It is known that men do not like to go to the doctor. However, if a tumor appears on the penis, many rush to consult a specialist. After all, a cyst on the head of the penis makes you feel awkward in front of your partner, prevents you from enjoying intimacy and causes anxiety. Don't wait for the problem to resolve itself. It is better to seek professional medical help from a urologist. The doctor will make an accurate diagnosis and give the necessary recommendations for treatment.
Causes and risk factors
Prostate cysts are divided into congenital and acquired. Congenital ones are formed as a result of disturbances in the intrauterine development of the fetus, acquired ones develop under the influence of environmental factors and diseases of the genitourinary system.
The direct cause of acquired prostate cysts is hypo- or hypersecretion of the prostate gland. With excess production, the juice thickens and accumulates in the acini. With further development, the secretion seems to surround the already formed formations, which subsequently transform into cysts.
Predisposing factors for prostate cysts:
- surgical treatment of prostate diseases;
- congestion in the pelvic cavity;
- long-term untreated prostatitis;
- tendency to constipation;
- chronic hypothermia of the body;
- genital injuries (acute and chronic);
- benign prostatic hyperplasia (prostate enlargement);
- lack of physical activity, sedentary work;
- bad habits (smoking, alcohol abuse);
- overly active sex life or its complete absence;
- casual sex;
- frequent consumption of fatty, smoked foods;
- chronic stress, overwork;
- professions involving heavy physical activity.
The essence of the problem
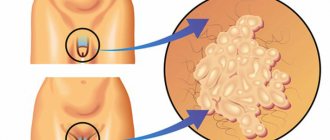
Genital warts are essentially genital warts and look like these “harmless” growths or may resemble overgrown cauliflower. This often leads to a neglectful attitude towards the problem. Papillomas do not cause any problems, they do not hurt, do not cause itching or other negative aspects. But warts on the genitals can be caused by human papillomavirus, which often provokes cancer of the penis and cervix. Condylomas pose a threat to both women and men, because this disease is sexually transmitted.
Human papillomavirus
The human papillomavirus (HPV) is very insidious and has more than a hundred varieties, many of which are unfavorable for humans. Cervical dysplasia, warts on the soles, genital warts are just a small part of the problems that can result from the spread of the human papilloma virus on the human skin and mucous membranes. The presence of a latent period during HPV infection makes it difficult to diagnose problems. Genital warts are a viral disease and are therefore transmitted through contact with a sick person. As a rule, this occurs during intimate relationships (genital, anal and oral sex), but domestic infection is also possible. There are statistical data about the acquisition of such a disease during childbirth by newborns. The male part of the population can “acquire” genital warts when the following HPV strains enter the body: 33, 18, 16, 11, 6.
Spread of infection
Do not be mistaken and think that HPV “rewards” only disadvantaged people and those belonging to a risk group - prostitutes, homosexuals, drug addicts, etc. Papillomavirus can spread in all segments of the population. The inexorability of statistics suggests that half of all people who are sexually active may have one or another type of HPV. Human papillomavirus scales are separated during sexual contact and invade new areas on the skin and mucous surfaces. Warts on the genitals should be a signal that you need to consult a doctor and protect yourself from the possibility of cancer.
Pathogenesis
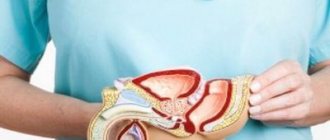
Prostate retention cysts develop in glandular organs that secrete thick mucous secretions, including the prostate gland. Neoplasms are the result of obstruction or complete blockage of the excretory ducts of the gland. In this case, the accumulation of a large amount of secretion develops, its compaction and encapsulation.
The causes of this condition include the formation of stones in the prostate gland, compression of the ducts by a tumor or scar. In some cases, obstruction develops when the ducts are blocked by mucus plugs. They occur when the viscosity and density of the mucous secretion of the prostate ducts increases.
Congenital prostate cysts form in cases of low concentrations of anti-Mullerian hormone. A decrease in it is observed with alcohol consumption or exposure to radiation in the early stages of pregnancy. If more than 1–2 cysts are detected, then there is a risk of malformations of the genitourinary system.
If the etiological factor is bacteria, then the exudate of the prostate cyst will contain a large number of microorganisms and leukocytes. In a non-infectious process, the secretion fills the lobules, gradually expanding them. Over time, the contents of the lobules become encapsulated, increase in size and compress the acini.
Clinical manifestations
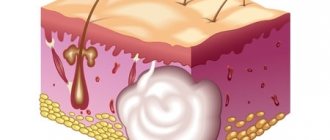
Cysts less than one centimeter almost always do not cause discomfort . An increasing atheroma makes itself felt by a noticeable dense tubercle that does not cause pain upon palpation. In the absence of an inflammatory process, the skin over the defect is smooth.
If an infection has entered the wen, the patient begins to suffer from severe itching, mild pain, redness of the epithelium around the formation, and increased temperature of the affected area.
Lack of timely treatment leads to significant swelling of tissue structures, severe pain, and hyperemia. At the same time, pathogenic microorganisms also infect other organs of the reproductive system.
The process of suppuration is dangerous due to the formation of an abscess. If the lipoma progresses well, it can open on its own, releasing a capsule with its contents.
Classification
There are two types of prostate cysts: congenital and acquired. Based on the nature of the damaging agent, neoplasms are divided into infectious (including parasitic, reaching large sizes), non-infectious, inflammatory and non-inflammatory. Depending on the course, the disease is classified into complicated and uncomplicated.
Congenital prostate cysts
Congenital prostate cysts are diagnosed extremely rarely and arise as a result of intrauterine infection of the fetus. This form of pathology is determined during examination of a patient with suspected infertility or prostate cancer.
More often, congenital prostate cysts form on the surface of the Müllerian duct, seminal vesicle, and ejaculatory duct.
Acquired prostate cysts
Acquired forms include:
- Multiple small neoplasms accompanied by benign cystic prostatic hyperplasia.
- Retention cysts of the prostate, developing as a result of expansion of the lobules of the gland against the background of acquired obstruction of its small ducts. Most often, neoplasms occur in the peripheral part of the gland or in the area of the internal opening of the urethra.
Depending on the location, prostate cysts are divided into:
- to extraprostatic (located outside the gland);
- intraprostatic (located on the inner surface of the prostate).
Based on the relationship of cysts to the midline of the gland, they are classified into types:
- Lateral, or lateral, cysts associated with gland hyperplasia, retention cysts of the prostate.
- Medial – cysts of the ejaculatory ducts.
- Median (central) – Mulleroi duct cysts.
Based on the number of cystic formations, single cysts and multiple cysts are distinguished.
Additionally, the clinic identifies false and true prostate cysts. In the first case, the cyst is an enlarged lobule of gland without exudate inside. True formations are filled with mucous secretion.
Price and cost of spermatic cord cyst surgery in children:
| Service | Price |
| Excision of spermatic cord cyst of category I complexity | 38000 |
| Excision of spermatic cord cyst of category II complexity | 55000 |
| Excision of spermatic cord cyst of III category of complexity | 73000 |
The price list published on the website is not a public offer agreement.
The provision of services is carried out on the basis of an agreement for the provision of medical services. We ask you to check the cost of services with your attending physician in advance. *Price includes:
- inpatient accommodation 1 day in a double ward
- operational aid
- disposable suture material Vicryl or PDS 5/0, 6/0
- application of an intradermal cosmetic suture - no need to remove the suture
- disposable surgical consumables
- constant telephone communication with the attending physician
- examination any day in the clinic within 30 days after surgery
The cost of the operation does not include:
- anesthesia care
- preoperative examination
- treatment of concomitant diseases.
Preoperative tests can be taken at our place or at a local clinic.
** This is not a public offer agreement. Check the cost of services on the day of your request.
Don't waste your precious time - call!
Our specialists will be happy to answer all your questions
+7
Our advantages
Experienced surgeons
Individual approach
Without pain and fear
Comfortable conditions
Symptoms of a prostate cyst
Small prostate cysts rarely manifest themselves clinically and do not require treatment. In the congenital form of the pathology, the patient consults a doctor with the onset of active sexual life, when hematospermia and pain during sexual intercourse are detected. In some cases, hematuria is also noted. Congenital prostate cysts are usually localized at the base of the gland and have a drop-shaped or spindle-shaped shape. The size of the congenital neoplasm usually does not exceed 4 cm.
If a cystic formation occurs in the area of the internal opening of the urethra, the patient has problems with urination. The symptoms of large prostate cysts are in many ways similar to the clinical signs of adenoma.
Urinary disorders are manifested by frequent urges, weakening of the stream, nocturia, tension in the abdominal muscles, burning and pain during urination, and a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder. Complete urinary retention or incontinence, ureteral blockage, pyuria, hematuria, and dysuria are often observed.
Erectile dysfunction with prostate cysts is characterized by weakened erection, discomfort during ejaculation, premature ejaculation, impotence, oligospermia, hematospermia.
General symptoms of prostate cysts include an increase in body temperature to low-grade levels, rapid fatigue, and nagging pain in the perineum.
Complications
Prostate cysts can be complicated by the following conditions:
- addition of a secondary infection;
- traumatic ruptures of the prostate;
- protrusion of the cyst into the lumen of the rectum;
- blocking (narrowing) of the urethral canal;
- stones in the prostate gland;
- prostate abscess;
- atrophy of gland tissue;
- deformation (compression) of blood vessels located next to the tumor;
- acute urinary retention;
- infertility due to obstruction of the vas deferens.
A breakthrough of a purulent prostate cyst can cause generalization of the infectious process and the development of massive intoxication. The result of the complication is death.
Diagnosis of prostate cyst
When palpated through the rectum, small prostate cysts are usually identified as dense, round formations. They can be filled with serous or serous-hemorrhagic fluid.
Laboratory and instrumental diagnosis of prostate cysts includes studies:
- rectal digital examination of the prostate gland;
- CT, MRI;
- Ultrasound of the bladder, kidneys;
- urethrography, vesiculography;
- transurethral ultrasound examination of the prostate;
- spermogram;
- blood, urine, ejaculate, prostate secretion tests;
- puncture of the neoplasm followed by histological examination of the contents.
For urinary disorders, uroflowmetry is used.
Treatment of prostate cyst
In most cases, treatment for prostate cysts is not required. The patient is registered with a dispensary in order to monitor the condition, timely detection of an increase in size, the presence of suppuration and malignancy. Regular examinations by a doctor are especially important for patients over 40 years of age, since in men of this age group, malignant degeneration of the cyst can occur quite quickly and without symptoms.
Conservative treatment of prostate cysts depends on the cause of the tumor and is often symptomatic. If signs of malignancy appear and the patient’s condition worsens, surgical removal of the tumor is required. Surgery varies depending on the stage and size of the prostate cyst. Types of operations:
- Puncture of the cavity followed by the introduction of a sclerosing agent into it.
- Laser enucleation of prostate cyst.
- Transurethral or transrectal surgery, laparotomy.
When to have surgery?
The most effective way to deal with pheniculocele is to remove the cyst. Since in a baby who is not yet one year old, the pathology can go away on its own, babies who are diagnosed with a spermatic cord cyst are usually observed by a doctor and are operated on when they reach the age of one and a half to two years.
If a diagnosis of spermatic cord cyst is made to a boy who is already two years old, then surgery is usually performed as quickly as possible. And in cases with an acute hernia of the spermatic cord, surgical intervention is performed urgently, since this condition is similar in symptoms to a strangulated inguinal hernia.
If the cause of the cyst is an injury, then at least three months must pass before surgery.
Prognosis and prevention
To prevent the development of prostate cysts and maintain the health of the genitourinary system, it is necessary to follow important diagnostic measures:
- Eat right (it is recommended to include more vegetables, fruits, herbs in the diet, exclude fatty foods, reduce the consumption of meat and meat products, give up fast food, and do not abuse coffee).
- Avoid excessive exercise (especially with a full bladder).
- Engage in adequate physical training in order to prevent congestion in the pelvis.
- Have a regular sex life with a regular partner.
- Avoid hypothermia.
- Treat diseases of the genitourinary system in a timely manner.
- Undergo regular medical examinations with a urologist-andrologist after 40 years of age.
The prognosis for timely detection of a prostate cyst and its removal or conservative treatment is favorable. Advanced stages of neoplasm development are fraught with infertility, breakthrough of a purulent cyst into the rectum, generalized intoxication and death.
You can sign up for a comprehensive diagnosis at our medical center by phone or by leaving a request on the website.
Our doctors
Kochetov Sergey Anatolievich
Urologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
35 years of experience
Make an appointment
Perepechay Dmitry Leonidovich
Urologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
41 years of experience
Make an appointment
Khromov Danil Vladimirovich
Urologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
Experience 36 years
Make an appointment