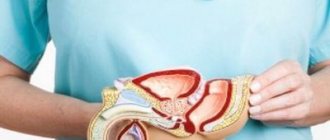
Almost everyone knows what papilloma is. They can be found on the skin of the neck, armpits and other areas of the body. But the appearance of papilloma on the penis and in the groin area in general causes significant concern among men, and for good reason.
Papillomas on the penis in men can be either a sign of a fairly harmless cosmetic defect or a symptom of a serious disease, sexually transmitted or leading to cancer.
The danger of each type of papillomas on the penis for human health can only be determined by a dermatovenerologist based on their examination, dermatoscopy and laboratory diagnostics, which may include:
- Scraping from the surface of papillomas for the type of human papillomavirus and syphilis
- Urethral swab for STIs
- Blood test for syphilis and HIV
- Histological examination of removed papilloma
Causes of papillomas
The cause of the appearance of papillomas in intimate places is the human papillomavirus (HPV), which circulates in the blood of almost every man and woman, starting from adolescence.
According to WHO, 80-90% of the population is infected with HPV. Most often, papillomas occur in young people who have a large number of sexual partners. Genital-anal papillomas are typical manifestations of human papillomavirus infection. In 90% of cases they are caused by the sixth and eleventh types of HPV.
In the daily life of every person, the following exposures increase the risk of infection:
- smoking;
- stress;
- using other people's hygiene products;
- visiting baths, saunas;
- shaking hands with carriers at the acute stage;
- decreased immunity.
Globally, the spread of HPV is influenced by many factors, including socioeconomic, medical, hygienic and geographic. The virus can stay in the body for years without showing itself. Its activation is provoked by a weakening of the protective forces of the immune system, which entails the appearance of papillomas in intimate places, both in women and men.
Pregnancy, hormonal imbalances, metabolic disorders, acute viral infections, long-term chronic diseases, poor nutrition and lack of sleep can also trigger the growth of papillomas in intimate places.
Condylomas acuminata - symptoms and treatment
The key point in the pathogenesis of the disease is the penetration of HPV into the host body. With a single sexual contact, the probability of infection is 80%, then, with a good state of the immune system, infectious agents are eliminated (destroyed).
Viruses of various types are adapted to a specific host. There are hundreds of types of viruses, many of them are not dangerous to humans, since they are tropic to the tissues of mammals, reptiles and birds and cause benign tumors in them (formation of papillomas).[3]
When studying HPV, three types of viruses were identified - alpha, beta, gamma. Of these, anogenital lesions are caused by papillomaviruses of the first group (α). Infectious agents belonging to the Beta and Gamma genera are more often found with papillomas of the keratinizing epithelium [3] - plantar and palmar warts appear.
In genera, when classifying viruses, types (genotypes) were identified. They are indicated by Arabic numerals. Of the hundreds of virion genotypes, particles with a high carcinogenic risk are isolated - these are α 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59. They are detected in 90-95% of cases with malignant processes of the cervix , vagina and vulva. Types 16 and 18 are especially significant. Such oncogenic types of HPV, containing E6 and E7 proteins in their DNA, are able to suppress the activity of the tumor suppressor proteins p53 and pRb, leading to the rapid malignant transformation of papillomas into carcinomas.
About 90% of cases of anogenital warts are caused by HPV α 6 and 11. These are pathogens of low carcinogenic risk.[5] This same low-risk group includes HPV 40, 42, 43, 44, 54, 61, 72, 81.
Penetration
Virions penetrate the basal layer of the epithelium through microscopic damage and then attach to cell membrane proteins. Next, they engage the mechanism of receptor endocytosis (with the participation of integrin and L1 protein from the viral capsid) and enter the cytoplasm. The L2 protein from the viral capsid promotes the release of viral DNA and its entry into the nucleus.[5]
Reproduction
Proteins E1 and E2 from the DNA of the virus are involved in the replication of the foreign genome in the nucleus of the affected cell. At the same time, the cell retains the ability to divide and reproduce its own DNA. By multiplying its DNA, the virus ensures its presence in the form of episomes in the cytoplasm (about 100 per cell). This joint “work” of the virus and the host cell leads to a failure in the processes of proliferation (cell reproduction) and differentiation in the basal layer, leading to visual manifestations.
Manifestations
Abnormal endophytic or exophytic growths of the epithelium appear - papillomas, spots or condylomas. Loose mucous membrane or atypical epithelium of outgrowths are prone to rapid traumatization and maceration (softening). Against this background, a secondary infection quickly develops, pain, discomfort, copious discharge, inflammation, swelling, unpleasant odor, and ulceration of condylomas appear.[2][3]
In the cells of the basal layer, active replication of the virus occurs; as condyloma cells differentiate, their blood supply is sharply depleted, and the central vessels are reduced. But, remaining in the upper layers of the epithelium in an inactive form, this is where the virus is dangerous in terms of contact infection.
During histoanalysis of biopsy materials, the epithelium is thickened, areas of acanthosis and papillomatosis are revealed. Koilocytes are detected (changed in size cells with light cytoplasm, many vacuoles, and a perinuclear light rim). Their nuclei are hyperchromatic. Cells with two or more nuclei are often found.[8]
From the above we can conclude: viruses that cause the formation of anogenital warts, in 90% of cases, belong to types α 6 and 11 HPV.[6][7] They have a low probability of causing malignancy (cancerous degeneration). However, there are frequent cases of joint persistence (residence) of viruses of different types in one carrier. This obliges the patient and doctor to be especially attentive to preventive examinations, their quality and regularity to prevent anorectal cancer .
Routes of infection
Infection is possible not only through sexual intercourse, although this is the most common cause. HPV infection is also possible through household means:
- when using common hygiene and tableware;
- through contact with an infected person in the acute stage in the presence of microtraumas;
- the possibility of HPV transmission through household items is still being debated.
The transplacental route of infection is rare - from mother to child, even at the stage of intrauterine development of the fetus.
Methods of infection
- Sexual, with vaginal or anal contact.
- Vertical, a newborn can be infected through a woman's birth canal.
- Self-infection, by transferring infection from one part of the body to another.
- A household contact virus, the virus remains active on hygiene items; it can be picked up in gyms and swimming pools.
- Contact, infection occurs through damaged skin or mucous membranes.
Probability of infection
Women and men have an approximately equal risk of becoming infected without knowing it at all, since the peak of infection occurs in adolescence and older, when alertness to herpesvirus, papillomavirus, and HIV infection decreases.
At the same time, more attention is paid to sexually transmitted diseases, which, however, are also characterized by high dynamics of infection.
The number of sexual partners remains an important point, since today more than 190 types of HPV have already been described and every year there are more strains of the virus. The International Agency for Research on Cancer identifies 12 strains that are associated with the development of cancer of various locations:
- cervix;
- vulva;
- vagina;
- anal canal;
- penis.
By choosing the smallest number of sexual partners, the risk of becoming infected with HPV, including its oncogenic strains, is significantly reduced.
It is necessary to remember about personal hygiene, as well as the existence of vaccination, which reduces the risk of developing HPV by 95%. It is more effective to vaccinate before the age of 14 years, but up to 25 years of age is also possible. The vaccine provides the greatest protection if it was administered before the onset of sexual activity.
Important
If papillomas appear on the head of a man’s penis, then curing them will not be easy, and the removal procedure will be painful.
First of all, doctors recommend that a man avoid promiscuous sex and use barrier contraception.
With early prevention and a negative test for the virus, a healthy man is offered vaccination against HPV. If the virus is detected, but papillomas have not yet had time to manifest themselves, it is advised to strengthen the immune system in order to avoid their growth.
There are several ways to strengthen your immune system:
- Improve your diet, add a vitamin-mineral complex or foods enriched with beneficial microelements and substances.
- Exercise.
In winter and in the off-season, immunologists advise strengthening the immune system with vitamin complexes and antiviral drugs.
Symptoms
If there are papillomas in intimate places, symptoms are divided into subjective (sensations, complaints) and objective (which can be directly seen by a specialist). Subjective ones include:
- the presence of growths (single or multiple);
- spots on the skin and mucous membranes of the genital organs;
- itching and other unpleasant superficial sensations in the affected area;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- if male papillomas in intimate places are located in the urethra, burning and painful itching and difficulty urinating may be observed.
The pathology is characterized by the presence of painful cracks and bleeding of the skin and mucous membranes.
Objective symptoms include:
- rashes;
- papules and spots;
- wart-like papillomas;
- pointed condylomas localized in the perineum and perianal area.
How does HPV manifest itself on the genitals?
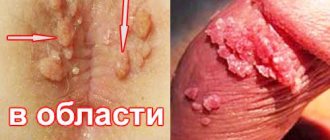
Genital papilloma may look like a small bump, a hair from the epidermis, or a ball on a stalk. This can be a single growth or a group of formations in the intimate area, a flat wart or a large growth similar in shape to cauliflower. What unites them is their location - neoplasms appear in the anorectal area, in the perineum, on the scrotum and directly on the penis in men, on the labia and in the vagina in women.
Important: HPV strains that cause papillomas of the vagina, labia, scrotum and head of the penis rarely provoke the appearance of growths on the oral mucosa. These are papilloma viruses 6, 11, 16, 18, 33, 35 and some other types. Laboratory tests can determine the exact strain of the virus. Well, such a symptom as growths on the inside of the lips and cheeks should be a reason to consult a doctor.
Diagnostics
In order to more reliably determine whether the neoplasm belongs to anogenital warts, a test is carried out with a 5% solution of acetic acid, after treatment with which papillomas in intimate places retain a grayish-white color with a changing, intensifying vascular pattern of normal skin. Laboratory tests can also be used in diagnosis - identification of the HPV genotype with a prognosis for the course of the disease.
To diagnose precancerous conditions against the background of papillomas in intimate places in women, consultation with an obstetrician-gynecologist and urologist is recommended when papillomas are localized in intimate places in men, for example, with intraurethral localization. If there are papillomatous processes in the anal area, consultation with a proctologist is recommended.
Treatment of papilloma virus in men
If a man has condylomas on the head of the penis, treatment is carried out in two directions:
- Remove growths.
- Conduct shock antiviral therapy.
None of them have any advantages, since the doctor prescribes treatment based on their examination data and the tests obtained. Often these treatments are complementary to each other.
Drug therapy complements the process of removing papillomas in men. With its help, the immune system is strengthened to avoid relapse, since removal of papillomas again brings the patient to the doctor with the same symptoms of the disease in 30% of cases.
The patient is prescribed immunostimulants: polyoxidonium, immunal, cycloferon, etc. These drugs are prescribed only by a therapist or urologist.
Treatment
To the question of how to treat papillomas in intimate places , modern medicine gives a clear answer: they need to be removed. Destruction of benign neoplasms can be carried out using various methods:
- electrocoagulation – exposure to high frequency current;
- cryodestruction - removal using cold treatment;
- laser removal – layer-by-layer treatment with laser radiation;
- chemical destruction - using special chemical solutions.
Classic surgical removal is also an option.
A specific scheme for how to completely and safely remove papillomas in intimate places is prescribed by a specialist in accordance with the localization of the process, the severity of the course, and concomitant diseases.
An important aspect of treating papillomas in intimate places is changing lifestyle and strengthening the immune system. An integrated approach avoids the emergence of new formations.
Why are papillomas on the genitals dangerous?
The disease must be treated. This is a strong recommendation from both specialists from the World Health Organization and leading dermatologists-oncologists of Ukraine. In addition to the fact that papilloma on the labia or papilloma on the penis looks extremely unattractive, the disease, as mentioned above, is also dangerous.
Let's start small. When wearing tight underwear, during hygiene procedures, or during intimate caresses, the growth can be injured. And this is fraught with bleeding and secondary infection.
Important: The intimate area takes on an ugly appearance. This may cause disgust on the part of the sexual partner. Without treatment of the pathology, the area where the growths are located may increase. New areas of skin are gradually involved. The formations grow, over time they can interfere with urination and defecation.
If the outcome is unfavorable, HPV in the vagina and on the penis can take on a malignant form. A benign condyloma yesterday can become an oncological tumor with metastasis to the pelvic organs tomorrow. That is why you should not ignore the problem.
Important: Aggressive types of HPV cause cervical cancer, cancer of the small lips, vagina, penis and anus.
Types of papillomas on the head
Single or multiple growths form on the head or frenulum.
Most often they have the form of finger-like protrusions.
Color pink or red.
In most patients, papillomas do not hurt or itch, do not swell and do not cause subjective sensations.
They simply exist, and this very fact causes discomfort.
The main types of condylomas under the head:
- genital warts;
- papules;
- spots;
- bowenoid papulosis;
- Bowen's disease;
- giant Buschke-Levenshtein condyloma.
Usually the formations appear as protrusions, papules or spots.
In the latter case, they can be difficult to detect due to the lack of relief.
Only the color of the skin changes.
All papillomas on the head are well vascularized.
You can see many blood vessels in them.
The most dangerous form of the disease is giant condyloma.
Although histological studies show that there are no signs of malignancy, it behaves exactly like a malignant tumor.
This condyloma does not metastasize.
But it is characterized by destructive growth with destruction of surrounding tissues.
After removal it often recurs.
The tumor has no clear boundaries.
It reaches enormous sizes during the natural clinical course of the disease.
Quite often, giant condyloma causes death.
What types of condylomas are there?
There are several types of condylomas based on their shape:
- Flat;
- Pointed;
- Wide.
Flat condylomas are flush with the skin and look like spots.
They are rare, but are considered the most dangerous.
Condylomas acuminata are growths.
They look like warts and rise above the surface of the skin.
Widespread condylomas are called condylomas, which are caused by the entry of treponema into the body.
Pointed formations are quite common.
Removal of condylomas from the foreskin and glans penis
HPV today is an incurable disease, because there is no medicine that would destroy the virus itself, but relapses are successfully removed. The sooner treatment is started, the greater the chances of getting rid of condylomas.
Treatment methods are divided into surgical and conservative. The latter include:
- Immunotherapy to enhance immunity
. It should be noted that immunostimulants should be taken carefully and only after consultation with a doctor, because they contribute to the development of oncology. Those. If you already have cancer, it will only get worse! Immunomodulators used in the treatment of HPV are of two types: based on interferon-alpha-2 (Altevir, Intron-A, Realdiron) and stimulators of interferon protein production by microphages and lymphocytes (Cycloferon, Arbidol, Amiksin). - The use of ointments that stop the proliferation of condylomas
(Oxolin, Viferon, Aldara cream, Panavir gel, Epigen cream). They are applied to the affected areas of the skin, stopping the further spread of atypical cells, healing tissues and increasing the intracellular production of interferons. - Immunostimulants and ointments
are used as a general course for several months in the initial stages of the disease. Their use is effective only for single small-sized condylomas.
Complications of papillomas on the head
But papillomas on the head pose a real threat to human health.
The very fact of their appearance indicates that there is a papillomavirus in the body.
They also often indicate an existing immunodeficiency.
And the more condylomas, the larger they are, the worse the immune system works.
Papillomavirus itself is not a factor that disrupts immune function.
But it acts as a kind of marker.
In people with good immunity, the appearance of papillomas of even minimal size is unlikely.
The papillomas themselves may pose a risk of such complications.:
- infection;
- rupture and bleeding;
- scar formation;
- Penis cancer.
A bacterial superinfection can join an existing papilloma.
Then the formation on the head turns red.
There is swelling and possible pain.
Over time, an abscess forms.
A pustule appears.
When pressed, pus is released from it.
In most cases, bacterial superinfection is superficial.
It does not cause serious complications.
After a week, the acute period of inflammation passes.
After 2-3 weeks, not a trace remains of the inflammatory process.
But sometimes the inflammation becomes deeper.
Then the patient requires medical attention to prevent a more serious bacterial infection.
Papilloma often detaches.
Since the penis itself, and the condylomas existing on them, are well supplied with blood, this is fraught with bleeding.
It can be difficult to stop him.
Especially if the detached papilloma on the head was quite large.
This formation can be injured during sexual intercourse.
It is also possible that clothing may be rubbed or injured by hard components (belt, buttons, zipper, etc.).
The injury may result in scarring.
This is an unfavorable outcome, since scarring in the area of the head and foreskin is fraught with phimosis.
Therefore, in case of injury or inflammation of condylomas, you should consult a doctor.
The doctor will take the necessary measures to normalize reparative processes and minimize the risk of scar formation.