflow of sebaceous gland secretions from the hair follicles create conditions for the proliferation of propionibacteria and the development of the inflammatory process.
The bacteria mentioned above produce chemotactic factors that attract polymorphonuclear leukocytes to the site of inflammation. Neutrophils concentrated in the follicle phagocytize propionibacteria and release hydrolytic enzymes that destroy the follicular epithelium. Purulent exudate from the follicle enters the dermis, causing inflammation and tissue destruction.
Depending on the localization of inflammation, papules, pustules, indurative and spherical (conglobate) acne are formed.
Papular acne is presented by clinically pink nodules with a diameter of 2–5 mm, hemispherical in shape, with a comedon at the apex. Subsequently, a pustule appears in its place. Inflammatory phenomena increase, pain occurs. After regression, pigment spots or small scars form in place of the pustules. Against the background of multiple papules and pustules, the inflammatory process around the hair follicle spreads to the surrounding tissue, a deep, dense, painful infiltrate with a bluish-purple coloration with a diameter of 1 cm or more occurs, and nodes (indurative acne) are formed. In these cases, surgical treatment is indicated, which, as a rule, entails gross cicatricial changes in the skin.
In this case, inflammation can develop at any stage of acne, occurring both in the superficial and deep layers of the dermis and even in the hypodermis, which determines the variety of clinical manifestations of the disease.
Considering the described mechanism of acne development, it would be advisable to consider the inflammatory process from the point of view of microcirculation disorders, which is one of the main links in the pathogenesis of this pathology.
Normally, the microvasculature (MCB) consists of repeating functional units - microdistricts (modules). Each of these units is a complex system consisting of arterioles, precapillaries, capillaries themselves, postcapillaries, venules, lymphatic capillaries and postcapillaries, nerve conductors, and interstitial substance. There are multiple anastomoses between the microvessels. In the places where they originate in the circulatory section of the MCR, there are groups of smooth muscle cells that form sphincters.
This entire complex provides and maintains metabolic and hemodynamic homeostasis in the microdistrict. Each module is separated from the neighboring one and has isolated paths for blood delivery and outflow.
Skin vessels have the ability to quickly and variedly respond to the influence of certain stimuli, which is based on the phenomena of vasoconstriction and vasodilation caused by vasomotor nerves.
To a greater extent, this applies to areas of the skin where there are a large number of arteriovenular anastomoses (face). Where there are few or none of them, vasodilation and vasoconstriction are determined by the state of basal vascular tone.
In acne, the initial hyperemic reaction of the skin is gradually complicated by stagnation of blood in the venules as a result of spasm of the afferent vessels, followed by the development of microangiopathies and blood stasis.
It must be emphasized that the progression of acne is characterized by dynamic changes in the vessels of the MCR. Already at the early stages of the disease, compensatory-adaptive processes develop in the form of opening of existing MCR networks, the formation of intervascular anastomoses, and an increase in the number and expansion of lymphatic terminals. This ensures adequate vascularization, normalizes gas exchange in tissues and the excretion of metabolites. With a long course of the disease, a significant reduction of the capillary network, restructuring of post-capillaries and venules, and their dystonia are observed, which play a significant role in the development of hemodynamic and metabolic disorders.
Thus, one of the conditions for successful treatment of acne can be considered the impact on these pathologically altered vessels, which can radically affect the morphofunctional state of microcirculation in inflamed areas of the skin.
Currently, there are various types of lasers used to treat vascular skin pathologies. These lasers differ both in output characteristics and in the way their radiation interacts with tissue.
For example, the Yakhroma-Med copper vapor laser simultaneously generates radiation of two wavelengths: green (511 nm), which is well absorbed by melanin, and yellow (578 nm), which coincides with the absorption peak of oxyhemoglobin. A filter is used to highlight one of the waves.
Green light is used to target pigmented formations, and yellow light is used to target vascular formations. The copper vapor laser, which is a quasi-continuous laser, nevertheless operates on the principle of selective photothermolysis. It is clear that a laser with such characteristics can selectively treat vascular or pigmented skin defects with minimal damage to surrounding tissue. The special advantages of a copper vapor laser are the absence of purpura after the procedure and the possibility of influencing deep-seated inflammatory elements of acne.
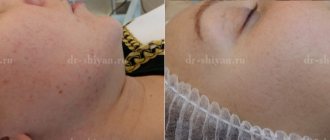
One of the main indications for the use of the device is severe manifestations of acne: indurative acne, widespread conglobate acne, interconnected by deep passages, with the formation of fistulous passages and the release of purulent exudate from them (Fig. 1, 2).
| Figure 1. A patient with indurated acne with purulent contents before treatment (a) and 7 days after treatment with a laser device (b) |
Treatment is usually carried out with radiation at a power of 0.7 W, then the power is slowly increased until some change in the color of the elements is achieved. During laser therapy, it is possible to open individual conglobates and release purulent contents from them. The discharge is removed, and the surface is treated with antiseptics (manganese solution, chlorhexidine solution, etc.). After the procedure, the surface must be treated with the wound-healing hydrocolloid emulsion Uriage Cicactiv, produced by the French dermatocosmetics laboratory Uriage. Cyclaktiv helps restore the skin structure after physical factors (laser, electrocoagulation, dermabrasion, etc.) and mechanical damage (abrasions, cuts, superficial burns, etc.). It contains several substances with different effects: sodium alginate and hydroxyproline provide wet disinfection of the wound, and D-panthenol, zinc gluconate and comfrey in combination with Uriage thermal water provide scarless healing. Cykactiv emulsion is applied to thoroughly cleansed skin 2 times a day until tissue integrity is completely restored.
To prevent the occurrence of pigment spots in areas affected by the laser, it is necessary to use dermatocosmetics with a maximum sun protection factor. Uriage laboratory specialists recommend the use of extreme protection cream SPF 60, SPF 90, and a stick for local application of SPF 60. Uriage sunscreens contain a complex of latest generation chemical filters that effectively protect against α- and β-ultraviolet rays, and mineral screens - micropowders, absolutely safe for any skin type, aquasponges (Uriage laboratory), which provide complete hydration of the skin during active insolation and powerful antioxidant protection in the form of a complex of vitamins E, C and Uriage thermal water.
At the Northwestern Center for Laser Medicine, 46 patients with various forms of acne were under our supervision. All patients underwent laser therapy. The age of the patients ranged from 15 to 38 years.
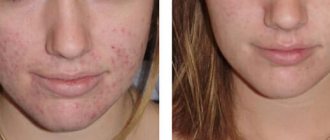
| Figure 2. A patient with a severe form of acne (widespread conglobate acne, interconnected by deep passages, with the formation of fistulous passages and the release of purulent exudate from them) before treatment (a) and 2 weeks after laser therapy (b) |
Mostly these were patients with severe forms of acne: multiple papular and pustular elements, indurative acne, widespread conglobate acne, interconnected by deep passages, with the formation of fistulous passages. Before laser therapy, all patients received traditional anti-acne therapy: antibiotics, vitamins, vascular drugs, externally - the entire arsenal of anti-inflammatory drugs. The positive dynamics were insignificant. The elements partially resolved, but formed again in the same place, and therefore these patients were sent for treatment by cosmetologists to the North-Western Center for Laser Medicine. The course of treatment ranged from 1 week to 1 month; after laser therapy, complete resolution of inflammatory elements was noted without the formation of scar changes, i.e., no complications were observed (see Fig. 1, 2). All patients were observed from 6 months to 1 year. As a result of laser exposure, no recurrences of pustular or conglobate elements were observed.
Thus, the use of high-energy laser exposure makes it possible to achieve significant success in the treatment of acne. In addition, such effects of laser radiation with a wavelength of 578 nm, such as a minimal zone of thermal damage, the absence of a wound surface and, therefore, minimal cosmetic losses, provide the laser with significant advantages over other methods in the treatment of severe forms of acne.
S. V. Klyuchareva, Candidate of Medical Sciences, St. Petersburg State Medical Academy named after. I. I. Mechnikova, St. Petersburg