Condylomas are one of those problems that force a woman to seek help from a doctor.
There are several types of condylomas, differing according to various authors and classifications.
In addition to violating the natural beauty of a woman, condylomas pose a serious danger.
For women, the appearance of various types of condylomas on the body, especially in intimate places, is a reason to immediately visit a doctor.
This is due to the peculiarities of the development of condylomas.
For men's health, condylomas pose no less danger.
It is necessary to distinguish between different types of condylomas, because they require different treatment methods.
Types of condylomas: genital, flat
There are several different types of condylomas.
These differences are based on the type of growth the virus causes when it enters the body.
According to the nature of development, the following types of condylomas are distinguished:
- 1.Endophytic;
- 2. Exophytic.
In addition, doctors distinguish such condylomas as:
- Pointed;
- Flat ;
- Wide.
Flat condyloma
Endophytic development is characteristic of flat condyloma.
The exophytic form is manifested by the appearance of genital warts.
It is accompanied by pathological proliferation of epithelial tissues.
Condylomas are the most common manifestation of the virus (HPV).
Before the discovery of the pathogen, the cause of the growths was considered:
- Trichomoniasis;
- Syphilis;
- Gonorrhea;
- Candidiasis;
- Taking antibacterial drugs.
There was also an opinion that this condition was a variant of the norm.
Because of HPV, genital and flat condylomas are formed.
When penetration into the body occurs, the human papillomavirus begins to develop deep into the cells.
In this case, only a round, flat seal is visible on the surface of the skin or tissues of the genital organs.
During colposcopy, an atypical zone with a clear contour is observed.
This type of condylomas in women is often located on the cervix.
Condyloma lata
Particularly worth noting is condyloma lata.
Condylomas lata form in humans as a consequence of the development of treponema pallidum.
At its core, such a neoplasm is a sign of the presence of secondary syphilis in humans.
Such condylomas appear in the second stage of syphilis.
Condylomas lata never cause cancer.
Manifestations of syphilis have been known since ancient times, but they learned to treat it relatively recently.
The appearance of growths on the skin of intimate areas is associated with the progression of syphilis.
Syphilis goes through three stages in its development.
Each stage is manifested by a whole range of symptoms.
The second stage of syphilis is the period when condylomas can be expected to appear.
Important! Most often, the bacteria is transmitted during sex.
It happens that a person becomes infected through household items.
This is a contact and household route of transmission of Treponema pallidum.
Symptoms of syphilis appear a month after infection with treponema.
The first sign is the appearance of hard chancre in the genital area, anus, and in the oral cavity.
These are small round ulcers that do not hurt, the edges are uneven and undermined.
Then there is an increase in the size of the lymph nodes.
In the absence of therapy, the chancre atrophies and disappears without a trace.
After this, the patient develops other rashes.
This stage is also characterized by other growths, after which traces remain.
Remember! Patients during this period are very contagious!
This happens because the plaques constantly become wet and discharge appears.
This liquid contains a large number of bacteria
In places where growths form, there is constant inflammation.
Therefore, formations can spread.
Their surface is uneven, looks like tubercles, and is covered with a gray sticky coating.
Upon examination, the doctor may identify growths that resemble mushrooms.
These areas sit on a wide base - a pedicle.
After treatment of condylomas lata, scar changes always remain.
They can grow to huge sizes
First, bubbles appear, they connect with each other and grow.
Inside such blisters there is usually serous exudate.
It happens that there is no characteristic rash on the body.
Therefore, when characteristic growths appear, it is necessary to perform an analysis.
The cause of the development of other forms of condyloma is the human papilloma virus.
Diagnosis and clinical manifestations
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out through visual examination and laboratory tests of blood, skin, and mucosal tissue samples. As a rule, it is enough for a gynecologist, dermatologist, urologist or other medical specialist to examine the genital area to suspect an infection. After all, as mentioned above, the human papillomavirus on the genitals manifests itself as unsightly growths.
Important: HPV enters the body through microtraumas of the skin and mucous membrane. He can “sleep” for several months and even years. In people with strong immunity, doctors often record self-healing. Well, when the body’s protective functions are weak or under the influence of unfavorable factors, the virus is activated. Genital papillomas appear in men and women.
Clinical manifestations of the pathology are chaotic division of epithelial cells. Many patients complain of discharge and itching. But the main symptom of the disease remains condylomas that grow at the entrance or even inside the vagina in women, in the labia minora, near or inside the anus, around the genitals in men.
To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor may prescribe cytology of cervical tissue samples, PCR testing, and smears for concomitant sexually transmitted infections.
Condylomas acuminata
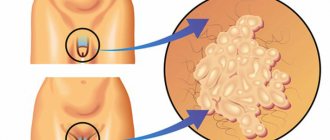
Genital warts look like long growths with a thin stalk.
The growths can be located separately from each other or combined into conglomerates.
There are other types of names, for example:
- genital warts,
- genital warts or
- viral condylomas.
Situations are possible in which inflammation develops in the condyloma.
This contributes to the addition of an additional infection.
Human papillomavirus infection (PVI) of the genitals is a disease that is transmitted during sex.
In recent years, the number of infected people has increased significantly.
This is facilitated by a disordered sex life.
Risk of condylomas:
- 1. Sexual life with a large number of partners;
- 2. Sex with an unknown man or woman;
- 3. Sexually transmitted infections;
- 4. Young age;
- 5. Smoking, alcohol intoxication;
- 6. Pregnancy period;
- 7. Diseases of the uterine mucosa;
- 8. Vitamin deficiency;
- 9. Decreased immunity.
It is conventionally believed that if a person has had unprotected contact with 3 or more partners during his life, the probability of his infection is 99%.
Genital warts - symptoms in women and men
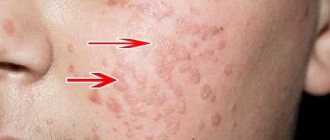
The symptom is the appearance of bright red formations.
The location of genital warts varies.
They develop in men:
- on the head of the penis;
- in the anal area;
- in the urethra;
- in the mouth.
In women, the symptoms of genital warts are similar.
Genital warts appear:
- in the anus;
- on the cervix;
- in the oral cavity;
- on the labia minora and majora,
- in the vagina;
- in the urethra;
- on the clitoris.
- on the vulva.
After anal sex with an infected person, growths develop in the anus area.
They manifest themselves as pain and discomfort during bowel movements.
Oral transmission of the virus can cause genital warts in the mouth.
Growths may appear after shaving.
This happens if a person uses someone else's shaving accessories.
Why are papillomas on the genitals dangerous?
The disease must be treated. This is a strong recommendation from both specialists from the World Health Organization and leading dermatologists-oncologists of Ukraine. In addition to the fact that papilloma on the labia or papilloma on the penis looks extremely unattractive, the disease, as mentioned above, is also dangerous.
Let's start small. When wearing tight underwear, during hygiene procedures, or during intimate caresses, the growth can be injured. And this is fraught with bleeding and secondary infection.
Important: The intimate area takes on an ugly appearance. This may cause disgust on the part of the sexual partner. Without treatment of the pathology, the area where the growths are located may increase. New areas of skin are gradually involved. The formations grow, over time they can interfere with urination and defecation.
If the outcome is unfavorable, HPV in the vagina and on the penis can take on a malignant form. A benign condyloma yesterday can become an oncological tumor with metastasis to the pelvic organs tomorrow. That is why you should not ignore the problem.
Important: Aggressive types of HPV cause cervical cancer, cancer of the small lips, vagina, penis and anus.
Routes of infection
HPV transmission occurs primarily through sexual contact.
The possibility of becoming infected during sex is 46–67%.
Homosexuals have a higher incidence of the disease.
Recently, there have been more and more cases of detection of the virus in the amniotic fluid during pregnancy.
Infection of children by parents is possible.
The incubation period of the disease ranges from a month to a year.
Typically, condylomas appear 3 months after sex with an infected partner.
Causes of synechiae
- Genitourinary infections - vulvovaginitis, vulvitis, etc. Infection is possible in the maternity hospital or at home, when swimming in stagnant natural bodies of water.
- Violation of intimate hygiene rules. Both a lack of hygiene and its excess are harmful.
- Allergy in a child. A reaction can occur to food (from the diet of a girl or a nursing mother), components of care products, washing powder, etc.
- Difficulties during pregnancy - intrauterine infections, severe toxicosis. If a mother had difficulties during pregnancy, her daughter increases the risk of developing synechiae.
- Genetics. The tendency to fusion of soft tissues can be transmitted from mother to daughters.
- Wearing tight synthetic underwear, which creates all the conditions for inflammation.
- Reduced estrogen levels. This is normal before puberty, but in some girls it causes synechiae.
- Dysbacteriosis. Pathogenic intestinal flora can provoke adhesions. Source: Z.K. Batyrova, E.V. Uvarova, L.S. Namazova-Baranova, N.Kh. Latypova, A.E. Donnikov Fusion of the labia minora in girls during early childhood: tactics of a pediatric gynecologist // Issues of modern pediatrics, 2012, vol. 11, no. 2, pp. 118-121
Buschke-Levenshtein condylomas
They are also called giant condylomas.
This form of the disease is a precancerous condition.
Degeneration into a malignant tumor occurs frequently!
Externally, Buschke-Levenshtein condyloma is similar to manifestations of skin cancer.
An experienced specialist will help you distinguish one from the other.
The usual location of giant condylomas is in the intimate areas.
In men, this can be the head of the penis, the foreskin.
In women, the labia are most often affected.
- 1. Giant condyloma forms many folds and looks like cauliflower.
- 2. Bacteria accumulate in these folds.
- 3. The consequence is the appearance of an unpleasant odor.
- 4. Infection and inflammation may develop.
During the examination, an increase in the nearest lymph nodes is recorded.
The growths can be localized in the lower abdomen, on the buttocks.
In difficult situations, they rise to the navel, chest and armpits.
Symptoms of vulvitis in women
How to detect the development of the disease in the early stages? It is enough just to be attentive to your health and not to neglect the obvious signs of pathology. The most characteristic symptoms of vulvitis in girls include the following local manifestations:
- Itching and burning are the main diagnostic signs of vulvitis in women. The patient experiences very severe discomfort, especially when the inflamed surface comes into contact with the fabric of the underwear. Also, burning and itching intensify and transform into pain during physical exercise, during sexual intercourse and after genital hygiene.
- Swelling and redness are easily detected by the naked eye. The patient notices hyperemia of the tissues of the labia, clitoris and vaginal vestibule, which is especially pronounced in the area of delicate mucous membranes.
- The roughness of the surface of the labia minora is a consequence of the enlargement of the sebaceous glands, which protrude above the smooth surface of the mucous membrane.
- Specific discharge - may have a different appearance and consistency. Most often, clear, watery leucorrhoea is observed, which does not have an unpleasant odor. However, some infectious pathogens cause putrefactive, purulent, curdled and even bloody discharge, which requires immediate contact with a gynecologist.
- The appearance of small ulcers and uncharacteristic plaque - these signs are not detected in all forms of vulvitis, but they allow a fairly accurate diagnosis to be made for herpetic, candidiasis and diphtheria forms of the disease.
- Changes in general condition include weakness and increased body temperature, acting as rare symptoms of vulvitis.
It is almost impossible not to notice the development of pulpitis, since even the less pronounced, from the point of view of symptoms, chronic form of the disease is characterized by causing severe discomfort to the patient. Acute vulvitis in women can deprive the patient of sleep and ability to work.
Treatment of genital warts
The disease is treated by dermatologists and venereologists.
The doctor must determine exactly whether the growth is genital warts or a sign of another disease
Genital warts must be differentiated from condylomas lata, characteristic of secondary syphilis.
In addition, diseases such as molluscum contagiosum and lichen planus have similar manifestations.
Diagnosing genital warts is not difficult.
This is carried out on the basis of patient complaints, external examination and tests.
The specialist examines the condition of the patient’s skin and mucous membranes.
If necessary, a test is done with 5% acetic acid.
To differentiate condyloma from other growths, take a cotton swab or napkin.
They are moistened with acetic acid and applied to the affected area.
If the neoplasm is a condyloma, after five to ten minutes it becomes whitish in color.
Detection of genital warts is a reason to get tested for syphilis and HIV.
If a specialist suspects the possibility of cancer, a biopsy may be prescribed.
Removing growths does not reduce the risk of cervical cancer.
Remember! If a woman has previously been diagnosed with genital warts, she needs to visit a doctor every year.
It is necessary to regularly take smears from the cervical canal for cytology.
This will help stop the cancer process in time.
What are the goals of treatment for diseases caused by HPV, and how is it carried out?
Diagnosis, treatment and prevention of genital diseases caused by HPV in men is carried out by urologists, in women - by gynecologists. Unfortunately, there are currently no methods of systemic action on HPV in the human body (antiviral agents) that could be used to completely destroy the virus. The main goal of treatment for OCs is their removal using electro- or laser coagulation, excision, cryodestruction (destruction by cold), as well as using chemicals, cell toxins (podophyllin) or immunomodulators applied topically. Removing OK solves mainly a cosmetic problem; there is no data confirming that removing OK helps to completely remove HPV from the body or reduce the risk of its sexual transmission or infection of the fetus during childbirth. There is no evidence that OC treatment has any effect on the likelihood of developing cancer. However, from a common sense point of view, removal of OCs should reduce the risk of development and recurrence of diseases caused by HPV.
The main goal of treatment of squamous epithelial lesions of the cervix is the prevention of cervical cancer. If a cytological Pap smear shows the presence of a lesion of unknown significance at the risk of malignancy, dynamic observation with Pap smears performed every 4 to 6 months for 2 years is indicated until there are 3 consecutive negative (without any pathological changes) smears. Women with high-risk intraepithelial lesions require immediate colposcopy and possibly biopsy of the detected lesions for more detailed histological evaluation. If CIN 1 is identified as a result of histological examination, dynamic observation is indicated, because the vast majority of such lesions undergo spontaneous regression to normal. For lesions of CIN 2/3, active treatment is required, which consists of cryodestruction, laser evaporation or loop electrosurgical excision (conical excision or conization) of the cervix.
Recent randomized clinical trials have shown that all three methods have similar rates of complications (2 - 8%), persistence (3 - 5%) and recurrence (13 - 19%) of lesions. Risk factors for persistence (lack of treatment effect) were a large affected area, relapse - older age, the presence of oncogenic HPV types 16 and 18, as well as previous treatment.
Why do genital warts recur?
Even if treatment is carried out on time, it does not guarantee against relapse.
The virus can become inactive, but remain in the body.
The reappearance of growths often occurs due to a decrease in protective mechanisms.
Decreased immunity causes the process to spread to intimate places.
When infected with the immunodeficiency virus, genital warts grow faster.
With this disease, giant colonies may appear.
Treatment of patients with HIV requires special experience from the doctor, usually it is surgical.
At the second stage, liquid nitrogen removal technology is used.
Vulvitis - inflammation of the external female genitalia
Inflammation during vulvitis affects the labia minora and majora, clitoris, vestibule of the vagina, hymen and surrounding tissues, including the skin of the pubis, inner thighs and anal area. The woman experiences a whole range of unpleasant symptoms, which manifest themselves primarily as itching and burning in areas of inflammation.
If a woman of reproductive age experiences vulvitis, it is very important to provide timely medical care and treat the disease. Advanced vulvitis spreads to the vaginal tissue, causing vulvovaginitis, and can lead to disruption of sexual and reproductive function. You can get detailed advice regarding the inflammatory process of the external genitalia, as well as get rid of the disease, by visiting the NEOMED multidisciplinary medical center.