Doctors Cost
Price list Doctors clinic
The Bartholin gland is located in the vestibule of the vagina, at the base of the labia majora. Its main function: moisturizing the vaginal and vulva area, producing lubrication during arousal. Pathogenic bacteria enter it quite often. This may be due to a general decrease in the body's resistance or changes in local immunity, wearing tight underwear made of synthetic materials, genital infections, poor hygiene, and much more.
Inflammation of the Bartholin gland is called bartholinitis. Bartholinitis provokes tissue swelling, blockage of the gland and is fraught with the appearance of an abscess. This is a complication that is characterized by the appearance of purulent contents. Opening up bartholinitis or an abscess is perhaps the most effective way to quickly get rid of the disease and return the gland to normal function.
Why does an abscess occur?
The causes of bartholinitis are very extensive:
- Infection with pathogenic flora (chlamydia, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis or other STI);
- Reproduction of opportunistic microorganisms - streptococci, Candida fungi, E. coli, etc.;
- Factors that reduce resistance to infection are previous severe illnesses, allergic reactions, poor hygiene, swimming in open water, injuries (for example, due to too active sexual intercourse, medical procedures), hypothermia, vitamin deficiency, etc.;
- Failure to comply with hygiene rules;
- Wearing tight underwear;
- Promiscuous sex life without the use of protection.
A combination of several pathogens at once is possible. It is worth noting that infection can enter the gland not only from the vagina, but also from the urethra, if cystitis or urethritis occurs. More rare routes of entry into the bloodstream and lymph from other foci of inflammation, for example, with tonsillitis, inflammation of the kidneys, etc.
Diagnosis of the uterus
As a rule, correct diagnosis of a vaginal gland abscess is not difficult and makes it possible to determine subsequent treatment tactics. To detect suppuration of the large gland of the vestibule of the vagina, the following diagnostic tests and tests can be performed:
- analysis of peripheral blood composition to determine the severity of pathological changes;
- biopsy of the cyst to exclude oncological processes;
- bacteriological culture from the patient’s genitals, which will help establish the presence of sexually transmitted pathologies.
The need for additional diagnostic examinations will be decided by the treating doctor on an individual basis. In this case, many factors will be taken into account: the presence and nature of pathological signs, the condition and age of the patient, the number of pregnancies and abortions, features of the menstrual cycle.
Abscess symptoms
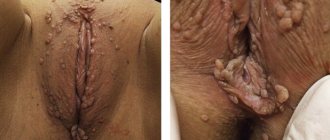
False and true abscess of the Bartholin gland are distinguished. If only the excretory duct is infected, and the glandular tissues are healthy, we are talking about a false abscess. The inflamed duct is filled with purulent contents, stretches, and its opening is blocked, while in the surrounding tissues, as a rule, there is no suppuration. A true abscess is characterized by suppuration of the gland itself.
A false abscess has an acute, rapid onset. A painful sensation appears in the area of the labrum major, depending on the side of the affected gland, increased pain with active movement, sitting and walking, during intimacy. On the side of inflammation, there is pronounced swelling and redness of the skin, while the skin easily moves to the sides. In addition to local symptoms, high body temperature is often noted - up to 38.5-39 C, fatigue, chills and loss of strength.
A true abscess has an even higher temperature - up to 40 C, and pronounced symptoms of intoxication. The pain is constant even at rest; there is a feeling of “pulsation” of the affected area. In this case, it is advisable to perform laboratory tests - there is an increase in the level of leukocytes and ESR. Swelling of the labia can reach 5 cm in diameter, the skin over the abscess becomes bright red, motionless when palpated. In some cases, there is an increase in the inguinal lymph nodes from the causative side.
Treatment
Technique for opening an abscess. Preparation of the surgical field is usual. The hair on the external genitalia is shaved off, the vagina is washed with some kind of disinfectant solution (potassium permanganate solution, etc.) and, to avoid contamination with pus, it is tamponed with a strip of sterilized gauze. For pain relief, we usually use ether or chlorethyl stunning. The incision area is lubricated with iodine tincture. The incision should be made large and brought to the lower pole of the abscess, otherwise there will be pockets in which pus will accumulate, resulting in a purulent fistula that does not heal for a long time. An incision is made at the site of clearest fluctuation, where the tissue covering the abscess is thinnest. After the pus has drained, the abscess cavity is sprinkled with white streptocide or wiped with a small tupper moistened with iodine tincture; then a strip of gauze or a thin rubber tube is inserted into the cavity to prevent the hole from closing prematurely. At the end of the operation, the end of the gauze strip is removed, and after a day it is completely removed. A pad of gauze and cotton wool is placed in front of the vulva to absorb the pus flowing from the wound. It is unnecessary to apply a bandage. The drainage tube is replaced after 2 days with a fresh gauze strip or a drainage tube of a smaller diameter. It is necessary to ensure that the hole does not stick together before the granulations fill the abscess cavity. Vishnevsky ointment gives satisfactory results. Gauze turunda soaked in Vishnevsky ointment can be used immediately after incision of the abscess of the Bartholin gland. If the inflammation recurs or a purulent fistulous tract remains for a long time, then a radical operation is necessary, i.e., removal of the gland along with its excretory duct.
Consequences and complications of an abscess
As a result of a chronic abscess of the Bartholin gland, a cyst can form - a cavity with dense walls and contents. This will also require the intervention of a doctor, so if the symptoms weaken, you should not refuse surgical treatment, that is, opening the Bartholin gland abscess. Even if the symptoms have gone away due to spontaneous opening, you should definitely consult a doctor: there is a high probability that the duct will become blocked again and the disease will become chronic. In addition, it is important to identify the causes of inflammation - diagnose STIs, receive treatment that corrects the function of immune forces, etc.
Contraindications
Drainage of the cavity should also be carried out in case of independent breakthrough of the abscess. If this happens, you should immediately go to the hospital, as purulent contents remain in the cavity, which can cause a relapse. The doctor installs special tubes to drain the remaining fluid, after which they are treated with an antiseptic.
In addition, the contents of the abscess can enter the bloodstream and cause sepsis. For this reason, you should never open an abscess yourself or ignore the symptoms.
Features of intervention for Bartholin gland abscess
If acute bartholinitis can be cured using conservative methods, then when an abscess forms, the only reliable and effective method of therapy is an autopsy. It lasts no more than 15-20 minutes and is carried out as follows:
1. The doctor treats the surface of the genital organs with antiseptic solutions and performs local anesthesia. In some cases, general anesthesia may be used, but such a decision will require careful preliminary preparation - examination to ensure there are no contraindications, restrictions on food and drink intake.
2. The abscess of the Bartholin glands is opened, the contents are evacuated, and washed.
3. A drainage is installed - a thin tube that will prevent the hole from closing prematurely and will ensure the outflow of the resulting fluid. Usually it is installed for a period of no more than 5-6 days.
The doctor will also recommend the use of antibacterial agents, anti-inflammatory drugs, solutions for local compresses; will explain the features of the rehabilitation period and give recommendations for accelerating healing during the first time after the intervention.
Conditions that increase the risk of developing bartholinitis
Experts identify background conditions that can increase the risk of developing bartholinitis, and, consequently, its complications such as an abscess
- Various local microtraumas, which include scratching, scratching, most often occurring during sexual intercourse (when insufficient lubrication is produced). These places of violation of the integrity of the mucous membrane are the entrance gates through which the infection enters.
- Violation of general rules of personal hygiene. It is especially important to maintain good hygiene during menstruation.
- Tight underwear, which can interfere with the physiological outflow of secretions produced by the Bartholin gland. This secretion, which stagnates, provides ideal conditions for the growth and reproduction of pathogens.
- Unprotected promiscuous sex life. Sexually transmitted infections themselves can cause bartholinitis and abscess of the Bartholin gland.
- Chronic infection in the body. Foci of chronic infection such as pyelonephritis, caries, and so on, increase the risk of bartholinitis. In this case, the spread of infection will occur through the flow of lymph and blood.
- A general decrease in immunity or local hypothermia. This leads to the body becoming more vulnerable.
- Hypovitaminosis.
- Previously undergone surgical interventions on the external genital or internal genital organs, during which the rules of antiseptics were violated, or if all recommendations were not followed after the surgical interventions.
Recommendations after surgery
After opening the abscess, it is important to carefully follow the doctor’s recommendations:
- Avoid sexual intercourse during the recovery period;
- Do not visit baths, saunas, swimming pools, ponds;
- Washing in the shower instead of lying in baths;
- Avoid overheating and hypothermia;
- Give preference to loose cotton underwear.
As a rule, recovery occurs quite quickly. At first, it is preferable to remain in bed to prevent stress on the perineal tissue.
Signs of bartholinitis
The symptoms that will occur directly depend on the course of the inflammatory process and its location. Depending on the type of course of the process, chronic bartholinitis, acute bartholinitis, subacute bartholinitis, as well as a recurrent type of bartholinitis are distinguished.
Depending on the type of inflammatory process, they distinguish: Bartholin gland cyst (which is represented by a cavity containing fluid inside), Bartholin gland abscess (which implies the presence of pus), and canaliculitis (in which the excretory duct of the Bartholin gland is inflamed).
Causes
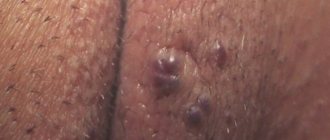
A vulvar abscess, even a small one, is a very serious disease. This inflammatory process is the necrosis of tissue under the influence of pathogens. Very often this situation occurs after shaving or hair removal, when a small wound forms at the site of hair growth.
A Bartholin gland cyst can also provoke the appearance of an abscess. This is a benign formation that occurs when the Bartholin gland on the labia is blocked. This gland secretes lubricant to keep the vagina moist. When an infection gets into the cyst, bartholinitis occurs.
There are also a number of factors that increase the likelihood of developing an abscess on the labia:
- increased sweating;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules, wearing dirty underwear;
- endocrine disorders, in which the secretion of the sebaceous glands is increased;
- injury to the skin without subsequent treatment with an antiseptic;
- ingrown hair due to improper depilation;
- poor nutrition, vitamin deficiency, weak immunity;
- hypothermia;
- diabetes;
- promiscuity.
Most often, an abscess is provoked by opportunistic microflora, that is, bacteria that constantly live on the skin and mucous membranes of a person. These are E. coli, staphylococci, streptococci, etc.
Prevention
Vulvar abscess is a terribly unpleasant disease that greatly affects a woman’s quality of life. To prevent the occurrence of an abscess on the labia, you must follow the following recommendations:
- Lead a healthy lifestyle, strengthen your immune system, eat a balanced diet.
- Avoid hypothermia, dress appropriately for the weather, and do not sit in the cold.
- Observe personal hygiene rules. You need to wash your face in the morning and evening, and blot your vulva with a clean, dry, individual towel.
- Sex with a non-regular partner should only be with a condom.
- If a woman removes hair in the bikini area, the skin must be treated with antiseptics before and after the procedure.
A healthy lifestyle and personal hygiene are the best measures to prevent abscess.
Share: