Fibroma (synonym - fibroblastoma) is a mature benign neoplasm arising from fibroblasts and connective tissue fibers.
It can be found in the skin, subcutaneous tissue or mucous membranes of any anatomical area. The most common fibroids are the uterus, skin, and mammary glands. There is no clear age association for this tumor (with the exception of fibroids of the uterine localization, it often debuts in women of middle age and does not occur after menopause).
Fibroma can be either single or multiple (fibromatosis). Its diameter varies from 0.01 to 20 cm.
Fibroma: origin and essence of the disease
The causes of dermatofibroma and other forms of this type of tumor are not known.
Some researchers believe that fibroids can form as a localized tissue reaction after minor trauma. Sometimes fibroids can have a genetic component, especially in people of Northern European descent. Some medications, including beta blockers, have been reported to cause changes in fibrous tissue. In addition, some fibroids may be influenced by hormonal imbalances or pathologies of endocrine organs, including problems with the thyroid and pancreas. Hyperhidrosis (increased sweating), inflammatory processes on the skin, especially chronic ones, as well as the influence of prolonged UV radiation, poor nutrition and bad habits can have a certain impact.
Causes of soft skin fibroids
Scientists have not yet established the exact causes of soft skin fibromas. It is believed that the appearance of acrochordon is provoked by the following factors:
- Endocrine disorders . It has been established that soft fibromas are more common in pregnant women (with increased levels of progesterone and estrogen), with diabetes mellitus, as well as with acromegaly (a disease caused by dysfunction of the pituitary gland).
- Irritating factor . Often soft fibroids form in places where mechanical friction occurs with jewelry (for example, a chain on the neck), clothing straps, belts, as well as in skin folds.
- Aging processes . The appearance of acrochordons is often associated with the natural processes of skin aging, since cases of soft fibroids are more common among older people.
- Human papillomavirus infection . Some scientists believe that soft fibroma is caused by human papillomavirus infection, but there is not enough research to confirm this fact at the moment.
Signs and symptoms
Fibroids are classified as benign formations.
They form a tumor-like growth of tissue, inside of which there is mainly fibrous (or connective) tissue. Signs of fibroids arise as a result of uncontrolled by the body, but slow and limited growth of a certain area of tissue. Rarely fibroids are malignant, and the reasons for this are trauma and malignancy of the formation. Different types of fibroids can develop anywhere, and if they are small in size, they require active monitoring or removal if they cause discomfort. Some women with uterine fibroids have no or only mild symptoms, while other women have more severe, debilitating symptoms. Common symptoms of a tumor include:
- heavy or prolonged menstrual flow;
- abnormal bleeding between periods;
- pain in the pelvic area;
- frequent urination;
- lumbago;
- pain during intercourse;
- infertility.
Common symptoms of dermatofibroma involve discomfort and may come and go. Symptoms of dermatofibroma are not severe and include:
- color change over time;
- itching;
- periodic swelling over the tumor;
- possible bleeding due to injury;
- sensitivity of dermatofibroma to touch;
- a small bump with a raised surface.
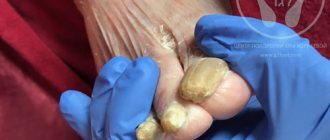
Symptoms of plantar fibroma are not severe and include:
- expansion of sizes over time;
- hard lump in the arch of the foot;
- pain when pressing, standing or walking;
- spread of additional fibroids over time.
Why does fibroma appear?
Fibroids can develop as a result of a hereditary predisposition. In addition, poor diet, smoking and excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages lead to the development of fibroids.
The causes of fibroids also include:
- hormonal imbalance;
- overweight;
- metabolic disease;
- frequent skin damage (scratches, bruises, cuts);
- endocrine diseases (diabetes mellitus, thyroid disease).
Abortions in late pregnancy, inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system and ovarian dysfunction can lead to the development of uterine fibroids. Breast fibroids can be triggered by prolonged breastfeeding or refusal of lactation.
Types, characteristics of fibroids
There are more than 10 different morphological variants. Pathologists give a description of what each form looks like and how it differs after histological examination - elastrophibroma, soft, dense fibroma.
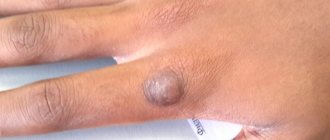
- Dermatofibroma is a single or multiple formation of intradermal localization, mobile and painless when palpated with unchanged color.
- Desmoid fibroma has another name - aggressive fibrosis, refers to mesenchymal tumors originating from excess collagen fibers and differentiated fibroblasts. They often progress and recur, forming in soft tissues, the retroperitoneum or on the abdominal wall.
- Chondriomyxomas are rare tumors that affect bone tissue - the edges of long bones, pelvis, ribs, vertebrae, feet, metatarsus.
- Angiofibriomas in the cheek and nose area, containing small tubercles with connective tissue fibers.
Varieties and places of appearance
In addition to types, tumors are divided into types. They depend on the location of growth and have different characteristics. There are different types of fibromas:
- soft;
- hard (dermatofibroma).
Soft fibroma is much less common than hard fibroma. The most common locations for its appearance are on folds or in places of friction - under the knee, armpits, neck, buttocks, on the chest, behind the ears, on the skin of the eyelids. Externally, it is a wrinkled fat sac, soft when pressed. Color varies: fibroids can be all shades of brown or indistinguishable from the skin. In the latter case, vessels are visible inside the sac. It most often occurs after 40 in women, less often in men, and never in children.
The danger with soft fibroids is that, due to their location, they can easily be torn off and become infected.
Dermatofibroma is diagnosed much more often than soft dermatofibroma; men, women, and children are equally susceptible to it. The places where the formation appears are the shoulders, back, legs, fingers, arms, stomach, feet, face, head. In addition, it is often found on mucous membranes. The shape resembles a smooth pea with a hard structure. Does not cause painful sensations upon contact. It can occur both on the surface of the skin and under it, while subcutaneous fibroma develops more slowly.
Diagnostics
Initially, experienced specialists - oncologists or multidisciplinary surgeons - conduct a detailed examination of the patient, record all the complaints that exist, palpate the formation and make a preliminary diagnosis.
Then you need to determine the nature of the tumor. After this, you need to conduct an ultrasound examination of the tissues where the tumor is located to determine its size, nature, and changes in the tissues. If necessary, an X-ray examination is performed. If questions remain, a biopsy of the suspicious area should be performed to rule out a malignant process. Fibroids can be detected by palpation (feeling with fingers or hands) performed as part of a pelvic examination, or diagnosed through imaging procedures such as ultrasound, computed tomography (CT), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
How to treat a neoplasm?
Treatment of growths is carried out with medication, folk remedies or removal. The first method, using medications, is the most gentle method of treatment. Possible if the tumor is small. For this purpose, Diprospan injection solution is usually used. It is a transparent or slightly yellowish viscous liquid, without impurities. The drug is administered intradermally, the dose is calculated individually for each case.
Diprospan is not suitable for subcutaneous or intravenous administration.
With an intradermal injection, the medicine is injected directly into the fibroid lesion, evenly chipping away. To do this, use a tuberculin syringe and a 0.9 mm needle. When injecting the drug into the fibroma itself, the needle should be 26 gauge.
The use of the solution may lead to side effects, and an overdose requires medical intervention. In addition, Diprospan should be used with caution with other medications, and the injection should be administered strictly intradermally, without penetrating into the vessels. Children should use the drug with caution and under mandatory medical supervision.
Complete removal
Complete removal of fibroids is necessary when they reach an impressive size or have been injured. It is also better to remove the growth located in an inconvenient place. Types of complete removal:
- Electrocoagulator - removal of growths using an electric current charge. It is performed without anesthesia. As a result, a dense crust appears at the site of the tumor, which disappears after 1.5 weeks. There are no marks or scars left.
- Using a laser is important for removing fibroids from the face, neck, shoulders or décolleté. Lasts 15-20 minutes without pain medication. There may be some stinging during the procedure. After removal, no traces remain, and the possibility of relapse is reduced significantly.
- By radio waves - the fibroma is cut off with a radio wave scalpel, without blood, pain or scars. The method is considered one of the most popular. The disadvantage is the high cost.
- Cryodestruction method - removal using nitrogen or dry ice. Suitable only for small tumors. Completely eliminates the possibility of relapse.
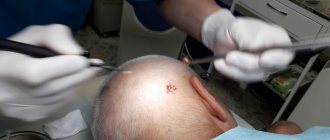
In addition to cosmetic ones, there is also a surgical method of removal. It is a conventional operation using a scalpel, which is performed under local anesthesia and lasts no more than a quarter of an hour. It is performed when cosmetic methods are powerless - if the fibroid has penetrated deeply or is large in size. The main disadvantage is the appearance of scars.
Folk remedies
Often people turn to traditional methods to remove fibroids. They involve all kinds of lotions, baths, taking decoctions and infusions, and so on. The most effective recipes:
- lotions from celandine juice;
- Lubricating with camphor alcohol 3 times - the effect will appear in a few months, the burning sensation that appears means the rapid disappearance of the fibroma;
- a mixture of iodine and aloe - put the plant leaf in the refrigerator for 72 hours, then grate it and pour 100 ml of alcohol, leaving for 20 days. Add 10 drops of antiseptic to the finished infusion. Rub into the tumor daily;
- daily lotions from potato juice;
- salt compress.
In addition to the external influence on the problem, it should be influenced from the inside by using infusions:
- Calendula - 50 g, pour 500 ml of alcohol and leave for 14 days. Drink a tablespoon three times a day.
- St. John's wort - tbsp. Soak in a glass of water for 4 hours, drink three times a day.
- Pine nut shells - pour 0.1 kg of nuts into 0.25 liters of vodka and leave for 14 days. Take 2 tbsp. 3 times a day.
- “Fresh” potato juice - 1 tbsp/3 times a day.
- Juice from cucumber leaves - chop the tops and add water for a couple of hours at the rate of 2 tbsp. for 400 ml. Take tbsp. three times a day.
A significant advantage of this method of treatment is its low cost and ease of finding ingredients. The downside is that the result requires long-term treatment. This treatment is suitable for growths not exceeding 1 cm in diameter.
Treatment methods
Dermatofibromas are harmless and treatment is not required unless there are warning signs or cosmetic concerns. If the patient wishes to remove dermatofibroma, surgical treatment is possible - surgery .
It is important to evaluate its consequences: the scarring and tissue changes that occur after surgical excision may look worse than the original lump. For plantar fibroids, non-surgical treatment options are preferred because the surgical procedure requires a long recovery period and can lead to complications that may be worse than the plantar fibroids themselves. Non-invasive treatments for plantar fibroids include:
- extreme cold or cryodestruction to reduce fibroids.
- pads or insoles to relieve discomfort when wearing shoes.
- stretching.
Most doctors agree that for severe cases of plantar fibroma, the smartest option is to resort to invasive treatments and surgery. Invasive treatments for plantar fibroids include:
- injections of corticosteroids into fibroids.
- surgical removal of the entire plantar fascia (which is associated with a long recovery period and a high risk of developing other foot problems).
- surgical removal of fibroids (with a high recurrence rate).
Treatment is indicated when dermatofibromas are bothersome or persistently irritated. In these cases, surgical removal and freezing with liquid nitrogen can be performed.
Treatment for uterine fibroids depends on the size, symptoms, and other factors. Asymptomatic fibroids may not require treatment. A myomectomy (surgical removal of uterine fibroids) may be performed to remove fibroids that are interfering with fertility in women who want to become pregnant. Hysterectomy (surgical removal of the uterus) is also commonly performed on patients with severe symptoms of uterine fibroids, but is not an option for women planning a pregnancy. Non-surgical treatment for uterine fibroids includes medications, uterine artery embolization and targeted ultrasound treatment.
The main methods for removing skin fibroids are
- laser
- surgical (excision with a scalpel)
- radio wave
- electrocoagulation (removal using high-frequency current)
Laser and radio wave methods are the most modern and in demand today, since they have a number of advantages: almost complete bloodlessness of the procedures, thanks to the “sealing” of the vessels during exposure; sterilization of the wound, which eliminates the possibility of infection.
The laser beam provides highly precise effects in area and depth of penetration, while causing minimal damage to healthy skin cells. Thus, an excellent cosmetic effect of removal is achieved - unaesthetic scars, pigmentation, burns do not occur . In most cases, it is possible to completely remove soft skin fibroids using a laser.
Predictions of why fibroids are dangerous
Dermatofibroma does not have serious complications.
Complications of plantar fibroids usually occur as a result of surgical interventions. These include flattening of the arch of the foot, postoperative nerve entrapment, and postoperative growth of larger and recurrent fibromas. Article sources:
- Desmoid fibroma. Staged, organ-preserving surgical treatment. Khvastunov R.A., Mozgovoy P.V., Lukovskova A.A., Yusifova A.A. Volgograd scientific and medical journal No. 2, 2022. p. 54-57
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2927520/ Central odontogenic fibroma: a case report with long-term follow-up. Marco T Brazão-Silva, Alexandre V Fernandes, Antônio F Durighetto-Júnior, Sérgio V Cardoso, Adriano M Loyolacorresponding
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3351722/ Literature survey on epidemiology and pathology of cardiac fibroma. SuguruTorimitsu, Tetsuo Nemoto, Megumi Wakayama, Yoichiro Okubo, Tomoyuki Yokose, Kanako Kitahara, Tsukasa Ozawa, Haruo Nakayama, Minoru Shinozaki, Daisuke Sasai, Takao Ishiwatari, Kensuke Takuma, Kazutoshi Shibuya
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
Types of soft tissue fibroids
Based on the type of histological structure, hard and soft fibroma are distinguished. The hard type of fibroma is a dense formation in connective tissue, rich in collagen and with a small number of cells. Soft fibroids are composed of elements of connective fibrous tissue (a large number of cells). This formation is soft to the touch. Soft fibroids often appear in the groin area, armpits, subcutaneous folds, eyelids and neck.
Often, many forms of fibroids are mixed formations - fibrolipomas (formations of fatty and connective tissues), fibroids (muscle and connective tissues). Along with fibroids, filamentous warts are common types of formations on human skin.
Fibroma after surgery
To carry out surgical intervention to eliminate fibroids, the following methods are used - traditional surgical excision with a conventional scalpel, laser, radio wave method. The most preferred and modern methods are radio wave and laser elimination of formation. With their help, this operation is performed almost bloodlessly. In addition, the surgical wound is immediately sterilized with a laser wave or beam.
The surgical wound heals quickly and optimally, and with small fibroids there may be a visible absence of traces of the operation. The minimal trauma of such surgical intervention gives the patient the opportunity to quickly resume a normal lifestyle. After radio wave and laser elimination of fibroids, relapses in most cases do not appear.
Author of the article:
Mochalov Pavel Alexandrovich |
Doctor of Medical Sciences therapist Education: Moscow Medical Institute named after. I. M. Sechenov, specialty - “General Medicine” in 1991, in 1993 “Occupational diseases”, in 1996 “Therapy”. Our authors